Author of the article
Yulia Kuprina
Certified lawyer. Total work experience in the specialty is 13 years.
By law, the installation of IMU (individual metering devices) is mandatory when there are no design difficulties. It happens that this cannot be done objectively, for example, due to the dilapidation of water pipes.
There are no fines for missing meters. But the owner of the apartment is “punished” with increased rent. If there are no mechanical obstacles to installing an IPU, but the owner refuses to install them, then payment for used water is determined using an increased coefficient. The figure turns out to be quite impressive.
The standard water consumption per person without a meter was calculated back in the 20th century and has remained at the same level for more than 25 years. In 2021, the indicator also did not change. It may vary slightly based on the design features of the building.
The legislative framework
The main document regulating the provision of services in the water supply sector is Government Decree No. 354. The current set of rules contains formulas for calculating the standard for the use of hot water and cold water. The values apply to residential premises with and without installed water meters.
Federal Law No. 210-FZ regulates the use of fixed rates in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The price for 1m3 of water is determined by the municipal service based on the meaning of this law. The cost of paying for water without a meter is determined for each subject of the Russian Federation individually.
Consumption of water without a meter significantly increases the amount on your receipt. Especially considering that incentive measures will gradually tighten. This is due to the fact that the state strives to minimize the possibility of various manipulations with payment for the resource used. For example, if in fact there are only one number of people living, but there are much fewer registered ones.
How to fill out a receipt
At the moment, almost all accruals for consumed resources are carried out automatically. This provides a more convenient calculation procedure and eliminates errors, but does not relieve owners of houses and apartments from the need to check information.
In some situations, you may need to fill out the receipt yourself.
Sample of filling out a receipt
Step-by-step instruction:
- The period of document generation is indicated. All values must be entered legibly, without errors or corrections.
- Personal information is entered into the corresponding line of the table: full name, address, household IPU number, if it has not been registered previously.
- The number of people registered in the apartment or house and the number of persons entitled to receive benefits are indicated.
- If any, the debt or overpayment is included. The name of the service is marked taking into account the unit in which it is measured and the time period.
- The volume of consumption for the billing period is entered.
- Enter the full amount to be paid, after which you need to calculate the total taking into account benefits.
- All information is clarified and confirmed by signature.
- If during the specified period the meter was being calibrated, then consumption will be measured based on the average value for 3 or 6 months.
The completed receipt must be submitted to the institution that provides admission.
Consumption rate of cold and hot water without a meter
There is no uniform consumption standard for all subjects of the Russian Federation. It is different for each region or region. It was calculated that in Russia the average rate of hot water per person without a meter was 4.75 m3, cold water per person per month - 6.935 m3. This is when there is no IPU. When a water meter is installed, you should pay for utilities based on its readings.
This data has advisory value. In the capital, the water consumption rate is established: for hot water supply - 4.75 m3, for cold water supply - 6.94 m3.
Factors that were taken into account when making calculations, based on average indicators:
- 30 liters – for a shower every day;
- 200 liters per week for daily needs;
- 200 liters per day – the filling capacity of the toilet tank;
- 200 liters per week – washing in the bathroom;
- Other consumption, which is associated with cleaning, washing dishes, laundry, etc.
The indicator of general household consumption may also be included in the “other” category. This includes cleaning the house, leaking pipes, and so on.
The monthly amount may be high. Therefore, installing water meters will quickly pay for itself.
Average figures are a rather overestimated indicator, even when the owner does not save on water consumption. Utilities have the right to increase the standard reading, but not more than its double value. For example, for Moscow: the maximum value of hot water supply will be 9.5 m3, cold water supply – 13.88 m3.
According to paragraph 28 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2016 No. 1498, from January 1, 2017, when there is no water meter in a residential building, the calculation is made based on the number of registered people. This also applies to those citizens who have a temporary registration.
How to take readings correctly
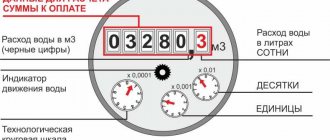
Most water meters have eight windows, five of them with black numbers. In the three right-hand windows the numbers are colored red.
