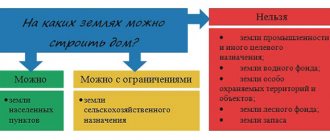
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, lands of populated areas (LNP) include areas located in the populated area itself or in the territory adjacent to it. The main task of these lands is the development of the city or settlement to which they belong. Residential buildings and public facilities are being built on such lands.
However, building a residential building or farming a subsidiary plot is not permitted on all plots. The reason for this is that all lands of settlements are distributed according to destination groups. So, if the site is intended for cattle breeding or gardening, then a commercial facility built on it will be considered illegal. For the owner of the building, this status means demolition, as well as a fine of 1% of the value of the site. In this case, the amount of the fine cannot be less than 10 thousand rubles.
To avoid such situations, it is necessary, even before construction, to find out everything about the purpose and type of permitted use of the site. This is easy to do, just know the cadastral number of the land and find the plot on the Rosreestr website (rosreestr.ru). Or send a corresponding request to local authorities. We will tell you how to do this correctly in this article.
VRI: Types of permitted use
Let's start with the main thing - the purposes of using the plots. VRI for each type of plot is prescribed in Article 83 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. Information regarding the permitted use of the territory of interest can be obtained on the Rosreestr website.
Let's take a closer look at what VRIs exist and what restrictions are imposed on landowners.
Residential
All areas with a cadastral code from 2 to 2.7 fall under the “Residential” classification. These figures imply the following types of buildings:
- construction (for individual residential construction). This item includes the construction of private residential buildings with a height of no more than three floors;
- Country construction . It is allowed to build houses of no more than 3 floors;
- Private household plot On such lands it is allowed to build a house, also no higher than 3 floors. At the same time, the following types of activities are permitted in the adjacent territory: planting seedlings, gardening, breeding and raising livestock;
- Townhouses . In such areas, the construction of semi-detached houses with common walls is permitted. The total number of blocks (entrances) should not exceed 10, height - a maximum of 3 floors. It is allowed to plant flower beds, plant trees, and build utility structures on the plots;
- Mobile housing . For example, campsites or tent cities;
- Mid-rise development . The construction of multi-storey, apartment buildings is permitted in these areas. The total height of mid-rise residential complexes, excluding basements, should be no more than 8 floors;
- Multi-storey development . Residential apartment buildings with a height of nine floors.
- Construction of service buildings . It is allowed to build utility rooms for housing and communal services.
Functional zones in the settlement
In the drawn up master plan for the development of the settlement, there are separate zones, compiled according to the functional criterion of their application.
Such zones have the following differences from each other:
- Determination of such zones by functionality;
- For specific options for objects that are permissible for construction within such zones;
- According to other features of the development and expansion of the borders of such territories.
To understand the situation more clearly, consider an example. A small village has a certain territory, which is considered settlement lands. For a more competent distribution of land resources within the framework of the activities of the village residents, part of the territory is declared an agricultural activity zone, part of the land is allocated for the stock of hay, and another area of the settlement’s land is allocated for the construction of a production facility in the form of a farm. At the same time, part of the settlement’s territory will be allocated for roads and infrastructure facilities that will ensure the functioning of each zone within the settlement’s lands.
Subtypes (subtypes) of VRI
Permitted uses are further divided into three types:
- Basic;
- Conditionally permitted;
- Auxiliary.
Let's look at them in more detail.
The main VRI determines the best use of the site and the choice of building on it. This means that if the site is located in a residential area of a populated area, it is most correct to issue a building permit:
- Residential building;
- Store;
- Publicly useful institution.
That is, the building must correspond as closely as possible to the zone in which it is located and not cause inconvenience to the residents of the locality.
Auxiliary VRI means that the buildings on the site are secondary in nature and must comply with the main VRI. In simple terms, the main VRI is the house, and the garage and outbuildings are the auxiliary type.
A conditionally permitted VRI of a site is formalized through the court. This happens as follows:
- The owner of the plot submits an application to the administration stating that, in his opinion, the land is not being used effectively;
- This application is sent to the court, which can either reject the request or add a new VRI. At the hearing on this case, both the initiator of the application and the neighbors of the site must be present.
Composition of the RFP
Land plots of settlements
The main territories included in the ZNP are classified as settlement lands. This is a narrower concept in comparison with the category of land and is included in this category. also acts as a type of permitted use (AUR) and is distributed:
- on plots intended for the location of residential buildings;
- areas where the construction of residential buildings is underway or is just planned.
In accordance with the Town Planning Code, settlement lands are divided into corresponding territorial zones, allowing the construction of houses of different heights . Low-rise buildings, less than three floors, intended for single-family residence and not allowing division into apartments, are erected within the territories intended for individual housing construction.
What is included in the concept of ZNP?
This is a place of settlement of a built-up land mass, having a variety of rural or urban types of settlements. It is an administrative unit. It is managed by local governments and is part of the state system. They may be:
- cities and urban districts;
- towns, villages, hamlets, etc.
