Happy owners of garden plots located in picturesque areas often decide to build a residential or garden house on their land.
Some people need a place to relax while gardening, others dream of a cottage where it will be comfortable to stay all year round.
how legal such construction is and what difficulties may be encountered.
Legal norms for the use of garden land
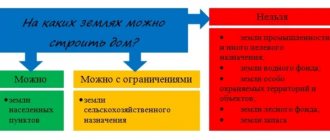
In accordance with the modern classification, there are 2 types of permitted use of land related to gardening:
- Type 1.5 involves conducting activities for the industrial cultivation of perennial crops.
- Type 13.2, in addition to agricultural activities, allows the construction of outbuildings and a garden house on the site.
Thus, only owners of plots with VRI 13.2 “Gardening” .
The category of land is also important: it is better if the plot is located on the territory of populated areas.
Additional information on garden plots located within the boundaries of populated areas can be obtained here.
If the category of land on the gardening plot is agricultural, then it will be very difficult to register there; only a garden house for recreation is allowed to be built there.
Detailed information can be found in the feature article.
What is a "dacha"?
Every year, from spring to late autumn, most of us spend a lot of time at our dachas, because fresh vegetables, berries and fruits grown with our own hands are much tastier and healthier. In addition to beds, bushes and trees, our “dachas” can contain various objects.
When we use the word “dacha,” we most often do not think about the type of site on which it is located, nor about what is located there.
Depending on the intended purpose of the site and the characteristics of the objects located at the “dacha”, several situations may arise, which we will consider further. The legislation does not contain the term “dacha”. Therefore, for convenience, I propose to use the word “dacha” to directly denote an object located on the site where you grow something.
Differences in the construction of a building for permanent and seasonal residence
The set of rules SNiP 30-02-97*, regulating garden buildings, highlights the difference between a garden and a residential building, in the possibility of registering residence in the latter.
Garden
Let's take a closer look at the features of a garden house:
- Is a residential property used for recreation
- Living inside it is temporary
- Such a residential building cannot be divided into separate apartments
- Construction is possible without obtaining a permit
A garden house can be considered suitable for living if the following are met:
- fire safety requirements,
- building codes and regulations (intact floors and walls, reliable foundation, protection from melt water),
- sanitary requirements (sufficient insolation, the presence of thermal insulation of walls to maintain optimal temperature inside the building),
- provision of engineering infrastructure (heating, lighting, water supply, sewerage, ventilation).
Residential
A residential building can be used as a permanent residence . Registration is permitted there.
When starting construction, it is necessary to clearly determine whether the building will later be designated as residential. Since the cost of refurbishment of a summer house practically corresponds to the construction of a new residential property.
There are currently several problems:
- many garden plots are not used for their intended purpose,
- owners do not develop plots due to the great difficulties with subsequent registration.
To solve them, Law No. 217-FZ was developed, which expands the concept of a garden plot and prescribes the possibility of building a garden or residential building on it.
At the same time, there are no restrictions on the category of land.
The law comes into force on January 1, 2019, after which unregistered seasonal country houses are also recognized as garden houses .
Re-registration of documents for constructed objects is carried out at the request of the owner.
The VRIs covered by the law include 13.2 and 13.3. Thus, owners of plots with such permitted use can construct garden and residential buildings.
Bringing the old VRI to the current classification is carried out at the initiative of the owner, but is not mandatory.
Peculiarities of registration of the purchase and sale of a land plot in the Moscow region (Moscow region)
In general, land real estate transactions in the Moscow region are mainly conducted through special agencies operating in the same region where the land is located. Since they have sufficient information about all local requirements and legal nuances of transactions. In addition, personal contact with the local administration of such realtors significantly speeds up the process. These are the realities of the land business in the Moscow region.
- The objects of purchase and sale transactions can only be land plots that have undergone state cadastral registration. When concluding a contract, the seller must provide the buyer with all available information about the encumbrances of the land plot (if any) and restrictions on its use.