The black numbers show the cubic meters of water used. They are what we need. The red numbers are liters of water used. When the value reaches 999 liters plus one more liter, the red part of the water meter is reset to zero, and a unit is added to the cubic meters section.
To obtain information about water consumption, you need to take readings from the black windows. If there are more than 500 liters in the red windows, then you need to round up - add one to the readings.
Follow the link for details on how to take readings from a water meter and what numbers to write.
Increasing coefficients
Since 2011, the increasing coefficient (IC) for water without a meter has been used in relation to owners who, for various reasons, have not installed water meters. In 2021 it is 1.5.
The increased coefficient is introduced to encourage citizens to install water meters. It is beneficial for the municipality for the owners to install individual metering devices, because one person can be registered in the apartments, but in fact there are more people living there. And actual water consumption increases several times.
Thus, it is necessary to multiply the current water consumption standard per person, the number of registered people, the tariff and the PC. The figure turns out to be large, and it encourages people to install water meters.
The coefficient is not entered when it is technically impossible to install an individual meter. For example, due to dilapidated pipes.
They plan to increase the increasing coefficient to 1.6. This suggests that the state will continue to raise this figure. Therefore, for owners of residential premises who have not yet installed an IPU and have the technical ability to do so, it is more profitable to buy a water meter.
Payment for housing and communal services without a contract
In 2021, paying for utilities without a contract threatens big troubles. State legislation has introduced new rules, according to which from now on contracts for the supply of resources with companies must be concluded directly with payers. Previously, this responsibility was assigned to the HOA, which led to negative consequences due to the huge accumulated debt of the population.
The law on mandatory conclusion of contracts and a number of other legislative innovations will help resolve the process of debt restructuring and restore balance in the utility sector. New radical sanctions for persistent defaulters can also affect the structure of the population’s total debt.
Formula for paying for water without a meter and example
There is no uniform tariff for water in Russia. Each subject has its own. This is due to the climatic characteristics of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as the level of density of people living in it.
Thus, the standard figure is not final when paying. How many cubic meters of water a citizen spends monthly is reflected in the current standard.
Thus, to independently calculate how much to pay for water consumption in an apartment without an IPU, you need to know the current tariff, the number of people registered at the place of residence, the standard and PC.
Let us calculate the consumption of cold water and hot water using the example of Novosibirsk.
Novosibirsk regional tariff HVS = 17.16 rubles. per 1 m3 Cold water standard = 5.193 m3 Increasing factor = 1.5 Number of registered citizens = 2 Thus, 17.16 * 5.193 * 1.5 * 2 = 267.335 rubles.
The owner of the residential premises will have to pay this amount for the consumption of hot water.
Now DHW. The increasing coefficient and the number of registered citizens are the same.
Novosibirsk regional hot water tariff = 100.10 rubles. for 1 m3 DHW standard = 3.687 m3 Thus, 100.10 * 3.687 * 1.5 * 2 = 1107.206 rubles.
The current tariff can be found by calling the city water utility.
If there are no officially registered people in the apartment, then the fee will be charged in this case as well. Then, instead of the number of residents, the value of the number of owners will be substituted.
The solution in this situation is to install water meters. If the water is not used, then you will not have to pay anything.
You can also contact the management company with a request to seal the water pipe. They will do this the next day after your request. Therefore, during the period of absence, no charges will be made for water consumption.
Another reason for the lack of accruals in a residential building that is not equipped with an IPU may be a document confirming military service, sick leave, and the like.
Taking readings
In order to correctly write off readings for submission to a service organization, you need to know exactly what to read.
The counter dial includes 8 digits. The first five black symbols are the main ones; they show the total number of cubic meters of water consumed. This information must be recorded on the payment receipt. The last three red digits are auxiliary, separated from the main ones by a comma and indicate the consumed liters.
At the moment, water meters are produced with three types of panels, but in the domestic sector, type No. 1 is considered the most popular and easiest to operate.
