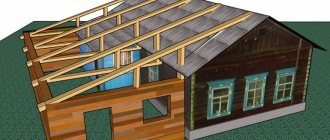
Stages of work to legitimize construction
You can begin formalities when planning work, upon completion of construction. In the first case, a sketch of the future object is drawn up, submitted for consideration to the relevant authorities,
receive permission and begin construction. It is worth noting that this option is considered correct. If there are inconsistencies or violations of safety rules, the plan will be sent for revision and will be reviewed again after changes are made. You can draw up a sketch yourself or with the help of specialists.
The second option provides for the start of the legalization process after the completion of construction, in fact. The main emphasis is on the possibility of obtaining supporting documentation. Both options involve going through the same stages of legalization.
- Collection of documents.
- Applying to the court for recognition of ownership of the extension. The plaintiff is the owner of the house, land plot, the defendant is the local administration.
- Payment of duty. In each case, the monetary equivalent of the legalization process is different.
Costs for the process of legalizing the extension
- The cost of representation in court depends on the number of meetings at which the lawyer will have to attend to defend the rights of the owner. Payment is possible after each meeting or after completion of the process. One trial with a lawyer will cost 6 thousand rubles, complex work costs about 30 thousand rubles.
- The state duty is 200-500 rubles.
- A power of attorney for construction permission and assignment of ownership rights will cost 2 thousand rubles.
- Forensic examination – about 15 thousand rubles.
- Entry into the cadastral register using the services of a lawyer - 20 thousand rubles, independently - about 500 rubles.
Whether you engage in the legalization process yourself or with the help of specialists is an individual decision.
The process of legalizing an extension by the court
The judge will require a technical examination. You can do this before filing a claim by contacting
specialist. The following questions should be received:
- Does it comply with safety regulations?
- Doesn't it conflict with the interests of the neighbors?
- Are sanitary and hygienic standards violated?
Based on the examination received, the court makes a decision on the legality of the construction and confirms ownership. This method of legitimation is most often used after construction is completed. Before starting the construction of a building, they apply to the administration for permission.
Stages of legalization of an extension, construction at the planning stage
- Project development.
- Applying to the department of architecture and urban planning for a construction permit.
- Conclusion of a supervision agreement.
- Submitting an application for a declaration, which indicates the start of construction.
- Obtaining a technical passport.
- Submitting an application for registration of a declaration.
- Preparation of documents for the registration service to obtain a cadastral passport and confirmation of ownership rights.
Legalization of a capital extension before the start of construction
You can go through the exact wording for a long time, but any major extension, even if it is a non-residential premises, but with a common wall with the house, is a reconstruction and must be approved before the start of construction, and not after.
Appolo10FORUMHOUSE Member
...I recommend that you first consider the legal side of the issue. To carry out a “reconstruction” (extension), you need to make a project and obtain a “reconstruction permit” from the local authorities. If you don’t do this, you will end up with “squatter construction”; the state is fighting this phenomenon, and every year it’s getting stronger…
And although the permit for individual housing construction was first abolished and then replaced with notification/approval, changing the places of the terms does not change the amount - notification of the planned reconstruction is a mandatory, not a recommended stage.
Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 51.1. Notification of the planned construction or reconstruction of an individual construction project or residential building (valid from 08/04/2018, Federal Law No. 340)
"1. For the purpose of construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project or a garden house, the developer submits on paper through a personal appeal to the federal executive body authorized to issue construction permits, the executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation or the local government body, including through a multifunctional center, or sends to the specified authorities by mail with acknowledgment of receipt or a single portal of state and municipal services a notice of the planned construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project or a garden house (hereinafter also referred to as the notice of planned construction) ... ".
As practice shows, today it is also possible to submit a notification remotely through the personal account of the Public Services portal. The form is filled out electronically and submitted in the appropriate section.
The notification form is standard and approved by executive authorities; when filling out, you will need to enter the following information.
- Full name, place of residence of the applicant, as well as details of the passport (or other identification document).
- Cadastral number of the plot (if any), its address or description of location.
- On what basis did the right to the plot arise?
- If there is shared ownership, information about other owners is also listed.
