Home / Real estate / Land / Categories of land plots
Back
Published: 11/02/2017
Reading time: 10 min
0
840
Forest plot is a land plot located within the boundaries of forest districts/forest parks and formed in accordance with the requirements of land legislation and the Forest Code.
- Rights to plots
- VRI for these lands
- Amnesty of forest areas
- Construction Who can apply for land transfer?
Legislation on forest resources
Forest fund lands are a special category of land, which is regulated by the Forest Code and the Land Code.
The forest fund includes areas covered with shrubs, trees and grass or not covered with forest vegetation (but intended for forest restoration in the future), as well as areas used for forestry and located within the forest fund.
The forest fund includes areas of non-forest and forest. It includes areas without vegetation, in particular:
- with felling - on which stumps remain;
- with young forest;
- with burnt and dead trees;
- with clearings and free from forest;
- with open spaces: isolated trees.
The Forest Fund includes all forests, except for forests in areas for defense purposes (used by the armed forces) and settlement lands.
They are indicated on maps with special signs.
Rights to plots
According to the Constitution, the forest fund of Russia is jointly owned by the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the federation. If a forest plot is located in areas of defense significance, then only the federation can be the owner.
Forest fund lands are prohibited from being used in free circulation: sales and purchase agreements are not allowed in relation to them and they cannot be the subject of a pledge.
At the same time, the legislation allows the transfer of such lands for the use of individuals and legal entities under agreements:
- rent;
- free use;
- concessions;
- short-term use.
Russians can freely use these lands to satisfy their needs: picking mushrooms and berries, hunting and fishing.
Citizens can restrict access to forest areas only in the event of life-threatening situations: for example, in the event of a forest fire or a threat to environmental safety.
What types of use of forest fund lands are there?
You can use forest areas for a fee or free of charge:
- Free use of land is possible only after a positive decision has been made by the local and subject government in your favor. The maximum period for concluding a free use agreement is 10 years.
The following have the right to receive forest lands for use free of charge:
- For private individuals who carry out a certain type of activity, for example, for beekeeping, the state provides land for free use for a period of up to five years.
- Northern peoples.
- People representing official religions.
- Persons working in state defense and protection of forest belts.
Forest lands, according to the submitted application, can be obtained by interested people for the period specified in the legislation. In the absence of such a clause in the contract, the document, after prior notice, may be terminated by one of the parties.
Paperwork for obtaining a forest belt plot must be completed accordingly. They should indicate the intended purpose of use permitted by law. It must coincide with plans for the development of forest belts in a specific region of the country. The decision is made within one month.
It is important to take into account that forest belts cannot be transferred for free use to non-profit institutions created by private individuals for the development and construction of dachas and houses.
- Indefinite use of forestry lands is possible if they are allocated by local governments to budgetary institutions or to private individuals.
An agreement for unlimited use can also be obtained by any person who wins the auction and submits an application indicating the cadastral number. A decision on such a request is made within two months.
The cost of land at the beginning of the auction is set by the authorities and is calculated from the annual rental amount or a certain percentage of the price according to the Cadastre. Only the above-mentioned citizens who managed to submit the necessary documents, submitted an application and made an advance payment can participate in the auction.
All papers must be submitted no later than five days before the start of trading. One person can leave one application. Based on the results of the auction, a document is drawn up, one copy of which is given to the winner. The execution of an agreement for the indefinite use of forest belt lands occurs after the end of the auction, 10 days later.
Download the agreement for the unlimited use of a land plot (sample)
Download the agreement for free, fixed-term use of land (sample)
VRI for these lands
Article 25 of the Forest Code identifies the following types of permitted exploitation of lands from the forest fund:
- harvesting of wood, resin, non-timber forest resources, food forest resources, medicinal plants;
- hunting farm;
- agricultural management;
- research and educational activities in the field of forestry;
- recreational activity;
- growing forest plantations;
- growing seedlings, berries, fruits and ornamental plants;
- geological research work;
- construction of reservoirs, linear facilities, wood processing;
- religious activity.
Concept of the Forest Code of the Russian Federation
On January 1, 2007, the new Forest Code of the Russian Federation dated December 4, 2006 No. 200-FZ came into force. When adopting it, the legislator had to take into account the shortcomings of the previous (1997) Forestry Code of the Russian Federation:
Forms of ownership of forest lands
Forest fund lands include areas covered with forest vegetation and areas not covered with forest vegetation, but intended for its restoration and forestry (clearings, burnt areas, areas occupied by nurseries, clearings, roads, etc.).
