Home / Real estate / Land / Categories of land plots
Back
Published: 11/02/2017
Reading time: 10 min
0
840
Forest plot is a land plot located within the boundaries of forest districts/forest parks and formed in accordance with the requirements of land legislation and the Forest Code.
- Rights to plots
- VRI for these lands
- Amnesty of forest areas
- Construction Who can apply for land transfer?
Legislation on forest resources
Forest fund lands are a special category of land, which is regulated by the Forest Code and the Land Code.
The forest fund includes areas covered with shrubs, trees and grass or not covered with forest vegetation (but intended for forest restoration in the future), as well as areas used for forestry and located within the forest fund.
The forest fund includes areas of non-forest and forest. It includes areas without vegetation, in particular:
- with felling - on which stumps remain;
- with young forest;
- with burnt and dead trees;
- with clearings and free from forest;
- with open spaces: isolated trees.
The Forest Fund includes all forests, except for forests in areas for defense purposes (used by the armed forces) and settlement lands.
They are indicated on maps with special signs.
Rights to plots
According to the Constitution, the forest fund of Russia is jointly owned by the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the federation. If a forest plot is located in areas of defense significance, then only the federation can be the owner.
Forest fund lands are prohibited from being used in free circulation: sales and purchase agreements are not allowed in relation to them and they cannot be the subject of a pledge.
At the same time, the legislation allows the transfer of such lands for the use of individuals and legal entities under agreements:
- rent;
- free use;
- concessions;
- short-term use.
Russians can freely use these lands to satisfy their needs: picking mushrooms and berries, hunting and fishing.
Citizens can restrict access to forest areas only in the event of life-threatening situations: for example, in the event of a forest fire or a threat to environmental safety.
Is it possible to register forest fund lands as property?
The only possible way to register a forest plot as a property from the point of view of the law is to change the category of land. And it is worth saying that when the issue concerns forests, this is a very difficult procedure.
Permission to change the category for subsequent re-registration of ownership is issued at three levels - local, subject of the Russian Federation and federal. You should contact the Forestry Department if the territory is demarcated, and the Government of the Russian Federation if the boundaries are not marked.
The procedure requires collecting an impressive package of documents. All of them must be impeccable from a legal point of view. Decisions on transfer are not made immediately; the process often drags on for several years. It is much easier to lease such land.
VRI for these lands
Article 25 of the Forest Code identifies the following types of permitted exploitation of lands from the forest fund:
- harvesting of wood, resin, non-timber forest resources, food forest resources, medicinal plants;
- hunting farm;
- agricultural management;
- research and educational activities in the field of forestry;
- recreational activity;
- growing forest plantations;
- growing seedlings, berries, fruits and ornamental plants;
- geological research work;
- construction of reservoirs, linear facilities, wood processing;
- religious activity.
In which forests you cannot build linear objects
The construction of linear facilities is not allowed in all forest areas. Thus, capital construction projects cannot be located in the following forest areas:
- in forests located in specially protected natural areas (clause 3 of the Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation dated July 16, 2007 No. 181 “On approval of the Peculiarities of the use, conservation, defense, and reproduction of forests located in specially protected natural areas”);
- in forested areas (clause 3 of Article 105 of the Forest Code);
- in urban forests (clause 5.1 of Article 105 of the Forest Code;
- in specially protected areas of forests (clause 5, clause 2, article 107 of the Forest Code).
In other categories of forest protection, placement of capital construction projects under linear objects is permitted.
Amnesty of forest areas
In July 2021, the State Duma adopted in its final reading a bill called the Forest Amnesty.
This law should solve the acute problem of illegal construction in disputed territories.
What do legislators understand by “disputed territories”?
Currently, the USRN and the Forest Register contain many intersections. According to the first register, this land belongs to areas on which the construction of housing and their transfer to private ownership are permitted. Whereas the Forest Register does not allow such use of the land included in its composition.
What is the essence of the Forest Amnesty?
She assumes that all controversial situations should be interpreted in favor of the Unified State Register of Real Estate. This means that all cases of use of lands from the forest fund registered in the cadastral register are declared legal starting this year.
The law refers to huge areas: in the Moscow region alone, the disputed territory includes over 185 hectares of land allocated for dacha or private development.
The forest amnesty has many advantages. Finally, it will resolve lengthy litigation to determine the categories of land plots. The law will also solve the problem of thousands of Russians who, by mistake of cadastral engineers, were allocated plots for dacha construction from forest fund lands. As a result, they had difficulty legitimizing the buildings. An amnesty will allow such citizens to secure property rights for themselves.
