Development – construction of structures on the territory of an entire populated area or area. All development rights are secured by articles contained in the Civil Code. In order for all construction requirements to be met, it is necessary to adhere to the standards and the planning project. There are three types of buildings: continuous, row and open. It happens in order to get more living space and to make a considerable profit.
Building density – what is it?
- Building density is also referred to as building percentage or building coefficient. It characterizes the total area of all floors of the building, parts of the structure that are located on the ground and buildings within the dimensions of the external walls, which falls on a unit of territory of the site or block. Measured in thousand m2/ha.
- There is also a definition of “building density of a block or residential area ”. This is the total area of all floors of the structure, parts of which are located above the ground within the dimensions of the external walls, also includes built-in and attached non-apartment area, which is measured in m2 and accounts for 1 hectare of a block or residential area.
The building density can range from 20% to almost 60%. The density of development varies depending on where it occurs. It is also worth considering that the greater the density, the larger the base of the area on which construction will take place. When ordering a drawing, architects must indicate the highest level of density.
Normative base
Determining the square footage of developments requires some awareness of current government rules and regulations. They are enshrined in a document called “Building Norms and Rules” (SNiP). It also contains a list describing the residential building and the provisions applicable to it. The appendices of this document regulate the rules for measuring the footage of premises between its partitions, walls and floors. Fireplaces and heating stoves, which were mentioned above, are indicated by decorative elements and are therefore not included in the calculations.
Regarding all open spaces (terrace, balcony, loggia), the space is measured between the walls of the planned building and the fences, that is, the internal contour is taken. When measuring the entire building, the building area is calculated equal to the dimensions of the horizontal section made by the height of the plinths and protruding external elements.
When it comes to a structure located on a support, the footage is determined to include the entire space under the structure.
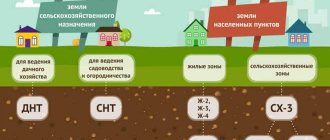
Regarding summer cottages and SNT, whose size does not exceed 0.06 hectares, and in some cases 0.12 hectares, the area occupied by buildings, platforms, paths and other things cannot occupy more than 30% of the total territory.
Building coefficient
The development coefficient is the correspondence between the area of the building and the area of the land.
- This indicator regulates the density of buildings and the congestion of the engineering and transport complex.
- An acceptable coefficient is 0.5 . This means that there must be free territory on the site. Without taking this into account, a colossal load is created on the site.
- The building factor includes the maximum permissible number of floors in a building.
- The value of this indicator is determined by authorized persons of the land and architectural departments of the area where the development will take place.
- The calculated indicator must be included in the construction documentation of the land - the register passport. It should also reflect all the necessary information about the intended purpose of a certain territory, the possibility or impossibility of constructing buildings on it and the optimal permissibility of floors, and do not forget to indicate the area of the buildings.
If the developer violates the established standards and the coefficient exceeds the specified value, then he will have to comply with the civil and land legislation of Russia. In this case, the construction is considered illegal and is subject to further destruction.
Development rules and rights
The Civil Code determines the legal mechanism, the socio-economic situation forms the goal, and planning projects determine exactly how and what exactly needs to be built.
Building density is often positioned in terms of an important coefficient: the correspondence between the area of a building, taking into account the number of floors, and the size of the site on which it is located. The meaning of this coefficient varies depending on the purpose of the building and its location
- for the execution of engineering structures;
- to organize transport infrastructure;
- to assess economic feasibility;
- on other important aspects.
Territory development plans ensure the compatibility of new and reconstructed buildings with the existing infrastructure, as well as an adequate standard of living for the population.
In residential areas, the construction of transit passages through courtyard areas is prohibited
The location of areas of social and business significance is important: medicine, culture, trade, catering, etc.
- Provide citizens with everything they need.
- Reify the normal and natural functioning of the development.
- Create opportunities for comfortable living.
- Organize transport services in all necessary directions.
Industrial territories by production category are located taking into account financial efficiency, safety, ecology and sanitation standards, in particular, transport services for workers, supply of raw materials and materials, shipment of products. In any case, industrial enterprises are located outside residential areas.
The calculation of the residential zone is done for 20 years.
Maximum built-up area of the land plot.
06 June 2015, 22:09 This is one of the most important parameters when developing the concept of a future warehouse, production or logistics complex. When designing in the Moscow region, it is necessary to be guided by the following: - the development coefficient of a land plot is the maximum possible territory of a land plot that we can occupy with warehouse or industrial buildings being erected; When determining the maximum development area of a land plot for an industrial or warehouse complex, it is necessary to multiply the total area of the land plot by the development coefficient, thus we will obtain the total development areas of all buildings of the future complex. Development coefficients for land plots of industrial territories in the Moscow region (excerpt from regulatory documents) Types of objects Development coefficient for land plots, not more than (percentage) 1.