- About the type of permitted use of the site (UR).
- On the type of permitted use of a capital construction project (CCA), residential or garden house.
- The purpose of submitting the notification (there is only one form, but it indicates not construction, but reconstruction).
- About the parameters of the planned extension, including setbacks from the boundaries of the site.
- A graphic representation of the location of the planned extension on the site (indicating the dimensions and distances to the boundaries).
- That in the future the extension will not be made into a separate capital construction facility (that is, the house will not be divided into independent parts).
- Postal address and email (if available) for feedback.
- The method in which the applicant wants to receive a response.
Documents for the land are attached to the notification if it has not yet been registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. If the house is located within the boundaries of a historical settlement, you will need to attach a text description of the facades and a graphic image. Within seven working days (twenty for historical settlements) from the receipt of the notification, local authorities must conduct an inspection and either approve the reconstruction or refuse approval. Upon receipt of consent, construction can begin, at the end of which a commission from local authorities will have to accept the object and issue a conclusion on compliance. In reality, it is usually enough to notify local authorities about the completion of reconstruction, provide a technical plan and state registration fees. And the municipalities themselves will submit an application for registration to Rosreestr within the same seven days.
In the second case, you will have to obtain consent through the court. If you do without notification and build at your own peril and risk, you can end up with a self-construction with all that it entails, and this is a minimum of bringing it into compliance, and a maximum of demolition.
IMHO FORUMHOUSE member
Any “redistribution that leads to an increase in area” is reconstruction. In the end, you will have to “legalize” not the extension, but the entire house again in changed coordinates. But without completing the “notify and agree” quest, you run the risk of squatting.
If the extension does not in any way affect the rights of neighbors or the neighbors are among those with whom it is possible to come to an agreement, then it is quite possible to live with such unauthorized construction for decades. But it will not be possible to sell, donate or bequeath an illegally reconstructed house. Yes, the powers that be are planning to extend the dacha amnesty, but it will be about houses that have already been built or reconstructed. And not about extensions being built in real time, bypassing current legislation.
Required documents
Before starting the process, it is necessary to obtain permission from certain authorities and collect a package of documents.
- Certificate of ownership of the land plot under construction.
- Certificate of ownership of the house.
- Technical plan.
- BTI certificate, cadastral passport.
- Extract from the house register.
- Legal documents.
- Consent of neighbors if the building is located on the border with their territory.
- Sanitary and epidemiological station act.
- Construction permit from water utility, fire, gas service.
Additionally, photos of the land plot, house, object are provided if construction has already been completed. In addition, a simplified system for legalizing buildings is in effect until 2020. If you arrive before this deadline, you can receive the necessary documents much faster.
Important notes from lawyers and experts
What nuances must be taken into account when applying for the legalization of extensions or individual buildings of private houses? First of all, even before officially contacting the authorized bodies or the court, you need to make sure that the neighbors agree to the construction of buildings.
This is necessary if the building or extension blocks the view for the owners of neighboring properties or creates other indirect obstacles.
If an extension is erected to a private house, it must be legalized taking into account the requirements of building rules and regulations for the placement of economic facilities - the presence of minimum acceptable distances from neighbors' facilities.
If a utility building is being built on the site, a minimum gap to the nearest residential building must be maintained (usually at least 5 meters according to fire safety requirements).
How to legalize an extension to a house if the land is owned
This option provides freedom of action. A person can do anything on his own land.
In practice, there are various kinds of legal restrictions, which are not at all a whim of the legislative bodies. Rather, it is an urgent need that is concerned about the interests of other citizens, especially neighbors. To legitimize an extension to a house, it must not contradict the interests of the public or cause damage to the environment.
Urban planning legislation regulates the placement of objects on a land plot; any construction must be approved. The process of legalization is necessary for the owners themselves, since the design of the house, appearance, and area change. There is a need to replace the technical passport. A self-built structure can violate safety rules and make the house unstable, which subsequently threatens collapses and other unpleasant consequences. To avoid this, resort to the help of specialists. The expert considers all these nuances and gives approval or disapproval.
To legalize an extension, it is enough to collect a package of necessary documents and go to court or the administration. However, if the completed extension does not comply with legal standards and requirements, it will be required to be demolished. That is why it is better to start the legalization process at the planning stage.