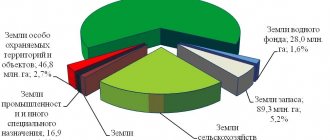
As of January 1, 2006, the area of forest fund lands amounted to 1104.9 million hectares .
The forest fund lands do not include land plots with forests located on them with an area of 70.2 million hectares, belonging to other categories of land that are state-owned and transferred to legal entities and individuals on the right of permanent (perpetual) use:
- on agricultural lands - 40.6 million hectares;
- on settlement lands - 1.9 million hectares;
- on lands of industry, transport, energy, defense - 4.1 million hectares;
- on lands of protected areas - 16.5 million hectares;
- on reserve lands - 7.1 million hectares.
Until now, forest lands and forests on lands of other categories were in federal ownership and their privatization was prohibited.
The new Forest Code establishes that the monopoly of federal ownership of forest lands is terminated:
- forest areas within the forest fund lands are in federal ownership:
- forms of ownership of forest plots as part of lands of other categories are determined in accordance with land legislation.
According to land legislation, forests on agricultural lands, on settlement lands, on industrial and transport lands, on lands of protected areas, on reserve lands (about 70.2 million hectares in total) can be owned by a subject of the Russian Federation, municipal property and private property .
It is now possible to purchase forests as private property on agricultural lands, on industrial lands and partly on lands of protected areas occupied by holiday homes, boarding houses, sanatoriums, and pioneer camps (about 47.0 million hectares in total).
Stay of citizens in forests
Citizens have the right to freely and freely stay in forests and, for their own needs, harvest and collect wild fruits, berries, nuts, mushrooms, other edible forest resources (edible forest resources), as well as non-timber forest resources.
Citizens are obliged to comply with fire and sanitary safety rules in forests, reforestation rules and forest care rules.
Citizens are prohibited from procuring and collecting mushrooms and wild plants, the species of which are listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, the red books of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as mushrooms and wild plants that are recognized as narcotic drugs in accordance with Federal Law of January 8, 1998 No. 3– Federal Law “On Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances”.
The stay of citizens may be prohibited or limited in forests located on defense and security lands, lands of specially protected natural areas, and other lands to which citizens’ access is prohibited or limited in accordance with federal laws.
The presence of citizens in forests may be limited in order to ensure:
- fire safety and sanitary safety in forests;
- safety of citizens when performing work.
Types (goals) of forest use
The use of scaffolding can be of the following types:
- timber harvesting;
- preparation of resin;
- harvesting and collection of non-timber forest resources;
- harvesting food forest resources and collecting medicinal plants;
- management of hunting and hunting;
- farming;
- carrying out research and educational activities;
- implementation of recreational activities;
- creation of forest plantations and their operation;
- cultivation of forest fruit, berry, ornamental plants, medicinal plants;
- carrying out work on geological study of subsoil, development of mineral deposits;
- construction and operation of reservoirs and other artificial water bodies, as well as hydraulic structures and specialized ports;
- construction, reconstruction, operation of power lines, communication lines, roads, pipelines and other linear facilities;
- processing of wood and other forest resources;
- carrying out religious activities.
Scaffolding can be used for one or simultaneously for several of the listed purposes.
The use of forests for business activities is carried out on forest lands by persons registered in the Russian Federation in accordance with Federal Law of August 8, 2001 No. 129-FZ “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs.”
The procedure for providing citizens and legal entities with forest plots that are in state or municipal ownership
Forest plots owned by the state or municipality are provided to legal entities for permanent (indefinite) use, lease or free-term use, and to citizens - for rent or free-term use.
Forest plots are provided for permanent (indefinite) use to state and municipal institutions and state-owned enterprises.
Forest plots are provided for free, temporary use to state and municipal institutions, state-owned enterprises, religious organizations, and to citizens as official plots for growing agricultural products for their own needs.
Under a forest plot lease agreement, the lessor provides the forest plot to the tenant for any permitted type of use.
The object of lease can only be forest plots that are in state or municipal ownership and have undergone state cadastral registration.
A lease agreement for a forest plot in state or municipal ownership is concluded for a period of up to forty-nine years
The term of the forest lease agreement is determined in accordance with the period of permitted use of forests provided for by the forestry regulations.
A tenant who has duly executed a lease agreement for a forest plot located in state or municipal ownership, upon expiration of its term, has a pre-emptive right to conclude a lease agreement for a new term.
