Not all lands in our country allow residential construction. The law clearly defines restrictions on the construction of buildings on certain categories of land plots. In this article we will look into whether it is permissible to build a house on a plot of land for private household plots, under what conditions this is possible, and what legal subtleties the procedure for obtaining permission to build a building involves.
Is it possible to build a dwelling on a private plot?
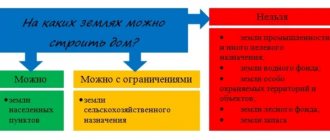
On the land of private household plots, in addition to growing agricultural products, raising livestock or poultry for your own needs or for sale, you can build a house for permanent residence.
The possibility of building a house on such a site depends on its location.
If the land is located outside populated areas, the plot is considered field land and, on the basis of clause 3, article 4 of the Federal Law “On Personal Subsistence Farming”, can be used for its intended purpose, but without the right to erect buildings on it.
In accordance with Art. 4 No. 112 Federal Law “On Personal Subsistence Farming”, a plot located inside the boundaries of populated areas is suitable for building a house and in some cases more convenient than a plot for individual housing construction. The tax on a residential building located on private household plot land, as well as on the plot itself, is significantly lower than the tax on individual housing construction (what are the taxes on private household plot land and property?).
You can find out which category the land belongs to from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. You can order it on the Rosreestr website or on the State Services portal.
Rules for maintaining private household plots in 2022
The management of private household plots is determined by the Law of July 7, 2003 No. 112-FZ (as amended in 2021). The land plot is allocated for the following purposes:
- cultivation of garden and vegetable crops;
- breeding livestock and poultry, as well as other animals (for example, fur animals);
- floriculture;
- growing grains, melons and other agricultural crops;
- use for haymaking and growing animal feed.
Important! The lands of private household plots in 2022 should be used for their intended purpose, but not for commercial purposes. The activity can be carried out by the owner of the site and his family members. It is allowed to sell surplus grown or produced products (goods). When satisfying your own needs, products are not taxed.
What kind of buildings are allowed?
On the land of private household plots, which belongs to the category of lands of settlements, the construction of houses with a height of no more than three floors for one family is allowed. These can be cottages or small private houses built from approved materials. The construction of production, utility and other buildings is also permitted. Such buildings include garages, bathhouses, sheds, warehouses and other buildings permitted by the VRI.
All buildings must comply with sanitary, environmental, fire and other standards.
It is prohibited to erect buildings higher than three floors and consisting of several apartments. It will not be possible to obtain permission to build a townhouse, multi-apartment high-rise building or commercial building (shop, kiosk, etc.) without changing the category or obtaining an additional VRI.
More details about what can be built on the lands of private household plots are written in a separate article.
What do you need permission for?
In 2021, the law on preferential registration of constructed permanent buildings is still in force. Thus, a previously erected but not registered building can be registered as a property in 2021 without a building permit.
Buildings for which construction permission is not required include all non-permanent buildings, i.e. not having a very deep foundation, which can be disassembled, moved, or disconnected from communication networks.
Such objects include sheds, some garages, buildings for keeping animals, sheds, warehouses and other auxiliary structures. When constructing such facilities, you only need to be guided by the requirements of SNiP. For the construction of capital objects - residential buildings, extensions to them, permission from local authorities will be required.
Consequences of lack of permission
If construction begins without permission, the administration of the municipality in whose department the private plot is located has the right to impose a fine on an individual in the amount of two thousand rubles. Such fines may be imposed throughout the construction period.
If a building is erected in violation of construction or other standards without the consent of neighbors, it will acquire the status of unauthorized construction. It will have to be legalized in any case, but at greater costs than if you obtain permission before construction begins.
What to do if a residential building is erected unauthorized?
Registering a house built on your own land is currently quite simple , if the structure:
- does not violate construction, fire and other regulations;
- does not interfere with others, does not violate their rights and does not pose a threat;
- does not cause any complaints from municipal authorities;
- built on a plot of private household plots related to the lands of settlements;
- has no more than three floors.
If the house meets all of the above requirements, you can obtain ownership rights administratively. To do this you need:
- Take an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate for the land plot, which should indicate the owner and classification of the land to which the private plot belongs.
- Obtain from the MFC or other authorized body the GPZU (urban planning plan for the land plot).
- Based on the GPZU, indicate the location of the constructed facility.
- Submit an application, house layout diagram and GPZU to the MFC or other municipal body to obtain a building permit.
- After receiving permission, order a technical plan from a cadastral engineer.
- Then submit all documents again to the MFC to receive an extract confirming ownership of the house.
Important! The algorithm for registering illegal construction may differ depending on the region where the object is located.
If for some reason it was not possible to register the property administratively, you will have to contact the judicial authorities.
You cannot immediately go to court without trying to formalize the construction in the usual manner. To apply, you must have a registration refusal on hand.
When applying to the court, you will need to pay a state fee, which is calculated from the cost of the unauthorized construction project. This will require an assessment of the constructed house.
It is better to draw up a statement of claim from an experienced specialist to avoid mistakes and refusal to satisfy the claim. For the court you need to provide:
- Claims and applications for participants in the case.
- Title documents for land.
- A report on the appraisal of the property that is the subject of the claim.
- Technical plan of the building or other document confirming the presence of an unregistered house.
- Documents confirming the absence of violations during the construction of an unauthorized building.
