- How to declare yourself bankrupt for housing and communal services
- How to pay for utilities correctly
- What to do with housing and communal services debts if the court declares you bankrupt
- How to file an application for insolvency of a citizen due to debts for housing and communal services
- Advantages of contacting Legal Bureau No. 1
Declaring a citizen bankrupt has become possible since October 2015. The mechanism for carrying out the procedure is determined by federal law (Federal Law No. 127), according to which the decision on financial insolvency is made by the court. Writing off debts in bankruptcy for utility bills is not an automatic decision made on the basis of a court order.
In this case, it is necessary to actively interact with the utility provider (ICU), which is the resource supplying organization.
Debts for housing and communal services: what to do?
According to Art. 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, owners and tenants are obliged to maintain the residential premises in which they live. This means that they must pay all utilities on time, including electricity, gas, water and others.
If a citizen does not pay for services, the management company can go to court. Based on the court order, enforcement proceedings will be opened, which may entail the seizure of not only movable, but also immovable property.
Important!
If you have a utility debt, the management company will contact the magistrate to obtain a court order. Its issuance takes a minimum of time and there is no court hearing.
In cases where the debt for housing and communal services is already large, and you cannot cope with the payments, personal bankruptcy remains the best solution. It provides debt write-off, not only for housing and communal services, but also for loans.
How to challenge a claim from a management company
The first step towards challenging claims from a service organization is to reconcile the actual debt with the amount specified in the application. If there are discrepancies, then it is necessary to “raise” the checks and carry out the correct calculation.
If there are compelling circumstances, attach documents to the counter-petition.
Such certificates may include:
- medical;
- from an educational organization;
- from other departments.
Restoring deadlines.
In a situation where non-payment of receipts occurred over several years, an application should be sent to the court to apply the statute of limitations.
Drawing up a petition to apply the statute of limitations
The petition is formed in a free style, as it is a simple document. No specific knowledge is required to compile the paper. The addressee is the highest authority in the area where the property is located. If the amount of debt does not exceed 50,000 rubles, then the petition is sent to the magistrate.
Compilation rules:
- In the upper right corner:
- name of the department (to whom);
- information about the applicant - a complete form indicating the address of residence (from whom);
- In the central part of the text is “a statement on the application of the limitation period.”
- From the beginning of a new line, a request is stated on the basis of Article No. 199 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation to consider the paperwork on the statement of claim from the Criminal Code “name”. Justify the application of the regulation by the date of the last payment. Additionally, indicate that the missed period was due to the fault of the management organization.
- At the bottom is a list of attached papers.
- Date and endorsement.
The document for appeal is sent as part of an open case. Otherwise, the paper will not be accepted for consideration. In this case, the debtor will be obliged to pay the receipts in full, including legal costs, penalties, and sanctions.
There are a number of nuances in drawing up a petition to apply the statute of limitations. Thus, the debtor is not recommended to:
- within the specified period, make payments to your personal account;
- to endorse accounting reconciliation acts from the management organization - to sign means to receive/agree with the debt;
- admit guilt and replenish the balance as an advance.
Note: if there is a large amount of unpaid bills, when proceedings are already underway, it makes no sense to make deductions. After the announcement of the court verdict, the owner will receive an invoice for the return of funds to the management company for the last three years.
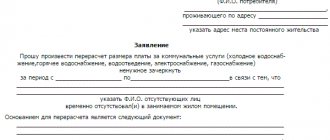
Sample application for application of the statute of limitations for payment of housing and communal services.
Required documents
If there is a dispute over accounts with the management company, you must attach documents to the application to apply the statute of limitations:
- receipt of payment of state duty;
- pay slips from the service organization for the last three years;
- own calculation, if the amount in the claim from the management company does not coincide with independent calculations;
- justification for a difficult life situation when the debtor had to direct funds to other areas - for example, for treatment.
Thus, any papers that are indirectly or directly related to the legal proceedings must be attached to the petition.