Warehouse facilities 60 2. Production facilities: Depending on the purpose of future production From 45 to 60 Thus, we draw the following conclusions: The maximum development area of the land plot of a warehouse complex is 60% of the total area of the territory, production varies from 45% to 60%, depending from destination. This value must be taken at the earliest stages of design, when developing the stage of pre-design decisions and at the stage of preparing presentation materials for the town planning council. The optimal development ratio when designing a master plan for a logistics complex is 50% to ensure maximum convenience for maneuvering areas for freight transport and permanent and temporary parking areas.
It is also necessary to provide space for engineering and auxiliary structures of the logistics complex, such as: checkpoints, pumping stations, hydraulic fracturing stations, fire tanks, administrative buildings, solid waste sites, sites for technological maneuvering of trucks, parking for passenger vehicles and storm drainage treatment.
“Permit to discharge pollutants into the environment”
, which is issued by the Department of Natural Resources on the basis of the “Calculation of Permissible Discharge”.
Recreational areas and recreation facilities
Beaches and parks in recreation areas 100 one-time visitors 15-20
Forest parks and reserves The same 7-10
Short-term recreation centers (sports, skiing, fishing, hunting, etc.) “ 10-15
Coastal bases of small fleet “ 10-15
Holiday homes and sanatoriums, sanatoriums, recreation centers of enterprises and tourist centers 100 vacationers and service personnel 3-5
Hotels (tourist and resort) The same 5-7
Motels and campsites “By design capacity
Catering, trade and public service establishments in recreation areas 100 seats in the halls or one-time visitors and staff 7-10
Gardening partnerships 10 plots 7-10
Percentage of land plot development for individual housing construction
It is important to respect the legitimate rights and interests of neighbors.
It is prohibited to clutter their territory with your own buildings, as well as to install fences that will interfere with the development of agriculture in the neighboring territory by cluttering structures and creating shadows. When determining the maximum development area of a land plot for an industrial or warehouse complex, it is necessary to multiply the total area of the land plot by the development coefficient, thus we will obtain the total development areas of all buildings of the future complex.
Site design: how much to deviate from what?
Site design
Red lines and boundaries with neighbors
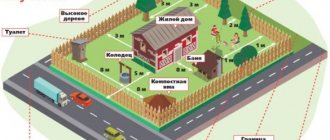
Red lines, according to paragraphs. 11 and 12 art. 1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are lines marking the boundaries of land plots, the boundaries of public areas, the boundaries of linear objects (gas pipelines, power lines, roads, etc.). In gardening villages and settlements with plots for individual housing construction or private plots, the indents from the red lines are, in principle, the same:
- for outbuildings from the red line of the street (road) - at least 5 m;
- for a residential building from the driveway (red driveway line) - at least 3 m;
- from outbuildings to the red travel line - at least 5 m.
Adjacent borders with neighbors are also essentially red lines, but they are not usually called that. A residential building must be located no closer than 3 m from the border with the neighboring plot. Most outbuildings can be built from the border with neighbors at a distance of at least 1 m. An exception is premises for keeping livestock or poultry: the barn and poultry house must be moved away from the borders of the neighboring one of the plot by at least 4 m. Example of zones for possible placement of residential and commercial buildings on the plot. Photo from the site chipmaker.ru We measure the distances between buildings from the base of the building or from its wall, if there is no base
If the house has protruding parts (bay windows, terraces, second floor extensions), then measurements are taken from the protruding part or from its projection. For outbuildings located at a distance of 1 m from a neighbor’s fence, it is necessary to provide for the drainage of rainwater from the roof so that the runoff does not fall on the neighbors’ property. In addition to sanitary standards, it is important to take into account fire breaks when locating buildings. It is important to know the materials from which the buildings are built.
Thus, for buildings made of non-combustible materials (brick, reinforced concrete, aerated concrete and for buildings with structures made of combustible materials, but insulated with non-combustible materials), the minimum distance between buildings is 10 m. For wooden buildings - 15 m. When placing buildings, it is important to take into account fire breaks To comply with fire safety standards, the specified distance is taken into account between the houses and buildings of neighbors, even those located across the street. Maintaining fire safety distances between buildings on the same site is not necessary. Blocked locations of buildings on adjacent plots are allowed. For example, the construction of two residential buildings next to each other, belonging to different owners, through a blank fire wall - a firewall.
