The land fund is the totality of all plots located on the territory of the Russian Federation. It is a national treasure and considered a strategic resource. Land registration and systematization is carried out based on their type and quality. The adopted reforms make the management and regulation process more transparent and understandable for all market participants.
In this article we will tell you what classifiers and codes of land plots are, why they are needed and how to correctly read their decoding.
What is a site classifier?
All lands on the territory of the Russian Federation have their own purpose. Each site has a so-called VRI (type of permitted use).
This concept can be found in various legislative and regulatory acts intended to determine the nature of permitted activities in a particular territory.
Distribution of land resources of the Russian Federation
Classification codes were introduced precisely to indicate that a land resource belongs to one of the existing categories. By analyzing the code, you can understand what can be done on a specific plot of land and what is prohibited by law.
Each land plot has its own code designation, name and description. The classifier contains all this information. And they are necessarily taken into account when concluding property transactions.
If you are planning to buy a plot, receive it from the state, or lease it, or inherit it, it is recommended that you learn how to analyze this data. Violation of these regulations is subject to administrative liability.
What is it and why is it necessary?
All lands in Russia are divided according to their intended and functional purposes. The principle of intended use assumes that the site must be developed in accordance with the purposes established by law (you can find out what the intended purpose of a site is or how to find out the category and VRI of land by cadastral number here). The functional purpose determines the specific type of activity permitted in the allocated territory.
The classifier of land categories is a systematic list of different types of territories and plots, combined into groups and assigning a symbol to each of them. Read about what the category of a land plot is and how it is established here.
A classification code is a set of signs used to unify each individual group.
Note! The classification code according to the functional purpose of the site is assigned to it until the boundaries of the territory are changed, despite changes in the classifier and innovations in legislation.
Read about the penalties for using land for purposes other than its intended purpose.
How to find out the VRI of a site?
The main function of code systematization is to reflect land use conditions. Re-registration of status is regulated at the level of local legislation, and each VRI is determined by a separate document.
You can obtain information about a plot of land purchased in the Moscow region in the following ways:
- Visit the Rosreestr website . To obtain the necessary data, you must pay the state fee, send a request, and review the information provided;
- Take an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate . This document has come to replace the cadastral passport. In it you can see information about technical information and rights in relation to the land plot. The extract can be obtained from the cadastral office or on specialized websites. The list of required documents includes a receipt for payment of the state duty, power of attorney, and passport.
Classification of the purpose of land plots
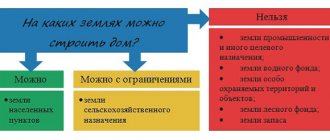
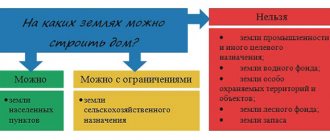
The category of land directly determines the options for its use. For example, it is prohibited to build a house on agricultural territory without prior approval of the construction from authorized government agencies. Therefore, it is important to know and be able to understand the types and methods of land classification.
The Land Code identifies 7 categories of intended use:
- Agricultural land (farms, gardens, meadows, etc.).
- Lands of populated areas (for residential buildings, buildings for domestic and commercial purposes, etc.).
- For industry and defense.
- Specially protected areas (read about the composition and legal regime for the use of lands of specially protected areas and objects here).
- Water fund lands.
- Forestry.
- Reserve lands are territories that do not belong to anyone and are in reserve (you can learn about the features of the exploitation and purpose of reserve lands, as well as how to transfer them to another category here).
The classifier distinguishes 12 types of intended use of land plots:
- agricultural;
- for housing construction;
- for capital construction projects;
- for organizing recreation areas;
- for conducting business activities;
- to suit the needs of enterprises;
- for transport;
- to ensure defense and security;
- for the protection and study of nature;
- forest areas;
- water bodies;
- public lands.
On a note. Intended and functional use are mutually complementary concepts.
The same plot cannot simultaneously belong to the agricultural fund and at the same time be intended for production needs.