A lease agreement for a forest plot located in state or municipal ownership is concluded based on the results of an auction for the sale of the right to conclude such an agreement.
Without an auction, lease agreements for forest plots owned by state or municipal authorities are concluded in the following cases:
- use of forests for mining, construction of reservoirs, construction and operation of power lines, communication lines, roads and other linear facilities;
- implementation of priority investment projects in the field of forest development.
The conclusion of lease agreements for forest plots that are in federal ownership, the property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and municipal property is carried out by state authorities and local government bodies, respectively.
The procedure for preparing and concluding a lease agreement for a forest plot located in state or municipal ownership, and the form of a sample lease agreement for a forest plot are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
5. Agreement for the purchase and sale of forest plantations (without registration of rights to a land plot) for timber harvesting
Under a contract for the purchase and sale of forest plantations for timber harvesting, the sale of forest plantations located on lands owned by the state or municipality is carried out.
The purchase and sale agreement for forest plantations specifies the location of the forest plantations (forest block and (or) forest taxation division) and the volume of timber to be harvested.
The validity period of a purchase and sale agreement for forest plantations cannot exceed one year (this differs from a lease agreement, which is concluded for a period of up to 49 years).
Exceptional cases of timber harvesting on the basis of a contract for the sale and purchase of forest plantations (without registration of land rights) are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Rates of payment per unit volume of wood harvested on lands owned by federal authorities, the property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and municipal property are established accordingly by the Government of the Russian Federation, government bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and local self-government bodies.
Lease agreements for forest areas owned by state or municipal property, and purchase and sale agreements for forest plantations are concluded based on the results of auctions held by increasing the starting price of the auction item.
The sellers of the right to conclude a lease agreement for a forest plot located in state or municipal ownership, or the right to conclude a purchase and sale agreement for forest plantations, are state authorities and local government bodies.
Powers of state authorities of the Russian Federation in the field of forest relations
The powers of government bodies of the Russian Federation in the field of forest relations include:
- establishing felling ages and the procedure for calculating the allowable cutting area;
- establishing a list of species (species) of trees and shrubs, the timber harvesting of which is not permitted;
- approval of the forest declaration form, the procedure for filling it out and submitting it;
- establishing rules for timber harvesting;
- establishing rules for the preparation of resin;
- establishing rules for harvesting food forest resources and collecting medicinal plants;
- establishing rules for harvesting and collecting non-timber forest resources;
- establishing rules for the use of forests for growing forest fruit, berry, ornamental and medicinal plants;
- establishing rules for the use of forests for scientific research and educational activities;
- establishing rules for the use of forests for recreational activities;
- establishing a procedure for using forests to carry out work on geological exploration of subsoil, development of mineral deposits;
- establishing a procedure for using forest areas for construction, reconstruction, operation of power lines, communication lines, roads, pipelines and other linear facilities;
- establishing rules for the use of forests for processing wood and other forest resources;
- establishing the form of a report on the use of forests and the procedure for submitting this report;
- establishing a procedure for determining the cadastral value of forest plots;
- establishing fire safety rules in forests;
- establishing sanitary safety rules in forests;
- establishing a procedure for organizing aviation work for the protection and protection of forests and performing these works;
- establishing the features of protection, protection, reproduction of forests, as well as the development and implementation of preventive and rehabilitation measures in areas of radioactive contamination of forests;
- establishing the form of the report on the protection and protection of forests and the procedure for its submission;
- establishing rules for reforestation;
- establishing afforestation rules;
- establishing rules for forest care;
- establishing a procedure for using zoned seeds of forest plants of the main forest tree species;
- establishing the form of the report on forest reproduction and afforestation and the procedure for submitting this report;
- establishing the procedure for forest management;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of forest resources and payment rates per unit area of a forest plot located in federal ownership for the purpose of leasing it;
- establishing the procedure for preparing and concluding a lease agreement for a forest plot that is in state or municipal ownership;
- approval of the form of a sample forest lease agreement;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of timber harvested on federally owned lands;
- establishing the procedure for preparing and concluding contracts for the sale and purchase of forest plantations;
- establishing the boundaries of forest areas, forest parks, as well as determining their number;
- implementation of state forest inventory;
- establishing the composition, procedure for development, validity periods of forestry regulations and the procedure for introducing amendments to them;
- establishing the procedure for maintaining the state forest register;
- establishing a procedure for monitoring and supervising the use, protection, defense, and reproduction of forests (state forestry control and supervision);
- implementation of state fire supervision in forests;
- approval of rates or methods for calculating the amount of damage caused to forests as a result of violation of forest legislation;
- classification of forests as valuable forests, allocation of especially protective forest areas and establishment of their boundaries;
- determination of the features of use, protection, protection, reproduction of forests located on lands of specially protected natural areas;
- classifying forests as operational forests, reserve forests and establishing their boundaries;
- other powers established by federal laws.