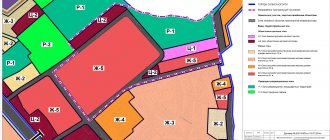
Limit parameters of permitted construction according to PZZ, GPZU
In addition to the types of permitted use, PZZ (GPZU) fix the maximum parameters for the development of a land plot.
So, what are the maximum development parameters according to land use and development rules? There are only three parameters:
- Building density (how many square meters of ground area can be built on one hectare of land). For example, density 000 will mean that 25,000 sq.m. can be built on 1 hectare, and 2,500 sq.m. on a land plot of 10 acres.
- Building height (in meters), for example 20 meters
- Development percentage (as a percentage of the total land area). For example, if the building percentage is 20%, and the plot has an area of 000 sq.m., then the building can be placed on no more than 2000 sq.m. The remaining 8,000 sq.m. must be free from development.
A more precise definition can be found in the PZZs themselves (for example, PZZ g.
Moscow): Limit parameters of permitted construction, reconstruction of capital construction projects, which include: 1) development density of a land plot - the ratio of the total floor area of all capital construction projects that are located and (or) can be located on a land plot (in square meters) to area of the land plot (in hectares), where: - the total floor area of a capital construction project means the total area of all ground floors of a capital construction project (including the technical, attic, and also the ground floor, if the top of its floor is above the average planning level of the ground at least than 2 m), which also includes the area of mezzanines, galleries and viewing balconies and other halls, verandas, loggias and balconies; external glazed galleries, as well as transitions to other buildings, measured in the dimensions of the external walls according to the external measurement; - the area of multi-light premises, as well as the space between flights of stairs wider than the flight width of more than 1.5 m and openings in floors with an area of more than 36 sq.m should be included in the total floor area of the building within only one floor; 2) the maximum number of floors or the maximum height of buildings, structures, structures, where: - the calculation of the number of floors of buildings, structures, structures is carried out in accordance with the provisions of the relevant set of rules, depending on the type of capital construction project; - maximum height of buildings, structures, structures - the vertical linear dimension of a building, structure, structure from each existing land mark within the boundaries of the land plot in accordance with the Unified State Cartographic Basis of the City of Moscow to the highest elevation of the structural element of the building, structure, structure (flat roof parapet; cornice, ridge or pediment of a pitched roof; dome; spire; tower; the highest structural elements of a building should also be considered exits to the roof, superstructures for placing technical equipment, made in permanent structures; in relation to religious buildings - the cross apple in relation to Christian churches, bell towers and belfries, kullas - in relation to mosques, taking into account minarets, the upper elevation of the dome, spire and other vertical structural elements - in relation to synagogues and other religious buildings), while roof antennas, lightning rods and other engineering devices when determining the maximum height of a building, structure, structure are not taken into account; 3) the maximum percentage of development within the boundaries of a land plot - the ratio of the total area of a land plot that can be built up with capital construction projects (hereinafter referred to as the development area), to the entire area of the land plot, where the determination of the development area of buildings, structures, structures is carried out in accordance with the provisions the corresponding set of rules, depending on the type of capital construction project. To change the rules of land use and development, you can use the service of our company for
Read more: Sample application for expulsion from kindergarten
Calculation of the number of residents of the block
Let's now see how many people will live in this quarter.
The number of residents of the Kzh microdistrict is determined by the formula:
Kzh=Skv/Zh, where
Sq - total area of apartments, w - housing supply.
The area of floors of residential sections, calculated along the outer edges of the walls of buildings, is Szh.fl = 38892 m2
Consequently, the actual total area of apartments calculated according to SP 54.13330.2016 “Code of Rules. Residential multi-apartment buildings." The updated version of SNiP 31-01-2003″ (approved by Order of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated December 3, 2016 N 883/pr) (as amended on December 19, 2019) will be approximately 20% smaller, since we must subtract the area of the external walls from Szh.et and partitions, as well as the area of staircases.
Sq = Szh.fl x 0.8 = 38892x0.80 = 31114 m2 - total area of apartments.
With a housing supply of 30 m2 per person, the population will be: Kzh = Sq / Zh = 31114/30 = 1037 people (total area of apartments divided by housing supply).
In order to present to the customer a complete architectural and urban planning solution for the development, it is necessary to clarify the required number of places in the kindergarten and school, and hence the area of their plots; the required number of service enterprises, parking lots and improvement areas depending on the population.
All buildings, roads, sites and landscaping elements should be placed on the territory of the block in accordance with the chosen architectural concept, as well as taking into account urban planning, sanitary and fire safety standards.
