Payment of utilities is the responsibility of all owners and responsible tenants of residential premises.
Failure to pay for housing and communal services in some cases leads not only to the disconnection of such services, but also to the forced eviction of defaulters. Methods to avoid eviction depend on the type of right to use the housing, the length of the delay in payments and other circumstances. Dear readers! To solve your specific problem, call the hotline or visit the website. It's free.
8 (800) 350-31-84
Legislative acts on the eviction of tenants for non-payment of housing and communal services
Failure to pay utility bills threatens with serious problems, which are supported by regulations drawn up according to the letter of the law. The Housing Code has a clear position on this issue. It is not so easy to evict from a privatized apartment for rent arrears. The same applies to forcing a resident to check out if he does not pay his bills. Any of these procedures can only be carried out through legal action.
A citizen who occupies public housing can be evicted from an apartment for non-payment of utilities. This will happen if the person has not paid rent for six months. In such a situation, the management company has grounds to file a claim in court.
The defendant has the power to prove that he did not pay for good reason. Even if the court makes a positive decision on the claim, the property owner is obliged to provide the evicted person with other housing, and not throw him out onto the street.
Article No. 293 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation says that the owner can also lose his home if he does not comply with generally accepted standards:
- Public order disturbance.
- Reconstruction of the building, which is not approved by government agencies.
- If the property is declared unsafe.
When the apartment in which there are utility debts is not the only property the debtor has, then it is much easier to evict him. In this case, the procedure involves the sale of real estate, and the proceeds are used to pay off the housing and communal services debt.
Identical regulations apply to living space that is issued with a mortgage loan. This is explained by Article No. 50 of Federal Law-102. The judicial authorities have the right to make a positive decision, without providing other housing.
Watch the video: “Rent arrears: are tenants at risk of eviction.”
Article 90 cooperative apartment eviction for non-payment
Despite the fact that Article No. 90 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation informs about the possibility of eviction of a person for failure to pay utility bills, this can only be done after filing a statement of claim and receiving a writ of execution. Moreover, the state is obliged to provide them with other living quarters. However, even after this, the debt will not go away and will have to be paid.
Bailiffs will be involved in the seizure of funds or personal property. First, FSSP employees will make an inventory of the contents in the defaulter’s apartment, and then issue an act of seizure of property. The items are then sold and the proceeds are used to pay off the debt.
New laws on evictions for housing and communal services debts in 2021
It doesn’t matter whether the living space is privatized or non-privatized, eviction for non-payment of utilities occurs strictly in accordance with the relevant acts. New rules in the edited Resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 14 dated July 2, 2009 establish a certain procedure for this procedure.
A person always has a chance to resolve the issue through a settlement agreement and not be forcibly deprived of housing. Here are the nuances that the management company or social employer. premises can go to court if the period of debt exceeds six months, and the state must provide other housing for living.
Where will they be expelled?
Many are interested in the question of where citizens who find themselves in debt and were forced to leave their homes as a sanction are evicted.
In this situation, there is only one possible option - these persons are settled in municipal apartments , if there are any available on the balance sheet of a particular municipality.
No one has the right to evict citizens anywhere, so if there are no vacant municipal premises, the tenant will have to postpone eviction.
Conditions for eviction for utility debts
Failure to pay utility bills threatens the loss of your place of residence and registration.
Eviction for debts on utility bills and the provision of other square meters occurs in accordance with the following conditions:
- if the area is isolated;
- at least six m2 is determined for each resident;
- the premises comply with sanitary standards and you can live there;
- location in the same locality.
You can evict and discharge a person from your home only on the basis of the following points:
- Court statement.
- Termination of the employment agreement.
- Imposing obligations to repay debt.
Note: the court does not always decide to provide a citizen with another living space. This most often happens if the property is municipal or the owner has changed (sale of an apartment or donation).
Reasons to pay for housing and communal services
Debt amount
There is no specific amount established by law. According to the law, funds are written off for housing office services on the tenth day of each month. On the 30th day, penalties begin to accrue.
However, if a citizen makes partial repayment of the debt, then even a judge will not be able to evict him for non-payment of utilities. This is due to the fact that the funds are transferred to the account of the management company. There is no specific debt figure. Only the time period plays a role here.
Non-payment period
The Civil and Housing Code states that eviction is possible only after 6 months of non-payment of debts. After this period has expired and a court order has been issued, a person may be forced to check out of the apartment with debts on utility bills. If these rules are violated, the defendant may need the help of a lawyer to defend his rights.
⛔ Can they be evicted from housing without providing another in return (“to nowhere”)?
Eviction without provision of alternative housing is strictly prohibited by law.
If there is arrears for utility services and eviction from a residential premises, the organization that initiated the eviction must provide a roof over the head of the person along with his family; eviction “to nowhere” does not occur.