Powers of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the field of forest relations
The powers of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation include the following powers in the field of forest relations:
- ownership, use, disposal of forest areas owned by constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of forest resources and payment rates per unit area of a forest plot owned by a constituent entity of the Russian Federation for the purpose of its lease;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of timber harvested on lands owned by constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- approval of the procedure and standards for the harvesting of wood by citizens for their own needs;
- establishing a procedure for citizens to harvest food forest resources and collect medicinal plants for their own needs;
- establishing a procedure for the procurement and collection of non-timber forest resources by citizens for their own needs;
- establishing payment rates for citizens under a contract for the purchase and sale of forest plantations for their own needs;
Transfer of the implementation of certain powers of the Russian Federation in the field of forest relations to government bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
The Russian Federation transfers to the state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation the exercise of the following powers in the field of forest relations:
- development and approval of forest plans of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, forestry regulations, as well as conducting state examination of forest development projects;
- provision of forest plots within the forest fund lands for permanent (indefinite) use, lease, gratuitous fixed-term use, as well as the conclusion of purchase and sale agreements for forest plantations, including the organization and holding of relevant auctions;
- issuing permits to carry out work on geological exploration of subsoil on forest lands;
- organizing the use of forests, their protection (including extinguishing forest fires), protection (except for forest pathological monitoring), reproduction (except for forest seed production) on forest fund lands and ensuring the protection, protection, reproduction of forests on these lands;
- maintaining the state forest register in relation to forests located within the boundaries of the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- implementation of state forest control and supervision;
- establishing a list of officials exercising state forest control and supervision.
Funds for the implementation of these delegated powers are provided in the form of subventions from the federal budget.
Subventions from the federal budget provided to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the implementation of delegated powers are distributed based on the area of operational forests, protective forests, the intensity of their use, the number of people living in the territories of the relevant constituent entities of the Russian Federation, fire danger indicators of forests according to the methodology approved by the Government of the Russian Federation .
Powers of local governments in the field of forest relations
The powers of local government bodies in relation to forest areas in municipal ownership include:
- ownership, use, disposal of forest areas in municipal ownership;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of forest resources and payment rates per unit area of such a forest plot for the purpose of leasing it;
- establishing payment rates per unit volume of wood;
- development and approval of forestry regulations, as well as conducting state examination of forest development projects;
- implementation of municipal forest control and supervision in relation to such forest areas.
10. Planning in the field of use, protection, protection, reproduction of forests
Planning in the field of use, conservation, defense, and reproduction of forests (forestry planning) is aimed at ensuring sustainable development of territories.
The forest planning document is the forest plan of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
The forest plan of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is approved by the highest official of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation (the head of the highest executive body of state power of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation).
The basis for the use, protection, defense, and reproduction of forests located within the boundaries of a forest district or forest park is the forestry regulations of the forest district or forest park.
Forestry regulations are drawn up for a period of up to ten years.
The forestry regulations for forests located within the boundaries of forest districts and forest parks establish:
- types of permitted use of forests;
- ages of felling, estimated cutting area, terms of use of forests and other parameters of their permitted use;
- restriction of forest use;
- requirements for conservation, protection, and reproduction of forests.
Forestry regulations are mandatory for implementation by citizens and legal entities engaged in the use, protection, protection, and reproduction of forests within the boundaries of a forest district or forest park.
The composition of forestry regulations, the procedure for their development, the terms of their validity and the procedure for making changes to them are established by the authorized federal executive body.
Persons to whom forest plots are provided for permanent (indefinite) use or lease draw up a forest development project.
The composition of a forest development project and the procedure for its development are established by the authorized federal executive body.
A forest development project is subject to state or municipal examination in the manner established by the authorized federal executive body.
The state forest inventory is carried out by the authorized federal executive body.
The procedure for conducting a state forest inventory is established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Comments (1):
Lepilov Valery Mikhailovich (Sterlitamak Bashkortostan) March 9, 2010, 23:17:03
The deadline for submitting a forest development project after signing the agreement is not specified.
(Answer)
your comment
Amnesty of forest areas
In July 2021, the State Duma adopted in its final reading a bill called the Forest Amnesty.