- The following terms of the land plot purchase and sale agreement are considered invalid: - establishing the seller’s right to buy the land plot back; — limiting the disposal of the land plot by the new owner (mortgage, lease, transactions with the plot); - limiting the seller’s liability provided that third parties present property rights to this object. These conditions also apply to the conclusion of a land exchange agreement.
- If the seller provides the buyer with false information about the encumbrances of the land plot and restrictions on its use in accordance with the permitted use, about permission to develop this land plot, about the use of neighboring land plots that have a significant impact on the use and value of the land plot being sold, about the quality of the land, which may affect the buyer’s use of the land plot, as well as other information that may influence the buyer’s decision to purchase this real estate property and the requirements for the provision of which are established by law, the buyer has the right to demand a reduction in the purchase price or termination of the purchase and sale transaction of the land plot and compensation for the damage caused to him.
Registration of land sale
In order to quickly complete a transaction for the sale of a land plot, it is advisable to prepare for it as thoroughly as possible. Study all the nuances and collect all the necessary documents. There must be a certificate of ownership of the land confirming that the person who intends to participate in the transaction, as the seller, can solely dispose of this land plot. Before the sale of a land plot begins, the seller carries out a geodetic check of the boundaries of the land plot. It is carried out by geodetic organizations on the basis of notarized copies of the certificate of ownership of the land plot, the technical passport of the BTI (if there are buildings), and the act of agreement with the land owners along the boundaries of the plot. Before selling a plot of land, its owner must obtain a cadastral plan from the land committee in the area where the land is located. The presence of this document will save the seller from unnecessary delays during the land sale transaction.
And now, when the title documents have already been collected, the cadastral plan of the site has been received, all the necessary certificates from technical and utility services have been prepared, the seller of the site must receive a certificate from the tax inspectorate about the absence of land tax debts. You must also obtain a certificate from the district authorities of the State Register stating that there are no restrictions on the use of land. After completing all these actions, we can assume that the seller is documented to be ready to sell the land.
The seller must provide the buyer with information about the area and size of the land plot and the buildings on it (if any) about the possibility of flooding and fire hazards. Information is also provided on decisions that limit the possibility of exploiting a property: liens and other encumbrances (rent, share in joint ownership of land, restrictions on the use of a reservoir and berth, etc.). However, the responsibilities of a conscientious land seller should additionally include informing the buyer about all the important features of the operation and formation of the value of the property. For a land plot, this is, first of all, information about the possibility of residential construction on the site (or lack thereof), the presence and environmental cleanliness of adjacent natural formations: forest lands, reservoirs, access roads to the land plot, distances from utility connection points, service centers and shops, the presence and character of neighbors. It is important for the seller to complete all this so that the sale of the land plot is carried out correctly and without subsequent claims.
Is it possible to get a registration?
Current law No. 66-FZ does not provide for temporary or permanent registration in a garden house . However, the decision of the Constitutional Court changed the current situation and made it possible to register through the court.
If registration is necessary, the owner can act in one of two ways:
- Convert a non-residential property to a residential one by contacting the authorized body of the local administration. A redevelopment project will be required, agreed upon by several authorities.
- Recognize the garden house as residential, suitable for living, in court. After a positive decision, registration is possible.
The most popular method is a court decision ; it requires less financial costs and time.
For a property to be recognized as residential, it must comply with all
- sanitary,
- construction,
- firefighters
standards.
If the garden house is the only available place for permanent residence, the likelihood of a positive court decision increases.
The package of documents attached to the claim for filing a lawsuit includes:
- The conclusion of an expert organization on the compliance of the object with SNiPs, issued on the basis of title documents and a technical passport.
- Conclusion of the SES on the compliance of the facility with sanitary standards. If the authority does not issue the required certificate, it can be replaced with a similar expert opinion.
- Conclusion of OGPN on compliance with fire safety standards or a similar conclusion of a third-party organization.
- A document confirming the actual residence of a citizen in a garden house, for example, a certificate from the chairman of the SNT.
