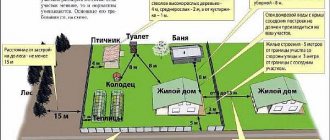
Many people living in apartment buildings or private houses increase their living space through redevelopment and the construction of extensions.
At the same time, you need to understand that registration of an extension to a private house or apartment building involves the collection of documents and papers. Until the building is legalized, local authorities will have the right to demolish it or fine you.
Today you will learn how to legalize an extension to a house, depending on whether it is private or multi-apartment, and what is required for this.
How to register an extension to an apartment building: list of documents
To build an extension in a multi-story building, you will need permission not only from the authorities, but also from the neighbors. Now we will talk about the documentary part .
Paperwork for this part of the house is necessary in the following cases:
- before the start of construction,
- when the structure has already been built, but is declared illegal.
In multi-storey buildings, extensions most often come in the following types:
- non-permanent structures - they do not have a foundation or they can be easily dismantled without the need to erect walls (sheds, etc.), in such cases, the consent of neighbors or permission from the authorities is not needed, a reconstruction act is simply drawn up,
- capital structure - such objects can directly affect the technical characteristics of the building and change its infrastructure (for example, a veranda or balcony); documented consent of neighbors and official authorities is required here.
To build permanent buildings, you need to prepare the following package of documents:
- consent to the construction from all the neighbors in the house - the resident of each apartment must sign that he is not against your extension,
- project of the future building,
- ownership documents:
- room plan,
- permission from Rospotrebnadzor,
- official permission from the local architectural committee and fire department.
When construction work is completed, an acceptance certificate should be drawn up, which must be signed by members of the acceptance committee:
- apartment owner,
- neighbours,
- representative of the design organization,
- representative of the local administration.
After signing the act, the registration of a technical passport is ordered from the BTI, and changes are also made to the certificate for the apartment.
To register an existing extension, you need the following documents:
- ownership documents,
- extract from the house register,
- permission from BTI,
- written consent of neighbors for construction,
- acts on the presence or absence of communications located in close proximity,
- design and plan of the built-in premises,
- photograph of the building.
Samples of the design of each document can be easily found on the Internet and based on them you can create your own.
What kind of extension is possible?
Most often, people build a loggia or balcony. In case of influence of the building on those. side of the building you need to obtain official permission or apply through judicial organizations.
A permit to leave the extension can be obtained from the official commission of the technical bureau. inventory.
A permit is issued if the extension is no more than 12 meters from the building, can be easily and quickly dismantled, or does not contain a solid foundation.
The agreement on the decision to leave the large extension is taken by the owners of all apartments in the apartment complex at an official meeting by voting by residents. If it is not possible to organize a meeting, collecting signatures is used as an alternative.
ATTENTION! Obtaining permits from other owners is also necessary when constructing an extension to an apartment building (barracks) or a two-apartment building.
How to legalize an extension to an apartment building
If you want to add a new balcony or veranda to your apartment, they must be recognized as non-residential. Many people often add additional rooms to apartments and it is very difficult to prove that they are non-residential .
When you have completed and prepared the entire package of documents, contact your local government, where the construction plan will be agreed upon and permission will be given. You will need to write a corresponding statement, a sample of which you can ask for on the spot. It will require you to indicate exact information about the developer and the site where the building will be built.
If the building is not intended for residence, the legalization algorithm is as follows:
- reconstruct a previously erected building,
- take a conclusion indicating what exactly was completed and what was dismantled,
- collect technical documentation,
- go to Companies House for permission.
If, based on all of the above, you are not given a permit, then you can go to court.
In most cases, it is possible to build an additional balcony on the ground floor of a high-rise building without any problems; sometimes the neighbors’ consent is not even required.
You must remember that if the built structure is located on a site that does not belong to you, then it can be demolished if it is not legalized. That is why the extension should be privatized in advance or rented. As a last resort, make a design for a building on stilts.
The site where the extension is located or will be located must be privatized. If it is impossible to obtain ownership of it now, then you can rent it. An emergency exit is to create a project for an extension standing on stilts.
Cost of the procedure
The cost of legalization is established through classification. In the case of registration of an unauthorized addition, if you do not call a lawyer for help, you will have to seriously spend money.
The usual cost in such a situation is 1000 rubles, but this amount may vary depending on the region and the lawyer. The appearance of a specialist in court, at least once, can cost five thousand rubles.
