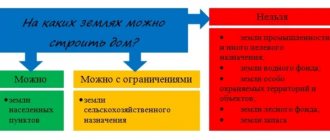
All land on the territory of the Russian Federation is divided into certain categories. The intended purpose, as well as the type of permitted use, depend on which category a particular site belongs to. For example, agricultural land - it is not difficult to guess what they are intended for, but not all the nuances may be obvious.
It is prohibited to go beyond the intended purpose and permitted use by law. To use land of a certain category for other purposes, it is necessary to first transfer the land from one category to another.
Registration issues
Registering on such a plot will be a little more difficult than building your own house on it. But what should we do for this? The thing is that the law allows registering persons only on settlement lands. Those. in areas intended for individual housing construction. But registration on agricultural land is not allowed. You need to think about this even before building a house on agricultural land.
In order to officially register in a house located in SNT or that is a dacha, it is necessary to transfer it to the category of settlement land.
There are cases when you can register on houses built on plots intended for gardening.
However, in this case, certain requirements are put forward for the house:
- capital foundation;
- no higher than three floors;
- compliance with lighting standards;
- communication systems must comply with sanitary and engineering requirements;
- registration of the house in the registry;
- being near a settlement or within its territory.
However, registration at a summer cottage is not always desirable. After all, if no one is registered there, then taxes are calculated at the minimum rate. And after registering there, the tax price increases noticeably. Also, in most cases, a court hearing may be required to declare a home compliant, which is undesirable for most citizens.
Other buildings on agricultural land
In fact, the construction of other non-residential premises on the territory of an agricultural plot is not limited by law. The main requirement is that the type of construction and its intended purpose coincide with the objectives of using a particular site.
So, for example, to store agricultural products you need a barn. Or, if there is a need to process products, then the construction of an appropriate building is allowed.
The main requirement for the construction of buildings on agricultural land is that only one building can be built for residential purposes. The remaining structures must have a different purpose.
Also, in order to ensure the civil legal status of real estate, the structure under construction must obtain a construction permit.
How to get permission?
As you know, in order to build a house on a plot intended for individual housing construction, it is necessary to provide the local government with technical documentation of the future construction and a document confirming ownership.
Most agricultural plots within SNT and dacha estates are not privately owned, but have the status of temporary ownership. In such cases, instead of a document confirming ownership, you can provide the charter of the cooperative or SNT.
In each individual case, the local government authority (district administration) makes a decision to issue a permit for construction on agricultural land, depending on other acts of local importance. So, before purchasing such a plot, it is necessary to make inquiries with the relevant authority about the possibility of erecting a building.
In fact, no permission is needed to build and live in such houses. Difficulties may arise in the future when installing power supply lines and selling real estate. Such complexities are very difficult to resolve. Therefore, it is advisable to act according to the law and follow the established procedure.
To build a cottage for residential purposes on the territory of a farm plot, it is necessary to obtain the appropriate certificate of farming. Such a certificate is issued by a local authority upon registration of a commercial organization.
What can be built
The right of ownership of these territories belongs to:
- Individuals, citizens of the Russian Federation.
- Legal entities (peasant associations, agricultural enterprises, country and garden cooperatives).
The owner has the right:
- sell the plot;
- pass on by inheritance;
- rent out subject to intended use;
- donate or pledge;
- use for construction.
Agricultural land is used for cultivation, processing, storage, transportation, and sale of products.
The owner has the right to build a residential building on agricultural land. It is allowed to assign an address to the building and register in it. The maximum height of the house is 3 floors.
If there are minerals, forests, or water bodies on the site, they can be used by the owner.
How to “register” at the dacha
This article discusses registration at a dacha, although the word “registration” has not been used in legislative acts for a long time. Today it has been replaced by the concept of “registration at the place of residence”. But the essence remains the same. Without “registration” it is difficult to find a job, register at a clinic, receive a pension, benefits, enroll a child in kindergarten or school, and much more. Although the Constitution guarantees freedom of movement and choice of place of residence.
It was this contradiction with the law that was cited by seven Russians who were prohibited from registering at their dacha with SNT, despite the fact that none of them had other housing. After receiving refusal from all authorities, they appealed to the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation. Now, according to the law, registration at the dacha is possible. Although it is difficult. We’ll talk about how to do this today.
Why didn't they register?
According to the law, you can only register a person at a place of residence in a residential building. In accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, an isolated premises is recognized as such, which is real estate and is suitable for permanent residence of citizens (meets established sanitary and technical rules and regulations, and other legal requirements).
Residential premises include: 1) a residential building, part of a residential building; 2) apartment, part of an apartment; 3) room.
But it seems that there is a plot of land in SNT on which a good-quality house was built, where there is water, sewerage, heating, etc. You can live in such a house all year round, so it seems that registering in a dacha should not be difficult. But very often they are not registered. The problem may be that the land plot on which the building stands does not allow for the construction of a residential building on it.
Dachas are located on garden plots, dacha plots or plots for vegetable gardening. And each of these areas has its own development rules, and this determines how to register at the dacha and whether it is possible to register at the dacha at all. Summer residents, gardeners, gardeners
Exist:
- A garden plot of land
is a plot on which a citizen has the right to grow various vegetables and fruits, but only a non-permanent residential building or other economic structures can be built on it. The very concept of “non-permanent residential building” implies that it is impossible to live in it permanently, in winter. A non-permanent residential building is a building that lacks at least one of the structural elements that influence the determination of its capital (deep foundation, reinforced walls, etc.), as well as its engineering support. That is, registration on a dacha plot that has this status is impossible. - garden plot of land
- a plot of land provided to a citizen or acquired by him for growing fruit, berries, vegetables, melons or other agricultural crops, as well as for recreation. The owner of such a plot has the right to erect a residential building (but not residential premises!). The law clearly states that it is impossible to register on a dacha plot of this type. - - dacha land plot
- a plot provided to a citizen or acquired by him for recreational purposes, with the right to erect a residential building without the right to register residence in it or a residential building with the right to register residence in it and economic buildings and structures, as well as with the right to grow fruit and berries , vegetables, melons or other agricultural crops and potatoes.
That is, the law “On gardening, gardening and dacha non-profit associations of citizens” previously allowed “registration” at dachas. But only if a residential building is built on the site. The registration ban applied only to buildings that did not have such status.
That is, when a citizen was provided with land, the documents indicated the permitted use - with the right to erect a residential building or with the right to erect a residential building. Those who received or purchased land with the right to erect only a residential building were unable to obtain registration at the dacha. They live in such a building all year round, it has everything, it stands on a strong and reliable foundation, but you cannot register in it. Although some of these “residential buildings” are significantly superior in technical and urban planning standards to dilapidated, old residential buildings in villages where citizens are still registered.
To wait or not to wait
After the ruling of the Constitutional Court, “dacha residents” had the opportunity to “register” at their dachas on their hundred square meters for permanent residence. But automatically taking advantage of this “granted” right is a big problem.
There are two possible options. And I must say, both of them are not easy.
Option one
. Wait until changes are made to the legislation. Until this moment, the Federal Migration Service will refuse registration, and residents will have to appeal these refusals in court, and this is a rather exhausting procedure.
The fact is that the decision of the Constitutional Court is not a norm of direct action. There are still amendments to be made to the current legislation. The law “On gardening, gardening and dacha non-profit associations of citizens”, according to which permanent registration at the place of residence is possible only in residential premises, but not in residential buildings. But this process is long, and you will have to wait more than one month. The law on amendments must undergo three readings and be approved by the President of the Russian Federation. According to the law, 6 months are allotted for everything from the date of the decision by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation. That is, we can wait for the corresponding law no earlier than November.
For your information! The Constitutional Court recognized that the subjects of the Federation “have the right to independently determine such a registration procedure, without waiting for these norms to be prescribed in federal legislation.” Although, until today, none of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have taken upon themselves the courage to establish such norms. Option two
. If you do not intend to wait for legislators to make appropriate amendments to legislative acts, or local authorities do this earlier, you can use another method - through the court.
There is a residential building on your garden or dacha plot in SNT, which means you have the right to register in it, if only this building is recognized as a residential building. Previously, the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Fundamentals of Federal Housing Policy” was in force, which provided for the right of citizens who own residential buildings located on garden plots of land and meeting the requirements of the standards for residential premises, to re-register them as residential buildings with personal plots on the right of private property.
But this provision became invalid on March 1, 2005, that is, from the moment the Housing Code of the Russian Federation came into force. But a new document regulating the procedure for re-registration of a residential building into a residential building was never adopted. There are no such laws at the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities, so the question of how to register in a dacha remains insoluble for many.
Recognize it as home...
