Would you like to consult a lawyer for free? Write to the chat on the bottom right or call the hotline, calls within the Russian Federation are free. We accept questions any day of the week.
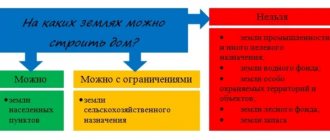
Some categories of land are designated for certain purposes and construction on them in 2022 is limited or prohibited. The question of whether it is possible to build a house on land for gardening interests many owners of such plots. It is regulated by Russian legislation and requires special consideration.
What can be built on gardening land
The rights of the owner of a land plot are determined by Art. 263 Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 40 Land Code of the Russian Federation. To answer the question whether it is possible to build a house on land for gardening, you need to know that all permitted buildings are divided into several categories:
- Garden house. Unlike a residential building, it is intended only for temporary (seasonal) residence while maintaining the garden. There are no communications connected to it, and no heating is provided. You can live in such a house, but you cannot register (with the exception of areas located within the boundaries of a populated area). To change the category of a garden building to a residential building is possible only through the court, where you will have to prove that it fully satisfies all the requirements for comfortable and safe living. The garden house does not have a postal address.
- Agricultural buildings. They are designed to provide garden maintenance. From any materials, at the owner’s discretion, you can build: greenhouses for growing seedlings or heat-loving plants (can be equipped with a heating system); sheds (including with basements) for storing property and carrying out auxiliary work, as well as keeping pets and birds; hangars for storing crops and equipment; woodsheds for storing firewood. The purpose of the buildings being erected is to ensure the cultivation of garden crops and harvesting, storage of tools and equipment, storage of equipment and crops.
- Other buildings: garage, toilet, summer kitchen, bathhouse, etc. These non-permanent buildings should provide comfortable living for people while caring for the garden.
Read more about whether it is necessary to obtain a permit to build a bathhouse.
Important! Any buildings on gardening land cannot be used for commercial purposes. Taking this into account, production workshops, healthcare and cultural facilities, retail outlets (shops), infrastructure structures and other buildings for commercial use cannot be built on lands for gardening.
Category
Article 7 of the Land Code determined that the lands of the Russian Federation are divided into 7 categories, among which there are settlement lands (ZNP) and agricultural lands (ZSN).
According to the classifier, a land plot with a VRI “Gardening” may belong to either one or another category.
Garden plot status
The status of a horticultural plot determines the following purpose of the land:
- growing fruit trees and shrubs;
- cultivation of nut plants;
- planting and growing vineyards, berries and other fruit bushes;
- harvesting fruits for making juices and other drinks;
- cultivation of mushroom mycelium and harvest processing;
- growing seedlings and seeds for the purpose of breeding new species;
- growing decorative varieties of crops and vegetables, incl. for nurseries;
- cultivation of spice plants.
Land for gardening may have different status depending on the location of the site. If it is located outside a populated area, then, as a rule, it belongs to the category of agricultural land. Within the boundaries of a populated area, such a plot may be given the status of a household plot.
The question of whether it is possible to build a house on lands for gardening is decided taking into account the status. It is not allowed to build permanent buildings (with a foundation) on agricultural lands, and even a residential building can be built on personal plots after obtaining permission from local authorities.
In addition, land for gardening can be privately owned, when the owner can fully dispose of it, or as part of a horticultural non-profit partnership (SNT). In the latter case, the permitted use of land on a lease basis is ensured. The question of whether it is possible to build a house on SNT lands is agreed upon by the general meeting of owners.
Read more about how to register a house in SNT in our article.
Permitted use
The VRI classifier immediately established 2 types of permitted use for gardening:
- Clause 1.5 “Gardening on farmland” . This refers to areas allocated for gardening from the ZSN land category. These areas are primarily intended for growing perennial crops on an industrial scale . Here you can build fences, greenhouses, drill wells for water supply, but you cannot build any permanent structures (structures with a foundation). Moreover, the construction of residential buildings on such lands is prohibited.
- Clause 13.2 “Gardening” . Such a VRI can be assigned both in the ZNP category and in the ZSN category. In this case, we mean areas intended for private gardening and for arranging a summer cottage. The classifier states that on such a site it is allowed to grow any melons, horticultural crops, vegetables and other agricultural crops. Also, the construction of a garden (summer, country) house and other necessary outbuildings is allowed here.
Obtaining a building permit in 2022
No permit is required for the construction of permitted non-permanent buildings and a garden house. If the site belongs to SNT lands, then the owner is obliged to comply with the norms of Article 34 of Law No. 66-FZ (https://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_18461/a716fd25e3cf9ba6d1b173acb5efae8f1e91ba3e/) and SP 53.13330.2011.
According to these documents, it is necessary to take into account the territorial land surveying project. All members of the SNT are required to have a Code of Development Rules, which is adopted at the general meeting of the partnership.
Permission in 2022 is required for the construction of a residential building on a site located in the territory of a populated area. To obtain it, the following documents are provided:
- document on the right of ownership or use of the site (extract from the Unified State Register, certificate);
- passport of the owner of the site;
- urban planning plan of the site;
- plot layout diagram indicating the location of the building for which permission is required.
Read more about how a permit to build a residential building is issued in our article.
An application addressed to the head of the local government body is submitted to the authorized municipal body with the specified documents attached. The decision is made within a month.
A garden house can be reclassified as a residential one by decision of local authorities or the court. Such permission can only be obtained by proving that the house meets the following requirements:
- The owner of the site has legal, sole ownership of the property, and the building is not mortgaged;
- During construction, all construction, sanitary, environmental and fire safety standards were observed, proof of which will require conclusions from relevant organizations;
- The house is provided with all necessary communications - electricity, water supply, sewerage, heating.