It is much easier to legitimize a non-permanent extension, at any time, if it is done smoothly, without errors. It is necessary to submit an application to the local BTI, a package of necessary documents for the house, land, with a request to make changes to the technical passport. A commission comes to the site and draws up a Construction Completion Certificate.
What to do if reconstruction is carried out without receiving notification
Since unauthorized construction by government authorities is prohibited, the rules by which the reconstruction of a house can be legalized if it has actually already been carried out without the appropriate permission are not directly established. However, until this arbitrariness is identified, you can act as usual, that is, through notifications from the administration. But if illegal reconstruction is discovered, which can be done by representatives of Rosreestr or the same administration, then the owner of the house will be sued and issued a fine. Then you will have to defend your rights in court and legalize or return the house to its previous appearance based on a court decision.
How to register an extension to a house if there is a second owner on the land
The solution to the issue begins with the permission of the second owner of the land to build an extension.
The document is notarized so that there are no claims in the future. After which you can begin to implement your plans. The process of legalizing a building is similar to the case when the land is owned by one person. Collect a package of necessary documents. Together with the consent of the other land owner, they are submitted to the appropriate authorities. If the second owner is against the building, and it already exists, the court has the right to order its removal. A new extension to the house should not infringe on the interests of neighbors, especially co-owners.
Refusal to legalize the extension
It happens that you can get a refusal when trying to legalize your extension. There are different reasons. The most common of them:
- during construction, all standards (fire, sanitary and other) were not observed;
- the design and the finished structure are different;
- the materials used in the construction of the extension are not safe;
- too close to the communications of an apartment building;
- the design spoils the appearance of the building;
- the apartment building is classified as an architectural monument;
- the extension was built without the consent of the owners and neighbors.
An example response from the architectural department.
Responsibility for illegal expansion of the house
Alas, if the extension has not been legalized, sooner or later it may be demolished by court decision. And its owner will be punished with a ruble.
What is the tax deduction when buying an apartment? You will find the answer here.
If construction rules are violated, an individual will be held administratively liable. According to the Federal Law “On violation of requirements during the construction of buildings and structures.”
For construction without permission, fines are provided for citizens from 2 to 5 thousand rubles, for officials and individual entrepreneurs from 20 to 50 thousand, for legal entities from 0.5 to 1 million rubles.
Thus, we can conclude that it is better to harmonize any structure with the law. Otherwise, fine fines. But it would be extremely annoying to lose part of your home.
To learn how to properly legitimize self-construction, watch this video:
How to legalize an extension to a house if it is already completed
In this case, there is only one option - through the court. You can prepare the necessary documents yourself or entrust the matter to specialists. In addition, the process of legitimizing finished objects depends on their nature. Legalization of non-permanent extensions - terraces, balconies, verandas, auxiliary buildings is carried out at any time according to a simplified system. It is enough to simply make changes to the technical passport by contacting the BTI. Buildings in the form of additions to the house - expansion in width, height - can only be legalized after construction through the court.
Reasons for refusal:
- non-compliance with sanitary standards;
- violation of fire safety rules;
- non-compliance with architectural standards;
- incomplete package of necessary documents;
- use in construction of uncertified materials that do not meet fire safety requirements.
Why is the extension needed?
An attached room is a part of the main building that shares one wall (sometimes two or more) and a foundation with it . As a rule, extensions have an internal connection with the house.
They can be heated or unheated, but at the same time, just like the main building, they have a roof, windows and walls.
An extension is always necessary when there is a desire to expand the space. Anyone can independently or with the help of a team of workers increase the area of their home. At the same time, maintaining the former comfort.
How to legalize the redevelopment of an apartment? Detailed information at the link.
It is important to first decide for yourself what it will be: a small terrace or an entire guest house with several rooms. Whatever it is, the structure will in any case extend beyond the perimeter of the house. This means that it must be taken into account as part of the housing stock.
Types of extensions
- Garage. You bought a car and need to take care of its safety. Adding a garage to your home is easy. But you will have peace of mind that in rainy and frosty weather your “swallow” is under its own roof. No registration is required here.
- Canopy. The lightest extension option, designed for relaxation and protecting the porch from the sun. A foundation is not required for its construction. The canopy can be easily installed and dismantled. It is not necessary to design such an extension.
- Porch. It is not a full extension.
- Living room. This will be a capital structure that will need to be formalized in accordance with all the rules.
- Bathhouse. By connecting the sauna to your home, you will not need to run home across the street immediately after the steam room.
- Kitchen. This is a rather troublesome extension, since it requires water, gas, sewerage and appropriate ventilation.
How to legalize an extension to a house under the dacha amnesty, step-by-step instructions
The essence of the project is free registration of land and real estate using a simplified system. Option
available to shareholders who received the plot before 10/30/2001. In accordance with Art. 51 clause 5 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the law is valid until 03/01/2008.
Step-by-step instructions for legalization of the dacha amnesty:
- Initially, owners of buildings and summer cottages must receive a document confirming ownership. Without it, further processing of documents is impossible.
- The land plot must have a land survey plan, the construction must comply with generally accepted urban planning and safety standards.
- You can register ownership of a plot of land under a dacha amnesty using a simplified system. Submit documents to the Federal Registration Service. An application, a passport, a receipt for payment of state duty, an extract from the business ledger, and title documents are required. The cadastral plan is issued free of charge.
- A construction declaration is submitted to Rosreestr, which must be legalized in 2 copies. The form is filled out with your own hand in blue, black paste without abbreviations or abbreviations. You must indicate the location of the construction of the object, address if available, name, graphic image, documents confirming ownership, cadastral number of the land plot. The declaration is reviewed within 30 days, if there are no comments, errors, or inaccuracies, a document is issued to the owner with the address assigned to the object. After which they begin to issue a cadastral passport, which is the final stage.
Registration of demolition of an old house
Last summer, an article on the demolition of capital construction projects appeared in the Town Planning Code, but Rosreestr began requiring relevant notifications much later.
The Ministry of Construction, by its order No. 34/PR, introduced notification forms that should be sent to the local administration 7 working days before the demolition of the house and within 7 working days after the demolition. The administration accepts these notifications only in person (it is not yet possible to submit them either through the public services portal or through the MFC) and as a result issues two acts. Previously, to cancel the entry from Rosreestr, the owners of demolished houses invited cadastral engineers, who inspected the sites and drew up inspection reports. Only on the basis of these acts did we deregister the houses, and now engineers are supplementing them with additional acts from the administration. This is the correct procedure for registering demolition, but some owners, without changing the area, layout and wall material, are building new ones in place of old houses. In this case, they do not receive any certificates. This risky option is resorted to in cases where new construction on the site is prohibited, for example, due to the sanitary protection zone of some enterprise or hazardous facility.
Lawyers, designers and cadastral engineers provide preliminary free consultations with home owners on issues related to registration of reconstruction. We clarify boundaries and draw up architectural designs. We receive notifications from the administration and coordinate the reconstruction. We formulate technical plans and make changes to cadastral registration. In addition, we prepare pre-trial expert opinions and protect interests at court hearings. We draw up conclusions about the technical condition of houses and transfer their purpose from non-residential to residential, and also assign addresses.
How to design extensions to avoid problems
How to legally register an extension to avoid fines and problems with the house
Ideally, a commission will visit the site to verify the parameters of the extension; based on the results of the inspection, they will issue a certificate of completion of the reconstruction. You can register a non-permanent extension either immediately after construction or after a while; there are no fines or sanctions for delays. It is theoretically possible to leave it without registration at all, but it is impractical - it is not known how the legislation will change, it is better to have the entire package of documents on hand.
Useful tips
Before deciding how to make a second floor in the garage, you should remember the following:
- Before construction begins, it is necessary to assess the condition of the garage: make sure that there are no cracks on the walls, that they are not warped; the foundation should not have any defects. The second floor is best built from foam blocks - a lightweight and inexpensive material.
- The second floor can be made in the form of an attic or box-shaped superstructure.
- At the stage of approving the project for a future 2-story garage, it is necessary to prove to the architectural office that the structure being built will not disturb the grass of third parties.