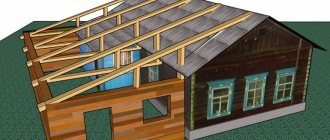
What is a house extension?
To begin with, it would be worth understanding what exactly a residential extension is. The law, namely the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, says that an extension is the reconstruction of an existing housing facility. The extension is not included in the original architectural plans, but, on the contrary, is considered a secondary structure to the main object. An additional building, contrary to popular belief, is not always a small object in comparison with the main dwelling. An extension can be of absolutely any size, regardless of the number of floors, area, height, etc. The concept under consideration is rather legal, since it is closely related to the registration and registration processes.
There are many reasons why home owners want to build an extension. Someone wants to create additional living space, someone is correcting the architectural mistakes of the property, and someone wants to build a cozy corner in the form of a veranda or summer gazebo. One way or another, any such extension requires strict documentation and proper legalization. Of course, some citizens decide to ignore the registration process, and therefore an unauthorized extension can legally be demolished. To prevent this, you must follow a number of simple rules, which will be discussed below.
SNiP requirements
SNiP 30-02-97 as amended in 2021 and SP 53.13330.2011 require obligatory distance from the object with territorial delimitation functions to other functional objects in the following parameters:
- The minimum distance from the fence to the house should not be less than 3 m, and measurements are taken exclusively from the protruding part - the edge of the roof, canopy, veranda or terrace, or the base extended for some purpose. Failure to comply with this rule in relation to a neighbor's fence may give rise to legal action and complaints to supervisory authorities. There are cases when a claim was satisfied on the basis of several tens of centimeters, because the distance to the neighbor’s fence was measured not from the edge of the roof, but from the foundation of the house.
- The construction of outbuildings for keeping livestock or poultry must be carried out at a distance of at least 4 m. This is provided not only by the rules of building regulations, but also by sanitary standards. A shorter distance is not allowed due to the possibility of clogging and contamination of neighboring crops, causing visual and olfactory inconvenience. The extension of such structures closely or at a shorter distance is strictly unacceptable. This rule also applies to a private house on a plot of land in a populated area and one built in a gardening partnership.
- A three-meter interval between a sauna, bathhouse, smokehouse or barbecue - any type of functional purpose from which the fence is exposed to a potential fire hazard is required in any case. Fire safety requirements are not limited to a distance of 8 m. But, since the state has entrusted the responsibility for compliance with them to homeowners, owners of one-story houses can rely on SNiP standards as amended in 2018. Those with two or more floors may face complaints from inspecting and supervisory authorities.
- Standards for planting trees, especially in non-profit gardening partnerships, are also ambiguous. As far as is known from the standards, when planting trees, it is necessary to focus on their height. But decorative, fruit or thorny shrubs are allowed to be planted from a neighbor’s fence at a distance of only 1 m. And a decorative flower bed of plants can be freely placed directly on the strip under the installed fence.
- Standards for the placement of garages, sheds and restrooms have been established more democratically. They are officially allowed to be erected at 1 m height. But here it is necessary to take into account other nuances. For example, that the construction of a septic tank requires maintaining other distances - from the water source and the neighbor’s house, as well as from other objects specified in the rules, if they are located near the local area. There is a special law regulating the construction of toilets and cesspools, and violating it risks serious administrative and legal liability.
Distances between outbuildings in the village according to the law
The norms provided for by the charter of a particular non-profit gardening partnership may provide for a greater or lesser distance between the fence and the road or buildings. The same applies to instructions from local authorities or regional legislation.
The optimal disposal in this case will be in accordance with the statute or order of the local authorities, which you need to be aware of. Before you build anything, you need to make sure that the construction complies with all existing regulations.
Sources
- https://law-divorce.ru/rasstoyanie-ot-navesa-do-zabora-sosedej/
- https://HomeMyHome.ru/navesy-pristroennye-k-domu-foto.html
- https://m-strana.ru/articles/-raspolozheniya-na-uchastke-zhilykh-postroek-zabora/
- https://dachadesign.ru/navesy-iz-polikarbonata/
- https://allo-urist.com/rasstoyanie-ot-navesa-do-zabora-sosedej/
- https://stroydomkin.ru/stroitelstvo-doma/normy/rasstoyanie-ot-doma-do-zabora
[collapse]
Non-permanent extensions
As already mentioned, the extension can be absolutely any object; the main requirement here is a direct connection with the main structure. And, nevertheless, there are some classifications that allow you to better understand what kind of house extension projects exist. One of the classifications will be given below.