Basic codes of permitted use of memory
The land plot classifier consists of 13 categories. All suburban lands can be classified into the following sections:
- Buildings and structures that are used for agricultural purposes (1.1-1.18) . They are particularly important objects. This is precisely the reason for strict supervision of activities carried out in these areas. The determining factor is the location of the land;
- Country and garden farms (13.1-13.3);
- Individual construction (2.0) . Private houses with an attached plot. An exception may be health institutions, hotel complexes, temporary housing and correctional institutions.
- Buildings intended for business activities (4.0).
- Land resources used for recreational purposes (5.0) . These include tourist centers, hotels, places for hunting and fishing.
- Industrial lands permitted for the location of production (6.0) . Many objects are located on the periphery.
- Security and Defense (8.0) . Test sites, settlements, observation towers and weapons depots.
- Resorts, conservation and study of natural resources (9.0-11.0).
- Properties held for public use (12.0).
DIRECTORY OF LAND CATEGORY FOR LAND TAX. CODES OF THE SUBJECTS OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
In accordance with the Order of Roszemkadastre dated June 15, 2001 N P/1119, the full cadastral number of a land plot is written in the form KNkk: Nzu, where - KNkk is the cadastral number of the cadastral quarter, consisting of the number of the cadastral district, the number of the cadastral district in the district and the number of the cadastral quarter in area (Nko: Nkr: Nkk); — Nzu — number of the land plot in the cadastral quarter; - “:” (colon) - separator of all components of the cadastral number.
4. Classifiers, code dictionaries (directories), lists of concepts used when generating exchange file elements
Table 4.1
Directory “Land categories for land tax (Chapter 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)”
| N p/p | Code | Land category name |
| 1 | 003001000000 | Agricultural land |
| 2 | 003002000000 | Settlement lands |
| 3 | 003003000000 | Lands of industry, energy, transport, communications, radio broadcasting, television, computer science, lands for space activities, defense lands, security lands and lands for other special purposes |
| 4 | 003004000000 | Lands of specially protected territories and objects |
| 5 | 003005000000 | Forest fund lands |
| 6 | 003006000000 | Water fund lands |
| 7 | 003007000000 | Reserve lands |
| 8 | 003008000000 | Land category is not established (Other lands) |
Table 4.2
Codes of subjects of the Russian Federation
| Code | Name of the subject of the Russian Federation |
| 01 | REPUBLIC OF ADYGEA |
| 02 | REPUBLIC OF BASHKORTOSTAN |
| 03 | THE REPUBLIC OF BURYATIA |
| 04 | ALTAI REPUBLIC |
| 05 | THE REPUBLIC OF DAGESTAN |
| 06 | INGUSH REPUBLIC |
| 07 | KABARDINO-BALKARIAN REPUBLIC |
| 08 | REPUBLIC OF KALMYKIA |
| 09 | KARACHAY-CHERKASSIAN REPUBLIC |
| 10 | REPUBLIC OF KARELIA |
| 11 | KOMI REPUBLIC |
| 12 | MARI EL REPUBLIC |
| 13 | THE REPUBLIC OF MORDOVIA |
| 14 | THE REPUBLIC OF SAKHA (YAKUTIA) |
| 15 | REPUBLIC OF NORTH OSSETIA |
| 16 | REPUBLIC OF TATARSTAN (TATARSTAN) |
| 17 | TYVA REPUBLIC |
| 18 | UDMURT REPUBLIC |
| 19 | THE REPUBLIC OF KHAKASSIA |
| 20 | CHECHEN REPUBLIC |
| 21 | CHUVASH REPUBLIC - CHUVASHIA |
| 22 | ALTAI REGION |
| 23 | KRASNODAR REGION |
| 24 | KRASNOYARSK REGION |
| 25 | PRIMORSKY KRAI |
| 26 | STAVROPOL REGION |
| 27 | KHABAROVSK REGION |
| 28 | AMUR REGION |
| 29 | ARHANGELSK REGION |
| 30 | ASTRAKHAN REGION |
| 31 | BELGOROD REGION |
| 32 | BRYANSK REGION |
| 33 | VLADIMIR REGION |
| 34 | VOLGOGRAD REGION |
| 35 | VOLOGDA REGION |
| 36 | VORONEZH REGION |
| 37 | IVANOVO REGION |
| 38 | IRKUTSK REGION |
| 39 | KALININGRAD REGION |
| 40 | KALUGA REGION |
| 41 | KAMCHATKA REGION |
| 42 | KEMEROVSK REGION |
| 43 | KIROV REGION |
| 44 | KOSTROMA REGION |
| 45 | KURGAN REGION |
| 46 | KURSK REGION |
| 47 | LENINGRAD REGION |
| 48 | LIPETSK REGION |
| 49 | MAGADAN REGION |
