The importance of land allocation and its main stages
Land allocation is a set of works associated with defining and securing the boundaries of land use directly on the ground and the mandatory legal registration of a package of documents.
Carrying out this work is a rather lengthy and complex process, which requires certain knowledge in the field of legislation, experience in working with government agencies and patience.
Land acquisition work can be divided into the following stages:
- Making a decision on the start of construction and carrying out technical and economic calculations confirming the effectiveness and feasibility of this work;
- Selection of land plots on which the construction project is planned to be located;
- Carrying out engineering survey work and drawing up a detailed design;
- Land allocation for the construction of a new facility and communications, which involves demarcating the boundaries of the site and state registration of the property;
- Registration of permits for construction work.
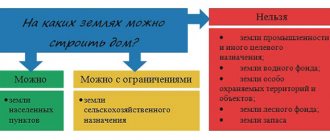
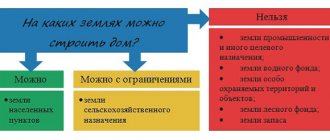
According to what laws are lands allocated?
The procedure for land allocation itself, in accordance with the law, is divided into two main phases; at the very beginning, the size of the land plot and the localization of its location are agreed upon in advance. After the seizure, the site is registered and documentation is generated. In order to have the opportunity to approve a land plot, a citizen must submit an application to the administration of the district where the land plot is located.
Read also: How microprocessors are made
At this stage, the conditions under which the land plot is transferred and the existing technical requirements for the installation of technical networks are formed.
Land for building a house.
The first thing I started with was studying the step-by-step instructions: “How to get a plot of land without special knowledge.”
Without this instruction, my idea of obtaining a plot of land would hardly have taken shape into a clear and understandable step-by-step scheme of actions.
Second , I watched in detail 7 video instructions on how to find vacant land in 40 minutes and draw up a diagram of a land plot.
The third block of theoretical training included step-by-step instructions: How to obtain a building permit and register on dacha land?
After studying these materials, I clearly understood what I needed to do and how to do it in order to get a plot of land.
In addition, I was given confidence by the understanding that I knew what to do if the administration began to “pressure” me with the registration of the land plot.
Land allocation project
To obtain ownership rights or register a lease of a plot of land, you must first draw up a land allotment project. It assumes the presence of a set of documents that are developed by land surveyors. The legality of their actions is confirmed by the presence of certificates. They are part of the staff of private or public land management organizations licensed to perform these works.
The land allocation project involves the calculation of technical and economic indicators. They are necessary to allocate a plot of land in kind and transfer it to private ownership.
Read also: Secrets of diamonds. Cut
What is land allotment?
Land allocation is a set of procedures for establishing a site on the ground, determining its boundaries, with the purpose of transferring it for free use or lease.
Experts analyze land allocation in a narrow and broad sense. In a narrow way, this is an area transferred for use. In the broadest sense, it is a part of the land to which the right has arisen on the basis of certain rules of law.
Registration of land acquisition consists of the stage-by-stage implementation of all procedures for determining, restoring or establishing the boundaries of a land plot, as well as its location and area.
Then all the collected materials and data are formalized in the so-called land management file (or as it is also called differently - land surveying).
To formalize the act of selecting a land plot or route, GeoCAD specialists perform:
- Preparation and approval of the Decision on the preliminary selection of a land plot.
- Engineering and geodetic surveys.
- Drawing up, coordination and approval of the Act on the selection of a land plot and route.
- Schemes of the location of the land plot on the cadastral map of the territory.
- Obtaining a construction permit, including the allotment of land plots, which is discussed in this section.
The provision of land plots for construction from lands in state or municipal ownership is carried out with work on their formation:
- without prior approval of the location of objects;
- with preliminary approval of the location of objects.
The provision of land plots for construction into ownership without prior approval of the location of objects is carried out exclusively through bidding (competitions, auctions) in accordance with Article 38 of the Land Code. The allocation of a land plot in this case is carried out by the territorial Administration and is not the subject of this article.
Coordination of the location of the object
The following steps can be distinguished in this procedure:
- Development of design documentation with establishment of site boundaries on the ground.
- Determination of the type of permitted use of land.
- Establishment of technical conditions for connecting the construction site to communications and engineering systems.