- Refusal to register administratively.
- Receipt for payment of state duty.
After considering the case and making a positive decision, you need to contact the MFC with a court order, passport and registration certificate for the house to obtain ownership rights.
Standards for the location of buildings on the land of private household plots
The owner of the land plot submits an application to the competent department of the commune, which is authorized to resolve this issue. They can be submitted to the MFC. After inspection, a construction permit or a reasoned refusal is issued within 10 days.
- If the detected defects are eliminated, the application can be resubmitted. Refusal to issue a permit may be appealed in court. The building permit is valid for 10 years.
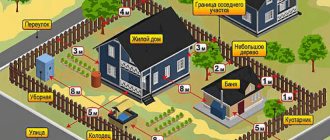
- Each building on private property must be located in accordance with construction, sanitary and fire safety standards:
- The distance to the road must be at least 5 m, and to the roadway - 3 m.
- The wall of the house must be at a distance of at least 1 m from the border of the land plot or fence.
- The distance between brick structures must be at least 6 m, and between brick and wooden structures - at least 10 m. Between wooden structures there must be at least 16 m.
- The distance from a residential building to toilets, rooms for animals and birds and lagoons must be at least 12 m.
It is necessary to maintain a distance of at least 8 m from outbuildings and bathhouses, wells, and septic tanks.
Construction registration procedure
It is much easier to obtain a building permit before building a house than to prove ownership after construction.
You can obtain permission by submitting an application to the MFC or another authorized body, depending on the region. Documents required:
- GPZU (urban planning plan of the site), is ordered from the MFC or from the architecture committee of the administration in whose department the land plot is located. The service is free. Time to receive 30 days.
- SPOZU (scheme of planning organization of a land plot). The diagram can be ordered from any specialized organization (for a fee, prices vary) or made by yourself.
- Certificate of ownership or other document for the land plot.
If the SPOZ is done independently and there are no difficulties in obtaining a town planning plan, the building permit will be completely free. The duration of the service is 10 days.
After completion of construction, you need to call a BTI technician or cadastral engineer to the finished house to draw up a technical construction plan.
The cost ranges from 10 to 15 thousand rubles, depending on the region and the cost of the engineer’s services. The production period for the registration certificate is 2 weeks.
How to register?
To register a new house built on a private plot with Rosreestr and register it for cadastral registration, you need to contact the MFC.
Important! Be sure to write an application for registering the property with cadastral registration! Otherwise, the application for property registration will be suspended.
Required documents:
- Applicant's passport.
- Document on land ownership.
- GPZU.
- Scheme with designated new building (SPOZU).
- Technical plan.
- Construction permit.
- Receipt of payment of the state duty (in 2021, the amount of the state duty is 2 thousand rubles).
The service is provided within 10 working days from the date of application.
After successful registration, you will receive an extract from Rosreestr confirming ownership of the new house.
Nuances for a guest house
The construction of a guest house on the plot of private household plots is permitted, subject to compliance with all the norms of existing legislation described above. The boundary of a house under construction must be no less than six meters from the neighboring plot and three meters from the main house. The package of documents for a guest house does not differ from the package for the main building if the structure is recognized as permanent.
If the site does not meet the established standards, the registration of the house as residential may be refused.
If the guest house is being built for temporary residence, a building permit will not be required. To register such a building, you only need a technical plan, documents for the site and an application.
Obtaining permission to build a house
To obtain permission to build a house, you must provide the following documents:
- an application addressed to the head of the local government unit;
- A document confirming the right to own or use a land plot (extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, certificate)
- Identity card of the owner of the site;
- GPZU;
PSEZ indicating the location of the construction site for which the application is being submitted for permission;
a detailed description of the house, its purpose, plan and technical characteristics (if the site is located on an area of historical significance, an illustration of the house’s exterior must be attached).
Confirmation of compliance with project documentation
According to Article 51 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, a building permit is a document confirming the compliance of project documentation with the requirements established by town planning regulations , a land planning project and a land surveying project (except for those cases when this is not required by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Only this document gives the right to construct and reconstruct capital buildings; without it, the construction will be called unauthorized construction and in most cases is subject to demolition.
This paper looks like this:
- in the upper right corner it says “Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 24, 2005 No. 698”;
- further indicates to whom it was issued (full name of the citizen or name of the legal entity, postal and actual address);
- in the center of the paper there is a “Construction Permit” (the number, name of the authorized federal executive body, the capital construction project, the address of the future structure are indicated);
- The validity period of the permit is written below, as well as for how long it was extended.
Reasons for refusal
If you were not given permission, you will be given a reasoned refusal.
Possible reasons:
- lack of land rights;
- non-compliance of documents with the urban planning plan (the object does not belong to the permitted types of buildings, the maximum parameters of the object are not observed, the minimum setbacks are not taken into account, as well as the location of the object in the restricted zone);
- non-compliance of documents with the requirements: for construction, reconstruction and permissible deviations;
- lack of necessary documents, in accordance with parts 7 and 9 of Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- lack of a communications plan;
- the object has already been built.
We can say that refusal follows in two cases:
- if errors were made in the preparation of documents;
- if construction has already been completed.
To turn things around:
- in the first case, it is necessary to correct all the shortcomings;
- in the second, try to appeal the decision in court.
Remember that by law, if your private household plot type of land is field, then any buildings are prohibited .