General rules for taking readings:
- The characters before the comma must be specified first. It is taken into account that when transmitting information there is no need to write off the leading zeros.
- If the last three digits are greater than 600, then it is advisable to round the value to the cube. This is not a violation.
Information from the meter should be taken according to the following scheme:
- The numbers on the dial (for example, 00015.784) indicate that more than 15 m3 of water was consumed during the corresponding period.
- The number of liters is rounded to 16 cubic meters. These readings are transferred for calculation.
- Next month the data will change and the dial will show 00022.184 (22 m3).
You need to understand that it is the current readings that are taken into account. But most often, the owner of the premises does not need to deal with the number of cubic meters; this is done by the service organization.
Standards and tariffs for water consumption by city for 2021
Current water tariffs and standards vary for each subject of the Russian Federation. They are established by local authorities based on regional characteristics, population density and other reasons.
The table displays the values of subject standards and tariffs for water without a meter in 2021. They are relevant for all apartments that have plumbing equipment and are connected to the utility network.
It is also worth considering that within the city the indicators may vary slightly. It all depends on the company that provides the resource. Consequently, the cost of water without a meter will vary.
| City | Hot water supply | Cold water supply | |||
| Standard | Rate | Standard | Rate | ||
| Moscow | 4,745 | 198,19 | 6,935 | 40,48 | |
| Saint Petersburg | 3,48 | 105,92 | 8,48 | 31,58 | |
| Permian | 2,8 | 162,31 | 5,72 | 33,03 | |
| Samara | 3,24 | thermal energy | 1682,40 | 8,13 | 31,60 |
| coolant | 37,55 | ||||
| Ufa | 3,24 | thermal energy | 2134,16 | 7,55 | 25,68 |
| coolant | 25,68 | ||||
| Omsk | 3,4 | thermal energy | 1397,84 | 6,7 | 17,08 |
| coolant | 17,93 | ||||
| Chelyabinsk | 2,56 | 60,48 | 6,06 | 25,14 | |
| Krasnodar | 2,65 | thermal energy | 1621,58 | 6,59 | 38,71 |
| coolant | 25,33 | ||||
| Kazan | 3,57 | thermal energy | 1541,90 | 8,96 | 20,59 |
| coolant | 20,59 | ||||
| Rostov-on-Don | 3,45 | thermal energy | 2205,66 | 6,5 | 20,59 |
| coolant | 49,79 | ||||
| Nizhny Novgorod | 3,77 | 88,84 | 6,74 | 19,04 | |
| Saratov | 3,18 | thermal energy | 1909,72 | 7,55 | 25,10 |
| coolant | 25,10 | ||||
| Novosibirsk | 3,68 | 108,19 | 6,47 | 18,56 | |
| Penza | 3,20 | thermal energy | 1780,64 | 6,67 | 39,86 |
| coolant | 25,10 | ||||
| Smolensk | 3,92 | 151,83 | 6,60 | 25,19 | |
| Kaluga | 3,20 | thermal energy | 2104,62 | 7,56 | 28,25 |
| coolant | 28,25 | ||||
| Belgorod | 3,17 | 110,04 | 7,45 | 25 | |
How to pay for water by meters
The procedure for making a payment may vary depending on the region and service company, but most often the standard scheme applies:
- Water meter readings are taken. Information must be submitted at a certain time. The exact period is not specified in the law and is set by housing and communal services enterprises and management companies independently. To avoid mistakes, it is better to clarify the period in the contract with the service provider. Information from the EIRC and other specialized organizations is accepted.
- Based on the data received, the service company makes a calculation and sends a receipt to the owner of the premises.
- Any authorized person can pay for the consumed resource. The easiest option is to give the document to a settlement center or bank.
It is taken into account that it is necessary to transmit water meter readings exclusively to the utility service provider. This role can be played by a homeowners’ association, a management company and supply organizations. Situations are also allowed when the main performer delegates the functions of receiving data to a specialized structure.
