Increasing living space by adding additional premises to a private household is not uncommon. But here a legal question arises - how to legalize an extension to a house on your own land? This will be discussed in the article.
From a legal point of view, an extension is subject to mandatory registration. In a good way, you need to obtain a construction permit before starting work. However, some citizens ignore or are simply unaware of this requirement. However, sooner or later the extension will have to be legalized.
Why do you need a permit?
An extension to a house, especially a permanent one, is the same piece of real estate as the house itself. Permission to build an outbuilding is obtained for the following purposes:
- To register ownership;
- To avoid possible demolition of the extension at the initiative of the authorities;
- To increase the market value of housing.
The construction of extensions without the appropriate permission does not give ownership of them, according to paragraph 2 of Art. 222 of the Civil Code.
Consequently, a building with such an extension cannot be sold, donated or bequeathed to heirs. In addition, unauthorized extensions and economic additions to houses can be demolished by government officials, especially if they were built in violation of town planning regulations.
For a house with an unregistered extension, the market value drops by 20-30 percent, since citizens prefer to buy a house and land with all the completed documents, rather than deal with their registration after the transaction on their own.
Ways to resolve the issue of legalizing an extension with example prices
This procedure includes the following costs:
- The state fee is 200-500 rubles .
- Cadastral chamber services - 20,000 rubles .
- Expertise carried out in court - 15,000 rubles .
This “minimum” set is suitable for those who deal with this issue on their own. These payments are mandatory and, unfortunately, cannot be avoided.
The situation is completely different for those who decide to seek the help of a lawyer. A one-time consultation costs about 1000 rubles. , representation in litigation 1 time – 6 tr. , on an ongoing basis - from 30 tr . Don’t forget about the power of attorney for the representative, executed by a notary – 2 tr .
Where and how to get it?
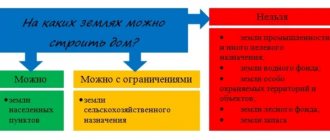
Permission to build an extension to a house on the site is issued by local authorities, in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 51 of the Town Planning Code.
In order for the authorities to allow construction, the owner of the site will need the following documents:
- Copy of the passport;
- Certificate from the Unified State Register of Real Estate on the ownership of the land under the future extension;
- Construction design diagram;
- Cadastral document for the plot;
- Extract from the urban planning plan.
A certificate from the Unified State Register can be ordered at the MFC at your place of residence by applying with your passport and paying a fee (300 rubles). It takes 3 business days to prepare the certificate. The project diagram is developed by the owner of the site independently or ordered from an architectural bureau.
The town planning plan of the area can be found in the city archives. This document is not required if the house is located in a dacha, garden community or outside the city.
In general, the procedure for obtaining a construction permit is as follows:
- Collect the necessary documents for the site;
- Contact an architectural bureau to develop a project;
- Submit the project and documents to the gasification and water supply department and obtain an act of consent for construction;
- Contact the architectural committee of the local administration with an application;
- Wait for approval (30 days) and receive a building permit document.
Gas and water supply specialists will check whether the planned construction overlaps with underground utilities.
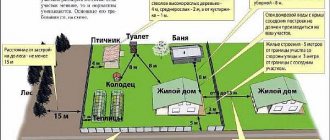
Capital buildings should not be closer than 2.5 meters to main lines.
In architectural bureaus, specialists check the proximity of the extension to communications, but if the owner of the site draws up a project on his own, he needs to assess the proximity of the building to gas and water pipes independently, according to urban planning documentation.
The architectural committee issues permission to build an extension to the house if there is a conclusion from the utility services and the declared project complies with urban planning regulations.
Registration procedure
There are two options for the development of events:
- The homeowner is planning to build an extension. If a home owner plans to add an extension to a residential property, he should seek help from a legal adviser to resolve the issue in accordance with all legal norms. After deciding the legal side of the law, it is necessary to use the services of a designer.
- A project for construction is drawn up, which is certified by local authorities. The project must be drawn up taking into account all legal requirements. After completing the above steps, you can begin collecting documentation and completing the registration procedure.
How to legalize and how much does it cost?
The next stage after completing the construction of the extension to the house is registration of ownership rights. Registration of rights is carried out by entering data into the Unified Real Estate Register (USRN) about the new parameters of the completed building. The registration procedure depends on the availability of a building permit.
Legal building
Registration of rights to an extension, the construction of which was permitted by the administration, occurs in the following order:
- Contacting the BTI to obtain a certificate about a new building on the site;
- Payment of state duty 350 rubles;
- Applying to Rosreestr with an application for registration.
The owner of the completed house presents the following documents to Rosreestr:
- Certificate received from the BTI;
- Receipt of payment of the duty;
- Construction permit;
- A copy of your passport.
Entering information about the owner of the new building formed after the extension is carried out within 7-10 days. The cost of registering a legal extension consists of the following payments:
- Payment for the services of an architectural bureau – 3,000-20,000 rubles;
- The fee for extracting from the Unified State Register is 300 rubles;
- The fee to Rosreestr is 350 rubles.
The cost of the bureau's services varies depending on the complexity of the project and the location of the site.
Unauthorized construction
Registration of ownership of an unauthorized extension is carried out in court. To do this, you should collect a package of documents:
- A certificate from the Unified State Register of Real Estate about ownership of the land under the house with an extension;
- Document on ownership of the house;
- A certificate from the BTI about the buildings on the site;
- Technical passport for the house;
- Description of the extension;
- Act of utility services on the lack of communications near the house;
- Conclusion of the engineering service from BTI.
If there is no plan for an enlarged building, it must be prepared by an architectural office. The BTI engineering service checks whether the extension complies with building codes (wall thickness, foundation strength, etc.).
If the building was built in violation of building codes, or is located at a distance of less than 1 meter from the border of the site, then the construction will not be legalized, and there is no point in going to court.
With the plan and documents for the building, you need to contact the gasification and water supply services to obtain a certificate of compliance of the extension with the standards.
After receiving the utility service act, you should go to court at the location of the site. The statement of claim must contain the following information:
- Full name and passport details of the plaintiff;
- Cadastral number of the plot;
- Technical characteristics of the extension;
- Data from public utility acts;
- Conclusion of the engineering service on the compliance of the extension with construction standards.
In the main part of the statement of claim, the owner of the plot describes the circumstances of the extension, explains why permission was not obtained and asks the court to recognize the extension of the house as legal on the basis of its compliance with all required standards. If you have any difficulties, you can contact qualified lawyers to help you file a claim and prepare the necessary documents.
The court satisfies the plaintiff's demand provided that the building complies with all requirements and regulations, as well as the absence of encumbrances on the site and claims from neighbors.
The cost of registration of unauthorized construction includes:
- Fees for preparation and execution of documents (650 rubles);
- Legal consultation (1000-3000 rubles);
- Departure of an engineering team to inspect the building (2500-5000 rubles);
- Fine for construction without permission (2000-5000 rubles, according to clause 1 of article 9.5 of the Administrative Code);
- Fine for operating an unauthorized structure (500-1000 rubles, according to clause 5 of Article 9.5 of the Administrative Code).
The cost of services for engineers, architects and lawyers differs depending on the complexity of the construction and the region of residence of the owner.
Documentation
Registration requires the presence of a certain list of papers. List of papers:
- papers proving the right of ownership of the property to which the extension was added;
- a package of papers issued by the utility service;
- paper from BTI;
- an extract from the house register listing all citizens registered in the given territory;
- design document for redevelopment of a property;
- extension project;
- if the extension is located in close proximity to the boundaries of a neighbor’s plot, written consent of the neighbors for construction will be required;
- papers from the utility organization (electricity, heat networks);
- an act authorizing the construction of an extension from the sanitary and anti-epidemic service;
- photographs of the land plot and residential building.
The list of documentation may change based on the characteristics of the property, its features, as well as the type of extension itself.
How to make a project?
When choosing a construction project, it is important to pay attention to the following factors:
- Technical feasibility;
- Functionality;
- Compliance with building codes.
Extensions are made to increase the area of the house or make the entrance more convenient. Project in Fig. 1 increases the living space by 2 times. It is carried out by completing three walls and adding ceiling beams to expand one of the roof slopes.
Rice. 1
Project in Fig. 2 increases the area of the first floor only and has a separate roof.
Rice. 2
Project in Fig. 3 It is an extension to the wall with an entrance door. One of the popular options serves as a hallway and entrance porch with wooden steps.
Rice. 3
An extension to the house allows you to profitably increase its area. To avoid having to collect a lot of certificates and go to court after construction is completed, you should obtain a construction permit in advance and comply with the norms of capital buildings.
What falls under the concept of an extension and whether these structures need to be documented
According to the current Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, the addition of any structure to a house that is not included in the original architectural plans and entails a change in its original key characteristics (area, volume) is a reconstruction. And the reconstruction of a house is under the jurisdiction of state supervisory authorities and is regulated not only by the Town Planning Code, but also by other regulations. Extensions are divided into capital and non-capital.
A major extension is a residential or technical premises, with one or more walls common to the house, of any area, for the construction of which additional land is used. The number of floors of the extension may or may not coincide with the number of storeys of the house, usually to a lesser extent.
A non-permanent extension is a secondary, non-residential structure that does not require a permanent foundation and changes the parameters of the house slightly. This could be a porch, balcony, open terrace or veranda, canopy and the like.
Both capital and non-capital extensions must be documented, but the process algorithm is significantly different.
Who lives happily and at ease in Rus'?
An extension will not cause much trouble to those who first obtain permits for reconstruction, and only then begin to carry it out. Any house designs for individual construction, exclusive house and cottage designs, ready-made house designs can be improved and adjusted to a specific person in accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation. And he suggests that the first step on this path should be to obtain a document from local governments authorizing changes to the project. And then, having made an extension, you will not need to worry about its legalization, and you can live happily and at ease in the house of your dreams.