- Signing a conclusion on holding an auction or on providing a site without auction events.
- Publication of the auction announcement in the media.
- The registration was put on the state cadastral register.
- Conducting an auction or transfer of land without such actions.
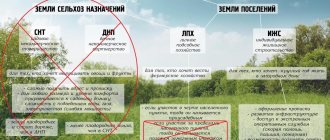
Permitted use of the territory of populated areas
The list of acceptable options for the exploitation of land plots within the boundaries of a settlement is specified in urban planning documents. For each territorial zone, the main, conditionally permitted and auxiliary types of exploitation are prescribed. The list of options (and their characteristics) is contained in the classifier approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development No. 540 dated September 1, 2014.
The owner of a plot of land from the land of settlements can, without additional approvals, choose one of the main types of use. A conditionally permitted type of use can be introduced by the owner only after discussion with a state or municipal body based on the results of public hearings (Article 39 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation).
Auxiliary uses are applicable if they are in addition to the main or conditional uses.
Step-by-step scheme for obtaining land for building a house.
Initially, I “pumped” the local administration’s website to search for already formed land plots, which the administration puts up for auction for the purpose of sale or lease.
Not many plots were offered.
But what struck me most was the cost.
The administration put almost all the plots up for auction at cadastral value.
In my opinion, this is outright “robbery”, since, as many people know, the cadastral value, as a rule, is many times higher than the market value.
This state of affairs convinced me of the wisdom of the idea of following the path described in the instructions: “How to get land” and applying for a plot of land that has not yet been formed.
The first thing to do was to find free land.
How does land transfer take place?
When performing land allotment, the following rules apply:
- taking into account the role of land as the basic principle for human existence and activity;
- priority of land protection;
- the interest of people and organizations in setting tasks that affect their rights to land;
- integrity of the sites and the buildings located on them;
- priority preservation of the most significant memories;
- taking into account the value of the use of sites;
- division of lands according to their intended purpose;
- separation of national and local property.
Also, land allotment operations are regulated by legislative norms and public measures to determine the nature of possible activities on the allocated site.
Preparing to search for a land plot.
I began my search for a plot of land by finding the Land Use and Development Rules (LRU) in force in my city.
Why did I need Land Use and Development Rules?
These Rules contain a city zoning map that contains very valuable information. I'll tell you more about this later.
I looked for the PZZ in a simple old-fashioned way - I typed “rules of land use and development of Khabarovsk” in the Yandex search bar. One of the links led to the document you were looking for.
Recently, I learned that you can also find Land Use and Development Rules through the FSIS TP system.
In a short video I showed how I searched for Land Use and Development Rules.
The Land Use and Development Rules are accompanied by an urban zoning map.
Using this map, I identified areas of the city in which you can get a plot of land for individual housing construction.
In my case, you can get a plot of land for building a house in zones Zh-1, Zh-2 and Zh-3.
As you can see, on the urban zoning map, the residential zones where it is possible to build a house are highlighted in yellow, and it was easy for me to determine the areas of the city in which to look for a plot of land.
Activities and principles of land transfer
Real rights
In accordance with the law, it is customary to divide the following types of rights to land plots:
- permanent use (in the absence of a specific period in the contract);
- lifelong inheritable ownership;
- rent;
- easement (use of “alien” land with some restrictions);
- free term use;
- private property.
How to make a coating waterproofing of the floor in a house before screeding?
Activities for the benefit of construction
In some situations, approval is not required to allocate land for construction:
- when the site is located in an urban or rural area for which the Urban Development Plan has been approved;
- provision of land territory in the interests of agricultural needs or strengthening forestry;
- carrying out individual housing construction.
Under other conditions, advance coordination with the local administration is necessary.
Territory coordination
In this event, the following procedures should be noted:
DEVELOPMENT OF LAND MANAGEMENT PROJECTS FOR LAND ALLOCATION
(according to the Laws of Ukraine “On the State Land Cadastre” and “On the Regulation of Urban Planning Documentation”, which came into force on 01/01/2013)
Process: A land allocation project is developed for each newly formed land plot. Even if you have used this plot over the past years and built or purchased a house on it, but this plot has not been privatized before. To do this you need:
STEP 1: SUBMIT YOUR APPLICATION
Submit an application (petition) “for permission to develop a land management project for the allocation of a land plot for ownership (rent, permanent use) for the construction and maintenance of a temple, chapel, residential building, utility buildings and structures (personal farming, etc. )" to the village (village, city) council, if the site is within the populated area, or to the district state administration and the department of the State Land Agency, if the site is outside the populated area. To the application (petition) you need to add : a copy from the general plan or planning diagram of the area (if available) or a copy from the Public Cadastral Map (https://map.dazru.gov.ua/kadastrova-karta), copies of title documents.