Service companies present different ways of taking testimony. The most convenient option is via the Internet or using programs. The traditional method is to enter the data on the form and leave it in a special box or take it directly to the organization’s office.
Calculation of water tariffs using the method of economically justified expenses (costs)
If tariffs for water or water transportation are established for the first time for an organization providing water supply or water transportation services (a new organization or water supply/water transportation services have not previously been provided), the Method of economically justified expenses (costs) is used for calculation. It is sometimes called the “GRP Method” (GRP stands for Required Gross Revenue). The methodology for calculating tariffs for water and water transportation using the method of economically justified expenses (costs) was approved by order of the Federal Tariff Service dated December 27, 2013 No. 1746-e “On approval of guidelines for calculating regulated tariffs in the field of water supply and sanitation.”
Calculation of water tariffs using the method of economically justified costs (expenses), performed by our specialists, includes the following steps:
Analysis of water supply network diagrams
A specification for water supply network diagrams is drawn up - information on the diagram is written down in sections between wells, indicating the numbers of wells, points of connection for subscribers, the lengths of network sections, diameters, the number of fire hydrants, the number of shut-off valves installed on the networks.
Master plan for calculating water tariffs
- Summary specification for water supply networks (PDF)
- Fragment of a water supply network diagram for drawing up a specification (PDF)
- Clarification of network lengths according to working design documentation (PDF)
- Calculation of the number of shut-off valves on water supply networks (PDF)
Read more about analyzing water supply network diagrams
Formation of a water consumption balance for the regulation period
The balance of water consumption for calculating water tariffs using the method of economically justified expenses (costs) is formed on the basis of water supply contracts or water transportation contracts concluded with consumers of services.
Water consumption balance (PDF)
Read more about creating a water consumption balance for the regulation period
Study of the technological process of water supply
The study of the technological process of water supply when setting water tariffs using the method of economically justified expenses (costs) includes:
- study of the technological scheme for lifting, purifying and transporting water; mechanical, chemical and other methods of water purification and disinfection;
- study of the chemicals used, reagents, their consumption rates for water purification and disinfection;
- studying the characteristics of equipment used in lifting, purifying and transporting water;
- study of the characteristics of metering devices for raised water, transported water and metering devices installed at consumers.
- Technological processes on VZU (PDF)
- Technological solutions on VZU (PDF)
- VZU technological diagram (PDF)
Read more about studying the technological process of water supply
Standard calculation of water consumption for technological needs, calculation of water losses during its production and transportation for the period of regulation
Calculation of water consumption for technological needs, water losses during its production and transportation in a centralized water supply system is carried out by our specialists on the basis of the order of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated October 17, 2014 No. 640/pr “On approval of the Guidelines for calculating losses of hot, drinking, technical water in centralized water supply systems during its production and transportation.”
Standard calculation of water losses (PDF)
Read more about the standard calculation of water consumption and losses
Formation of water supply balance
The water supply balance for calculating water tariffs is formed for the regulation period based on the calculated volume of water consumption and the calculated standard water consumption for technological needs and the volume of water losses during its production and transportation.
Water Supply Balance (PDF)
Read more about creating a water supply balance
Calculation of standard consumption of materials (chemical reagents and other materials) for water purification and disinfection and the costs of their acquisition
Calculation of the standard consumption of materials for water supply to take them into account in the water tariff is carried out in accordance with the technological process and standards for material consumption.
Chemical Quantity Calculation (PDF)
Read more about calculating the standard consumption of materials and the costs of their acquisition
Calculation of standard electricity consumption and costs for the purchase of electricity
Calculation of standard electricity consumption for inclusion in the water tariff is carried out on the basis of information obtained from studying the technological process of water supply. Electricity consumption for technological needs for water supply is calculated for the regulation period:
- based on the characteristics of the electrical equipment installed (at water intake, treatment stations, water pressure boosting stations) - type, brand, power, quantity;
- hours of operation of installed electrical equipment - calculated taking into account the volume of lifting, pumping and purification of water, the productivity of installed equipment, and the demand factor.