Rules for filing a claim in court
An application for the application of the statute of limitations on claims from the Criminal Code should be submitted before the decision is made. Otherwise, the owner will be required to pay the full debt. Therefore, when transferring enforcement proceedings to the FSSP, it makes no sense to write a petition to reduce the contribution.
The application must be submitted in written format. You can submit a petition orally only during the hearing, until the judge leaves for a meeting.
Options for submitting an application:
- through State Services or any other remote method;
- by mail – registered letter, with notification and description of the contents;
- employee of the department office.
As feedback, legal specialists of the management company can provide evidence about the interruption of the period. To avoid having these documents attached to the case, the consumer should not agree with the charges, sign the papers, or deposit funds into the personal account. Even a small payment can cause the debt to be recognized - the court will refuse to satisfy the petition from the owner.
State duty amount
Payment of the state fee for filing a petition to apply the statute of limitations is part of the court costs. That is, the applicant does not need to pay immediately, since collection will occur from the losing party.
Legal costs
A document confirming the need to pay the costs can be submitted to the FSSP for forced collection within six months from the date the resolution comes into force. Before this date a decision is made, after which a ruling is made.
The Code of Civil Procedure of Russia contains the following information on the payment of state duty:
- Art. No. 98, paragraph 1 indicates reimbursement of costs by the participant in the case who was found guilty by the court. Exceptions are provided in the same article, part No. 2. According to the provisions, the expenditure portion also includes monetary expenses incurred by the parties in the framework of appeals to the appellate, cassation and control departments.
- In paragraph No. 2 of Art. No. 98 spells out the rules for cost distribution.
- Article No. 100, paragraph 1 regulates the award of bearing the burden of expenses for representation of interests in court (lawyer) upon a written application within reasonable limits.
- Art. No. 88 indicates the component of the costs, as well as the size and procedure for paying the state duty.
Is it true that housing and communal services debts can be written off through bankruptcy?
Anyone who finds themselves in a difficult financial situation and does not know how to proceed can have their housing and communal services debts written off through bankruptcy. Unfortunately, management companies do not write off debts. If you don't pay, sooner or later they will go to court.
On a note!
We do not recommend taking out loans, and especially loans from microfinance organizations, in order to repay debts to the management company. This will only worsen your already difficult financial situation.
Debts are written off through bankruptcy:
- for utilities
- loans and mortgages
- loans from microfinance organizations
- on promissory notes
- taxes and fees
- traffic police fines
- other financial obligations, with the exception of current payments, alimony and compensation awarded in case of harm to the health or life of third parties
Exclusively for residents of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region of St. Petersburg and Leningrad Region
from
Blog
Photo source: https://www.pexels.com/
Although Mr. Chibis constantly chirps that the population regularly pays for housing and communal services, there is a group of owners from whom it is almost impossible to collect the debt. Most often, these are marginal individuals who can only be submitted to the Cabinet of Curiosities, and even then they will not take them, since there are too many applicants for one place. The period of debt of such comrades is calculated in years, which means that there is a need to write off such debt in accounting with all the ensuing consequences. We'll talk about the consequences...
The Herods don’t pay... We are starting to write off the debt...
Accounting.
The debt of the owner of the premises to the management organization must be recognized as uncollectible and written off from the balance sheet in full, including VAT.
, if one of the following events occurred (clause 77 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n “On approval of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 34n):
- the statute of limitations has expired (in the case of debt for housing and communal services, it is three years);
- the debtor organization has been liquidated;
- the debtor organization is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities as an inactive legal entity;
- The bailiff issued a decision to terminate the enforcement proceedings and return the writ of execution to the recoverer due to the impossibility of collection.
Write-off of bad debts is documented with the following documents:
- settlement inventory act (INV-17). Please note that since 2013, this form is not mandatory for use
, so an organization can develop its own form of the act. - order from the head of the organization.