This law should solve the acute problem of illegal construction in disputed territories.
What do legislators understand by “disputed territories”?
Currently, the USRN and the Forest Register contain many intersections. According to the first register, this land belongs to areas on which the construction of housing and their transfer to private ownership are permitted. Whereas the Forest Register does not allow such use of the land included in its composition.
What is the essence of the Forest Amnesty?
She assumes that all controversial situations should be interpreted in favor of the Unified State Register of Real Estate. This means that all cases of use of lands from the forest fund registered in the cadastral register are declared legal starting this year.
The law refers to huge areas: in the Moscow region alone, the disputed territory includes over 185 hectares of land allocated for dacha or private development.
The forest amnesty has many advantages. Finally, it will resolve lengthy litigation to determine the categories of land plots. The law will also solve the problem of thousands of Russians who, by mistake of cadastral engineers, were allocated plots for dacha construction from forest fund lands. As a result, they had difficulty legitimizing the buildings. An amnesty will allow such citizens to secure property rights for themselves.
The adoption of the forest amnesty law had many opponents. They fear that the priority of the Unified State Register of Real Estate will lead to a massive withdrawal of land from the forest fund and the destruction of a huge tract of Russian forest. It is assumed that the forest amnesty will lead to mass construction in forests in areas of large cities.
Thus, according to ecologists, the forest fund may be reduced by 1.7-4 hectares, which has very negative environmental consequences.
The law also equalizes the rights of those who unwittingly became the owner of a plot in the forest fund and those who seized this land by criminal means as a result of the use of fraudulent schemes.
Both of them, as a result of using the implemented legal norms, will be able to become full owners of forest areas.
Whose territory is this?
Who is the owner? The owner of such lands is the state, on whose balance sheet all forest zones of the Russian Federation are listed. Forests are in federal ownership, as stated in Article 8 of the Forest Code, but can be transferred to the responsible management of municipalities on the basis of permanent, unlimited use rights. Only the Government of the Russian Federation can dispose of forest lands on the basis of Resolutions. A number of decisions are made by the Ministry of Forestry, reporting to government agencies.
The regulations for all permissible actions are guided by the norms of the Forest Code of the Russian Federation (LC RF), adopted on December 4, 2006 under No. 200-FZ and Article 101 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. All forest zones are subject to cadastral registration, alienation procedures are necessarily registered in Rosreestr and are allowed only on the basis of federal public hearings, with an appropriate decision of the Government of the Russian Federation based on the provisions of Article 1 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
The exception is forest zones that act as security zones for railway tracks, which may belong to Russian Railways. Suburban green areas are often included in the context of a populated area and belong to the lands of settlements, managed by the local administration.
If forests are artificial, they can be reproduced by owners of artificial reservoirs and dacha farms, but to a limited extent, with the consent of the municipality.
Read about what applies to forest lands here, and from this article you will learn about the legal regime for their use, as well as who can become the owner of such areas.
Construction
Construction work is allowed on forest lands. But you cannot build a private house on them. The legislation allows the construction of the following types of buildings in forest areas:
- gatehouses and other buildings of this kind;
- tourist camps;
- physical education complexes;
- health resorts.
Private buildings are allowed to be erected only on the lands of populated areas and agricultural lands. At the same time, development of forest fund lands was often carried out due to an unclear division of lands into categories.
Transfer to settlement lands
The transfer of forest fund lands to the land of populated areas may be required if it is necessary to carry out construction work on the lands or use them for other purposes not provided for by the current edition of the Land Code.
Also, a plot of land from the Forest Fund cannot be registered as a property until it is excluded from the forest register.
Such transfer to the land of a populated area is carried out in exceptional situations and this procedure requires a special procedure.
Thus, according to current legislation, such a translation is permitted in the following cases:
- when such a change is provided for by forest management documentation/territorial planning documentation;
- when the features of settlements change;
- in order to create protected areas, classify lands as historical, cultural, environmental zones;
- if there is no need for land management in forestry;
- if it is impossible to further use the land for its intended purpose;
- when there is a need for land for defense purposes, etc.
Checking out of an apartment and registering in another can be quite simple; you need to collect the necessary package of documents and contact the relevant authorities. How long will a large family have to wait to receive the treasured land? Find out about this from our article.
Do you dream of getting a plot of land for farming? Here are step-by-step instructions on how to achieve your goal as quickly as possible.