Calculation of standard energy consumption (PDF)
Read more about calculating standard consumption and costs for purchasing electricity
Calculation of labor costs and social contributions from the wage fund
The calculation of labor costs and social contributions from the wage fund for inclusion in the water tariff is carried out on the basis of the norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation, the staffing table, the Regulations on wages, the Collective Agreement, orders for additional payments, combinations and other local acts of the regulated organizations.
In accordance with the technological process, the characteristics and quantity of installed equipment, and the length of networks, the standard number of main production workers and operational management for water supply is calculated. The number of junior service personnel for the maintenance of water supply facilities is calculated - cleaners of industrial premises, cleaners of production areas. If there are vehicles and special equipment, the standard number of drivers, tractor drivers and machinists is calculated.
Calculation of the standard number for water supply (PDF)
Learn more about calculating labor costs and deductions
Calculation of depreciation expenses
Expenses for depreciation charges for inclusion in the water tariff are calculated on the basis of inventory cards (OS-6), commissioning certificates (OS-1, OS-1a), depreciation rates, initial cost, useful life and operation, data about reconstruction and modernization.
Calculation of depreciation charges (PDF)
Read more about calculating depreciation expenses
Calculation of repair costs
Repair costs in the water tariff include the following costs:
- for major repairs of water supply facilities by contract and economic means;
- for routine repairs of water supply facilities by contract;
- for materials for routine repairs carried out economically for water supply facilities.
Pipes for repair work
Gate valves for repair work
Read more about calculating repair costs
Calculation of rental costs and leasing payments
The calculation of costs for renting water supply facilities is carried out in accordance with clause 44 of the Government of the Russian Federation Decree No. 406 dated May 13, 2013 “On state regulation of tariffs in the field of water supply and sanitation.” The rent included in the tariff includes:
- depreciation deductions;
- property tax;
- land tax (or land rental payments);
- other obligatory payments of the owner related to the ownership of leased property.
Rent calculation (PDF)
Read more about calculating rental costs and leasing payments
Calculation of costs for purchased products
Costs for purchased products are calculated if the regulated organization purchases water from another resource supply organization or pays for water treatment services or water transportation.
Learn more about calculating costs for purchased products
Calculation of workshop costs
The calculation of shop expenses for the formation of water tariffs consists of determining the amount of general production expenses directly related to the type of water supply activity.
Shop water supply costs include the following types of expenses:
- labor costs and deductions from the wage fund of shop personnel;
- electricity costs for workshop electrical equipment;
- costs of depreciation on fixed assets for workshop purposes;
- labor protection costs;
- training costs;
- water testing costs;
- costs for maintenance of water supply facilities;
- emergency dispatch service costs;
- costs of household goods for water intake and/or water treatment plants;
- costs for low-value and quickly wearing items, fixed assets worth up to 40 thousand rubles and a useful life of less than 1 year;
- other industrial services for water supply.
Shop expenses (PDF)
Read more about calculating workshop costs
Calculation of administrative expenses
The calculation of administrative expenses for the formation of water tariffs consists of determining the amount of general expenses (general operating expenses) - expenses accounted for in account 26 “General expenses”. Administrative expenses for the period of regulation for the enterprise as a whole are calculated on the basis of concluded contracts for general business purposes, actual costs and justified planned expenses for the period of regulation. The tariff for drinking water, calculated by the method of economically justified expenses (costs), includes the share of administrative expenses attributable to the type of water supply activity in accordance with the method of distribution of indirect costs reflected in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
- Distribution of General Business Expenses (PDF)
- Administrative expenses (PDF)
Read more about calculating administrative expenses
Calculation of expenses for paying taxes and fees
Calculation of expenses for paying taxes and fees to take them into account in the tariff for drinking water, calculated by the method of economically justified expenses (expenses) consists in determining the amount of expenses necessary to pay taxes and fees related directly to the type of activity “Water supply” and the share of costs for payment taxes and fees for general production and general economic purposes related to the type of activity “Water supply”.