It is separated from other territory of municipal lands by boundaries that are established by the relevant legislative acts and entered into the State Real Estate Cadastre in accordance with the norms of Federal Law No. 218-FZ of July 13, 2015. The territory of settlements, including urban ones, is considered valid only within the established boundaries , which is given in the provision of clause 1 of Article 83 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, and the establishment of the composition of lands of this category is considered in Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
Here are located various fragments of the settlement’s infrastructure required for the organization, functioning and life support of this system. The different functional purposes of city zones correspond to different ways of their placement throughout its entire area.
Help: It is permissible to use a combination of several zones in one complex, when several of their types serve one purpose.
Territory zoning - what is it?
This is a breakdown of the area of a settlement into zones based on their functionality. The procedure for territorial zoning is determined on the basis of the corresponding legal regime regulating the use of:
- surface of the earth;
- location of above-ground facilities;
- location of underground facilities.
Zoning provides for the aggregate use of the site along with above-ground and underground communications according to standard rules provided for all types of settlements. Based on the zoning of the city territory, blocks and zones are distinguished :
- residential;
- administrative;
- public business or business districts;
- engineering and transport infrastructures;
- for agricultural use;
- special purpose;
- green areas, cultural, historical and other recreational places.
Their list is given in paragraph 1 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. The blocks are located in the center of the urban settlement; on the outskirts, zoning is limited to no quarter division, focusing on the intended purpose of the zones. A rural settlement is also divided into zones without defining neighborhoods.
Special purpose
Regardless of the variety of zones included in the administrative unit, they are all focused exclusively on the preservation and development of the settlement, and can only serve purposes related to the organization of residence and receipt of necessary services by citizens of the settlement.
Reference. That is, this is the development of urban and rural settlements in accordance with the needs of their population, corresponding to the standards of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation and the types of permitted use.
Responsibility for misuse of land
The state provides for administrative liability for inappropriate use of land. Despite high fines, many landowners break the law. Why is this happening?
Quite often, people, wanting to save on taxes, begin to use land for other purposes. For example, a store or workshop is being built on a site for individual housing construction.
Indeed, it is much more profitable to use an existing plot for business than to buy a new one. In addition, taxes on commercial plots (for doing business) are much higher than usual.
As practice shows, enterprises and firms that operate on sites with other purposes that are not suitable for this purpose do not live long. One complaint to Rosreestr is enough, and its sender can be anyone. Most often this is:
- Neighbour;
- Prosecutor's office.
- Russian Federal Migration Service.
After receiving such a complaint, an inspector comes to the site. If the fact of misuse of land is confirmed, then a letter is sent to the owner indicating the violations that must be eliminated.
Activities prohibited on such land plots
It is not allowed to do anything here that does not serve the development goals of the city or town. Especially if such an action could lead to a deterioration in the quality of life for the citizens of the locality.
Attention: For activities that do not correspond to the intended use of the lands of the settlement, administrative liability is imposed.
Because of this, the following is unacceptable:
- Disturb the urban landscape by arbitrarily building up the territory.
- Damage the ecology of a settlement, including through the systematic release of waste from hazardous industries into the atmosphere, lakes or rivers, or onto the soil surface.
- Use the urban environment for livestock farming. Otherwise conduct agricultural activities outside the plots for private plots.
- Set up landfills in populated areas, including landfills for radioactive and other waste.
- Place cemeteries and conduct burials.
- Cut down trees in the green zone, build up the green zones with residential buildings.
- Conduct trade in places not intended for this purpose.
If the above and similar violations are detected, you should file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor.
Peculiarities of maintaining private household plots on the lands of populated areas
The construction of facilities for personal subsidiary plots on the territory of populated areas differs from construction on agricultural land. In both cases, on the territory of private household plots you can engage in one of three types of activities:
- gardening;
- horticulture;
- livestock breeding.
The difference is that private household plots can be built freely in populated areas. But to build private household plots on farmland, you will need permission from a special commission. The main criterion for the construction of buildings and structures in the second case is the permanent intended use of the land.
Punishment for using ZNP for other purposes
If at the time of detection of a violation there is a cadastral assessment of the value of a plot of land, liability involves the imposition of a fine in the following amounts:
- for citizens – 05–1% of the total cadastral value (at least 10 thousand rubles);
- for officials - 1–1.5% of the cadastral value of the site (not less than 20 thousand rubles);
- for legal entities – 1.5–2% of the total cost (at least 100 thousand rubles).
If the value was not determined according to the cadastre, then a fine is imposed in the following amounts:
- for citizens – 10–20 thousand rubles;
- for officials – 20–50 thousand rubles;
- for legal entities – 100–200 thousand rubles.
The use of lands in settlements other than for their intended purpose in accordance with their belonging to one category or another is grounds for bringing to administrative liability under Part 1 of Article 8.8 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation No. 195-FZ dated December 30. 2001 (with amendments and additions).