The adoption of the forest amnesty law had many opponents. They fear that the priority of the Unified State Register of Real Estate will lead to a massive withdrawal of land from the forest fund and the destruction of a huge tract of Russian forest. It is assumed that the forest amnesty will lead to mass construction in forests in areas of large cities.
Thus, according to ecologists, the forest fund may be reduced by 1.7-4 hectares, which has very negative environmental consequences.
The law also equalizes the rights of those who unwittingly became the owner of a plot in the forest fund and those who seized this land by criminal means as a result of the use of fraudulent schemes.
Both of them, as a result of using the implemented legal norms, will be able to become full owners of forest areas.
Transfer of land from the forest fund to another category
There are several circumstances on the basis of which a transfer is possible:
- Changing the purpose of the territory in forest management documents.
- Adjustment of settlement boundaries.
- Availability of an appropriate environmental assessment report.
- Inability to operate the site for its intended purpose.
- Ending the need to meet forestry needs.
In other circumstances, changing the category of land is not allowed.
To make a transfer, you must submit an application to the authorized body. Any interested person can do this.
The application shall indicate the following information:
- cadastral number of the plot;
- the category to which the land currently belongs;
- desired category;
- justification of the reason for the transfer.
The following documents are attached to the completed application:
- extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate;
- civil passport/extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs;
- conclusion of an environmental impact assessment (if required by law);
- estimated data on forestry losses.
The application with a package of documents is sent to the authorized department of the municipality or other body. If consideration is refused due to documents not meeting established requirements, the applicant will be notified within 30 days. If the papers are accepted for consideration, the result will be known after three months.
When a decision is made on the application, the authorized body sends a report. This document contains information about the land plot, as well as the verdict. If a change of category is allowed, the applicant can submit documents to the municipality to register ownership of the plot of interest.
Construction
Construction work is allowed on forest lands. But you cannot build a private house on them. The legislation allows the construction of the following types of buildings in forest areas:
- gatehouses and other buildings of this kind;
- tourist camps;
- physical education complexes;
- health resorts.
Private buildings are allowed to be erected only on the lands of populated areas and agricultural lands. At the same time, development of forest fund lands was often carried out due to an unclear division of lands into categories.
Transfer to settlement lands
The transfer of forest fund lands to the land of populated areas may be required if it is necessary to carry out construction work on the lands or use them for other purposes not provided for by the current edition of the Land Code.
Also, a plot of land from the Forest Fund cannot be registered as a property until it is excluded from the forest register.
Such transfer to the land of a populated area is carried out in exceptional situations and this procedure requires a special procedure.
Thus, according to current legislation, such a translation is permitted in the following cases:
- when such a change is provided for by forest management documentation/territorial planning documentation;
- when the features of settlements change;
- in order to create protected areas, classify lands as historical, cultural, environmental zones;
- if there is no need for land management in forestry;
- if it is impossible to further use the land for its intended purpose;
- when there is a need for land for defense purposes, etc.
Checking out of an apartment and registering in another can be quite simple; you need to collect the necessary package of documents and contact the relevant authorities. How long will a large family have to wait to receive the treasured land? Find out about this from our article.
Do you dream of getting a plot of land for farming? Here are step-by-step instructions on how to achieve your goal as quickly as possible.
How can local self-government bodies exercise new powers in the field of forest management from January 1?
From January 1, 2022, local governments will begin to exercise powers in the field of forest management. This is provided for by Federal Law No. 304-FZ dated 07/02/2021. The changes apply to urban and municipal districts, urban and rural settlements.
LSG bodies will:
- make decisions on the creation and abolition of forest areas on the lands of settlements;
- establish the boundaries of created forest areas;
- develop and approve forestry regulations for these forest districts;
- implement forest management measures in forests located on the lands of settlements in the municipality.
How to decide to create a forestry
Document: New issues of local importance for settlements are enshrined in paragraphs 20.1, 20.2 of Article 14, and for municipal and urban districts - in paragraphs 26.2, 26.3 of Article 16 of Law No. 131-FZ
Before deciding to create a forestry district, prepare a graphic description of the location of its boundaries and the boundaries of the district forest districts created within it. Such a description is a mandatory appendix to the decision of the local self-government body on the creation of a forestry district. Include in it a list of coordinates of characteristic points of the boundaries of the forest district and district forest districts. Determine the location of the boundaries of district forestries taking into account the standards for their area. They are established by the Forest Management Instruction, approved by Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources dated March 29, 2018 No. 122 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 122).
Then decide to create forest districts and district forest districts on municipally owned lands, as well as to establish the boundaries of the forest district.
What forest management activities will local self-government bodies implement?
Forest management is an activity that includes five types of activities. All of them are specified in Article 68 of the LK.