There are permanent and non-permanent buildings. Non-major extensions are small changes made to the main architectural design. These are such minor elements as:
- porch, new entrance to the house;
- showcase, various projections;
- stairs, small sheds;
- balconies or terraces.
Designing a non-permanent extension is quite simple. You don’t even need to take out special permits before starting the construction process. All that is needed is to make some changes to the technical documents. Among other things, non-permanent extensions include:
- A garage, if it is being built on the territory of a gardeners' partnership, or on land that does not belong to a capital construction project.
- Construction of auxiliary buildings. It is difficult to say what can be included here; even the Russian Supreme Court has not fully clarified this. Most likely, auxiliary outbuildings include sheds, small fortifications for something, hanging objects and other non-residential buildings.
- Construction of buildings that do not affect common structures or communications.
All of the above objects are non-capital and therefore do not require special permission for construction.
Do you need to follow the rules?
The norms of SP, SNiP and SanPiN were not invented so as to ensure that they are observed. For neglect of instructions, administrative liability is provided, which is regulated by Art. 9.4 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation. The first time the offender will receive a verbal warning. If it is not eliminated, a fine of 1 to 2 thousand rubles will be issued.
More serious sanctions will follow if it is proven that disregard for the rules has caused harm to nature or neighbors. The first time the offender faces a doubled fine, that is, from 2 to 4 thousand rubles. Repeated violation is punishable by an even larger fine of up to 5 thousand rubles. Litigation over non-compliance with the distance to the fence is not uncommon.
It is noteworthy that establishing the fact of non-compliance with the minimum distance between a house, building or tree and a fence is not yet a reason to force the violator to solve the problem. Demolition, relocation of a building, or removal of green spaces can only be achieved through the courts. However, the best option is to maintain a distance from the house to the fence and avoid conflicts.
House extension projects: capital type
Now it’s worth talking about what capital construction projects are. The Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation regulates the norm according to which construction work on the construction of additional capital-type facilities must comply with the original standards (those that have been preserved since the construction of the house itself). Capital extensions include objects in which further residence is planned. At the same time, additional land area is required for the construction of such facilities.
The question of how to design an extension to a house will be somewhat different in this case, depending on who exactly is the owner of the home. Thus, all responsibility for the construction of additional buildings should rest with the direct owners of the houses. However, there are situations when the house is divided into several families. How to act in such a situation will be discussed below.
When can they refuse?
It is better to obtain permission for construction work before it begins. The court may refuse to build an extension if it finds violations or inconsistencies in the submitted documents.
If an unauthorized building already exists, then a decision will most likely be made to restore the site to its previous form, which will entail financial costs. Here is a list of reasons that are guaranteed to lead to refusal:
- Any underground communications must lie at a distance of more than 2.5 meters from the building. This is a mandatory requirement for any residential buildings.
- During the work, the supporting structures of the main building were affected. In this case, it will not be possible to design an extension, because there is a threat to the integrity of the building.
- When construction was carried out using outdated technologies or low-quality materials were used.
The design of the extension contains a lot of nuances that need to be taken into account. For example:
- It is better to design the extension in 2021. Starting next year, it is planned to tighten the registration procedure;
- After filing a claim, there is a set period for the executive body to accept the application for consideration. The response is sent by mail to the applicant. We recommend that you do not wait, but periodically check with the court secretary whether the claim has been accepted for consideration or ignored.
Please note that judicial refusal is regulated by legal norms. In particular, an application may be refused for two reasons: a decision on the issue has already been made or the claim has been drawn up incorrectly. If the denial states another reason, you may file a complaint.
To correctly draw up a claim, we recommend using the services of a lawyer.
Registration of non-permanent construction
How to legalize a non-permanent extension? It's actually very easy to do this. First of all, you need to find a local technical inventory bureau (BTI). After this, a complete package of documentation for the house is collected, which should be taken to the above-mentioned authority. The bureau draws up a special application for amendments to technical house documents. This can be done both before the construction of the extension begins and after. The question of which of these two options is more convenient is obvious. The best option would be to design an already constructed non-capital facility, because all the data is already known exactly, and major changes are unlikely to follow. But there is one small problem here. Although this is unlikely, the BTI may refuse permission for an extension. Of course, there must be serious reasons for this. That is why it is better to play it safe and coordinate the construction of a non-capital type facility in advance.
A special acceptance committee must come from the bureau to draw up a certificate of completion of the reconstruction. When the BTI returns the full package of documents, the issue can be considered resolved.
If there are several owners in the house, then a written agreement for an additional non-capital type object from each of the residents will be required.
Collection of documents for registration of a major extension
A house extension project can be called a reconstruction of an existing building. Legalizing a capital additional structure is not as simple as a non-permanent one. However, there are quite a large number of options here that you can act on legally. The most common and convenient way to register an additional object is to register an “unauthorized building”. We are talking about those cases when the registration of an object occurs after its construction.
To avoid problems, it’s worth calculating and preparing everything correctly. The following documents must be collected:
- statement of ownership of the land plot, as well as the house that needs to be reconstructed;
- technical passport and home ownership plan;
- cadastral plan of the site;
- a project for a permanent extension (this can be a plan, sketch, diagram - the main thing is that everything is correctly and clearly designed);
- written consent of other house owners for reconstruction;
- neighbors' consent to reconstruction;
- statements from resource supply organizations (water supply, energy, gas supply, etc.) that the reconstruction will be safe and will not create problems.
All documents are submitted to the local government authority. Sometimes the authority may request other documents, for example, from the fire department, architectural company, etc.
Fire safety standards
Fire safety requirements include a number of points that will help avoid a fire:
- the supply of electricity from the house to the garage is carried out with an insulated cable in accordance with PTEEP standards, without breaks or bare spots;
- the wire is placed in a metal sleeve;
- fuses are installed at the input;
- light bulbs with protective shades;
- presence of a fire extinguisher in the garage and car;
- no heating;
- floor with anti-slip coating, resistant to oils;
- a box with sand for removing spilled fuel and lubricants and extinguishing fires on the floor;
- outside fire shield;
- do not leave the car with an open fuel tank;
- smoking area outside the garage.
It is better to observe fire safety in the private sector so that outbuildings and the house on the entire site do not burn down
You should not store cans next to your car in the garage. It is better for them to make a room behind the garage with a separate entrance.
Electric heating devices and switched-on power tools must not be left unattended.
Immediately during construction, create paths 70–80 cm wide around the base. They will protect the foundation from wastewater and ensure free passage.
The process of registering a major extension
How to register an extension to a house? Having collected all the necessary documents and submitted them to the local government, you will have to wait for special consent for the reconstruction. In essence, this document provides the right to build an additional facility. If the construction is completed, a state commission is invited to inspect the constructed structure. Experts evaluate the construction for compliance with the original plan, sanitary standards, and architectural rules. Based on the results of the inspection, a conclusion of compliance will be issued, which will need to be submitted to the Technical Inventory Bureau (BTI). At this stage, all necessary changes will be made to the technical documentation of the structure.
With the received documentation you need to go to the Russian real estate register. This way the extension will be officially registered. Rosreestr will have to pay a fee for the entire registration process.
Thus, the entire process of registering a major extension is not so simple. In any case, you will have to “sweat” with the documentation - regardless of what type of additional building it is - be it a summer extension, a garage, a covered living area, etc.
Why do you need a fence on your property?
The legislation of the Russian Federation allows owners of suburban areas to produce enclosing structures of any configuration. You can find transparent and opaque, wooden, stone, steel and other fences. Regardless of the materials, all fences have common tasks:
- Decorating the land plot if the fence has an aesthetic appearance.
- Masking the yard and the activities taking place on it from prying eyes.
- Preventing possible encroachments on property by neighbors.
- Protecting the area from dust and noise from the road, from strong winds and from debris.
- A guideline for maintaining the distances specified in building codes.
Due to their many advantages, fences are found in almost all suburban areas in Russia, regardless of the region. Only the appearance, dimensions and selected material change.
Necessary documentation to legalize an unauthorized extension
Many residents solve the problem before it occurs, and some solve it after. Those who first built the object, and only then decided to formalize it, solve difficulties after they have occurred. How to register an extension to a house if it was built without permission? It’s worth noting right away that everything here is not as simple as with the construction of a non-capital type facility. The entire registration process will be decided through the courts. Whether it is convenient or not is up to each owner to decide individually.
