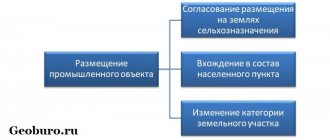
The entire territory that makes up our country is divided into categories.
This division is enshrined at the legislative level and is regulated by the Land Code of the Russian Federation. This is done to establish control over the intended use of land. There are seven categories in total. The most common category of land is agricultural land.
The law gives a clear definition of agricultural land, classifies it into types and sets out the options for use. Detailed information about this is contained in Chapter 14 of the Land Code.
What it is?
The category of agricultural land contains areas that are not part of cities and villages , intended for carrying out various agricultural work on them.
Agricultural lands are in second place in terms of area among all categories, second only to forest lands.
On the territory of the Russian Federation they occupy approximately 386 million hectares. For comparison, the area of land in populated areas is approximately 20 million hectares.
Agricultural lands are under special state control.
They are a valuable resource and source of food .
Therefore, it is important to use the land for its intended purpose, to prevent its littering and pollution, deterioration of the soil condition, and exposure to harmful factors.
How to transfer agricultural land to another category
The transfer of plots from the category of agricultural land to the territory of populated areas can be initiated by:
- owner of the allotment;
- local governing bodies;
- the owner of the building, which is located on the disputed site;
- other interested parties.
In order to transfer agricultural land for the needs of individual housing construction, an application should be drawn up to the local governing bodies that have the authority to resolve this issue. The application must indicate:
- cadastral number of the allotment;
- officially assigned cadastral number of the plot;
- the name of the existing land category and the one to which it is required to be transferred;
- an explanation of the reason why the land category is being changed;
- a document confirming the authority of the owner of the site.
Read more about how to transfer agricultural land to another category.
After considering the submitted application and adopting a positive conclusion on it, the executive body issues a decision to transfer the allotment to individual housing construction, private household plots or dacha construction. This solution should consist of:
- reasoned explanation of the need for translation;
- descriptions of the territory;
- designation of the area and boundaries of the site;
- cadastral number.
In the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, up to 2 months are allotted for consideration of a transfer request, and at the government level this period is extended to 3 months. The decision must be sent to the applicant within 2 weeks.
Composition of agricultural land
The category of agricultural land includes the following types of land plots:
Farmland
These include areas for sowing and growing various agricultural crops, as well as for grazing animals.
Farmland is the most fertile territory that provides the country with crops, therefore they have priority status and are under state protection. Farmland is under special control:
- with artificial irrigation,
- used by research institutes of any level,
- with a high cadastral value (10% above average).
Depending on the functions performed, the lands are divided into :
- arable land,
- haymaking,
- pastures, etc.
The most fertile lands endowed with mineral resources include arable land.
Arable land is a type of land that is annually cultivated and various crops are grown on it.
Hayfields are used only for storing hay for the winter. Sowing and harvesting are not carried out on such lands. Although there are also artificial hayfields.
Pastures are also usually not seeded or cultivated. Used only for grazing livestock.
Various types of farmland can be distinguished:
- Low quality,
- average quality
- High Quality.
On farmland it is permissible to build only those buildings and structures that are necessary for carrying out agricultural activities. It is prohibited to build residential or industrial facilities in such areas.
For on-farm roads and communications
These include roads needed to access and maintain agricultural land. They must meet certain standards specified in SNiP 2.05.11-83.
On-farm roads, depending on their purpose, can be of the following types :
- connecting agricultural objects to each other (I category of roads),
- connecting agricultural facilities with main roads (II category of roads),
- field auxiliary roads for servicing individual lands and their parts (III category of roads).
On-farm roads should occupy the minimum possible area.
They include:
- directly the strip for placing the road surface,
- drainage ditches,
- a safety strip of 1 meter on each side of the road.
Planted with trees and shrubs
These are lands planted with trees and shrubs to protect the environment from the influence of negative factors.
Protective forest belts are created:
- on gardening and country farms,
- around the fields
- along roads and railways.
Cutting and renewal of plants occurs only in agreement with local authorities.
With water features
Territories with closed water bodies are included in the category of agricultural lands only if they are located within the boundaries of these lands . At the same time, lakes or ponds can be used both for fish breeding and for watering nearby areas. Such objects are divided into two types:
- reservoirs of artificial origin,
- bodies of natural origin.
Occupied with agricultural buildings
For effective implementation of agricultural activities, auxiliary buildings are necessary.
They are not residential and are intended for storage and primary processing of grown products. For these purposes, the least fertile areas are allocated.
In addition to this criterion, there is a second, very important one - logistics. The location of the buildings must be accessible to a defined pool of surrounding cultivable land.
The concept of rational land use
In relation to agricultural lands and especially fertile lands, the problems of rational land use are relevant. It should not deplete the soil, but, on the contrary, contribute to the preservation and enhancement of land resources of the agro-industrial complex. Key ideas of rational land use:
- lands should be used in the most natural way possible for them;
- maximum yields are limited by potential fertility and can be increased artificially solely through soil depletion;
- it is necessary to maintain an optimal balance of arable land, hayfields and pastures;
- forest belts and other protective plantings must be preserved and restored;
- Industrial and other non-agricultural uses of agricultural land should be minimized.
During the Soviet period, rational land use was ensured by a planned economy. Collective and state farms were large agricultural producers, provided with seed, equipment and fertilizers of adequate quality.
The regime of land exploitation was more gentle and scientifically based. In modern Russia, areas of agricultural land have been crushed, which makes it difficult to change crops, carry out reclamation work, control pests and implement other appropriate measures.
Tenants, being temporary workers and not permanent owners of land, are interested in maximizing profits regardless of the deterioration of soil quality. The list of problems can be continued. One thing is obvious: the system of rational land use in the Russian Federation is just being formed.
Agricultural land use
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, agricultural land can be used for the following purposes:
- implementation of agricultural activities by enterprises,
- creation of personal or farm enterprises,
- growing vegetable and fruit crops,
- creation of dacha partnerships,
- growing and breeding animals and fish,
- research activities.
Important! Since 2015, our country has used a classifier of types of permitted land use (VRI). The document clearly and in detail indicates the types of permitted intended use of each category, including agricultural land.
Before it came into force, these issues were dealt with by the local government bodies of each individual entity. More information about the VRI classifier can be found here.
Land for agriculture
Russian legislation distinguishes several groups of lands, mainly these types correspond to the types of activities that are permitted on them. There are 6 groups in total:
- Land suitable for establishing pastures, growing crops, and farming. This also includes water channels;
- Territories suitable for growing industrial crops: berries, rice, tea;
- Territories suitable for the construction of buildings used in the production of farm products;
- Territories occupied by reservoirs specially used for fish breeding;
- Land occupied by forests;
- Lands unsuitable for agricultural production, but adjacent to them, not belonging to a populated area. This includes, for example, swamps and ravines.
If the plot is suitable for the landlord, then he will be interested in learning how to register ownership of the land if it is leased. What is an apartment card and where can I get it? Find out about this in the material.
Are you planning to buy an apartment? You can find out in detail all the information about this type of real estate in our article.
Features of farmland
Farmland has a number of features compared to other types of farmland. They are enshrined in law (Article 79 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
- The most fertile lands are under state protection, as they are its national treasure and most important resource.
- Such lands can be used only for their intended purpose, that is, for agricultural activities. Inappropriate use is punishable by law .
- Farmland with a high cadastral value is not subject to transfer to other categories of land
- The construction of any types of buildings in areas protected by the state is prohibited.
In exceptional cases, in agreement with regional authorities, farmland with poorer soil quality and low cadastral value may be transferred to another category of land.
Among other things, the legislation establishes requirements for persons using farmland:
- the plots must be developed within 2 years,
- while carrying out its activities, maintain soil fertility,
- If necessary, provide authorities with information about the chemicals used.
Redistribution Fund
The Land Redistribution Fund is a unified database of agricultural plots that have temporarily fallen out of circulation, that is, not used for their intended purpose.
Its main function is the formation of a fund of land and their further transfer for use to individuals or legal entities under certain conditions.
This is done so that strategically important farmland does not stand idle, because this is economically unprofitable.
An agricultural plot falls into the distribution fund under the following conditions :
- in case of voluntary refusal of the owner from the site,
- in the absence of heirs after the death of the owner,
- during forced seizure of land by the state.
Don’t know how to find out the category of your land plot?
If you know its cadastral number or location, read detailed instructions here.This article will help you decide on the category of site for construction.
Ownership of agricultural land
obtain ownership of land classified as agricultural:
- individuals (for farming),
- legal entities (farms, agricultural enterprises, dacha partnerships, etc.).
When purchasing farmland, the owner receives the right:
- transfer the plot by inheritance,
- rent out
- sell,
- present,
- pledge.
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, , as well as stateless persons, cannot be the owners of agricultural land The legal basis for the transfer of ownership of agricultural land is enshrined in the Federal Law “On the turnover of agricultural land” No. 101.
If the owner sells his agricultural land, representatives of the municipal authorities of the subject have priority rights to purchase such plots.
Where can I find information about unused areas?
To obtain a plot of land for use, you can find information about unoccupied plots in the Russian Federation Redistribution Fund. Local authorities can provide information about located and temporarily unused lands for transfer to individuals or legal entities for use under certain conditions.
Agricultural land automatically falls into the fund if it is abandoned, if the only owner dies or if the plot is forcibly alienated by the state.
Agricultural territory can be taken for temporary use or property rights can be registered. Buyers, as a rule, are:
- farmers;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- dacha partnerships;
- various agricultural enterprises and agricultural holdings.
Providing
Providing agricultural land for use essentially means transferring such land for rent for its intended use. In this case, the plots remain the property of the state.
To obtain a plot you must :
- Submit an application to the appropriate authority.
- Collect a package of documents.
- Wait for a decision.
- Conclude a lease agreement.
The law provides for a number of benefits and advantages when transferring agricultural land to certain categories of persons (for example, small peoples to support and preserve their way of life).
Seizure
The legislation stipulates that the state has the right in some cases to forcibly confiscate agricultural land from the owner.
This decision is made in court and can be challenged within the appropriate period. The main reasons for the seizure of farmland:
- the agricultural plot has not been used for its intended purpose for three or more years,
- the site is used irrationally, which leads to a decrease in soil fertility and deterioration in the quality of agricultural land.