| 50 | MOSCOW REGION |
| 51 | MURMANSK REGION |
| 52 | NIZHNY NOVGOROD REGION |
| 53 | NOVGOROD REGION |
| 54 | NOVOSIBIRSK REGION |
| 55 | OMSK REGION |
| 56 | ORENBURG REGION |
| 57 | ORYOL REGION |
| 58 | PENZA REGION |
| 59 | PERM REGION |
| 60 | PSKOV REGION |
| 61 | ROSTOV REGION |
| 62 | RYAZAN OBLAST |
| 63 | SAMARA REGION |
| 64 | SARATOV REGION |
| 65 | SAKHALIN REGION |
| 66 | SVERDLOVSK REGION |
| 67 | SMOLENSK REGION |
| 68 | TAMBOV REGION |
| 69 | TVER REGION |
| 70 | TOMSK REGION |
| 71 | TULA REGION |
| 72 | TYUMEN REGION |
| 73 | ULYANOVSK REGION |
| 74 | CHELYABINSK REGION |
| 75 | CHITA REGION |
| 76 | YAROSLAVL REGION |
| 77 | MOSCOW |
| 78 | SAINT PETERSBURG |
| 79 | JEWISH AUTONOMOUS REGION |
| 80 | AGINSKY BURYAT AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 81 | KOMI-PERMYAK AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 82 | KORYAK AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 83 | NENETS AUTONOMOUS OKRUG |
| 84 | TAIMYR (DOLGANO-NENETS) AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 85 | UST-ORDA BURYAT AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 86 | KHANTY-MANSI AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 87 | CHUKOTKA AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 88 | EVENKI AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
| 89 | YAMAL-NENETS AUTONOMOUS DISTRICT |
Table 4.3 Pages:
6 of 23 contents next —>
How are plots divided by type of permitted use?
The main systematization of VRI occurred back in 2014. They are divided into:
- main type of permitted use
- auxiliary VRI
- conditional VRI
The areas to which the main VRI have a full code. They can only be used as specified in the documentation governing the Land Trust. If a citizen violates the instructions established for certain areas, sanctions are imposed on him. The personal opinion of the owner does not matter.
When disposing of areas classified as a conditional type of permitted use , it is also prohibited to go beyond the scope of the systematized classifier. The only difference between these VRIs is the broader regulations.
The attitude towards the desires of the citizen in this case is more loyal than in the previous one. The buildings comply with the prescribed installations, but if necessary, you can place something of your own on the site. In this case, the classification code will reflect the linking of the property to the defining point. In this case, it is necessary to coordinate actions with the employees of the town planning chamber.
Auxiliary species are never used as independent definitions. This is due to the lack of sufficient legal force. Land plots are tied to them if there are nuances that cannot be circumvented.
The legislative framework
Clause 3 of Article 36 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation determines that the conditions and procedure for the use of land are based on federal laws, these include:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation (first part):
- Article 260 “On land ownership”;
- Article 284 “Confiscation of a land plot that is not used for its intended purpose.”
- Land Code of the Russian Federation:
- Article 7 “Composition of lands by category”;
- Article 8 “Assigning lands to categories, transferring them from one category to another”;
- Article 37 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “Types of permitted use of land plots and capital construction projects”;
- Article 39 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “Procedure for granting permission for a conditionally permitted type of use of a land plot or capital construction project”;
- Article 94 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation “The concept and composition of lands in specially protected areas.”
- Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated September 1, 2014 No. 540 “On approval of the classifier of types of permitted use of land plots.”
Important! In some cases, land legal relations are regulated by the norms of natural resource codes (forest and water).