- Water tax calculation (PDF)
- Calculation of land tax (PDF)
- Property Tax Calculation (PDF)
Read more about calculating expenses for paying taxes and fees
Calculation of standard profit
The calculation of the standard profit taken into account in the water tariff consists of determining the amount of the following types of water supply costs:
- costs of repaying loans and credits, paying interest on loans and credits used to implement the investment program for water supply, as well as for replenishing working capital for water supply;
- costs of capital investments in water supply for the period of regulation in accordance with the approved investment program for water supply (excluding interest on loans and credits attracted for capital investments in water supply);
- expenses for social needs provided for by the collective agreement of the regulated organization.
Standard profit (PDF)
Read more about calculating standard profit
Calculation of water tariffs
Calculation of water tariffs consists of the following steps:
- formation of the required gross revenue (GRR);
- distribution of non-residential income by half-year for the regulation period (for the 2nd half of the year, the corresponding deflator index is applied for each item of expenditure);
- calculation of water tariffs by half-year for the regulation period:
water tariff in the 1st half of the year = NVV 1st half of the year / volume of useful water supply in the 1st half of the year;
water tariff in the 2nd half of the year = NVV 2nd half of the year / volume of useful water supply in the 2nd half of the year.
Calculation of tariffs for drinking water
Calculation of tariffs for drinking water (PDF)
Formation of a production program for water supply
The formation of a production program for water supply is carried out in accordance with the Methodological Recommendations for the development of production programs of public utility organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated October 10, 2007 No. 101.
Production program for water supply part 1
Production program for water supply part 2
Read more about the formation of a production program for water supply
Formation of a tariff proposal (tariff application) for setting water tariffs
Formation of a tariff proposal (tariff application) for setting water tariffs consists of the following stages:
- creating folders with calculation tables (calculation of water tariffs);
- creating folders with supporting documents on the basis of which water tariffs are calculated;
- writing an explanatory note;
- writing an application for setting water tariffs;
- writing a statement on the choice of regulation method when setting water tariffs;
- compiling an inventory of all documents;
- numbering of documents in folders with inventories;
- signing of the tariff proposal (tariff application) by the head of the regulated organization and certification of signatures with the seal of the regulated organization;
- scanning all tariff offer documents and recording them on electronic media;
- stitching together all tariff offer documents, certifying them with the signature of the manager and the seal of the regulated organization;
- sending a tariff proposal to the state regulatory body in the field of tariff setting to establish water tariffs for the regulated organization.
Volumes of tariff proposal for water
Inventory for tariff application for water tariffs 1
Inventory for tariff application for water tariffs 2
Explanatory note for calculating water tariffs 1
Explanatory note for calculating water tariffs 2
Explanatory note for calculating water tariffs 3
Energo Tariff Holding LLC provides full support for generated tariff proposals (applications) when approving tariffs by regulatory authorities, as well as when challenging approved tariff decisions in the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia and the courts.
We also calculate tariffs for sewerage.
Our advantages
NORMATIVE BASE
We monitor changes in current legislation. We use only current regulatory documents. When conducting examinations, documents that have legal force during the disputed period are used.
QUALITY AND TIME GUARANTEE
An Agreement is concluded, which specifies all essential conditions, which guarantees compliance with deadlines and obtaining a high-quality final result.
We carry out turnkey work.
COMPETITIVE PRICES
We do not inflate the cost of services.
The price always corresponds to the amount of labor resources expended and time to complete the Contract.
WIDE SELECTION OF SERVICES
We make calculations of all types of tariffs, standards, prices.
We carry out all types of technical and economic examinations.
We carry out calculations and examinations for exclusive services.
EMPLOYEE QUALIFICATIONS
The diverse qualifications of our specialists allow us to carry out non-standard projects and find the optimal solution for complex tasks.
INDIVIDUAL APPROACH
Individual approach for each client. We take into account the specifics of the activity, the composition of the property complex, the availability of supporting documents from the Customer and his wishes.
Full confidentiality.