After a positive court decision is made, you must obtain a mailing address . To do this, contact the local administration.
If the plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area, then assigning an address does not cause difficulties. If the plot is located at a short distance, the owner can initiate its inclusion within the boundaries of the locality. This decision is made at the local leadership level.
It is also possible to obtain an address without including the plot of land in the boundaries of the settlement, but the procedure is more complicated. The postal address of such houses will coincide with the address of the site on which it is located.
After assigning a postal address, the owner initiates cadastral changes and receives a new technical passport for the garden house as a residential property.
Responsibility for unauthorized constructions
Liability for buildings in a gardening non-profit partnership without obtaining permission is provided for in Art. 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The violator will not be able to obtain documents confirming ownership, and he will be banned from using and living. It is also impossible to sell, donate or bequeath such a building.
According to Art. 25 Federal Law No. 169 “On architectural activities in the Russian Federation”, as well as Art. 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a citizen may be required to demolish an unauthorized structure, as well as return the site to its original appearance.
Only a court can recognize a building as illegally erected by issuing an appropriate decision, which must enter into legal force.
District commissions and local administrations do not have the right to demolish a house on their own or force the owner to do so. But their powers include issuing orders that may become the basis for the imposition of administrative fines. In addition, they have the right to apply to the court to declare the building illegal, including in relation to buildings for which the ownership rights were registered with violations.
Article 24 of Federal Law No. 169 provides for the imposition of administrative sanctions. In particular, they may be required not only to eliminate the violations committed, but also to hold them accountable in accordance with Art. 9.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, namely:
- for violation of technical regulations and requirements for the construction of buildings, impose a fine on an individual in the amount of 1,000 to 2,000 rubles;
- for deviations from the design values of building parameters, which may pose a risk of being fined 2,000 - 4,000 rubles;
- Repeated violation will result in a fine of up to 5,000 rubles.
Permission to build a residential building
A special document that allows the developer to carry out reconstruction and construction of permanent buildings is called a building permit.
Based on the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (subclause 1, clause 17), it is not required for construction on garden plots.
In order to avoid problems with neighbors during the construction of objects, it is necessary to take into account the rules for the location of buildings from borders, roads, and other objects according to SNiPs.
If it is planned to build an object, subsequently registered as an individual residential property, then the owner can obtain permission in a simplified manner in accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Part 9, Article 51).
To do this, he needs to contact the body authorized in the field of urban planning and submit the following documents:
- of a legal nature,
- urban plan,
- plot layout diagram with the designated location of the facility under construction.
The obtained permission will be submitted to the court.
Details
Requirements for objects
How to obtain a permit so that you can start building a house in SNT? First, make sure that both the future house and the land fully comply with legal requirements. The following requirements apply to residential buildings on land for gardening:
Up to 3 ground floors are allowed.- The height of the building should not exceed 20 meters.
- The minimum housing area is 1 living room (from 8 square meters), a living room (from 12 square meters), a dining room or kitchen (from 6 square meters), and there must also be a storage room, a bathroom and a toilet.
- The minimum ceiling height from floor to ceiling should be 2.7 meters, and in the attic 2.3 meters.
- The living room and kitchen must have windows that let in natural light.
- It is necessary to arrange a ventilation, heating, drainage system, as well as water supply and electricity.
- The minimum temperature in the house during the heating period should be 20 degrees in the living room, 24 degrees in the bathroom, and in the toilet and kitchen from 18 degrees.
Please note that if you are planning to build a garden house and not a residential one, then you do not have to comply with the temperature requirements. There are also additional requirements for land allotment:
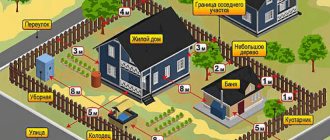
- There must be a minimum of 300 square meters of land.
- The minimum distance from the building to the neighboring border is 3 meters.
- The distance from the fence to the house wall is (minimum) 5 meters.
- The permissible distance from technical networks is from 0.6 to 10 meters (it all depends on the degree of pressure and the network).