In the accounting records of the management organization, debt write-off is reflected in the following entries:
Dt 63 - Kt 62 (76)
Bad debt, against which a reserve for doubtful debts was created,
Dt 91 - Kt 62 (76)
Bad debt not covered by the reserve was written off
Dt 007
Bad debt is reflected in the off-balance sheet accounting of the management organization
The amount of debt written off for housing and communal services must be reflected in off-balance sheet account 007 within 5 years from the date of debt write-off
with the hope that the debtor will suddenly become a dollar millionaire and pay off the previously written off debt.
If a miracle does happen and the debtor pays the debt previously written off to an off-balance sheet account, the following entries are made in the accounting records of the management organization:
Dt 51 (50) - Kt 62 (76)
The receipt of money from the debtor is reflected
Dt 62 (76) - Kt 91
The repaid debt is taken into account in income (previously we put it as expenses)
Kt 007
A bad debt repaid by the debtor is written off
Tax accounting.
If everything is clear with the accounting of writing off bad debt amounts, then there are some peculiarities regarding the taxation of these amounts.
Income tax.
The criteria by which a debt is considered bad for income tax purposes are absolutely similar to the above criteria for writing off debt in accounting, so we will not dwell on them.
Please note that the debt of the owner of the premises cannot be considered a bad debt if this debt can be offset against the repayment of the management organization's counter-payables to the owner.
Amount of debt written off, including VAT:
- if the management organization has not previously created a reserve for doubtful debts for the purposes of calculating income tax, it is included in non-operating expenses on the basis of paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the management organization previously created a reserve for doubtful debts in tax accounting, the amount of debt written off is written off against the previously created reserve. If the amount of the formed reserve for doubtful debts is less than the amount of the bad debt being written off
, the amount of excess debt over the amount of the reserve is included in non-operating expenses on the basis of paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Simplified taxation system.
Start to be sad, but writing off bad debts is not reflected in any way when calculating the single tax under the simplified taxation system
(I would like it that way).
The reason is that, according to clause 1 of Article 364.17 of the Tax Code, the date of receipt of income for the purposes of calculating the simplified tax system is the day of receipt of funds in bank accounts and (or) at the cash desk (cash method). And since the money has not been received, it is quite logical that the list of expenses taken into account when calculating the simplified tax system and named in Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not include expenses for writing off bad debts
.
This position, in particular, was expressed in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2021 N 03-11-06/2/9909.
Personal income tax.
Personal income tax and bad debts are made for each other. If you don't believe it, you'll get it...
From January 1, 2021, a new version of clause 1 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is in effect. Clause 5 has been added to this article, according to which the date of actual receipt of income
by an individual is defined, in particular,
as the day when a bad debt is written off in the prescribed manner from the organization’s balance sheet
. This position was expressed in particular in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2017 N 03-04-06/65512.
When writing off a bad debt of an individual, the management organization, on the basis of clause 1 of Article 24 and Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is recognized as a tax agent and must fulfill the duties provided for tax agents by Articles 226 and 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, including the obligation no later than one month from the date the end of the tax period in which the relevant circumstances arose, notify the taxpayer and the tax authority at the place of registration in writing about the impossibility of withholding tax and the amount of tax
.
A form of information on the income of an individual “Certificate of Income of an Individual” (Form 2-NDFL), approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 30, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
The tax office will send the citizen a tax notice about tax payment
. It must be paid no later than December 1 of the year following the year in which the individual received the income.
If the management organization does not send Form 2-NDFL to the tax authority in relation to each individual for whom receivables have been written off, it will be held liable
:
- organization (IP) in the amount of 200 rubles for each unsubmitted certificate
(clause 1 of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); - the head of an organization in the amount of 300 to 500 rubles (note to Article 2.4, Part 1 of Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- You can discuss the article and ask questions here.