1. Design of forest areas.
2. Design of operational, protective, reserve forests, as well as especially protective forest areas.
3. Fixing on the ground the location of the boundaries of forest districts, district forest districts and lands on which operational, protective, reserve forests, as well as specially protected forest areas are located.
4. Forest taxation.
5. Design of forest conservation measures.
Approve the forest management plan. How to do this, in what order and how often to make changes to the plan - the Government will decide (Article 67.2 LC).
Activities can be carried out comprehensively in various combinations or separately for each forest district, district forest district or forest area. Let's consider what work needs to be done as part of individual forest management activities.
Design of forest conservation measures
As part of the design, the types and volumes of forest conservation measures are determined (Article 69.2 of the Leningrad Code). Activities may include, among other things, cutting down dead and damaged forest plantations. Design is carried out simultaneously with forest taxation or separately from it. Without taxation, design should be carried out on the basis of the results of forest pathological surveys, state monitoring of forest reproduction, and the classification of lands intended for reforestation as lands on which forests are located. This work must be carried out no later than two years before the year of designing forest conservation measures.
On a note:
Who can engage in forest management
Forest management can be carried out by municipal institutions subordinate to local self-government bodies. They have the right not only to carry out municipal tasks, but also to carry out reforestation and afforestation work under agreements with persons using the forests. If you have not assigned the responsibility to carry out forest management activities to the institution or persons who use the forests, purchase the work in accordance with Federal Law No. 44-FZ dated 04/05/2013 “On the contract system...”. A municipal agency or contractor must carry out forest management in accordance with Instruction No. 122.
Design of operational, protective, reserve forests and specially protected areas
Before starting to design operational, protective, reserve forests and especially protective forest areas, you need to:
- check whether there are grounds to classify forests as such types of forests and identify their specially protected areas;
- determine the location of the boundaries of the lands on which operational, protective, reserve forests, especially protective forest areas are located within the boundaries of forest districts, district forest districts and forest plots;
- determine the categories of protective forests and the boundaries of the lands on which they are located;
- prepare a graphic description of the location of the boundaries of the lands on which production, protective and reserve forests are located
Note: Follow Instruction No. 122. It specifies the criteria for determining the priority of designing categories of protective forests
Fixing on the ground the location of forestry boundaries
In order to fix on the ground the location of the boundaries of forestry areas, including district ones, and the lands on which operational, protective and reserve forests, especially protective areas are located, it is necessary to arrange quarterly clearings, install quarterly and boundary pillars, and other information signs. In this case, a quarterly network project is used. It is prepared during the implementation of forest management work (Article 68.3 LC).
The boundaries are fixed as part of forest conservation measures.
Forest taxation
Forest taxation is the determination of the volume of felled and growing trees, the stock of plantings, the growth of trees and plantings. Taxation is carried out during forest management, allocation of cutting areas for felling, and forest inventory. The goal is to obtain up-to-date and reliable information about forests and forest resources, their condition, quantitative and qualitative characteristics. This information will be needed when designing forest conservation measures, for using forests, improving their quality, increasing their productivity, etc. (Article 69.1 LC).
When assessing forests:
- identify sets of forest plantations that are homogeneous in species composition, age and productivity;
- determine the location of the boundaries of forest taxation units;
- determine the predominant and accompanying tree species, forest conditions, condition, diameter, height of trees, etc.
Important detail: From January 1, 2023, when carrying out forest inventory work using ground methods, it will be necessary to photograph forest plantations. Include photographs in forest management documentation
What will change in the rules for providing sites for timber harvesting?
From January 1, local self-government bodies will be prohibited from providing municipally owned forest plots for timber harvesting if the forest taxation of these plots was carried out more than 10 years ago.
To provide a forest plot, you will need project documentation for it in the form of an electronic document. It must be signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature and approved by a decision of the local self-government body exercising the authority to provide forest plots. Documentation can be sent for approval via the Internet, including through the government services portal (Article 70.1 of the Labor Code).
There will be more reasons to refuse approval of the design documentation of the forest area. Refusal will be possible in two cases.
1. The location of the designed forest area completely or partially coincides with the location of another area designed in accordance with a previously made decision to approve the design documentation.
2. The design documentation for the forest plot was prepared in violation of the requirements for the formation and modification of land plots.
What changes to expect in 2023
From March 1, 2023, stricter rules for preparing for logging operations and cutting down forest plantations will apply. Also, more stringent requirements will begin to apply to specialists and organizations that carry out work on forest management, allocation and taxation of cutting areas.