If a permanent extension was erected, but the owner forgot about registration, then you will immediately have to prepare the following package of documents:
- contract of purchase, gift, inheritance, etc. - any document confirming ownership of housing;
- extract from the house register;
- housing permission for the construction of an extension;
- documentation from the BTI for the main object (to which the extension belongs);
- written agreement between neighbors;
- statements from public utilities (gas services, fire inspections, water supply companies, etc.);
- reconstruction project (sketches, drawings, etc.);
- photo of the house and extension.
If all the necessary documentation has been collected, you can finally ask yourself the question of how to arrange an extension to a private house.
In agreement with neighbors
In accordance with the Civil Code, neighbors can enter into an agreement to erect a shed in violation of sanitary standards. However, it is advisable to clarify compliance with fire safety requirements.
As a rule, a controversial situation is the construction of a canopy on a boundary or a slope towards neighbors.
If the owner of the neighboring house does not object, then such construction is not prohibited. The neighbors' decision must be made in writing and certified by a notary.
The document will help protect the rights of the owner in the event of a quarrel between neighbors or the sale of an object by the owners of a neighboring plot.
Legalization of unauthorized extension
Brick extension, panel, open or closed - all this is completely unimportant; if a capital object was erected without premature registration, then it is called “unauthorized”, and registering it will not be so easy. The owner is obliged to collect all documents for the house, plans for the extension, and go with them to the local administration.
She will most likely refuse to register the object. This refusal will need to be addressed to the district court. The entire package of documents is also sent to the court, to which a statement of claim must be attached. If the court is satisfied that all grounds for registration are present, the case will be won. The owner will pay the fee and register the extension with the BTI.
Possible problems
The process of registering an extension seems simple only at first glance. Of course, if we are talking about a non-capital additional facility, then everything will take shape relatively easily and quickly. If the owner of real estate is thinking about a major extension, then everything will be very long and difficult. Moreover, the process may even turn into complete hopelessness; Thus, an additional building may be demolished due to its recognition as illegal. In this case, the bailiffs will not care how many years the unregistered object stood, and whether it interfered with anyone or not.
Problems may also arise with neighbors. So, if the extension was built in accordance with all the rules and regulations, but for some reason the neighbors do not want to recognize it, the administration will most likely grant a legal refusal to register. How to avoid rejection? How to register an extension to a house without problems? Some tips will be provided below.
Design and location
Based on their structural features, there are several types of buildings with a polymer coating, these include the following canopies:
- built-in, they are planned at the construction design stage;
- attached sheds, can be attached to any outbuilding;
- separate, installed on the site as a separate, targeted structure.
Additionally, do-it-yourself canopies can be divided into stationary and mobile, collapsible and sliding, characterized by increased functionality.
How to avoid problems?
To arrange a major extension without problems and all sorts of difficulties, you need to take into account a few simple rules. So, when an additional construction project is only in the project, it is necessary to agree in advance with all neighbors and owner-occupiers (if any). It will not be very pleasant to find out that the neighbors refuse to give consent to the construction of an extension when the plans are already ready.
When constructing an extension of any type, capital or non-capital, it is necessary to take into account the original design of the original structure. Thus, the extension must necessarily coincide with the architectural features of the main living space. Otherwise, the BTI will simply refuse to register the extension. It is also important to pay attention to the following points:
- a complete package of documentation must be collected with permissions from various authorities attached to it;
- you need to check the ownership documents;
- it is desirable to eliminate all possible architectural violations at the original site, as well as to avoid mistakes during the construction of the extension;
- When constructing an additional facility (especially a capital type), only safe and certified building materials must be used.
Separately, it is worth noting the so-called dacha amnesty. The question of how to register an extension to a house under the dacha amnesty is currently not at all relevant. The fact is that the relevant provisions of the law of 2006 cause a lot of criticism due to their complexity and ill-conceivedness. The so-called simplified form of registration rather causes many problems and difficulties. Only persons who are members of partnerships and dacha cooperatives can pay attention to this form.
Qualifications of designers - who should design the extension and who is best to look for
The design and other documents for an extension during reconstruction can only be drawn up by a design organization that is a member of the SRO. This point must be checked at the stage of concluding the contract, since otherwise a negative expert opinion will be received. It is also advisable to verify the qualifications and experience of the designer, especially in similar types of work. For example, the Smart Way company always offers examples of previously completed orders, so the client can immediately make an objective and informed decision. Contact us, we will explain in detail the legal requirements for the design and approval of an extension, and offer favorable terms of cooperation.