Usually the customer asks to provide at least two or three conceptual solutions for the development of the block, so that there is plenty to choose from. In our case, we can make an option with a smaller number of sections, but increase the number of floors of half of the residential buildings to 5 floors.
Next, the selected development option undergoes all approvals in the prescribed manner.
Building area
An above-ground floor is considered to be a level with the top of the floors located above two meters. Undergrounds and interfloor spaces below 1.8 meters are not considered above-ground floors. If the building consists of several parts with different numbers of floors or is located on a sloping area, which necessitates the construction of several floors, all its parts are calculated separately. Multi-apartment buildings floors also have their own characteristics.
The total area is determined here using reduction factors:
- for a loggia - 0.5.
- for terraces and balconies - 0.3;
Multi-level apartments, as a rule, are equipped with inter-apartment staircases. If the height of the flight is more than 1.6 meters, its footage must also be taken into account. The dimensions of a residential building are determined by summing up the data obtained from measurements on each floor.
Construction volume of the building
Construction volume of the building
- construction volume of the above-ground part of the building located above ground level;
- the construction volume of the underground part of the building (if any), located below ground level.
- for a building with an attic floor (attic), multiplying the horizontal sectional area of the building (along the outline of the external contour of the external walls above the base) by the height of the building;
- for a building without an attic floor by multiplying the vertical cross-sectional area (along the contour of the outer surface of the walls, roof surface, floor surface of the first floor) by the length of the building;
- for rooms with inclined, multi-level, curved surfaces of enclosing structures of walls and ceilings, multiplying the area of their horizontal section along the outer contour of the walls at floor level by the height (or by the average height in case of a curved outline of the ceiling) from the floor to the top (backfill - if there is a structures) of the attic floor;
- for basement and basement premises, multiplying the horizontal sectional area of the building by the height from the floor surface level to the floor surface level of the first floor.
- in total for parts of the building and floors, differing in space-planning and design solutions.
- attached premises, different from the main building in terms of functionality and with enclosing structures made of materials different from the materials of the building’s construction system, balconies and terraces;
- projections of architectural and structural elements, including: canopies (canopies), porticoes, relief architectural details of facades, terminal devices of engineering equipment (pipes, antennas, etc.);
- spaces under the building on supports and arched openings (passages) under the building, interfloor through arched openings, underground channels, ventilated undergrounds of buildings (built on permafrost);
- non-permanent objects (tents, kiosks, canopies, gazebos, platforms), attached and built on.
Building length Building height
- between the mark of the passage surface for fire engines and the lower boundary of the opening opening (window) in the outer wall of the upper floor (including the attic or mezzanine, not taking into account the non-residential attic space);
- or half the sum of the floor and ceiling marks of the upper floor premises with non-opening windows (openings);
- or to the upper boundary of the roof fence in use.
Floor height Room height
What is the built-up area?
Design and construction
It happens that the building is located on supports. In this case, the building area includes all the space underneath, including passages. How to determine the number of storeys of a building? All floors are considered above-ground, including the attic, technical (in the case when the level of the top of its ceiling is located 2 or more meters above the planning level). The underground (of any height) and the interfloor space do not apply to above-ground floors if its height is less than 1,000 m. 8 m. There are cases when different parts of the building have different numbers of floors.
Sometimes a building may be located on a site that has a slope, then on one side the number of them may be large. In this case, the number of storeys is calculated separately for each of the parts. According to other rules, parameters are calculated for summer cottages and gardening partnerships.
If you have an attic
When it comes to an attic room, when calculating, you should pay attention to the slope of the ceiling and its height. If the inclination is 30 degrees to the horizon, the estimated height is considered to be one and a half meters, if 45 degrees - 1.1 meters
If the angle is inclined from 60 degrees or higher, take into account the space whose ceiling height is from half a meter. In the case of intermediate values, interpolation is resorted to. If the room has a height less than specified, a coefficient of 0.7 is applied. The minimum height of the walls is taken to be 1.2 meters if the slope is 30 degrees and 0.8 meters if the slope is from 45 to 60 degrees. There are no restrictions when the inclination exceeds 60 degrees.
Calculation of building density of a land plot
Association of specialized lawyers Sign up for a consultation Describe the situation and receive a free analysis of the prospects for your case within 30 minutes Order Building density in populated areas plays a big role.
sq. m. per 1 hectare of land. The most optimal density indicator should be no less than 20% and no more than 55%.
However, in practice these values may be subject to gradation. So, for example, in some areas it can reach 80-90%. In this case, when deciding to build a new building, you can increase it by adding several floors.
