Agricultural land is land that is located outside of populated areas, intended and provided for agricultural needs. According to current legislation, they can be used in the following forms:
- for agricultural production;
- for other purposes, which include: personal subsidiary plots, peasant (farm) farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture, livestock farming, country house construction.
The general legal regime for them is to provide land directly for agricultural purposes.
Agricultural lands should be distinguished from agricultural lands. The latter include land that may also belong to other categories, in particular, lands of non-agricultural enterprises or state forest resources transferred for temporary use for agricultural purposes to citizens and agricultural enterprises.
Agricultural lands directly serve the cycle of growing agricultural products, including lands occupied by warehouses, administrative buildings, roads and other infrastructure elements.
Two features of the legal regime should be noted:
- The priority position of agricultural lands, according to which lands suitable for agricultural needs are provided primarily for agricultural purposes, and for non-agricultural needs land plots that have a non-agricultural purpose, are not suitable for agriculture or agricultural lands of the worst quality according to the cadastral assessment are provided. The law provides for protection against unjustified withdrawal of land from agricultural use.
- Not all lands, without exception, that are suitable for agricultural needs can be used directly for agricultural activities; for example, there are restrictions on the use of land in protected areas.
Agricultural land - what is it?
The definition is given by the Land Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Land Code of the Russian Federation). In Art. 77 says that these are lands that meet two criteria :
- located outside the populated area;
- designed and used for agricultural needs.
What applies to such lands
Categories of agricultural land are also enshrined in the Land Code of the Russian Federation:
- agricultural grounds;
- territories containing objects for the protection of such lands - communications, roads, forests and water bodies;
- territories containing buildings and structures for storing and processing received products.
Who can use
Categories entitled to use agricultural land:
- peasant farms (peasant farms);
- personal subsidiary plots (LPH);
- citizens engaged in gardening, vegetable farming and livestock farming;
- non-profit organizations, religious communities and consumer cooperatives;
- Cossack societies;
- organizations carrying out scientific and research activities;
- indigenous peoples of Russian regions.
Types of permitted use
In Art. 78 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation defines the types of permitted use of agricultural (agricultural) land :
- conducting agricultural production;
- creation of protective facilities on the site (growing green spaces);
- conducting scientific and research work related to agriculture;
- fish farming;
- creation of hunting grounds.
Important! Misuse of land is prohibited by the Land Code of the Russian Federation. In case of violation, the owner is held accountable in the form of a fine, compensation or seizure of the site.
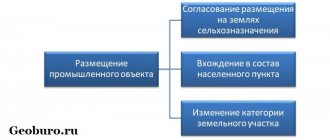
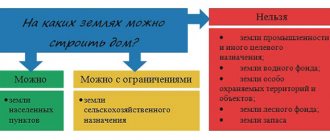
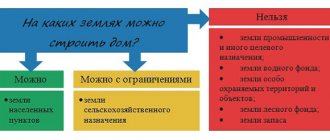
Owners of agricultural plots often wonder what can be built on agricultural land. Construction is permitted for the following objects :
- warehouses for storing agricultural products;
- premises for its primary processing;
- infrastructure necessary for the operation of the facility - roads, power lines, gas pipelines;
- private houses only for peasant farms and for small peoples;
- temporary structures without foundation.
What cannot be done on such lands?
On land intended for agricultural activities, you cannot do anything that is not related to agriculture. Absolutely forbidden:
- build residential buildings (we wrote in detail about whether building a house on agricultural land is allowed here);
- develop infrastructure;
- build highways;
- build industrial enterprises;
- used as industrial waste dumps.
Restrictions are primarily related to the preservation of ecology and landscape. In no case is it permissible to dump industrial waste onto such areas, so as not to destroy the top fertile layer of soil and pollute the environment where livestock grazing areas are allocated.
Secondly, the prohibitions are due to the unity of the agricultural ecosystem, which develops only in the absence of gross and drastic human intervention in the natural habitat. Therefore, special standards are observed here that do not allow changes in the quality of soils, landscape and ecology.
The value of such lands
All agricultural lands have a special protection status, but even among them there are particularly valuable ones.
Particularly valuable categories of plots are identified as part of agricultural lands:
- with particularly fertile soil;
- where important research and development is carried out;
- owned by state and municipal agrotechnological enterprises;
- belonging to research and educational institutions;
- peat deposits;
- natural reserves with special regime.
In relation to such areas, a special security regime and enhanced control over the activities carried out on their territory are introduced . The transfer of such lands to another category is carried out in exceptional cases.
For example, when changing the boundaries of a site, during the construction of linear objects on them (power lines, gas pipelines), during the construction of defense facilities or for the extraction of minerals on them.
For reference
Agricultural land is one of seven categories of plots, distributed according to intended use. The legal regime for determining territories is regulated by the Land Code of Russia. Here's what that distribution looks like for 2021:
- Agricultural land.