So, let's move on to preparing the documents.
Obtaining a building permit in SNT: step-by-step instructions
Before starting the construction process, it is important to contact local administrative authorities and obtain permission. Otherwise, the construction will be declared illegal. Obtaining permission and registering rights in Rosreestr consists of such actions.
Preparation of documentation for local authorities
It is required to submit a notification about planning the construction of a garden or residential building. The notification must include the following information:
- Full name of the administration.
- Information about the applicant (registration or residence address, full name, passport details, telephone numbers and email address).
- Information about the land plot - cadastral number, type of use right (for rent or ownership), address, rights on the part of other people other than the applicant (if any), purpose of the land plot in accordance with the excerpt from the cadastre).
- Information about the property - type (residential or garden), type of work (reconstruction or construction), height, number of floors, area, all indents and distances).
- External description of the building - information about the architectural design, color scheme, graphic images (the appearance of the housing is required to match the specific region, which is why it is important for the applicant to get it approved by the cultural committee and the local administration).
- In order to obtain construction permits from SNT, be sure to attach to your application a diagram of the facility reflecting the location on the site.
- Additional information - which option is chosen for informing the applicant about the status of the application, consent to the processing of confidential data, and also confirmation that the building is indivisible.
- Signature and date of sending the notice.
Below is a sample. Also, copies of the Russian Federation passport and documents establishing land rights are required to be attached to the notification; if the applicant’s right is registered, then such documents do not need to be attached, and if there is no registration, then the condition becomes mandatory.
Contacting the administration
Next, you need to go to the department that is responsible for issuing permits for the construction of non-residential and commercial properties. As a rule, this is a committee or department for urban planning and architecture. If a plot of land is located in a territory with a special status (for example, an area with environmental protection), then it is required to send a notification with documents to the regional committee that manages such lands. If there are different methods for submitting documents to authorities:
Personal appeal to the administration.- Through the official website of State Services.
- By registered mail so that you receive notification of delivery (there is no need to notarize the documents).
Residents of the capital can also contact for help, appointment only by phone.
Getting permission
The municipality considers the application and makes a positive or negative decision. In the first case, a person receives a notification within 7 working days, and if the structure is on the territory of a cultural or historical monument, then the period for sending the notification increases to 20 working days. If there is no answer, this can also be regarded as a positive decision. The notice is valid for 10 years. But a negative answer may come in this case:
- The construction project contradicts the purpose of the land plot.
- The object does not meet the standards and technical requirements.
- The applicant does not have rights to the land (for example, the lease agreement states that all actions must be agreed upon with the tenant, but the applicant did not fulfill this condition).
If the shortcomings can be corrected, then in the future the applicant can apply to the administration again.
How to notify the administration about the completion of construction?
After this you need:
- Complete construction work before the end of the validity period of the permit issued by the municipality.
- Contact a cadastral engineer and get technical. site plan.
- Notify the administration about the completion of work (maximum period is one month from the date of completion of construction work, the methods are the same - directly, through the State Services website, MFC or by mail).
Notification of completion of construction will be similar to notification of planned work to obtain a permit. You only need to indicate the details of the document on the state fee for registration of rights in the register. The following documents must be attached to the notification:
- Those. site plan.
- A receipt for payment of the state duty for 2000 rubles (details can be obtained from the MFC or Rosreestr).
- An agreement on shared distribution if several people own a land plot at once).
Within 7 working days, the applicant will be notified that the residential property complies with the standards and legal requirements. But sometimes even those who claim that they have received permission to build on the SNT site, after notification of the completion of construction, receive the most pleasant letter stating that the requirements have been violated. The reasons may be:
- If the object was built without complying with technical parameters.
- If the house contradicts the purpose of the land plot.
- If the applicant provided false information.
Such cases are usually considered in court on an individual basis.