But in other zones (most often the outskirts) the density indicator can be significantly lower than 20%.
In this case, some financial problems can be observed, since the maintenance and maintenance of transport and engineering infrastructure will be very expensive. And don’t forget about the road surface; the construction and repair of roads in areas with low building density is very rarely done, which affects the quality characteristics of the roads.
Find out on our website: . All articles Land law Land management Land ownership Land supervision Categories of land Call us Or on the website and we will contact you Make an appointment Place of work
Calculation of heating by room area
Of course, ideally, such thermal calculations should be carried out by appropriate specialists, but this often costs a lot of money. Isn't it fun to try to do it yourself? This publication will show in detail how heating is calculated based on the area of the room, taking into account many important nuances. By analogy, it will be possible to calculate heating in a private house; the calculator built into this page will help you perform the necessary calculations. The technique cannot be called completely “sinless”, however, it still allows you to obtain results with a completely acceptable degree of accuracy. The room, its area, ceiling height. Insulation of the floor and “neighborhood” above and below The number of external walls and their main location relative to the cardinal points and the “wind rose”. Degree of wall insulation Number, type and size of windows Availability of entrance doors (to the street or to the balcony) Required thermal power (including 10% reserve) Area 78.5 m² 10.87 kW ≈ 11 kW 1. Entrance hall. 3.18 m². Ceiling 2.8 m. Floor laid on the ground. Above is an insulated attic. One, South, average degree of insulation. Leeward side No One 0.52 kW 2. Hall. 6.2 m². Ceiling 2.9 m. Insulated floor on the ground. Above - insulated attic No No No 0.62 kW 3. Kitchen-dining room. 14.9 m². Ceiling 2.9 m. Well-insulated floor on the ground. Upstairs there is an insulated attic Two. South, west. Average degree of insulation. Leeward side Two, single-chamber double-glazed windows, 1200 × 900 mm No 2.22 kW 4. Children's room. 18.3 m². Ceiling 2.8 m. Well-insulated floor on the ground. Above is an insulated attic Two, North - West. High degree of insulation. Windward Two, double-glazed window, 1400 × 1000 mm No 2.6 kW 5. Bedroom. 13.8 m². Ceiling 2.8 m. Well-insulated floor on the ground. Above is an insulated attic: Two, North, East. High degree of insulation. Windward side Single, double-glazed window, 1400 × 1000 mm No 1.73 kW 6. Living room. 18.0 m². Ceiling 2.8 m. Well-insulated floor. Above is an insulated attic Two, East, South. High degree of insulation. Parallel to the wind direction Four, double-glazed window, 1500 × 1200 mm No 2.59 kW 7. Combined bathroom. 4.12 m². Ceiling 2.8 m. Well-insulated floor. Above is an insulated attic. One, North. High degree of insulation. Windward side One. Wooden frame with double glazing. 400 × 500 mm No 0.59 kW TOTAL:
21 Dec 2021 marketur 99
Share this post
Percentage of land plot development
Construction coefficient (development coefficient, Building Ratio) is a coefficient established by law that determines the total area of buildings on a land plot (in m2). Electricity at the border of the plot. The landscape is calm. Technical planning has been carried out over the entire area of the plots, the elevation difference is less than 0.5%. There is good year-round access to the border of the plot, the roads are cleared of snow in the winter. The plots are adjacent to the forest on both sides.
The Lutosnya River is 300 meters away. Transport accessibility: regular bus No. 50 from the railway station. “Lobnya”. The plots are located at a considerable distance from the highway, far from noisy cities, in a picturesque and environmentally friendly area of the Moscow region. A wonderful place for summer holidays and year-round living for the whole family.
General numbers and parameters
The building density is determined by the perimeters of objects and the lines between them. When renovating existing housing stock, very difficult conditions usually arise.
Calculation and strict compliance with the necessary standards and requirements are mandatory. But the legal aspect (primarily the norms of construction, architectural and other fundamental rules of development) always intersects with the “non-legal”, but essential aspect - the interests of residents. Moreover, the latter have a very specific material expression as homeowners and subjects of very specific rights to proper comfortable living.
The requirement of “non-visibility” must be ensured - a special custom in residential construction, meaning the impossibility of seeing the interior of another building from the windows of one building. However, in practice, especially with linear development of high-rise buildings of the same type, this requirement is forgotten.
Lines from the perimeter of industrial buildings to residential buildings and socially significant objects, as well as to the boundaries of preschool and general education organizations, health care, cultural and recreation centers are usually designed to be more than fifty meters.