Rules for preparing for logging work
From March 1, 2023, it will be impossible to carry out logging work without a taxation description of the cutting area
From March 1, 2023, before carrying out logging operations and felling of forest plantations, it will be necessary to carry out the allotment and taxation of cutting areas. If this need arises when citizens harvest wood for their own needs or as part of forest conservation and forest management measures, the local government body will have to attract a contractor on a competitive basis according to the rules of Law No. 44-FZ.
Then you will need to draw up a taxation description of the cutting area. The law allows only certified specialists to be involved in this work. From March 1, 2023, it will be impossible to carry out logging work without a taxation description of the cutting area.
Requirements for specialists who perform forest management work
On March 1, 2023, new requirements for persons performing work and providing services for forest management, allocation and taxation of cutting areas will come into force. It will be possible to attract only taxi engineers and taxi technicians. These specialists must:
- pass certification for the right to carry out forest management activities;
- be included in the special register of Rosleskhoz.
Work and provision of services for the allocation and taxation of cutting areas will be carried out by legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who have at least two certified employees on staff. The qualification requirements for these specialists and the procedure for their certification will be approved by Rosleskhoz.
Concept and composition of forest lands
According to the LC RF, the use, conservation, protection, and reproduction of forests are carried out based on the concept of a forest as an ecological system or as a natural resource.
In accordance with Art. 101 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, forest lands include forest lands (lands covered with forest vegetation and not covered with it, but intended for its restoration - clearings, burnt areas, open spaces, clearings, etc.) and non-forest lands intended for forestry (clearings, roads , swamps and others).
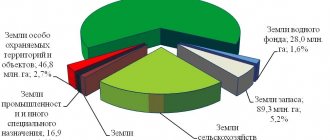
The central place among the objects of forest relations is occupied by the forest fund, which is formed by all forests, with the exception of forests located on defense lands and lands of urban and rural settlements, as well as forest fund lands not covered with forest vegetation. The total area of forest fund lands and forest lands not included in the forest fund is 1179 million hectares, or 69% of the territory of the Russian Federation.
The assignment of lands to forest fund lands and the transfer of forest fund lands to lands of other categories are carried out in the manner established by the land and forestry legislation of the Russian Federation. In accordance with the Land Code of the Russian Federation, forest and non-forest lands are included in the lands of the state forest fund.
Forest lands are intended for cultivation, rational use and reproduction of forests. They can be covered with forest vegetation, and also temporarily not covered, but are intended for its restoration - cutting down; burning; dead forest stand; sparse; vacant lots; clearings; areas occupied by nurseries, open forest crops, and other lands where natural or artificial reforestation processes are taking place.
Non-forest lands of the forest fund include lands not covered with forest, but intended for forestry needs, lands occupied by clearings, roads, agricultural lands, as well as lands located within the boundaries of the forest fund, occupied by swamps, rocky placers, and other lands inconvenient for use. The boundaries of forest fund lands and the boundaries of lands of other categories on which forests are located are determined in accordance with land legislation, forestry legislation and legislation on urban planning activities. Forest fund lands are delimited from lands of other categories in accordance with forest management procedures, with data on the boundaries of forest fund lands being entered into the state real estate cadastre.
Purchase and sale, pledge and other transactions that entail or may entail the alienation of forest areas, as well as forest areas not included in the forest fund, are not allowed. Transactions with the rights to use forest areas and the rights to use forest areas not included in the forest fund are carried out in the manner established by the forestry legislation of the Russian Federation, and in the part not regulated by it, by civil legislation. Tree and shrub vegetation can be transferred from one person to another in the manner prescribed by civil legislation and land legislation of the Russian Federation.
In Art. 4 of the RF LC defines the circle of subjects participating in forest legal relations, which are: the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities, citizens and legal entities. Relations between individuals and legal entities with the Russian Federation, its constituent entities and municipalities as holders of power in the field of forest relations are built on the basis of the norms of constitutional, administrative and other branches of law that are more public in nature than forest law. However, the LC RF enshrines the principle of priority of forest legislation in regulating property and administrative relations in relation to relations in the field of use, protection, protection and reproduction of forests. This approach to delimiting the spheres of action of various branches of Russian legislation follows not only from the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but also from the norms of the relevant industries. So, in Art. 129 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation it is noted that land and other natural resources can be alienated or transferred from one person to another in other ways to the extent that their circulation is permitted by the laws on land and other natural resources.
The Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation is a federal executive body that carries out the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of study, use, reproduction, protection of natural resources, including management of the state subsoil fund and forestry, use and protection of the water fund , use, protection, protection of the forest fund, forest reproduction. The Federal Forestry Agency is a federal executive body that carries out the functions of implementing state policy, providing public services and managing state property in the field of forestry. Control and supervision of the condition, use, protection, protection of the forest fund and forest reproduction is carried out by the Federal Service for Supervision of Natural Resources.