Registration of an object in Rosreestr
The last step in which the applicant does not need to apply to Rosreestr independently, since the application for registration is sent by municipal authorities. After dispatch, the owner will be informed. When registration is complete, registration can be considered complete. The owner receives an extract from the register. Moreover, if the municipality for some reason did not send an application, the owner can do it independently. In this case, Rosreestr sends a request to the municipality to obtain all the necessary information.
Liability for construction without permission
A building that was built without permission cannot be inherited, donated, or sold. Such a house does not have official documents, which makes legal transactions impossible. Illegal buildings can attract high taxes, which are several times higher than standard fees. If there is an illegally built house on a SNT site, the owner must go to court and prove that the property complies with safety requirements and urban planning standards. The resulting decision from the court is sent to Rosreestr. Sometimes the municipality itself goes to court to demolish an unregistered building, and to prevent such cases, filing a counterclaim is required.
How to change the status of a garden house into a residential one
The legislation establishes the following methods for converting a garden house to residential status:
- Reconstruction - in this case, the procedure is similar (first they notify the administration about construction, etc.).
- Applying to the housing authority with an application to change the purpose of the garden house (attach a technical plan and title documents for the property).
In the role of reconstruction, extensions can be used - additional garages, bathhouses, living quarters that are combined with the house. Attics and additional floors can also change house parameters, and therefore belong to reconstruction work. At the same time, major repairs, renovation of floors and roofs are not included in the reconstruction process. The transfer of non-residential premises in a house to residential premises can be considered a recommendation, despite the fact that the area of the house and the number of floors have not changed.
We do not recommend demolishing an old house and building a new one in its place, pretending that reconstruction has been carried out. It is better to order an inspection from a cadastral engineer - according to it, the house will be declared unfit for habitation, after which it will be allowed to be demolished, and then you can notify the municipality about the planned construction work. If this is not done, then local authorities may recognize the house as an unauthorized construction and refuse to register it, which will require the initiation of legal proceedings.
Nuances
You do not need to obtain a building permit from SNT if you plan to build a gazebo, bathhouse or garage. It will be enough to draw a plan, attach to it an application for registration, a receipt with payment for 2000 rubles, title documents for the land and send it by registered mail to Rosreestr. If you plan to build a bathhouse or a garage for a car, and the main house is not decorated or is missing altogether, then you will need a permit for the construction of such outbuildings. If this is not done, then the object will be recognized as an unauthorized construction, and then demands for demolition will be put forward.
Advantages and disadvantages
When deciding to start building your garden plot, it is important to understand all its pros and cons, and not act under the influence of a trend for your own country houses.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons, especially if you have no previous experience of living in a private home and caring for it.
What benefits does the owner receive when building a house on garden land:
- The plot is already owned or is much cheaper than for individual housing construction.
- Low payments for the use of utility infrastructure.
- No noisy neighbors or freeways outside your windows.
- Your own home is built in accordance with personal concepts of beauty, including exterior and interior decoration. Compliance with building codes is mandatory.
- The progress and speed of construction depends on your desire and financial capabilities.
- Favorable environmental conditions: clean air, water, land, natural sounds of wildlife around.
What are the main disadvantages of living on a garden plot:
- Building a house that meets all requirements and standards is expensive.
- SNT members pay considerable annual fees, which go towards maintaining infrastructure facilities.
- Low transport accessibility. Public transport outside the city runs on schedule, with large intervals. This leads to the need for each family member to have their own car.
- The infrastructure is poorly developed. Troubleshooting (broken wires, broken water tower) takes a lot of time.
- The peculiarities of the winter climate with heavy snow drifts impose restrictions on physical activity.
- Maintaining your home during the cold winter months requires significant effort.
- Registration in a garden house is possible only through the court.
- The arrangement of social and transport infrastructure, even for garden villages located within the boundaries of a populated area, is carried out at the expense of the owner-gardeners. The new law No. 217-FZ provides for co-financing programs for such expenses, but it is not yet known whether there will be funds for them in the regional budgets.
In some cases, the owner may initiate changes to the VRI of his plot. More details about the procedure can be found in a special article.
Read more about the main differences between garden land and individual housing construction in a separate article.