After receiving permission “to develop a land management project for the allocation of a land plot for ownership (rent, permanent use) for the construction and maintenance of a temple, residential building, utility buildings and structures (running a personal peasant farm, etc.)”
STEP 2: DEVELOPMENT AND APPROVAL OF THE LAND MANAGEMENT PROJECT
You need to : contact a land management organization that has certified land management engineers and the necessary technical equipment (GPS equipment and total stations) on its staff and enter into an agreement to perform land management work.
After developing a land management project and entering information about the land plot into the National Cadastral System, the Cadastral number of the land plot will be determined. Next, you need to coordinate the land management project with the following authorities:
— If construction is not planned on the allocated land plot, then only the territorial department of the State Land Agency approves the project;
— If it is planned to build a temple, residential building or other structures on a land plot, then it is necessary to additionally coordinate the land management project with the city or district department of urban planning and architecture;
— If the land plot borders an object of a natural reserve fund or is located on its territory (forest, reserve or reservoir), then such a land management project must additionally be approved by the environmental authority (ecology):
— If the land plot borders on an object of historical and cultural significance or is located on its territory, then such a land management project must additionally be approved by the cultural heritage protection body (archaeology);
STEP 3: APPROVAL OF THE LAND MANAGEMENT PROJECT
After receiving all approvals, the land management project for the allotment of the land plot must be submitted for approval to the authority that granted you permission to develop it.
STEP 4: OBTAINING TITLE DOCUMENTS FOR LAND
After receiving a decision (instruction, order) “on approval of a land management project for the allocation of a land plot and transferring it into ownership or permanent use,” the land management project, together with an application and a receipt for payment of state registration, must be submitted to the State Cadastral Registrar for state registration of the land plot .
State registration of a land plot is carried out within two weeks and as a result you should receive an “Extract from the State Land Cadastre”, which will contain information about the size, address, cadastral number of the land plot and information about its owner.
Extract from the State Land Cadastre together with the original decision (instruction, order) “On approval of the land management project for the allotment of a land plot and transferring it into ownership and use”, you must submit copies of title documents to the State Registration Service in your city, district , adding an application for carrying out state registration of rights and a receipt for payment of state duty and services for state registration.
Within two weeks, the registration service issues you a “Certificate of state registration of rights to real estate (land plot).” Currently, this document is an analogue of the State Act on a land plot.
HOW TO REGISTER A LAND AND REGISTER TITLES TO IT?
On January 1, 2013, a new procedure for registering land plots and ownership rights to them came into force. From now on, the plot must first be registered with the State Land Cadastre, and then the data must be entered into the State Register of Property Rights to Real Estate.
The initial registration of rights to land plots is carried out by the State Registration Service. And in the secondary market (purchase and sale, inheritance, etc.), the role of registrars should be performed by notaries.
The procedure for the initial registration of a land plot and registration of ownership rights
1. The applicant submits an application for registration of a land plot and a package of land management documentation to the state cadastral registrar.
2. The cadastral registrar, within 14 days, checks the compliance of documents with legal requirements and registers the land plot (or provides the applicant with a reasoned refusal).
3. The cadastral registrar issues the applicant a free extract from the State Land Cadastre and sends an application for registration of rights to the land plot and a package of necessary documents to the State Registration Service.
4. The state registrar, within 14 days, issues a certificate of ownership (use) and transfers it to the cadastral registrar.
5. The cadastral registrar transfers the certificate of ownership and use to the applicant.
Since 2013, the issuance of paper versions of state certificates on the right of ownership and use has been cancelled, they are replaced with a certificate of ownership or use. All information about land owners, transactions and restrictions is now stored in a single land registry.
Registration and change of ownership of land is now done in the Ministry of Justice - the state registrar service of the Ministry of Justice. Land resources authorities are assigned only the technical part, checking exchange files, determining the cadastral number.