As the number of meetings increases, the price of a lawyer’s services will increase exponentially. Legal representation team can vary from 25,000 to 30,000 rubles, in terms of cost.
How to register an extension: legal subtleties
When designing an extension to a high-rise building, lawyers advise taking into account the following:
- register the building as a non-residential property so that you are not subject to fines,
- collect technical documentation in advance to know for sure whether it is possible to build something in your case,
- it is better that the site is privatized,
- it is better to legitimize the premises as separate property,
- the structure must not interfere with or disrupt communications,
- Involve lawyers for registration.
Lawyers' recommendations
Thanks to the recommendations of specialists, you will be able to complete the necessary documents the first time.
Use the following tips:
- The extension should be registered as non-residential property.
- Before you start processing documents, collect technical documents. The design should not violate the integrity of existing communications.
- The house must be located on a site that is your property or is the shared property of all apartment owners. If the extension is located on someone else's property, you will not receive permission.
- The extension can be designed as part of the living space, but it is better to register it as a separate property.
Thus, you have the opportunity to add a balcony or veranda to your apartment. It is important that all documents are completed correctly and in a timely manner.
The video story will tell you how to legalize the extension of a balcony
When can registration be refused?
Neighbors and permitting authorities may refuse their consent to the construction of a structure or its official registration in the following cases:
- if the design does not correspond to the project,
- if it does not meet the technical requirements,
- if low-quality building materials are used,
- when outdated construction technology is used,
- when an extension spoils the appearance of the building,
- if the building is an architectural monument,
- if the construction is contrary to the interests of neighbors.
When can they refuse to approve an extension?
Typically the grounds for refusal are:
- Mismatch between the design and the existing project;
- Failure to comply with technical requirements: close location to the house's communications (they must be at least 2 m from the extension) and damage to load-bearing structures;
- Construction materials that do not comply with building codes;
- Use of outdated construction technology;
- When the windows (completed balcony) overlook the center of your city;
- Damage to the aesthetics of an apartment building;
- When a given house is included in the list of architectural monuments;
- Inconsistency with the interests of others (lack of consent of neighbors).
Plus, it is prohibited to install a balcony close to the house when it expands the housing. This is fraught with the destruction of the load-bearing walls of an apartment building.
How to register an extension to a private house and is it necessary to do it?
There is an opinion that if you are the owner of a site where there is a private house, then you can add anything to it without permission from any authorities, but this is not so.
If you want to add something to your private home , then remember the following:
- the placement of buildings is regulated by town planning legislation and everything needs to be agreed upon,
- an extension changes the area and design; if the house belongs to several people, then their share in it also changes, and this needs to be documented officially,
- during construction, the structure of the house is damaged, which can sometimes be unsafe,
- If there is no official permission for the construction next to a private house, then you will not be able to conduct real estate transactions with it, subsequently you may be fined, and the extension may be demolished.
Permission is not required only for the construction of non-permanent extensions to the house, for example:
- balconies,
- verandas,
- terraces, etc.
Fine for illegal extensions in 2021
If you erected an extension without permission without approval from the administration and without notifying Rosreestr about changes in the parameters of the house, then this fact will be considered a violation.
Such non-compliance with urban planning and administrative legislation entails certain consequences.
Citizens who carry out illegal additions to a private house bear administrative responsibility. Property owners for so-called unauthorized construction or reconstruction are liable in accordance with Article 9.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, as well as clause 2.222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes that the violation must be eliminated by demolishing the unauthorized extension or returning the property to its original condition . The perpetrators will be required to carry out this work at their own expense.
Also in accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses, paragraph 1. Article 9.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Reconstruction of a residential building without obtaining permission from the authorities shall entail a fine in the amount of 2,000 to 5,000 rubles.
How to legalize an extension to a private house
It is also necessary to legalize non-permanent structures, but this is very simple and can be done even after you have built them. Just take the documents home to the BTI and write a statement about the changes to the technical documentation. The acceptance committee will arrive and draw up a refurbishment report.
But if we are talking about legalizing a capital extension, then everything is more complicated. It can be registered after the final construction, but it will require additional registration in court as an unauthorized construction. To avoid this, it is better to do this at the design stage.
The following documents will be required:
- confirmation of ownership of land and house,
- site plan and technical certificate,
- cadastral plan,
- building design,
- if the house has other owners, they must submit an application for work,
- consent of neighbors,
- conclusion of gas, energy or water and sewerage organizations on the safety of connecting the facility to communications,
- permissions from firefighters, SES and architectural department.