As practice shows, if a person had an apartment for use under a social tenancy agreement, then he must be provided with housing in such a way that it must meet sanitary standards, and its area is provided at the rate of 6 square meters for each person living together with the debtor . Most often these are rooms in dormitories, which are less comfortable housing than the previously provided apartment.
Amount of debt to limit travel abroad
How to get out of the debt hole on credits and loans
Nuances of eviction of a debtor for housing and communal services from an apartment
A person can be forced to leave the premises only as a last resort. Practice shows that before trials there is a long pre-trial procedure. Citizens who find themselves in a difficult situation should try to negotiate with utility companies or persons responsible for social rent of the premises.
The debtor can protect himself if he partially repays the existing debt. The main condition for the court is the absence of activity on the account for six months. If this period has not expired or is interrupted by partial repayment, then no authority will accept the claim from the management company.
Utility companies do not want to participate in legal proceedings. They will bombard the debtor with demands for payment. Then they can de-energize the premises, turning off the gas, electricity and water supply. The main thing for them is that the debt is repaid. Therefore, most often the management company makes concessions.
Procedure for working with debtors
If you write an application for installment or deferred payment, you can pay off the debt gradually. Only complete ignoring of requests will prompt utility companies to file a lawsuit. In this case, after the decision, the citizen will have to immediately repay the debt in full with penalties and penalties. Moreover, the defendant will be required to pay penalties and costs of the proceedings.
If a person is unable to repay debts in full, then bailiffs have the right to seize property and freeze accounts using a writ of execution. The property will be put under the hammer, the debt will be repaid, and the remaining money will be returned to the defendant under the deed.
This documentation will state:
- inventory of property;
- independent cost assessment;
- a message that the items are kept by the state for two months.
After this, the property is put up for auction.
With a minor child and pregnant women
No court will be able to forcibly evict a minor child from an apartment for debts unless the state provides another living space. When the debtor is in trouble, then, most likely, the highest authority will offer the management company to make concessions and make payment in installments.
A minor child, even one who has not yet been born, is protected by the state until he reaches the age of 18.
During the heating season
If production occurs in winter, then there may be some relaxations. Not a single judge will rule to evict a person from an apartment for debts on utility bills, to the street in the winter.
It’s another matter if he has real estate or close relatives who have living space. The statistics are that most often the courts decide to wait until spring. In this case, the debtor receives an additional delay to resolve the current situation.
From a council apartment
It is easiest to evict a person from a municipal apartment for rent arrears, especially if he has other real estate. The social rental agreement indicates that the square meters belong to the state. The contract is terminated. A citizen renting housing will be required to vacate the premises, in accordance with Article No. 90 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
From privatized housing, if the apartment is owned
Warning the debtor about debts for housing and communal services
Having a certificate of ownership does not guarantee that a person will not be evicted from his square meters. If the amount of debt is large and the owner is not able to repay it, and there is no other property besides the apartment, then the court may rule on the sale of the property.
The claimant, under a writ of execution, can seize the property and put it up for auction. After such a procedure, the defendant will receive the remaining money from the sale of the apartment.
According to the social lease agreement
The situation is similar if the housing is not your own, but rented. Eviction occurs through a judicial procedure with the provision of temporary accommodation. In this case, the person will have to not only look for money to pay off the debt, but also a new living space.
Where will they be evicted?
The court will order the allocation of temporary living space only if the person has nowhere to go. This point applies to both owners and persons who purchased real estate through mortgage lending.
They can be moved to a dormitory or cooperative building that complies with regulations. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 446 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, claimants do not have the right to describe all property. The article contains a detailed list that reflects items that are not subject to seizure.
With a minor child
If we are talking about eviction of a family with a minor child, then it is worth first checking whether there are circumstances that could exempt the family from such a measure.
So, if the mother is on maternity leave or is recognized as unemployed and the child’s father lost his job due to circumstances beyond his control, does not receive wages for a long time or has an income below the subsistence level, then most likely by a court decision this family will be exempted from such a measure and will taken under control .
When they cannot evict for debt on housing and communal services
There are a lot of legal issues that protect the tenant. Not all citizens accumulate debts due to negligence or unwillingness to pay. Circumstances often arise that explain the current situation. Even if the management company sues, a citizen can defend himself and prove that he was forced to accumulate debts.
Valid reasons for non-payment of housing and communal services
The defaulter may apply if he has valid reasons. In this case, any judge will side with the defendant.
Such circumstances include:
- insolvency;
- job loss;
- the large family;
- there are children under 18 years of age;
- disability or illness.
Note: There are also other reasons, but they are not considered valid. For example, alcohol or drug addiction, problems within the family, or the defendant’s forgetfulness.
Consequences of going to court for persistent defaulters of housing and communal services
Valid reasons for non-payment
The legislator protects the constitutional right of citizens to housing and therefore establishes cases in which failure to pay money for the services of public utilities will not be recognized as grounds for eviction.
Such reasons include:
- sudden job loss;
- loss of ability to work due to long-term illness;
- the defendant receiving disability;
- illness of a loved one, requiring large financial expenses.
Each of these grounds will have to be confirmed by the defendant in court. This can be done by providing the justice body with medical documents, an extract from work about layoffs, and a certificate from the labor exchange about registration.
Eviction through court for utility debts
For this procedure, the management company or owner must file a claim with the judicial authorities. It is possible to expel a guest only after receiving a writ of execution. Then follows the discharge of the person from the occupied area.
Who can file a claim
If the property is privately owned and the tenants do not pay for housing services, then the owner has the right to evict them before the expiration of the social tenancy agreement in court. The management company also has this right if the owner does not pay the utility bills, as well as representatives of municipal authorities when a person lives in a state apartment.
Procedure
To have an idea of how the trial process occurs, you should consider the step-by-step instructions:
- File a claim.
- Collect the necessary documentation.
- File a claim with the court.
- Provide evidence base.
- Get IL.
Eviction of a person occurs according to a writ of execution with the participation of bailiffs. However, the procedure will be lengthy – in some cases it takes up to six months.
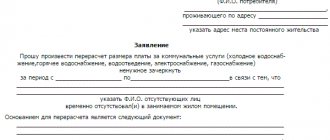
Statement of claim for eviction for housing and communal services debts
The claim is drawn up strictly according to the sample. The court's decision will depend on the literacy and completeness of the data.
Required items:
- name of the authority;
- Full name, address and contact information about the applicant;
- information about the defendant;
- indication of regulations;
- listing of the attached documentation and evidence base.
You must submit your application at the location of your home. There is a state fee for the claim. Only pensioners and beneficiaries can receive a deferment from its payment.
In any case, the plaintiff has the right to include this amount in the demands, as well as indicate other types of expenses that the defendant must compensate.
Eviction for debts on housing and communal services
Documentation
List of required documentation, without which the application will not even be accepted for consideration:
- A claim filled out strictly according to the form on a government-issued form.
- Plaintiff's identity card.
- A list of documents that confirm the violation of his rights by the defendant.
- A receipt indicating that the duty has been paid.
- Housing rental agreement, if the plaintiff is a government representative. Certificate of ownership when the claim is brought by an individual.
- Extract from the house register.
- A certificate stating that there is arrears in utility bills - when submitting an application by the management company.
- Testimony of witnesses.
- Evidence base.
- A protocol that specifies the violated regulations.
Note: a certificate from the housing and communal services department stating that there is a debt is the main evidence. It should be clearly stated there that utilities have not been paid for more than six months.
Arbitrage practice
Let's look at an example from legal practice:
The citizen did not pay for utilities for more than six months and was unable to provide valid reasons for his inaction. The management company filed a lawsuit and collected evidence. Due to the fact that the person was a tenant, the department decided to evict the citizen into temporary housing and pay the debt to the utilities within six months. If any property were registered in the name of a citizen, temporary housing would be denied.
Procedure
The decision to evict an apartment due to non-payment of housing and communal services is made in court. The management organization files a claim against the person , and the court considers the case.
If everything in reality is as the management organization claims, then the person who is subject to deportation is notified that such a decision has been made.
Next, the decision is transferred to the bailiff , who must first notify the person about the imminent eviction, and then come on the day of the procedure to check whether the court decision has been executed. The bailiff must also provide the person with other social housing.
Suspension (restriction) of access to resources and services
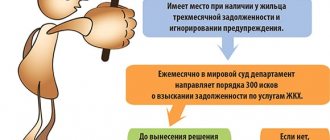
Article 117 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 N 354 determines that the Contractor limits or suspends the provision of utility services, having previously notified the consumer, in the event of incomplete payment by the consumer of the utility service in the amount of two monthly amounts.
To do this, the debtor must be notified and invited to pay in full within 20 days from the date of receipt of the notice.
. The legislator proposed using any mechanisms for prevention. It can be delivered against signature, sent by registered mail, reflected in a receipt, etc. But there is an important nuance here: restricting access to the service should not harm law-abiding residents.
This makes it relatively easy to turn off the electricity
or
gas supply
.
But heating
or
sewerage
in an apartment building is impossible. Management companies put plugs on the water supply, and careless residents simply twist them off. By the way, if the defaulter wants to return the benefits of civilization, it is not enough just to pay off the debt: he will have to pay a fee for the services of the contractor.