- Territories of settlements. Such lands are allocated for residential development and infrastructure development.
- General purpose. This category includes areas allocated for the development of the industrial complex, mining, energy and transport needs.
- State protected areas. This includes environmental protection zones, areas that are national treasures and cultural heritage, and sanatorium and resort treatment areas.
- Water resources. These are territories with water protection zones.
- Forest fund. Plots of land used for forestry development.
- Stock These are territories temporarily excluded from circulation and preserved for state needs.
Having dealt with the general definitions, let's move on to specifics. In particular, what are agricultural lands?
Construction on plots for farming
Peasant farm lands - what is it? This is a type of agricultural territory in which the activities of peasant farming are deployed. The construction of private residential buildings is permitted on peasant farm lands while agricultural activities continue.
Important! If a house is built on the plot, and agricultural activities are not carried out on it for a total of two years out of the last five, the plot is subject to seizure.
The owner of such a plot will need to have documents confirming the occupation of agriculture indicating the period of its validity, for example, contracts with suppliers and buyers.
But even if a building permit has been obtained, this does not mean that anything can be built . There are restrictions on buildings. Requirements for erected buildings :
- does not exceed 3 floors;
- not divided into separate apartments;
- complies with sanitary standards for residential buildings.
A citizen has the right to register in a building erected on a summer cottage . And if the house is built on land used for gardening or horticulture, registration will not be possible.
It can be useful:
How to arrange a land lease for a period of 49 years
What is a public easement on a land plot?
The procedure for registering a land plot with state cadastral registration
Concept and composition of agricultural land
Good afternoon
Not every plot that is allocated for horticultural or gardening activities makes it possible to build residential buildings on its territory. The main purpose of such buildings is permanent residence in it. Although it can be very difficult to obtain permission to register in this premises. Land plots that are intended for gardening or vegetable gardening are usually classified as agricultural land, but they can also be part of settlement land plots. The category of a land plot affects whether a residential building can be erected on it or not. The following outbuildings can be erected on agricultural land, in accordance with the classifier: barn; bath; greenhouse; garage; a garden house that is not intended for living, other buildings for household purposes. At the legislative level, construction on land that is allocated for gardening or gardening is not prohibited, although it must be remembered that not every building can be erected. Article 40 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation and Article 263 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation state that the owner of the land has the right to build buildings on his property at his own request. In order to build a residential building on land, you need to find out about the category of the land plot, and you need to find out this in the near future. We must remember that the construction of a residential building is prohibited on a plot of land that is intended for agricultural or gardening activities. Accordingly, it will not be possible to register anyone in it. You can find a way out of this situation, for example, change the purpose of the land or build a garden house on the territory of the garden plot, and install communications into it (heat, gas, electricity, etc.). And to change the status of a non-residential building to residential, you just need to write an application to the local government authority. If the land plot is located within a municipality, then the construction of a residential building on its territory is not prohibited at the legislative level, although there are nuances.
A residential building is intended for permanent residence of a person and makes it possible to register in this premises only if the citizen is the owner of the house or has received written or oral permission. The purpose of garden houses is seasonal recreation in spring and summer. It is impossible to live in them for a long time, because communications have not been carried out. Most often they are used for storing agricultural equipment. The owners of such real estate live in garden houses for several days in the spring and in the summer, when the garden and vegetable garden require care. A private house is intended for living at any time of the year, all communications are connected to it, and you can spend time in it in comfort. Important! A garden house can be converted into a residential one, and most owners carry out this procedure, only the house must meet the following criteria: safety. Safety standards must be observed and all communications must be connected; the land on which the building is built must belong to the owner of the building and must not be under encumbrance. If the site meets the criteria, we go to the local government with an application.
If on a site that belongs to a citizen of the Russian Federation, the construction of a residential building is prohibited for some reason, then we need to find out whether it is possible to change the VRI to: individual housing construction. The advantage of this option is that engineering networks and infrastructure are created at the expense of the state. In this case, a project, a construction permit and approval from various organizations are mandatory. For this option, the land plot must belong to the lands of settlements; for running a dacha farm. With this option, the land will cost less and, accordingly, you will have to pay less taxes. With this option, the building can be registered within the framework of the “dacha amnesty”; personal subsidiary plot on the territory of the municipality. The area may be large, but in this case the procedure for registering the structure will be simplified; Peasant farming is suitable for owner-farmers. The land area can be large. Land intended for gardening differs from others in soil fertility, it is high. In order to change the VRI of such land, it is necessary to provide evidence of deterioration in soil fertility or have full justification for this procedure. Prohibited structures VRI varies depending on the type of territory on which the land plot is located. If the category of land prohibits the construction of buildings on it, then these buildings cannot be built and used on it. On land intended for gardening, which belongs to a residential or agricultural zone, it is prohibited to build: an industrial facility; business, commercial, domestic and municipal buildings; healthcare, social or cultural facility; shopping complex or store; infrastructure building.