Access to information about all lands of Ukraine is now open.
HOW TO LEGALIZE SELF-BUILDING?
In accordance with Part 3. Art. 19 of the “Law of Ukraine “On Freedom of Conscience and Religious Organizations”, the construction of religious and other buildings by religious organizations is carried out in the manner established by the current legislation for civil purposes.
Self-building is any building (house, extension, garage, barn, shop, church, office building, additional floor of the house) for which there are no documents of ownership or permits for construction (permit to start work, design documentation, act/certificate on commissioning) or the construction process itself without permits.
Samostroy in official documents is defined as “unauthorized construction.”
Law of Ukraine dated December 22, 2011. No. 4220-VI, the fine for unauthorized construction has been increased from UAH 850.00. up to 10730.00 UAH. and a new fine was introduced for the operation or use of houses in the amount of UAH 48,285.00. Total – 59015.00 UAH . This is the current price for self-building.
It should be noted that in 2013 there is a moratorium on the collection of the above fines. In 2014, there is no such moratorium anymore
HOW TO LEGALIZE SELF-BUILDING: ORDER AND METHODS
Currently until 01.01.2014. to legitimize self-construction in 3 main ways, namely:
- Legalize self-construction through the BTI (houses built before 08/05/1992)
- Legalize self-construction in a Simplified manner (houses built before 03/12/2011)
- Legalize self-construction through a Construction Passport (houses built after 03/12/2011)
LEGALIZE SELF-BUILDING THROUGH BTI
To legalize self-construction through the BTI, you need a minimum of documents:
- State certificate for a land plot
- Technical certificate
- Copies of title documents
LEGALIZE SELF-BUILDING IN A SIMPLER PROCEDURE
to legalize self-construction in a simplified manner according to the order of the Ministry of Regional Development No. 95 of March 19, 2013. Now, in 2013, GASK has only 10 (ten) days to make a decision on accepting a house (self-construction) into operation. To take advantage of the simplified procedure for commissioning an illegally built house in 2013, you must have title documents for the land (state certificate of ownership, use or lease agreement) and do a technical inspection of the building structures and utility networks of the house (receive a technical report). The same requirements existed before.
The procedure for commissioning under a simplified procedure is determined by order of the Ministry of Regional Development and Construction dated March 19, 2013 No. 95. This order came into force on April 29, 2013.
THE PROCEDURE FOR LEGISLATING SELF-CONSTRUCTION IS FOLLOWING:
1). Collection and submission of documents to the local GASK Inspectorate
2). Checking compliance with building standards during the construction of a house by the GASK Inspectorate
If violations are found during the inspection, this will be grounds for refusal to legitimize . In this case, GASK will issue an order to eliminate violations. Until they are eliminated, squatter building cannot be legitimized .
MOST COMMON BUILDING CODE VIOLATIONS
- The fire safety distance to neighboring houses or outbuildings has been violated ( min. 9.0 m , DBN 360-92 “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements”);
- The distance to the adjacent border of the site from the most protruding wall structure has been violated ( min. 1.0 m , DBN 360-92);
- There is no act of fire-prevention treatment of wooden house structures (DBN V.2.2-15-2005 “Residential buildings. Basic provisions”, GOST 16363);
3). Registration and issuance of declaration.
LEGALIZE SELF-BUILDING THROUGH A CONSTRUCTION PASSPORT
to legalize self-construction through a Construction Passport for the development of a land plot in accordance with the Law of Ukraine “On the Regulation of Urban Development Activities” and Order of the Ministry of Regional Development No. 103 dated 07/05/2011.
LEGITIZATION OF SELF-CONSTRUCTION THROUGH A CONSTRUCTION PASSPORT CONSISTS OF THE FOLLOWING STEPS:
1). Collection and preparation of documents (including the conclusion of the architectural authority, technical specifications, copies from the cadastral plan, topographic and geodetic survey, etc.)
2). Obtaining a Construction Passport
The grounds for refusal to issue a Construction Passport are:
— discrepancy between the intentions for developing the site and the requirements of urban planning documentation, building codes, state standards and development rules.
