The category of land in settlements implies certain rules for their use. To better organize land use, zoning of the territory of a city or town or village is also carried out. When creating separate zones, the type of permitted use of land, urban planning requirements, and economic justification are taken into account.
Separate territorial zones of land in populated areas have their own legal regime and their own purpose. Zoning of territories is carried out according to the development plan of the city or village, approved by local authorities.
Classification
In each settlement, several main zones are identified after the territorial division of the area:
- The most important and, as a rule, the largest zones are residential.
- There are also public and business zones.
- Production.
- Engineering and transport zones are distinguished.
- Recreational areas are needed.
- Special purpose zones and military facilities are identified.
- There may also be areas for agricultural purposes.
The boundaries of territorial zones must coincide with the boundaries of individual land plots. Each zone has its own urban planning regulations that meet land use standards. It depends on the location of the zone, area and purpose of this land plot. The plots may be located within the same zone, in which case the same town planning regulations apply to them.
What are town planning regulations? This is the definition of the basic legal regime for a plot of land and everything that is on it or under its surface.
ATTENTION! Owners or tenants of land plots are required to comply with urban planning regulations.
This regulation and types of permitted use are the basic norms that must be taken into account when using land plots located within a particular territorial zone.
What is zoning of a land plot?
Territorial zones are land areas united by the possibility of developing specific types of objects.
On the master plan, such zones are distinguished by color and also by letter designation. Territorial zones detail functional zones, that is, they establish urban planning regulations in individual territories, giving each land plot a legal regime. Functional zones of the legal regime of land plots do not establish, but influence it indirectly through territorial zones established in accordance with the Land Use and Development Rules (LRU).
How to find out the category of land and type of permitted use
If the purpose of the land plot corresponds to the list of objects that can be located in this zone, then the owner of the plot can change the type of permitted use free of charge.
I am ready to advise you free of charge by phone (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
The call is free for all regions of the Russian Federation
Town planning regulations
This concept includes types of permitted use, maximum and minimum sizes of plots, maximum sizes of permitted construction. The town planning regulations also establish restrictions on the use of land plots.
Town planning regulations apply to all land plots located within the boundaries of one zone. It is the basis for the legal regime of land management. Taking it into account, both lands and objects located on them are used.
Features of the residential area
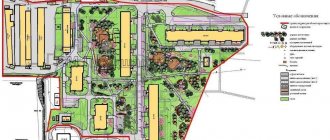
A zoning map for each locality can show different zones that have their own purposes. Residential zones are present on the map of any city or town or village. The composition and types of areas in the zone are varied. It includes areas where apartment buildings and individual construction are being built.
Also in the residential area there will be social, household and cultural facilities. What kind of houses can be located in a residential zone?
These are multi-storey, mid-rise and low-rise buildings. Also in this zone, the construction of private houses and cottages is underway. There may also be other types of buildings here. The main purpose of this zone is to accommodate residential buildings .
Public, cultural, and domestic buildings play a secondary role here, but settlements also cannot exist without them. Therefore, when developing an urban development plan, the construction of administrative buildings, cultural and social buildings is also envisaged next to residential buildings.
ATTENTION! Also on the territory of settlements, zones are allocated for the construction of industrial complexes and enterprises, for the creation of infrastructure and transport facilities.
For the safety of residential areas, these objects must be separated from residential buildings by sanitary protection zones.
Owners of industrial and economic facilities must take care of their improvement and comply with sanitary and environmental standards. This work is carried out at their expense. Territorial zoning of each settlement is carried out taking into account not only urban planning, but also land legislation.
This is a complex and responsible process that allows for planned, rational use and development of every meter of the settlement’s territory. Zoning is carried out on the basis of regulatory documents adopted by local authorities.
What is the plan
Depending on your own skills, the layout of a land plot can be a primitive sketch on a paper sheet, a clear drawing on graph paper, maintaining scale, or a full-fledged sketch, drawn by hand or created in a graphics editor. The correct plan displays all future objects on the site - a house and auxiliary buildings, small forms, paving, landscaping, engineering structures (well, borehole, septic tank). It is not a fact that the site is able to accommodate all the “wants”, so first they create a “skeleton”.
- They display the exact shape of the yard, the lengths of all sides, schematically the neighboring buildings and fence (if any), nearby objects (forest, road, street, pond, etc.) and distances to them.
- Indicate the orientation of the site to the cardinal points.
- If there are trees or shrubs on the site that it was decided to leave, they are also marked on the plan.
It will not be possible to build up and plant a plot of land solely according to your own understanding - there are building rules that regulate not only the distances to neighboring objects, but also between your own. Therefore, when choosing a place for a house, outbuildings and vegetation, you will have to take into account the cardinal directions, insolation and wind rose, plus take into account current standards.
In one of the thematic materials they were discussed in detail.
Why is development planning carried out?
- This is necessary for the successful development of the municipality.
- Allows you to preserve cultural and architectural monuments, the ecology of the surrounding space.
- It is also possible for development planning to determine the future boundaries of a given administrative unit.
- The rights of land owners are protected.
Thanks to development planning, an attractive investment climate is created in the settlement, because land plots can be used for different purposes - for residential and industrial capital construction, for business, for creating recreation areas.
Rules for the use of land in a settlement and a development plan are approved by local authorities with the simultaneous development of certain documents:
- These are town planning regulations for territorial zones.
- Zoning map.
- Regulations on land use regulation.
- Rules for changing the types of permitted use of land plots.
- The procedure for holding public hearings on various issues related to land use.
- Procedure for holding public hearings.
Each plot of land within the lands of a settlement belongs to a specific territorial zone.
It is subject to one or another town planning regulation. The boundaries of the site cannot go beyond the boundaries of its territorial zone. When combining several plots into one, you need to take this into account; you cannot combine plots that are in different zones.
How to find out the type of zoning of a land plot
To find out in which functional zone the land plot is located, we turn to the urban zoning map of the settlement territory. An urban planning zoning map of an urban or rural settlement (scheme-map of functional zones) is a graphic part of the PZZ of settlement territories, which establishes the boundaries of all territorial zones included in the master plan of the settlement.
For this:
- We go to the official website of the settlement on the territory or near which the land plot is located;
- We find the section “General plan and diagram of functional zones” on the website, or immediately type in Yandex the phrase “General plan and diagram of functional zones of village X” and follow the first link.
- We find the land plot we are interested in on the map and remember the territorial zone in which it is located.
I propose to immediately move on to the abbreviations that indicate the zoning of territories on the general plan.
Features of lands of settlements
Lands of settlements are a large category, which includes areas with various purposes. For convenience and more rational use of these land areas, they are divided into separate zones provided for by urban planning regulations.
The following zones are distinguished on the territory of the settlement:
- residential;
- production:
- public and business;
- zones of engineering systems and transport infrastructure;
- special purpose;
- agricultural;
- defense significance;
- others for their intended purpose.
Table of land zoning types
| Zone type | Name of the zone in the current General Plan | Designation on maps | Name of the zone in the draft change | Designation on maps |
| Residential areas | Collective gardening zones | Zh1 | Development zone of single-family (individual) residential buildings (detached and/or semi-detached), collective gardening, including public and business development facilities, as well as engineering infrastructure facilities related to serving the living population | 1 railway |
| Development zones with detached and/or semi-detached single-family (individual) residential buildings | Zh2 | |||
| Low-rise multi-apartment residential development zones | Zh3 | Zone of low-rise multi-apartment residential development with the inclusion of public and business development facilities, as well as engineering infrastructure facilities related to serving the living population | 2ZhD | |
| Mid-rise multi-apartment residential development zones | Zh4 | Zone of mid-rise and multi-storey residential development with the inclusion of public and business development facilities, social and engineering infrastructure facilities | 3ZhD | |
| Zones of multi-storey multi-apartment residential development (9 floors and above) | Zh5 | |||
| Residential development zones in the historical center of St. Petersburg | Zh6 | |||
| Zones of historical residential development on the territory of the historical suburbs of St. Petersburg (Pushkin, Pavlovsk, Peterhof, Kronstadt, Lomonosov) | Zh7 | |||
| Public and business zones | Multifunctional public and business development zones | D1 | Zone of all types of public and business development with the inclusion of residential buildings and engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | D |
| Areas of location of healthcare facilities, culture, secondary vocational and higher vocational education, administrative, research institutions, religious buildings | D 2 | |||
| The regulations on territorial planning do not establish | D3 | Zone of all types of public and business development and water transport facilities, including residential buildings and engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | DI | |
| Production zones | Zones of enterprises of IV and V hazard classes (100 m and 50 m) and accompanying public and business facilities | P1 | Zones of industrial, transport and logistics, warehouse facilities, engineering infrastructure, including public and business development objects related to servicing this zone | PD |
| Zones of enterprises of I, II and III hazard classes | P2 | |||
| Engineering and transport infrastructure zones | Zones of expressways, continuous traffic roads and urban highways | U | Zone of urban expressways, highways of continuous traffic and urban highways including engineering infrastructure facilities | U |
| Zones of urban transport and engineering infrastructure facilities | I1 | Zone of engineering and transport infrastructure facilities, communal facilities, sanitary cleaning facilities including warehouse and production facilities | I1 | |
| Air transport facility zones | AND 2 | Air transport facilities zone including public, business and engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | AND 2 | |
| Railway transport facility zones | I3 | Zone of railway transport facilities including objects of public, business and engineering infrastructure related to servicing this zone | I3 | |
| Water transport facility zones | I4 | Water transport zone including public, business and engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | I4 | |
| Agricultural use zones | Areas of agricultural land, nurseries and greenhouses | C1 | Zones of agricultural land, nurseries and greenhouses and agricultural production facilities including industrial, social and engineering infrastructure facilities | WITH |
| Zones of agricultural production facilities | C2 | |||
| Recreational areas: | Areas of sports facilities and beaches | P0 | Zone of sports facilities and beaches including engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | P0 |
| Forest and forest park areas | P1 | Zone of forests and forest parks | P1 | |
| Green areas for general and limited use | P2 | Zones of public green spaces and green spaces of limited use with the inclusion of objects permitted in accordance with the legislation on the protection of green spaces, including flat sports facilities | P2 | |
| Areas of recreation and entertainment facilities, tourism and spa treatment, hotels and boarding houses of various types | P3 | Zone of recreational facilities, sports, leisure and entertainment, tourism and sanatorium-resort treatment, hotels and boarding houses, dacha stock with the inclusion of engineering infrastructure facilities related to servicing this zone | P3 | |
| Other green areas | Not marked | Zone of palace and park complexes and historical parks | P4 | |
| An area of green spaces that perform special functions with the inclusion of objects permitted in accordance with current legislation | P5 | |||
| Special purpose zones | Areas of cemeteries, crematoria | K1 | Zone of cemeteries, crematoria including social and engineering infrastructure facilities | K1 |
| Areas for storing consumer waste and other similar facilities | K2 | Areas for storing consumer waste including engineering infrastructure facilities | K2 | |
| Zones of military and other sensitive facilities | K3 | Zones of military and other sensitive facilities including social and engineering infrastructure facilities | K3 | |
| Water areas | Intracity water areas. | AG | Intra-city water areas | Not designated |
| The water area of the Gulf of Finland adjacent to the city | AF |
Purpose
Designated residential zones are lands where the construction of residential buildings and cultural and community facilities can be carried out. Residential buildings are built as part of industrial construction or individually. Also, the town planning regulations for this zone allow the construction of other objects related to the housing program.
IMPORTANT! Buildings of medical, educational institutions, cultural or household facilities are being built next to residential buildings.
How was zoning carried out?
Most settlements have a long history. When they were laid out and developed, no separate zones were allocated. Urban planning and territorial zoning have been used recently in the development of new areas and improvement of old ones.
The most modern norms for the allocation of individual functional territories were included in the Land Code.
ATTENTION! In 2004, a new Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation was issued, which indicates the need to regulate land use using town planning regulations.
Now in many cities and towns there are objects that do not comply with urban planning regulations for the zone in which they are located. Whenever possible, such facilities are moved or simply not used for their original purpose. If they do not pose a danger to the population, they can continue to be used.