Article 51 of the Town Planning Code of Russia establishes that construction is permitted only for the following objects: a garage on a plot intended for gardening; an auxiliary structure that does not relate to capital construction (shed, shed, hangar). You do not need to obtain permission to build a residential or garden house. Although if the land plot is located on the territory of a horticultural non-profit association, the owner must comply with the provisions of Article 34 of Federal Law No. 66-FZ and the Building Code SP 53.13330.2011. These norms oblige the owner to take into account the territorial survey or planning project during construction. A set of rules for the development of gardening associations is approved at the meeting.
They are also determined by various parameters, especially: planning solutions for individual land plots; quality and appearance of fencing; remoteness of construction projects from other objects and fencing; arrangement of a compost pit; distance from the road of a residential building. Entry and membership fees go towards the territorial development of the association. Also, from the general budget, security of the association areas and the territory itself, a barrier and a checkpoint are provided. If necessary, the general meeting determines the location of waste tanks and the procedure for garbage removal. If the owner of the site violates the rules, then the construction projects are recognized as unauthorized, and by a court decision the owner will be obliged to remove this object (Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). How to change the category of land for gardening Such issues are decided by local governments.
The owner of a plot of land must go to any branch with the following package of documents: documentary evidence of the applicant’s identity; application to change the category of a land plot; documents for a plot of land; an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate with a description of the site; territory planning project; graphic diagram with a mark of the property; a power of attorney certified by a notary, if necessary. Remember that in order to quickly resolve the issue, you need to clarify the list of documents with a local government employee. The list is not final and may change depending on the situation. After the application is submitted, the owner receives a receipt indicating the date of acceptance and the list of accepted documents. By law, the review period should not exceed one month. You do not need to attend a hearing in person to obtain a building permit. And all because there are no open hearings on these cases. Problems may arise with land plots that were allocated for gardening. Unlike land plots in populated areas, they are more fertile. To obtain a permit, you must prove that the soil has become less fertile recently. After studying the case materials, the head of the local government body makes a decision (verdict): satisfaction of the owner’s requirements; refusal to satisfy the owner's demands. The refusal is appealed in court. If the decision is positive, data on the plot of land is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate 15 days after the announcement of the verdict. After this, anyone can contact the Rosreestr authorities to enter new information into the register. Basic rules for the location of buildings on a garden plot
Important! SNiP 30-02-97 establishes that when erecting a building on a plot of land, it is necessary to comply with the minimum distance to the boundaries of land surveying with a neighboring plot: a residential building must be at a distance of 3 meters from the wall or the protruding part of the house more than 50 centimeters from it; animal premises at a distance of 4 meters; outbuildings at a distance of 1 meter. Also, do not forget about the necessary gaps between buildings on the land plot to the street toilet and other buildings for animals and the compost pit or heap: from the cellar to the residential building, the distance is at least 12 meters; from the shower (bath) to the living space at a distance of 8 meters; from the well at a distance of 8 meters. Please note that the possibility of building a house on a plot of land intended for gardening, close to neighboring buildings, is described in the statutory documents of the gardening non-profit partnership. Partnerships may introduce additional standards to SNiP or slightly reduce the requirements. If some points of the regulations are not observed, it is not necessary that the building will need to be demolished; it will be enough to eliminate the non-compliance or move small buildings. Buildings and paths should not occupy more than 25% of the territory. Remember that the site must be used for its intended purpose.
Russian legislation establishes the possibility of demolishing buildings that were carried out without permission, but this can only be based on a reasoned decision of a local government body or court. This is possible: when building on a piece of land that does not belong to the person who erected the building. If ownership of a land plot in a horticultural non-profit partnership or other association is not documented, do not start construction; in case of violation of construction norms and rules during the construction of a residential building. In most such cases, the building will have to be demolished if violation of the rules threatens the environment or human safety; when the rights of other persons, for example, neighbors, are infringed. If you have a plot of land for gardening, you need to find out what buildings are allowed to build on it. Maybe it would be better to re-register the purpose of the land plot.
Construction on plots for private household plots
The restrictions imposed on construction on private plots are even stricter than on peasant farms . The construction of only foundationless structures - cabins or small summer houses - is allowed. This is carried out without obtaining approvals. With approval, it is allowed to build other non-permanent structures necessary for farming - chicken coops, greenhouses, etc.
The construction of hangars on concrete slabs remains a controversial issue . On the one hand, the SkhN land does not prohibit this, since the foundation is not being built. On the other hand, the building is quite massive and can harm the soil. The issue remains at the discretion of the governing bodies.