- The topic of debt forgiveness was discussed in detail at our webinar. More details at the link
What you need to know if you decide to go bankrupt with utility debts
The first thing you need to decide on is how to write off debts. An individual who does not pay utility bills can go bankrupt in different ways:
Through the arbitration court
To do this, an application for recognition of financial insolvency is submitted, based on the results of which a debt restructuring or sale of property is introduced. If you do not have a stable and sufficient income that will help restore solvency, we recommend that you immediately proceed to the sale of property.
It is convenient that you can go to court for any amount of debt, but if it exceeds 500,000 rubles, then this is no longer a right, but an obligation of a citizen. Otherwise, the creditors themselves, including the management company to which the debt arose, can apply to the court.
Through MFC
Bankruptcy in case of debts for housing and communal services through multifunctional centers is carried out differently. Firstly, this method is used only if the non-payment ranges from 50 to 500 thousand rubles. Secondly, enforcement proceedings should be closed against the defaulter due to the lack of property that could be sold.
This limitation makes bankruptcy through the MFC more difficult than through a standard court procedure. It turns out that this is only possible if the management company or another creditor goes to court, receives a decision or order, but is unable to receive the money due to the debtor’s lack of property.
Consequences and penalties for non-payment of utility bills
If utility bills are not paid on time, the debt grows every month. In addition to accumulating the principal amount, the management company has the right to impose a penalty (Article No. 153 of the Housing Code of Russia). If received payments are ignored and their repayment is put on hold, then the resource supplying enterprise has the right to collect at any time.
Note: if a citizen has a difficult financial situation, experts recommend applying for a benefit to pay for housing and communal services or filing an application for restructuring. Reasons for applying - illness, serious accident, loss of job, etc.
In the absence of deductions on issued invoices, the supplier, within the framework of PP No. 354, can take the following measures:
- cut off the power;
- stop the gas supply;
- shut off the hot water supply.
Additionally, the owner of the premises faces sanctions in part 14 of Art. 155 of the Housing Code of Russia or the imputation of a penalty under Article No. 330 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The last type of fine is applied unilaterally to a party to the contract who fails to fulfill its obligations.
Please note: the legislation also provides for harsher punishment for lack of payments - litigation, eviction from the apartment.
How does bankruptcy happen with housing and communal services debts?
To write off debts for housing and communal services in bankruptcy, you need to draw up an application for recognition of financial insolvency, prepare a set of documents and submit them for consideration. The court will consider the application and introduce bankruptcy proceedings.
Utility debts will be included in the register of creditors' claims and will be repaid after current payments. Even if the debtor does not have any property, the debt will be written off.
On average, the write-off procedure takes about 6-8 months, provided that the case is handled by an experienced lawyer.
Non-payment of housing and communal services: punishment and algorithm of actions
The structure, amount of contributions, procedure for accrual and payment of housing and communal services are indicated in Articles 153-157 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. All benefits provided by law are provided to owners or tenants of premises immediately after signing contracts that reflect the rights and obligations of the parties.
Article 153. Obligation to pay for residential premises and utilities (Federal Law No. 188)
As a result of regular non-payment, the debt accumulates, and penalties are added to the amount. If receipts are issued and sent, but are not cleared by recipients, housing offices and utility providers, this is regarded as ignoring the requirements.
What is the threat?
Due to refusal to pay for housing and communal services, their consumer is subject to various sanctions. According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 345 of 05/06/11, in addition to the accrual of progressive fines, penalties, and penalties, it is possible to limit the supply of resources (water, electricity), and subsequently turn them off completely.
ATTENTION! Housing and communal services enterprises are required to notify the debtor in writing about the termination of the provision of services and set a repayment period, after which the punishment will be carried out.
The citizen also faces a trial, and in extreme cases, deprivation of premises. The latter is acceptable, for example, if the property belongs to government agencies and acts as collateral in a mortgage. Moreover, the amount of debt is over 5% of the cost of the premises; payment for services has not been made by the person for more than six months. Eviction is unacceptable if the property is the only residence of its owners. It is common that the management company (MC) uses illegal methods of influencing people: posting a list of debtors in their home, refusing to issue a certificate of family composition. There are also problems with registration and deregistration from housing. During the work of bailiffs, it is possible to impose a ban on a citizen to travel abroad, restrictions on driving a car (if the debt is more than 10 thousand rubles).
What's the best way to proceed?
How to act correctly in the presence of debt directly depends on the reasons for its formation. Some citizens, due to their convictions, do not want to pay off certain expense items in receipts, others intend to wait until the statute of limitations expires, and still others are in dire financial straits. Accrued fines, penalties (due for the consumption of unpaid services), and penalties additionally contribute to the growth of debt. Therefore, if a difficult life or financial situation arises, it is recommended not to wait for claims from housing and communal services, but to act on your own. You can confirm your difficult financial situation and receive a subsidy or apply for debt restructuring. The first one is available through MFCs (multifunctional centers). They apply to the management company for restructuring.
Writing off debt on payments for housing and communal services is possible if:
- death of a citizen;
- liquidation of the debtor organization;
- declaring a person bankrupt;
- loss of a person's ability to work due to illness or injury;
- expiration of the statute of limitations.
In some cases, recalculation is possible, which will reduce the amount of monetary obligations. However, the grounds for it, outlined by law, must be respected at the same time:
- no one lived in the premises for more than 5 days;
- it does not use individual metering devices.
Recalculation is not made for general house items (repairs, cleaning the entrance, etc.) and heat supply costs.
Video - Ways to write off debts for housing and communal services
What needs to be done to write off housing and communal services debt?
Bankruptcy for housing and communal services and other debts (for example, for loans and traffic police fines) allows you to start your financial life with a clean slate: all debts that have accumulated due to non-payment of utilities will be written off:
- cold and hot water supply
- heating
- gas
- domestic gas in cylinders
- wastewater disposal (sewerage)
- garbage removal and others
To deal with debt obligations to the management company, seek legal help. This will help not only choose an effective bankruptcy option, but also properly prepare for the procedure.
Our lawyers will completely take care of the case of declaring your financial insolvency in court, including drawing up an application, collecting the necessary documents, interacting with the management company and other creditors, if any.
If the deadline has passed, will the debt be written off after 3 years or the claim period?
Debt write-off after the expiration of the claim period can be achieved if:
- During the court hearing, it will become known that the defendant has gone through bankruptcy proceedings;
- The statute of limitations will interrupt the flow of the debt;
- They will establish a time frame, where the starting point is the moment when the service provider learned about the debt.
Legislation on writing off housing and communal services debts older than three years
According to Chapter 26 of the Civil Code, the expiration of the statute of limitations is not a basis for terminating an obligation. Debt write-off is a right, not an obligation, of the creditor.
Possible actions of management companies and homeowners associations in the event of debt formation
There are 5 ways to collect debt from a debtor to a management company:
- Preventive measures, that is, preventive work to prevent the occurrence of debts. For example: consequences following non-payment;
- Pre-trial collection - pre-trial collection measures that can help in repaying the debt. For example: conversations with debtors, general meeting of owners;
- Collection through court - collection of debt in court;
- Ensuring the execution of a judicial act of collection;
- Bankruptcy of individuals, that is, the ability to pay off debt through their property.
In addition to the title company, your homeowners' association also has an impact on the repayment of your debt. It can:
- Post the list of debtors for public viewing;
- According to Russian Government Decree 354, HOAs have the right to limit the debtor’s use of utilities;
- File a claim in court to collect the debt;
- Accrue penalties.
Consequences of utility debt
The law provides the following penalties for failure to fulfill obligations:
- Article 155 of the Housing Code - a penalty is charged for each day of delay;
- Government Decree No. 154 - the management company has the right to limit the debtor’s use of utilities;
- Article 3 of the Civil Procedure Code - when the amount of the debt exceeds the permissible norms several times, the management company has the right to collect the debt with the addition of a penalty in court;
- Article 3.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses - a person who fails to fulfill his obligations under a contract may be subject to an administrative fine;
- According to Article 83 of the Housing Code, a persistent defaulter can be evicted from the house.
Accrual of penalties and how to calculate its size
Citizens who have not paid or paid, but not in full, debts for utility services must pay a penalty in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate
- From 1 to 30 days of debt no penalties are charged
- From 31 to 90 days inclusive, penalties will be charged in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate
- From 91 to the day of actual payment, the refinancing rate will be 1/130
Restricting access to resources
If the debtor does not repay his debt within 90 days, then the management company has the right to disconnect the debtor from utilities (except for cold water and heating). If the owner independently tries to connect to the services, he will face a fine of 10 thousand for individuals, 30 thousand for officials and 100 thousand for legal entities.
Eviction
Sometimes severe measures, such as eviction, may be taken against persistent defaulters. Owners can collect debt through court. In the case where the debtor lives in an apartment that belongs to the municipality, he is evicted to a smaller apartment.
What are the risks of rent arrears?
The expiration of the statute of limitations can be punished by the state in different ways: it all depends on the amount of the debt and on what category the owner of the service premises belongs to:
- Owner of a privatized apartment;
- Owner of municipal housing;
- Owner of the rented premises.
In a privatized apartment
Obligations begin from the moment you begin living in the apartment, regardless of whether it is a temporary or permanent owner. In this case, the debtor will be punished on a general basis
In public housing
In this case, a three-stage system operates:
- A letter is sent to the debtor with information about the debt. The same letter notes that in case of refusal of the debt, the case will be taken to court;
- If the first point does not help, then a second attempt is made to reason with the debtor: the management company makes a call or reminds about the debt in a personal meeting;
- If the debtor still does not pay the debt, then the case is taken to court and the debtor is punished in accordance with the general procedure.
In a rented apartment
Renting an apartment does not relieve you of the responsibility and obligation to pay for utilities. If payment is overdue for more than half a year, an eviction procedure for an apartment with a smaller area is possible.
Consequences for credit history if payments are late
Utility debts are equivalent to credit debts and are entered into the credit history.
In order for your debt to be included in your credit history, one application to the court by the utility service provider is enough. After this, the debtor has 10 days to repay the debt, after which his data and file on the debt are transferred to the credit bureau. Having utility debt can be a huge barrier to getting a loan.
Option for judicial resolution of the dispute
When all possible options have been exhausted, the only option left is to go to court. If it is possible to involve a lawyer, he will help you file a claim in court. It is served where the defendants live. A claim is drawn up according to the general rules. All requirements are stated briefly and concisely. The application must be dated and signed by the applicant.
If the application is accepted, then within five days the judge will make a decision to initiate a civil case. The case will be considered within 2 months, but sometimes it can be reduced. If we rely on law enforcement practice, then the demands put forward by the plaintiff are almost always satisfied. The court will divide the debt on utility bills. The decision will be sent to the service provider. Starting next month, each user will receive a separate receipt.
Utility payments must be paid in full and on time. Unscrupulous payers must clearly remember that no one is going to pay their debts.
Housing and communal services in 2021 – how much will tariffs increase and what’s new in this area
Every year, Russians notice in their receipts an increase in tariffs for paying for housing and communal services. This is due to the fact that the costs of providing networks are constantly growing.
However, in each region there is a bar beyond which the tariff growth rate cannot go; most often it does not exceed inflation and is within its limits. Therefore, in 2021 this figure should not be higher than 4%.
FAS reports that the increase in prices for utilities in the regions will not exceed 3.3%.
If the indicator is nevertheless exceeded, the FAS will personally determine the violation and issue instructions to lower the threshold.
Another pleasant moment for Russians was the proposal by official Dmitry Ionin about the possibility of compensation for housing and communal services. He proposes either to reimburse part of the payment of bills from public funds, or to reduce tariffs in the regions.
This is due to the difficult economic situation of the population, and is offered precisely as another support for citizens during a difficult pandemic period.