3). Verification by the GASK Inspectorate of the developer’s compliance with building codes and regulations
If violations are found during the inspection, this will be grounds for refusal to legitimize. In this case, GASK will issue an order to eliminate violations. Until they are eliminated, squatter building cannot be legitimized .
4). Registration and issuance of declaration
Registration of the declaration is carried out within 30 days from the date of submission of documents (in practice longer), provided that the declaration is drawn up in accordance with the order and there are no violations when checking building regulations.
FOR INFORMATION
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine took into account the Presidential amendments and lifted the moratorium on the allocation of land plots owned by urban territorial communities.
The moratorium on the allocation of land plots has been canceled until January 1, 2015, the official statement says.
This is provided for by the final version of the Law “On Amendments to Section V” adopted by Parliament on September 19. The final provisions of the “Law of Ukraine” On the regulation of urban planning activities “regarding the suspension of the ban on land allocation.”
LAND CODE OF UKRAINE
Article 123
The procedure for granting land plots for permanent use to legal entities
1. The provision of land plots to legal entities for permanent use is carried out on the basis of decisions of executive authorities and local governments on projects for the allocation of these plots.
2. The conditions and terms for the development of projects for the allocation of land plots are determined by the agreement concluded by the customer with the contractor of these works.
3. A legal entity interested in obtaining a land plot for permanent use from state-owned or communally owned lands submits a corresponding petition to the district, Kyiv and Sevastopol city state administrations or the village, township, city council.
4. Documents justifying its size, purpose and location are attached to the application for the allocation of a land plot.
5. The relevant district state administration or village, town, city council considers the application within a month and gives consent to the development of a project for the allocation of a land plot.
6. The project for the allocation of a land plot is agreed upon with the land user, the land resources authority, environmental and sanitary-epidemiological authorities, architectural and cultural heritage protection authorities, and after receiving the conclusion of the state land management examination of the objects that are subject to it, it is sent to the relevant state administration or rural, village, city council, which consider it within a month and, within the limits of their powers defined by this Code, make a decision on the provision of a land plot.
7. When providing a land plot for use by regional state administrations, the Council of Ministers of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea or the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, rural, township, city, district, regional councils, district state administrations at the location of the land plot give their opinion accordingly to the regional state administration, the Council, Ministers of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea.
8. When providing a land plot for use by the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, the Council of Ministers of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, regional, Kiev, Sevastopol city state administrations give their conclusions and a project for the allocation of a land plot to the central executive body for land resources, which reviews these materials within a month submits them to the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine.
9. The refusal of local government bodies or executive authorities to provide a land plot for use or leaving the application without consideration may be appealed in court.
Article 61
Restrictions on the use of land plots of coastal protective strips along rivers, around reservoirs and on islands
1. Coastal protective strips are a conservation area with a regime of limited economic activity.
2. In coastal protective strips along rivers, around reservoirs and on islands, it is prohibited:
a) plowing of land (except for preparing the soil for grassing and afforestation), as well as gardening and vegetable gardening;
b) storage and use of pesticides and fertilizers;
c) arrangement of summer camps for livestock;
d) construction of any structures (except for hydraulic engineering, hydrometric and linear), including recreation centers, dachas, garages and parking lots;
ґ) construction of garbage dumps, manure storage facilities, liquid and solid industrial waste storage facilities, cemeteries, cattle burial grounds, filtration fields, etc.;
e) washing and maintaining vehicles and equipment.
3. Objects located in the coastal protective strip can be operated if its regime is not violated. Buildings that are not suitable for use, as well as those that do not comply with established management regimes, are subject to removal from coastal protective strips.
4. The regime of economic activity on land plots of coastal protective strips along rivers, around reservoirs and on islands is established by law.
Article 62
Restrictions on the use of land plots of coastal protective strips along seas, sea bays and estuaries and on islands in internal sea waters
1. In coastal protective strips along seas, sea bays and estuaries and on islands in internal sea waters, it is prohibited:
a) construction of landfills for household and industrial waste and wastewater storage tanks;
b) installation of cesspools for the accumulation of household wastewater with a volume of more than 1 cubic meter per day;
c) construction of filtration fields and creation of other structures for the reception and disinfection of liquid waste;
d) use of strong pesticides.
2. The regime of economic activity on land plots of coastal protective strips along the seas, sea bays and estuaries and on islands in internal sea waters is established by law.