What happens if the construction is illegal?
If an illegal building is discovered, penalties are applied . The mildest punishment is a fine. The amount of the fine and the amount of punishment are determined in accordance with Article 8.8 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. This depends on the cadastral value of the site, the type of its use and the legal form of the owner.
The minimum fine is 0.1% of the cadastral value (but not less than 2,000 rubles) for individuals, 1% of the cadastral value (but not less than 100,000 rubles) for legal entities. The maximum fine is 1% of the cadastral value for individuals and 6% for legal entities.
Note! In addition to a fine, a type of punishment such as forced demolition of the building is used. This method is used in cases where the construction harms the area.
And the most severe punishment is confiscation from the owner of the plot . It is applied in the absence of previous decisions on the part of the owner of the execution site. The plot is subject to seizure if no agricultural activity has been carried out on it for 3 or more years, or if the work carried out causes irreparable harm to the land. The calculation of the period of non-use of land excludes the time spent on restoring the territory after natural disasters or emergency situations.
Fines for misuse of the site
Since land is a public property and is a valuable and specially protected property in any form, it is under the close attention of the state. This is especially true for agricultural land. Using them for other purposes or, for example, not using arable land by stopping their cultivation, watering or reclamation can cause irreversible damage to them.
To prevent such conflicts, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for sanctions for violators in the form of fines and forced termination of land ownership.
Art. 284 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the seizure of a land plot that is not used for its intended purpose, and Art. 285 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation implies the seizure of land due to its use in violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
If such violations are observed over a period of 3 years, the confiscation of the corresponding land plots is inevitable.
At the same time, the fact of seizure of land is not a basis for canceling the need for compensation on the part of the offender for the damage caused to him.
For inappropriate use of agricultural land, Art. 8.8 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes the following penalties:
- for individuals – from 0.5% to 1% of the cadastral value of land with a minimum fine of 10 thousand rubles;
- for officials - from 1% to 1.5% of the cadastral value of land with a minimum fine of 20 thousand rubles;
- for legal entities - from 1.5% to 2% of the cadastral value of land with a minimum fine of 100 thousand rubles.
When the cadastral value of a land plot is not determined, the penalties are:
- for citizens – from 10 thousand to 20 thousand rubles;
- for officials – from 20 thousand to 50 thousand rubles;
- for legal entities – from 100 thousand to 200 thousand rubles.
If the misuse of land caused harm to the environment, then maximum penalties are imposed.
How to change the type and category of permitted use of a land plot
What to do if a citizen needs to change the type of use of the territory? Changing the type and categories of permitted use of a land plot is carried out only by decision of local authorities , however, any interested citizen or legal entity has the right to apply for a transfer. Information about changes is entered into Rosreestr and the Unified State Register of Rights to Real Estate (USRE).
The question of how to change the type of permitted use of a land plot is regulated by the Land Code of the Russian Federation and Federal Law No. 172.
Categories into which transfer is possible:
- settlement lands - for the development of individual housing construction;
- industrial lands - for the construction by private individuals of industrial facilities and complexes;
- reserves - for the protection of natural areas.
The list of documents to change category is as follows:
- Russian Federation passport for a citizen or Unified State Register of Legal Entities extract for a legal entity;
- extract from the Unified State Register;
- written consent of the owner of the site for transfer to another category;
- appraiser's conclusion on the value of the site;
- conclusion of the environmental commission;
- cadastral passport of the territory;
- application for transfer.
The application, along with the collected package of documents, is submitted to the Land Department . Authorized employees review the application and make a decision. The review period is 30 days. If a positive decision is made, the procedure for changing data about the site in Rosreestr is launched.
Possible reasons for refusal to change category :
- the site is especially valuable for agriculture;
- the land is part of the territory development program;
- There is a restriction on changing the category of land.
If a positive decision is made, you will need to pay a state fee of 350 rubles.
There is an important point when transferring land to a type of use such as summer cottage construction. Gardening, vegetable gardening and dacha construction are carried out only by non-profit organizations - consumer cooperatives and partnerships. That is, the transfer of such lands to persons and firms engaged in commercial activities is impossible.
What changes have occurred in land legislation in 2021?
Main changes:
- Now you can legalize independently annexed land to your main plot;
- it became possible to register a plot for free if there is a shortage of professionals in the locality;
- A citizen of the Russian Federation can register ownership of almost any vacant land plot.
You can find out how to correctly draw up a land donation agreement and a land deed of gift in this article.
Agricultural lands are on a special account with the state, so all your actions should be coordinated with the authorized bodies.
In fact, construction on such lands is not prohibited, but it is better to check with the local authorities which buildings will not raise questions from them. The same applies to the planned field of activity, be it livestock farming or road construction.
You can get more information on how to properly use agricultural land in the following video lesson: