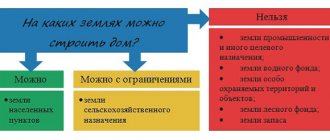
What types of permitted uses are there in the territorial zone Zh?
This territorial zone is intended for development of residential buildings of various heights. There are several options for zone F, and each has its own digital designation. Territorial zones Zh-1 - Zh-4 differ in density of development - from individual housing construction to multi-storey buildings. Residential zones allow the construction of commercial, domestic and social facilities. Each residential zone has its own types of permitted use.
- Territorial zone Zh-1: individual housing construction (the rest is in catch-permitted forms);
- Territorial zone Zh-2: Blocked development and low-rise construction, commercial and social facilities;
- Territorial zone ZH-3: Mid-rise construction, commercial and social facilities;
- Territorial zone Zh-4: Multi-storey construction, commercial and social facilities;
A feature of the territorial zones Zh-2 - Zh-4 is the possibility of assigning several main types of permitted use to a land plot at once. For example - residential building + shop + restaurant.
Attention!
In the land use and development rules of some municipalities, the territorial zones Zh-2 - Zh-4 are combined into a separate zone of multi-apartment residential development, Zh-1 - Zh-2 are combined into a development zone with individual and semi-detached residential buildings.
Name VRI / Typical zone F / Code (numerical designation VRI):
- For individual housing construction (Zh-1) 2.1
- For personal farming (F-1) 2.2
- Vegetable gardening (G1-G2) 13.1
- Objects for garage purposes (G-1) 2.7.1
- Blocked residential development (Zh-2) 2.3
- Low-rise multi-apartment residential development (Zh-2) 2.1.1
- Mid-rise residential development (Zh-3) 2.5
- Multi-storey residential development (Zh-4) 2.6
- Objects for garage purposes (G1-G4) 2.7.1
- Utilities (G2-G4) 3.1
- Social services (G2-G4) 3.2
- Household services (G2-G4) 3.3
- Outpatient services (G2-G4) 3.4.1
- Pre-school, primary and secondary general education (W2-W4) 3.5.1
- Cultural development (G2-G4) 3.6
- Religious use (G2-G4) 3.7
- Outpatient veterinary care (G2-G4) 3.10.1
- Business management (G2-G4) 4.1
- Markets (G2-G4) 4.3
- Stores (Zh2-Zh4) 4.4
- Public catering (G2-G4) 4.6
- Hotel services (G2-G4) 4.7
- Vehicle maintenance (Zh2-Zh4) 4.9
- Sports (W2-W4) 5.1
- Ensuring internal law and order (G2-G4) 8.3
- Historical and cultural activities (G2-G4) 9.3
- General use of water bodies (G2-G4) 11.1
- Land plots (territories) for public use (Zh2-Zh4) 12.0
Conditionally permitted and auxiliary species must be looked at in the approved land use and development rules. A complete list of VRI for each zone is in the Classifier.
Land categories. Types of permitted use
The entire land fund of the Russian Federation is divided into categories. The category of a land plot determines its intended use. In fact, the concepts of category of land plot and intended purpose from the legal side are equivalent. The relationship of land to a certain category is legally established in accordance with the Land Code of the Russian Federation. The legally established category of land makes it possible to preserve the properties of the land plot over time and excludes inappropriate use of the land. There are seven categories in total. Land in the settlement category is intended for low-rise construction.
The type of permitted land use (APL) specifies the purpose for which the site is used. For this purpose, a special classifier has been compiled, which contains codes and descriptions of VRI areas of all types. This document was approved by order 540 of September 1, 2014.
Until November 2015, low-rise development, according to Order 540, included exclusively territories allocated for individual housing construction (IHC). Sites allocated for the construction of low-rise apartment buildings (up to four floors) were classified as lands intended for mid-rise construction. As a result, situations arose when high-rise buildings (up to 8 floors) were built next to individual or two-three-story houses. This caused dissatisfaction among residents and conflicts; a stream of various requests and complaints poured into the local administration. Although formally the legislation was complied with by local authorities and permitting bodies.
To solve the problem that arose, a change was made to the classifier of VRI of land plots by order No. 709 of the Ministry of Economic Development dated September 21, 2015 and a new type of VRI of land appeared - 2.1.1 “low-rise multi-apartment development”.
According to the VRI classifier, low-rise residential buildings include:
We recommend that you read:
3 types of permitted use of land in settlements
- Land intended for individual housing construction (classifier code 2.1). On lands of this type it is allowed:
- build individual residential buildings with a height of no more than 3 above-ground floors;
- to equip a household plot to grow vegetables and melons, berries and ornamental plants, build greenhouses and greenhouses, plant fruit and berry trees and bushes;
- locate individual baths and garages, various utility buildings.
- Land for personal farming. VRI 2.2. It is also allowed to keep farm animals on a plot with this type of VRI.
- Semi-detached houses of block type. VRI 2.3. In these areas, the construction of only blocked houses (penthouses), auxiliary buildings, garages for personal vehicles, cultivation of berries, fruits, vegetables, and various ornamental crops is permitted. Construction of recreation areas, sports grounds, children's play areas.
- Lands marked as “Low-rise multi-apartment residential development” (VRI classifier code 2.1.1). On land plots of this type it is permitted:
- place multi-apartment residential buildings. Houses must have a maximum of 4 floors (including underground or attic);
- grow fruit and berry and ornamental plants, vegetables;
- build garages for personal vehicles, sheds, and auxiliary structures for various purposes;
- locate facilities in buildings to service the infrastructure of residential buildings and the residents living in them. Service facilities can be located in built-in or attached premises. They should occupy no more than 15% of the total area of the premises of a low-rise building;
- create recreation areas, children's play areas, grounds for sports games and sports.
In areas with VRI 2.1.1, the construction of exclusively multi-apartment low-rise housing is permitted. The construction of individual houses is unacceptable.
To obtain a permit for the construction of a low-rise building, you must have a plot of land with the type of intended use of settlement and VRI corresponding to the type of house project.
Territorial residential zone Zh-1
Zone of individual housing construction.
In this zone, the construction of residential areas with single-family residences is permitted. The main types of uses (WU) include:
- placement of private housing with garden plots;
- creation of communications and engineering support facilities.
Among the conditionally acceptable VRIs are: kindergartens, schools, shops (if the building is separate), laundries and pharmacies, parks, clinics, service businesses and sports grounds.
The list is quite extensive. It includes all possible organizations necessary to maintain residential development. But there are also auxiliary uses here. For example, outbuildings, vegetable gardens, wells, bathhouses, etc. The maximum possible characteristics are also provided for the zone: minimum plot area, distance from one border to another, etc.
Territorial residential development zone Zh-2
Zone of blocked development and low-rise construction.
In this zone, houses with several apartments are being built. Their maximum height is four floors. This is provided for by the main uses. They also include:
- blocked buildings with territory near the house;
- low-rise multi-apartment residential buildings;
- shops and markets;
- administrative buildings;
- facilities to serve area residents;
- hotels and childcare facilities;
- schools, gyms, cultural centers;
- libraries, post offices, pharmacies.
The list of conditional VRIs includes: dormitories, individual housing, clinics, shopping malls, markets, veterinary hospitals, etc. Among the auxiliary types: children's and sports grounds, parking lots, garages, squares, boulevards and the rest.
What is a low-rise residential development?
In current legislation, the concept of low-rise residential development is not clearly defined.
The Town Planning Code distinguishes three main low-rise buildings:
- Individual residential buildings (IDH). They are single-apartment buildings with a personal plot on which it is allowed to erect various outbuildings, grow vegetables and ornamental plants, plant fruit trees and shrubs. The land usually belongs to the owner of the site.
- Blocked residential buildings, which have become widespread for the following reasons:
- the use of common walls allows you to reduce the cost of building a house;
- the cost of land for one household decreases;
- the cost of supplying communications per household is reduced, and their technical implementation is simplified.
Blocked residential buildings are characterized by the following features:
- consist of blocks;
- one family lives in each block;
- each block has its own output;
- the blocks are connected by common walls;
- there are no openings in the common walls;
- each block has a separate output.
Block construction houses are characterized by a separate plot of land adjacent to the house for each block in which one family lives.
On the land it is allowed to build garages for personal cars, auxiliary and outbuildings, plant fruit trees, berry bushes, arrange beds, greenhouses, greenhouses, grow vegetables and other crops. The construction of recreation areas, children's play areas, and sports grounds is also permitted. We recommend that you read:
Types of permitted land use
- Low-rise apartment buildings:
- consist of one or more entrances;
- each entrance consists of several apartments;
- the number of entrances in the house does not exceed four;
- number of floors – from one to three.
In addition, Article 35 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation introduced the concept of medium-rise residential buildings (up to 8 floors) and multi-storey residential buildings.
Low-rise buildings include individual, blocked-off, multi-apartment, low-rise residential buildings, up to three floors inclusive.
Territorial residential zone Zh-3
Mid-rise construction zone.
Within this zone, the construction of mid-rise mixed-type buildings is envisaged. It houses facilities no higher than eight floors and with an extensive list of services for the local population. But other buildings can be erected. List of main VRI:
- mid-rise residential development;
- shops and markets;
- parks and sports grounds;
- primary and secondary schools;
- service companies;
- healthcare organization;
- cafes, snack bars and more.
Conditionally acceptable types are offices located on the first and second floors of residential buildings, or in separate buildings. They also include local shopping centers, water tanks, individual garages, car washes and other types of buildings. There are also auxiliary VRIs (parking lots, fire hydrants, etc.).
Territorial residential zone Zh-4
Multi-storey construction zone.
The height of residential buildings is nine or more floors. In addition to them, the construction of other objects that meet the requirements of urban planning regulations is allowed. Also included in the main types:
- multi-storey residential development;
- shops and markets;
- household services;
- cultural development institutions;
- sports activities;
- healthcare organization, etc.
Conditional types include religious use of land, entrepreneurship, placement of warehouses and vehicle maintenance. And auxiliary types are detached garages (owners are people with disabilities), guest parking lots, utility areas, etc.
ZH-2 DEVELOPMENT ZONE WITH LOW-RISE RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
The zone is intended for the development of multi-apartment low-rise (up to 4 floors, including attic) residential buildings; placement of social, cultural and consumer services for the population, mainly of local importance, and other objects in accordance with urban planning regulations is allowed.
Main types of permitted use
— Low-rise apartment buildings up to 4 floors, including attic
— Blocked residential buildings of 1-3 floors with adjacent plots
— Multifunctional service, administrative and business facilities in combination with residential buildings
— Hotels up to 4 floors, including attic
— Special residential buildings for the elderly and disabled
— Children's preschool institutions
— General educational institutions (schools)
— Multidisciplinary institutions of additional education (music, art, theater and other schools)
— Libraries, lecture halls of the house of creativity
— Institutions of culture and art (clubs, cultural centers, cinemas, museums, exhibition halls, etc.)
— Sports and recreational facilities (gyms, swimming pools, courts, skating rinks, etc.)
— Administrative, economic, business and public institutions
— Trade, catering and consumer services enterprises
— Baths, saunas, dry cleaners, hairdressers, laundries
— Pharmacies
— Dairy kitchens,
— First aid stations
— Strongholds for the protection of public order
— Post offices, post offices, telephone and telegraph points, bank branches
— PBX, regional communication centers
— Housing maintenance services, emergency services
Gardening, gardening
Conditionally permitted uses
— Individual residential buildings with private land plots
— Dormitories
— Outpatient clinics: territorial clinics for children and adults, specialized clinics, dispensaries
— Confessional sites
— Institutions of secondary specialized vocational education
— Boarding schools
— Social protection institutions
— Multifunctional shopping and entertainment centers and complexes
— Trade and exhibition complexes
— Markets
— Ambulance stations
— Box-type garages for individual passenger vehicles
— Veterinary hospitals
Auxiliary permitted uses
— Playgrounds: children’s, sports, utility, recreation
— Dog walking areas
— Guest parking
— Parking lots for individual passenger vehicles (open, built-in, underground, multi-level)
— Garages for individual passenger vehicles (open, built-in and attached, multi-level, box type for the disabled)
— Separate garages for disabled people
— Gardens, squares, boulevards
Limit (minimum and (or) maximum) sizes of land plots, maximum parameters of permitted construction, reconstruction of capital construction projects located in the Zh-2 zone
Requirements for the parameters of structures and boundaries of land plots in accordance with the following documents:
— Set of rules 42.13330.2011 “SNiP 2.07.01-89*. Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements”;
— SP 54.13330.2011 “SNiP 31-01-2003 Residential multi-apartment buildings”;
— SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises”;
— SP 30-102-99 “Planning and development of low-rise housing construction areas”;
— other current standards and technical regulations
| Minimum distance of residential buildings from the red line | m | |
| 2. | Minimum distance from the walls of preschool institutions and secondary schools to the red lines | m |
| 3. | Minimum distance between the long sides of buildings for buildings of 2-3 floors | m |
| 4. | Minimum distance between the long sides of buildings for 4th floor buildings | m |
| 5. | Minimum distance between the long sides and ends of buildings of 2-4 floors with windows from living rooms | m |
| 6. | Minimum gaps between the walls of buildings without windows from living rooms | m |
| 7. | Maximum building height | m |
| 8. | Maximum percentage of land plot development | % |
| 9. | Minimum land plot size | sq.m |
- The nature of the fencing of land plots on the street side must be maintained in a single style, with clearances, for at least one block on both sides of the streets in agreement with local governments. The maximum permissible height of fences is accepted to be no more than 1.8 m.
11. On the border with an adjacent land plot, it is allowed to install fences with gaps that provide minimal shading of the territory of the neighboring plot and a height of no more than 2.0 m (by agreement with adjacent land users - solid, no more than 1.7 m in height).
12. Hedges should not protrude beyond the boundaries of land plots, have sharp thorns and thorns on the side of the main facade (main facades) of the house, adjacent footpaths and sidewalks.
How to change the type of permitted use of a land plot in the territorial zone Zh?
Changing the type of permitted use within the territorial zone F is possible to one of the main VRI, conditionally permitted by the VRI, or with the assignment of an additional VRI.
- If the choice is between the main types indicated in the land use and development rules, it is enough to indicate the current and desired VRI in the application. The translation is carried out on request. The transfer may be hindered by encumbrances, restrictions on building density, or the inclusion of a land plot in various security zones.
- The assignment of additional VRI specified in the current PZZ is carried out in accordance with the agreed procedure, subject to the predominance of the building site of the main VRI over the object planned for placement with additional VRI (house + permanent garage). It is necessary to carry out preliminary approval by the architecture committee.
- The assignment of a conditionally permitted type of use is carried out by agreement, with the holding of public hearings, with the approval of the owners of neighboring plots. A thorough analysis will be carried out to ensure compliance with urban planning regulations, environmental protection zones, and security zones; coordination with the owners of linear objects will be required.
Economic justification may serve as a basis for changing the VRI to a conditionally permitted type of use. For example, the owner wants to build a shopping center on the site. In order for the plot to be assigned the appropriate type of use, it is necessary to refer to the active growth of new residential buildings in the area and, as a result, the lack of retail outlets for the population.
In addition to justification and petition to the authorized bodies, to change the type of permitted use in the territorial zone Zh you will need:
- the applicant's identity card;
- or documents for the organization;
- confirmation of rights to the site;
- extract from the Unified State Register or lease agreement;
- GPZU with information about the allotment.
Before applying, you should find out the current use and check the land for any restrictions or restrictions.
In the capital, applications and documents are submitted to the Moscow City Property Department. In the region, the appeal is submitted to the Committee of Architecture and Urban Planning of the local municipality. Based on the results of the review, a response is issued, and if the change in type of use is approved, new data is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate. By entrusting the collection of documents and filing an appeal to the authorized bodies to our lawyers, you receive a guarantee of a positive decision.
Zh-1. Development zone for low-rise residential buildings
It is allocated for the placement of residential buildings with 1-3 floors and social, cultural and other facilities necessary to create conditions for the development of the zone.
Minimum fire distances, maximum number of storeys of buildings, structures and structures, as well as other parameters of permitted construction and reconstruction not established in these rules, are adopted in accordance with the design assignment, current technical regulations and local urban planning standards.
| № | Type of permitted use | Limit (minimum and (or) maximum) sizes of land plots and maximum parameters of permitted construction, reconstruction of capital construction projects |
| Main types of permitted use | ||
| 1. | Low-rise residential buildings | 1. The minimum size of land plots is 0.06 hectares; The minimum size of a land plot for an existing residential building is 0.03 hectares. The maximum size of land plots is 0.15 hectares. 2. From the red line of the streets, the distance to a low-rise residential building is at least 6 m; from the red line of passages - at least 3 m. 3. Minimum fire distances: - between buildings (as well as between outer buildings and groups of buildings in adjacent areas) should be taken in accordance with current technical regulations (current standards); for individual residential buildings, the specified distance must be at least 6 m. Blocking of residential buildings, as well as outbuildings on adjacent land plots, is permitted by mutual agreement of homeowners during new construction, taking into account fire safety requirements. 4. The distance to the border of the neighboring land plot must be at least: - from a low-rise residential building - 3 m; - from buildings for keeping livestock and poultry - 4 m; - from bathhouses, parking lots and other buildings - 1 m. 5. Maximum number of floors - 3. 6. Maximum percentage of development - 30% for individual residential buildings, 50% - for low-rise and multi-apartment blocked and sectional residential buildings. |
| 2. | Individual residential buildings | |
| 3. | Dorms | 1. Maximum percentage of construction – 30%; 2. Other parameters are determined in accordance with current urban planning standards. |
| 4. | Buildings of financial institutions | 1. The dimensions of the land plot are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Buildings of credit and financial institutions are recommended to be located with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. In residential areas, administrative buildings should be located along the building line facing the red lines of the block (microdistrict). 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 5. | Public order points | 1. The dimensions of land plots, location features, number of storeys and other parameters are determined according to the design instructions and in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 6. | Objects of culture and art of regional and local significance | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. It is possible to place built-in and built-in-attached cultural and art objects in residential areas. 2. Buildings of cultural and art objects are recommended to be located with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 7. | Objects of preschool education | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Preschool education facilities should be located with a minimum distance from the red lines of 25 m, in areas remote from main streets, utility and industrial enterprises, and parking lots. In the new design of preschool education facilities, they are designed to be free-standing with a capacity of no more than 350 seats. The design of attached preschool education facilities is allowed in cramped multi-storey buildings, provided there is a separate fenced area with separate entrance and exit, the capacity of such facilities is no more than 140 places. 3. Maximum number of floors – 2. 4. Maximum building percentage – 40%. 5. The area of landscaping on the territory of the preschool education facility must be at least 50%. |
| 8. | Objects of primary and secondary general education | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Newly designed primary and secondary general education facilities should be located on a separate site with a distance from the red line of at least 25 m. The capacity of such facilities should not exceed 1000 people. 3. The maximum number of floors is 3; in dense buildings, 4 floors are allowed. 4. The maximum percentage of construction is 40%. 5. The area of landscaping on the territory of the preschool education facility must be at least 50%. |
| 9. | Objects of additional education for children | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. The minimum setback from the red line is 25 m. 3. The maximum percentage of development is 40%. 4. The area of landscaping on the territory of the facility for additional education of children must be at least 50%. |
| 10. | Outpatient clinics | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. The minimum distance from the red lines is 30 m, the recommended distance from residential and public buildings is at least 30-50 m, depending on the number of floors of the outpatient clinic. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. 4. Maximum number of floors – 3 floors. |
| 11. | First aid stations | 1. The dimensions of land plots, location features, number of storeys and other parameters are determined according to the design assignment and in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 12. | Pharmacies | 1. The dimensions of land plots, location features, number of storeys and other parameters are determined according to the design assignment and in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. Pharmacies can be located in separate low-rise buildings, built-in or built-in-attached to the first floors of multi-apartment residential and public buildings. The placement of pharmacies is allowed along the building line facing the red lines. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 90%. |
| 13. | Objects of consumer services for the population of district and local significance | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. In a residential area, it is allowed to place public service facilities for the population that do not have a sanitary protection zone, mainly built-in and built-in. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 14. | Public catering facilities | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. In the area of low-rise residential development, it is allowed to place public catering facilities with a number of seats up to 50. 3. It is recommended to place separate public catering facilities with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 4. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 15. | Retail objects | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. In the zone of multi-storey residential development, it is allowed to place built-in, attached and built-in retail trade objects with a selling area of up to 250 sq.m; free-standing shopping complexes with a retail area of no more than 1500 sq.m. 3. It is recommended to place separate retail facilities with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 4. The maximum number of floors is 2 floors. 5. The maximum percentage of development of land plots of shopping complexes is 60%. The maximum percentage of development of land plots for retail trade objects is 80%. |
| 16. | Fire protection facilities | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Setback from the red line – 10 m. 3. Maximum percentage of development – 60%. |
| 17. | Sports and recreation facilities | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. It is recommended to design built-in and built-in-attached sports and recreational institutions in residential buildings that form the development front of residential streets. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 18. | Built-in and built-in-attached parking lots | 1. Design features, number of parking spaces and other parameters are determined according to the design assignment, current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. |
| 19. | Open ground parking lots | 1. The area of the site for parking one passenger car should be 25 sq.m., if the parking lot adjoins the roadway - 22.5 sq.m. |
| 20. | Engineering and technical support facilities of district and local significance | 1. The dimensions of land plots, location features, number of storeys and other parameters are determined according to the design assignment and in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. |
| 21. | Communication facilities and structures of regional and local significance | |
| 22. | Public toilets | |
| 23. | Street and road network | |
| Auxiliary permitted uses | ||
| 1. | Recreational areas for children and adults | 1. Specific dimensions of the sites are 0.7 sq.m/person. 2. The distance from the windows of residential and public buildings is at least 12 m. |
| 2. | Recreational areas for adults | 1. Specific dimensions of the sites are 0.1 sq.m/person. 2. The distance from the windows of residential and public buildings is at least 10 m. |
| 3. | Sites for economic purposes | 1. Specific dimensions of the sites are 0.3 sq.m/person. 2. The distance from waste disposal sites to the windows of residential and public buildings is at least 20 m. |
| 4. | Sports grounds | 1. Specific dimensions of the sites: 2 sq.m./person. 2. The distance from the windows of residential and public buildings is at least 10-40 m, depending on the noise characteristics. |
| 5. | Green spaces | 1. The area of the green area of the microdistrict (block) of low-rise residential development (excluding areas of general education and preschool educational institutions) must be at least 6 square meters. per 1 person or at least 25% of the area of the microdistrict (quarter). The share of green spaces in non-residential areas within the urban planning zone Zh-1 should be at least 40%. |
| 6. | Guest parking | 1. The specific size of the territory for placing guest parking lots to serve residents of a residential microdistrict is 2.0 sq.m./person. 2. The number of spaces in on-site guest parking lots is determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 3. The area of the site for parking one passenger car should be 25 sq.m., if the parking lot adjoins the roadway - 22.5 sq.m. |
| 7. | Dog walking areas | 1. Specific dimensions of the sites are 0.1 sq.m/person. 2. The distance from the windows of residential and public buildings is at least 40 m. |
| Conditionally permitted permitted uses | ||
| 1. | Administrative buildings | 1. The dimensions of the land plot are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Administrative buildings are recommended to be located with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 2. | Mid-rise residential buildings | 1. The minimum plot size is determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Residential buildings with apartments on the first floors should be located, as a rule, indented from the red lines. Along the red line it is allowed to place residential buildings with public premises built into the ground floors or attached. 3. The distances between houses within a block (group of houses) are taken in accordance with fire safety standards and insolation standards, while the distances (household gaps) between the long sides of mid-rise residential buildings with a height of 2-3 floors must be at least 15 m, and a height of 4 floors - at least 20 m, between the long sides and ends of the same buildings with windows from living rooms - at least 10 m. In conditions of reconstruction and in other difficult urban planning conditions, these distances can be reduced subject to insolation and illumination standards and ensuring that residential areas are not visible premises window to window. 4. Maximum number of floors – 4. 5. Maximum building percentage – 35%. |
| 3. | Multi-storey residential buildings | 1. The boundaries and sizes of plots in multi-apartment residential buildings, which are in common shared ownership of the owners of premises in multi-apartment buildings, are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. Residential buildings with apartments on the first floors should be located, as a rule, indented from the red lines. Along the red line it is allowed to place residential buildings with public premises built into the ground floors or attached, and on residential streets in the conditions of reconstruction of existing buildings - residential buildings with apartments on the ground floors. 3. Maximum number of floors – 16 floors. 4. The maximum percentage of construction is 30%. 5. The minimum size of a land plot for an existing residential building is 0.03 hectares. |
| 4. | Hotels | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. It is recommended to place hotels with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 3. The maximum number of floors is 3. 4. The maximum building percentage is 30%. |
| 5. | Gardening | 1. Sizes of land plots: - within the boundaries of land plots of gardening associations. |
| 6. | Personal subsidiary plot | 1. Sizes of land plots: - for personal farming - from 0.01 to 0.15 hectares. |
| 7. | Horticulture | 1. Sizes of land plots: - for gardening - from 0.01 to 0.06 hectares. |
| 8. | Housing and communal services facilities | 1. The dimensions of land plots, location features, number of storeys and other parameters are determined according to the design assignment and in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. Placement on the intra-block territory is not allowed. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 9. | Veterinary hospitals | |
| 10. | Hotels for animals | |
| 11. | Objects of wholesale and small wholesale trade | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. It is recommended to place separate retail facilities with a minimum distance from the red line of 6 m. 3. The maximum number of floors is 2. 4. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 12. | Car service companies | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. In residential areas, it is allowed to locate only car service centers with a sanitary protection zone of no more than 50 m in separate buildings facing the red lines of main streets. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 13. | Religious buildings | 1. The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with local urban planning standards. 2. It is recommended to place churches with a minimum distance from the red line of 3 m. 3. It is recommended to design parish churches as one-story, one-story with a basement, or two-story. 4. It is possible to build built-in and built-in-attached churches. 5. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 14. | Industrial enterprises and municipal warehouse organizations of IV-V hazard classes | 1. The dimensions of land plots, maximum number of storeys, gaps between buildings and other limiting parameters are determined in accordance with current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. In residential areas, it is allowed to locate only industrial enterprises and utility and warehouse organizations of no higher than class V sanitary hazard in separate buildings facing the red lines of main streets. 3. The maximum percentage of construction is 80%. |
| 15. | Facilities related to enterprise services | |
| 16. | Warehouse facilities of various profiles | |
| 17. | Temporary objects | The sizes of land plots are determined in accordance with the design assignment, current technical regulations and local urban planning standards. 2. In residential areas, temporary retail facilities may be located along the building line facing the red lines of the block (neighborhood). 3. Maximum number of floors – 1. |
In cases where the border of the sanitary protection zone of industrial enterprises and other facilities that require its establishment passes through the territorial zone Zh-1, new construction on a section of the territorial zone that falls within the boundaries of the sanitary protection zone is possible only after the development of a project to reduce the borders of the sanitary -protection zone, if its new borders do not pass through the territorial zone. If part of the territorial zone is located in a zone set back from an external highway, new construction is possible subject to the requirement of compliance with regulatory noise protection.
How to transfer your land plot to the territorial zone Zh?
Changing the territorial zone involves adjusting the gene. plan and rules of land use and development. For these purposes, an appeal is submitted to the authorized bodies (local municipality or City Commission in the Moscow Committee for Architecture and Architecture). The application must provide justification for such changes:
- The territorial zone is changing in order to increase the efficiency of use of the site or real estate - present the facts of the inefficiency of the land in its current state, attach the corresponding calculations.
- The owner of the plot suffers harm - it is necessary to analyze in detail all aspects of it (reduction in the value of the plot, reduction in the cost of real estate, etc.).
The reasons may be different. For example, the applicant purchased a plot of land planning to build an apartment building on it, but the current territorial zone only allows the construction of parking lots and other similar facilities. By proving the feasibility of building a residential building, you will convince the commission to change the current zone.
When making changes to development rules, authorized bodies try to maintain a balance between the interests of owners and public interests. When a change in the territorial zone leads to the development of the territory, it will be easier to implement it. Sometimes the procedure requires the organization of public hearings, in other situations the decision is made by the head of the local municipality.
A reasoned response is given based on the documents received and the petition. The following must be attached to the application:
- a situational plan, where the boundaries of your site and the real estate located on it are marked;
- documentation for the land, including an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, a lease agreement or other confirmation of rights;
- a diagram of the planned development, which indicates the location of objects and their economic indicators.
It may take up to two months for your application to be processed. Geobureau lawyers will help with the transfer of your land plot to the territorial zone Zh.
How to change the territorial zone of a land plot Zh-1 – Zh-4 to another zone Zh?
When the current territorial zone does not allow the construction of necessary real estate objects or the conduct of certain activities, it is necessary to contact the authorities to change it. In Moscow, the application is submitted to the City Commission on Urban Planning, Land Use and Development. In the region, changes in territorial zones are carried out by local authorities (the head of the municipality).
To change the zone Zh-1 - Zh-4 to another, but within the territorial zone Zh, serious reasons will be required:
- the plot was mistakenly placed in two different zones, making it impossible to obtain a building permit or otherwise use the land;
- the selected zone provides for the conduct of activities (usually commercial), but the current zone limits this;
- it would be more profitable to use the site in a new territorial zone (the integrated development of the area will improve, the efficiency of land use will increase, etc.).
The reasons for transferring an allotment from one zone to another must be worked out in detail. They are indicated in the application, and the attached documentation must contain evidence of the need to change the zone. For these purposes, you can contact expert organizations to carry out calculations.
Most often, owners apply to change the territorial zones Zh-1 to Zh-2, Zh-2 to Zh-3, Zh-3 to Zh-4, i.e. In order to extract commercial benefits, the building density is increased. An increase in building density may be hampered by the lack of infrastructure necessary for living - the load on kindergartens, schools, clinics, etc. Sometimes, to overcome this limitation, developers take on additional obligations for the construction of socially significant facilities.
Otherwise, the procedure for changing the territorial zone is standard:
- the application is submitted to the authorized body;
- a draft amendment to the PPL is created;
- public hearings are held (if the situation requires);
- the project and recommendations are reviewed by the head of the administration;
- a decision is made and updated data is entered into the Unified State Register.
Our company’s lawyers will go through preliminary approvals, help you draw up a substantiated application, and transfer the plot of land to a suitable territorial zone.
Additional materials:
Changing the permitted use of land plots - services
Changing the category of land plots - services