Terms of a transaction
Transfer of forest land into ownership is impossible. But exceptions are allowed to this rule. Registration of ownership is permissible for lands that can be transferred to another category. Suburban green areas can be quite easily converted into settlement land. True, the government requires compliance with legislation that provides for their exclusive use for their intended purpose - as forest recreation areas for citizens.
More often, burnt areas - areas after a fire, or open spaces - areas after deforestation are registered as the property. Re-registration is permissible if restoration is not planned in such treeless areas. Sometimes forest areas are interspersed with coppices that do not have woody vegetation and can be converted into agricultural land, which can be purchased or privatized.
The main condition for provision is that the land mass has ceased to be of value to the state, and sometimes its maintenance becomes unprofitable. If an applicant for registration of a site submits a project for the development of a forest zone, which is recognized as relevant, he can count on receiving a permit.
The grounds for recognition of the right to transfer land to another category may be:
- An application submitted to a government agency.
- Attached documents confirming the unsuitability (other reasons for unprofitability) of using the specified part of the forest. With the application of the zone development project.
- The decision of the Government of the Russian Federation on the transfer of land to another category, with subsequent registration of ownership.
Sometimes, instead of ownership, it is more advisable to issue a long-term lease of a forest area for its intended use.
Control
State administration is divided into general forest management (it is dealt with directly by the Government of the Russian Federation and/or authorized executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) and special (Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation and the Federal Service for Environmental Management).
The Government of the Russian Federation establishes:
- preparation and approval of investment projects for forest development;
- a list of tree and shrub species whose timber is prohibited from being harvested;
- sanitary and fire regulations;
- the procedure for performing aerial work to protect and ensure safety;
- defining and changing the boundaries of green and forested areas;
- other rules provided for by the LC RF.
Useful tips and tricks
- Be sure to study the legal norms necessary to contact the authorized body.
- For citizens, it would be best to make an initial request to compile a list of documents. This will help avoid fuss and paperwork.
- It is recommended not to build unauthorized buildings in the forest, as the administration will refuse to obtain permission to register property.
- Do not confuse the dacha amnesty with the forest amnesty - these are different concepts. The first means that a citizen can independently deal with issues of registration of ownership of a plot. The second means that these issues are dealt with by authorized persons without the participation of interested parties.
- It must be borne in mind that it is impossible to register the areas of cemeteries, specially protected, military and protected areas, and parks as property.
- For each allocated forest area (not transferred), a special report must be compiled annually. Reports must be registered and stored with the local municipal authority.
- For a selected area, it is possible to transfer from one category to another.
IMPORTANT !!! At each stage, it is recommended to check the documentation and validity of the decisions of the authorized bodies.
There are often cases when employees withhold certain important information or neglect their powers and legal norms. In such problematic situations, you should file a complaint with the court.
How to purchase shelterbelt plantings?
It is not prohibited to purchase trees and other plantings in the forest belt for felling. As a rule, a contract for this type of activity is concluded for a period of up to one year. To determine the cost, the rate per unit volume is taken and multiplied by the total number of trees cut down. For private individuals, rates are determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
A document confirming the purchase and sale must be signed at the end of the auction. Its conditions may be changed in the event of serious incidents on the purchased lands, as well as a change in the type of activity.
An agreement for the purchase of forest belt plantings allows you not to overpay for rent, but to obtain land for a narrowly targeted purpose.
Important! All contracts must be filed with Companies House. To do this, you will first need to create a cadastral plan of the territory.
Compound
It includes forested, non-forested lands and forests themselves. Boundaries are established by law (land and forestry codes) - LK of the Russian Federation dated December 4, 2006 N 200-FZ (as amended on December 29, 2017). The exception is forest plantations located on agricultural lands, water resources, urban and other populated areas, as well as on defense lands.
Based on the functions performed, economic importance, location, it is classified into 3 groups. These are forest plantations:
- National parks, natural monuments, reserves, in which only sanitary and maintenance fellings are allowed, performing various sanitary and health-improving, protective and water protection functions, where reforestation cuttings are allowed. They are divided by protection categories.
- In areas with a well-developed ground transport network, where population density is high and biological resources are insufficient. Forest use should be carried out in a limited manner.
- Richly forested regions - they mainly meet the needs for wood. Requires preservation of ecological functions. They are divided into main and reserve (harvesting there is not planned in the next 20 years).
Forest lands are areas covered with vegetation or uncovered (wastelands, clearings, burnt areas), but necessary for restoration.
Non-forest lands - clearings, roads, swamps, etc.