Let's consider what needs to be done to achieve recognition of a country house in gardening as a structure suitable for living all year round and to register on a summer cottage. You need to apply to a court of general jurisdiction to establish the legal fact of recognizing your country house as suitable for permanent residence. This application is submitted in accordance with Chapter 28 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
The following documents must be submitted to the court:
- Documents for ownership of land and house.
- BTI technical passport, which gives the technical characteristics of the house - what kind of foundation it is, whether the walls are solid or not, etc.
If your interests will be protected by a third party, a power of attorney will be required. The submitted documents must confirm that this building is suitable for permanent residence, that the house is capital enough to live in it permanently.
At the court hearing, the issue of the possibility of recognizing a residential building as a residential building will be considered. Your ability to obtain registration at your summer cottage will depend on this decision. If the court finds that a residential building meets all sanitary, technical standards and rules, then it is recognized as a residential building. You can register in such a house. If the court comes to the conclusion that it is impossible to live in it year-round, and the house does not meet the established standards, then you cannot count on “registration”.
The Housing Code recognizes a house as residential if it can be lived in all year round. We can definitely say that a garden building that does not have electricity or heating cannot be recognized as a residential building. The same applies to temporary buildings that do not have a foundation: there can be no question of registering in such buildings.
But the absence of a centralized sewerage system and hot water supply in a one- and two-story residential building cannot serve as a basis for declaring a residential premises unsuitable for year-round living.
Don’t be afraid to spend money on court costs or state fees, without which the court will not consider your application. The fee will be 100 rubles.
...or not admit it
Residential premises located in hazardous areas of landslides, mudflows, snow avalanches, as well as in areas that are annually inundated by flood waters and in which it is impossible to prevent flooding using engineering and design solutions are considered unsuitable for living.
In a word, you shouldn’t waste time and go to court to have your shack made of tin sheets and other improvised materials recognized as a home, no matter what important reasons you have for this.
In order to “win” in court, the premises in which you intend to “register” must be of good quality and have all the conditions for permanent residence in it. Any examination should confirm this. Your goal is to prove in court that this is exactly the case, that your personal house on a garden or summer cottage meets all standards. And that here you will not have problems with water, nor with light, nor with heating in winter, nor with other benefits of civilization.
For your information
Another important point: a house built on a site must be located within the boundaries of a populated area, within transport accessibility, have an address and be connected to utility networks. After the court has ruled in favor of recognizing the building as a residential building, the next step is that with this document you have the right to apply to the Federal Migration Service to register persons permanently residing there.
Pro and contra
Making a decision in favor of registering on a garden plot will be viewed positively by Russians. Today, many people are building not only houses, but entire palaces in their summer cottages and gardens, in which you can live all year round. But registering in such mansions is problematic, and here’s why:
- According to officials, allowing “registration” on garden plots will lead to the emergence of new settlements. And if people are “registered” and live in the area, they need clinics, schools, kindergartens, public transport, roads and other infrastructure. And all this will require additional funds.
- Today, a house with a garden plot costs less than an individual residential building on land for individual housing construction (individual housing construction). But with the advent of the opportunity to be registered on a dacha or garden plot, the cost of the plot will also rise. Indeed, in this case, the garden plot will not differ from the plot for individual housing construction in almost any way.
- According to officials of the Federal Migration Service, registration on a garden plot of land will not lead to an influx of guest workers. But if a person (the owner of the house) is registered in a residential premises located on a garden plot of land, and a relative from near (or far) foreign countries comes to stay with him, then in accordance with the law, the gardener must notify the FMS of his arrival. Naturally, the owner of the premises will register it at the place of his “registration”. So what will stop the owner of the property from registering other foreigners - not relatives, and for money! Moreover, now the registration of foreigners is a notification procedure, not a permitting one.
Only numbers
Of the almost 20 million garden plots registered in Russia, about 1.5–2 million belong to Moscow residents. Most of them have buildings for permanent or temporary residence.
By the way
When deciding on the issue of recognizing a building as a residential building, it will not be superfluous to read the Regulations on recognizing premises as residential premises, residential premises unsuitable for habitation and an apartment building as unsafe and subject to demolition or reconstruction, this document was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 28, 2006 No. 47.
It mentions the requirements that residential premises must meet.
A comment
Maxim Borodynya, lawyer
The mandatory conditions for a person to “register” at a dacha are as follows: a) the residential building must be suitable for permanent residence; b) the land plot must be intended for gardening (and not for anything else, gardening, etc.); c) the site must be located on lands classified by their category as lands of populated areas.
The most serious of the existing restrictions for registration in a passport of registration at a summer cottage is the third. The fact is that you can register in a residential building built on the so-called settlement lands, on the land of a populated area - it can be a town, village or some kind of municipal entity. Where there must be a first-aid post, a store, a playground, all the necessary communications... That is, the registration status on the garden plot must be supported by additional social infrastructure. And the majority of dachas are located on agricultural lands, and the already mentioned decision of the Constitutional Court does not concern them.
Theoretically, it is possible that summer residents from a garden partnership of 200-300 or more houses will decide to “register” on their hundred square meters. Please. But only on the same allocated lands will they have to equip a first-aid post, a store, a playground so that the village corresponds to its status... But they will voluntarily want to vacate their plots for this!
Is it possible to transfer agricultural land to residential land? Such a decision is made at the level of the regional governor at the request of the head of the district administration. The head of the administration prepares a written order, it is submitted “to the top” for approval, and a decision is made to transfer agricultural lands to settlement lands. Or not accepted.
Summarizing
The Land Code specifies all types of land, including lands of settlements, settlements and agricultural purposes, between which there is a clear gradation. And there is also a separate law on agricultural lands, which clearly states that municipal authorities, by their own decision or by decision of the federal authorities, can seize these lands at any time for their own needs: for the construction of a federal road or some kind of shopping and entertainment center. And the summer resident will be asked to vacate the site, providing compensation in return.
How to allocate a land plot of the SNKh in the water protection zone
The country's water protection zone is under state control, which is carried out through:
- executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- a government body that is specifically authorized to manage the use and protection of the water fund;
- government body specifically authorized to protect the natural environment.
Art. 112 of the Water Code of the Russian Federation establishes that plots of land within water protection zones are allocated to citizens and legal entities in accordance with the provisions of the land legislation of the Russian Federation in the process of coordination with a specially authorized state body for managing the use and protection of the water fund.
In practice, the procedure for allocating land plots in water protection zones is under the control of Roskomvod.
The legislative framework
What laws govern registration in a village or village:
- The Housing Code of the Russian Federation determines what constitutes residential premises and answers a lot of other housing questions;
- The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation establishes criminal liability for fictitious registration, i.e. not for the purpose of actual residence;
- Law No. 5242-1 of June 25, 1193 fixes the possibility of every citizen for free and independent self-determination in matters of place of residence within the country;
- Government Resolution No. 713 is the main legislative act that explains in detail the features of the registration procedure;
- The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes a fine if a person has exceeded the period during which he can be unregistered anywhere;
- Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated April 14, 2008. No. 7-P Moscow - an act that made it possible to register in dacha and garden partnerships, in private household plots and on agricultural lands.
You can learn about the difference in the concepts of “registration” and “registration” from our article.
Types of permitted use
Agricultural areas are used for the following purposes:
- organization of personal farming;
- maintaining a peasant farm;
- construction of a country house;
- horticultural plantings;
- fisheries management;
- organization of research activities;
- hunting management;
- livestock farming and grazing.
To expand the territory of allotments for the needs of the industry, a land redistribution fund is being created. It is formed under the following conditions:
- the owner officially abandoned the land plot;
- no right of inheritance of land;
- the territory was forcibly seized in accordance with the law.
A citizen has the right to run a household. The procedure for the provision of agricultural land is established by Federal regulations depending on the type and purpose of the activity.
Types of permitted use of agricultural land in 2022
The use of agricultural land is permitted at the legislative level in relation to:
- areas along which roads are laid, as well as rights-of-way;
- plots allocated for economic buildings;
- lands on which forest belts protecting fields and forest areas for other purposes are located;
- pastures;
- haymaking;
- arable land;
- fallow lands;
- gardens
Also, the types of permitted use of agricultural land in 2022 allow:
- breeding of domestic animals and poultry;
- creation of fisheries;
- construction of residential premises for recreation, construction of a permanent house, temporary buildings, agricultural infrastructure;
- laying of pipelines, power lines, highways, engineering structures and communications.
Art. 79 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, as the most valuable types of permitted use of agricultural land, subject to careful protection, designates the following territories:
- arable land;
- allocated for vineyards, gardens, shrubs;
- fallow lands;
- pastures;
- haymaking
At the same time, productive agricultural plots located on lands whose cadastral value is higher than average prices in a given area are considered the most valuable components of the land fund.