All documents along with the application must be submitted to the local government ; if there are no violations, then you will receive a document on consent for construction. When you finish it, you need to call the commission to draw up an acceptance certificate. The issued conclusion on compliance with standards is referred to the BTI, where changes are made to the technical documentation. After this, the object is registered in Rosreestr and a fee is paid for re-registration of a private house.
Varieties and documentation
According to generally accepted standards, extensions are divided into two main types:
- non-permanent - this is the name given to reconstruction buildings that do not have a solid foundation as a basis. For example, the porch or stairs of a large building located on the street. This category also includes shop windows, terraces, canopies and other quickly disassembled and assembled extensions that do not have a solid base;
- capital. Balconies, verandas, loggias are the main types of permanent structures. They differ from non-permanent buildings by the real influence on the economic and technical properties of an apartment building, determined by the height, width and other parameters of the constructed structures.
The acceptance certificate is all that is required for registration of non-permanent buildings. There is no need to obtain special permits; construction can begin immediately.
But permanent buildings require more attention and a huge package of paper, which includes:
- Consent to construction from all residents of the building.
- Construction project.
- Living area plan.
- A document about who owns the property - agreement of purchase and sale, gift, inheritance, and so on.
- Approval from Rospotrebnadzor.
- Characteristics from the fire department inspection.
- Certificate from the Committee of Architecture and Urban Planning.
Once all the papers have been collected, submit your application to the administration. In any case, management must approve your project so that you can begin construction. Many people immediately come to the court with an application, believing that this way they will receive a positive decision faster.
It should be noted that the city or district administration may issue a refusal. Here are the main reasons:
- If the apartment building is located in the city center and is considered an architectural monument.
- If the construction will destroy the house and worsen its visual appearance.
- If the project is agreed upon, but old technologies and materials will be used in its creation.
Having received permission from the administration, begin construction immediately. And after work, be sure to draw up an acceptance certificate and contact the technical office. inventory. It is from the BTI that you must receive an official conclusion on the redevelopment of the living space.
POSSIBLE DIFFICULTIES
Construction of a balcony is a set of works that are aimed at increasing living space through architectural changes in the building. When it comes to a building of historical value, applicants are often refused. It is easier to obtain permission if we are talking about a multi-storey building that has a standard design and is not of interest from a historical point of view. In practice, approval to enlarge a balcony or build an extension is obtained by owners of real estate located at a great distance from the central part of the city.
As a rule, to obtain permission to build a balcony (extension), you must contact the authorized bodies and submit a certain package of papers. If the house is one of the historical monuments of the city, you can forget about expanding (constructing) a balcony or an extension.
Often the reason for refusal is the disagreement of any of the residents living in the neighborhood. A person may feel that building a balcony spoils the view from their window or creates additional safety risks. As a result, difficulties arise in obtaining permission. To avoid delays, it is important to prepare the necessary documentation in advance and coordinate the issue with your neighbors.
We take into account the nuances
The construction of a balcony on the ground floor requires compliance with a number of important nuances.
- Any balconies or loggias must be placed on a reliable platform. A solid foundation is especially important for structures whose territory is planned to be permanently included in the living space.
- The foundation of the extension must fit tightly to the base of the building, otherwise high-quality insulation of the balcony will be difficult.
- The roof (if there is one) must be located at an angle relative to the wall, otherwise the unimpeded descent of snow and the outflow of rainwater will become impossible.
- The balcony door should open towards the room. This will make the extension space more spacious, and will also protect residents from unpleasant situations with automatic plastic structures slamming shut.
The issues of finishing balconies built on the ground floor are important not only from an aesthetic point of view, but especially from the point of view of the safety of family members. Being as if “in the palm of your hand”, you should not get carried away with panoramic or stained glass glazing. For reliable protection, you can use durable forged grilles; a good solution would be to install an alarm system.
A protective lattice barrier on the ground floor is an absolute necessity Source hotel-a.ru
How much does it cost to add a balcony on the first floor?
Typically, the cost of just adding a balcony itself costs residents at least one hundred thousand rubles . It depends, of course, on the materials chosen, the quantity and quality of windows, and the complexity of the design of the project.
In addition, duty payments and those that may be required of you by utility organizations are added to this amount. They are not always ready to give their permission for free.
Also included in the total cost is the cost of developing the project , because an experienced designer who will take into account all possible requirements of the authorities and the location of pipes and cables underground does not work for free.