You can register in a house only after it has been recognized as residential.
Differences between gardening and individual housing construction
The main difference is that gardening farms are designed for seasonal operation.
This is where their specific differences arise:
- They may not have permanently operating utilities, that is, gas, light and heat can only be supplied during the land development season, before the onset of frost - just like in holiday villages.
- Here, in principle, a postal address may not be provided, which will make official registration at the place of residence impossible.
- The construction of the house is not guided by the urban planning plan, therefore it allows for the construction of a unique structure.
- Building a house is not necessary, but cultivating the plot and planting garden crops are required.
The characteristic features of land for individual housing construction are as follows:
- Mandatory installation of permanent utilities. Active development of infrastructure.
- Availability of registration and postal address, permission to live with family permanently.
- Construction follows a clear plan corresponding to the building area. The construction of a residential building in accordance with established urban planning regulations is mandatory.
- Development of the local area with horticultural crops is not required.
Reference: the cadastral value of land plots, and, accordingly, land tax, are approximately the same.
Standards for the location of buildings on the ground for gardening
Certain restrictions on the location of buildings on the site are established by SNiP 30-02-97:
- from a residential building to the wall of a neighboring building there must be at least 3 m;
- to the premises with animals - at least 4 m;
- to outbuildings - at least 1 m;
- there should be at least 5 m to the road, and 3 m to the driveway.
- the wall must be removed from the border of the site or fence at a distance of at least 1 m.
- the distance between brick or stone structures must be at least 6 m, and between a stone (brick) and wooden structure - at least 10 m.
- wooden buildings are separated from each other at a distance of at least 16 m.
- from a residential building to a toilet, premises for animals and birds, settling tanks should be at least 12 m.
- There should be more than 8 m between buildings and a bathhouse, well, and septic tanks.
In general, on a gardening site, all buildings and paths should occupy no more than ¼ of the total area.
Changes under the “dacha amnesty”
Starting next year, the simplified procedure for registering land and houses will remain, but changes are being made to the procedure for registering rights to an object built on dacha land. Today, a house built on a plot of land, which is intended for dacha farming (construction), gardening, can be registered in a simplified manner according to the declaration. The owner does not need to invite specialists to fill it out; he can enter all the information himself; no one checks the accuracy of the specified data. But from January 1, 2021, after Law No. 218 “On State Registration of Real Estate” comes into force, instead of a declaration to register a house on dacha land, it will be necessary to draw up a technical plan of the property, for this purpose cadastral engineers will be invited. So the current difference in the design of houses built on plots with different purposes will disappear.
“Even today we recommend that clients register a built house not according to a declaration, but on the basis of a cadastral passport, which is prepared after the house is registered with the BTI,” says Gulnaz Perevozchikova, a lawyer at AREVERA-Real Estate. “For the sale of such an object in our company, registered according to the declaration, technical registration and execution of technical documentation (as well as the presence of land surveying) is a prerequisite.”
Liability for violation of construction rules
Construction on lands for gardening and SNT without approval is recognized as non-intended use of land. Punishment for such an act is provided for in Article 71 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. At the municipal level, a fine of up to 2,000 rubles on the owner of the site at any time during construction or after its completion.
If payment is late, a double fine may be imposed. If execution is refused, the fine is collected through the Bailiff Service forcibly.
Houses built without approval are given the status of unauthorized construction. If the owner does not legitimize the building in the prescribed manner, the court issues an order to demolish the structure within a specified period at the expense of the owner.
Gardening plots are allocated for the intended use of the land. They can be used to build garden houses, agricultural and utility buildings of a non-permanent type. A residential building can only be built on a site within a populated area after agreement with local authorities. Unauthorized construction is recognized as an administrative offense and is punishable by a fine.
If you need advice, our land lawyer will help you.
Changes from 2021
Until 2021, areas with the type of permitted use “Gardening” are regulated by Federal Law No. 66. The new Federal Law No. 217, which will come into force on the first day of 2021, changes the situation.
Compared to the old bill, it will bring several significant changes :
- Now lands with the VRI “Maintaining Gardening” can be dacha, horticultural and vegetable gardening. Starting from 2021, dacha lands will be liquidated and become horticultural . This division brings more specificity to the legal status of allotments: permanent and non-permanent structures can be built on horticultural plots, and only non-capital structures can be built on garden plots.
- From 2021, individual gardeners whose plot is located on the territory of the SNP can take part in meetings of the association and influence its decision-making. But they will not be able to participate in the elections of board members, chairman, etc.
- From now on, within one village there can be only one SNP . Previously there could have been several of them.
Documents for the land plot
The owner of the land you are purchasing must have title documents. For plots that are sold as a property, such a document is a certificate of ownership (today it has been replaced by an extract from the Unified State Register of Rights to Real Estate, which is requested from Rosreestr). Those documents on the basis of which the right of ownership arose: purchase and sale agreement, certificate of inheritance, gift agreement. In addition, the owner must have a cadastral passport of the land plot. If the land plot was acquired during marriage, the notarized consent of the second spouse to carry out the transaction will also be required.
If the land plot is leased, the title document will be the land lease agreement. The seller must have the order on the basis of which this agreement was approved, as well as the cadastral passport of the land plot. The list of criteria when choosing a site is quite large, but if the buyer does not take into account at least one of them, he may well find himself in a situation where it will be impossible to build on the site he owns.
Using maternity capital to purchase land
If buyers of a plot plan to use maternity capital funds to build a house, they need to choose among plots intended for individual housing construction or private household plots. The fact is that in order to receive maternity benefits, the family must provide the Pension Fund with permission to build a house, and its administration will issue it only on the condition that the site is intended for individual housing construction or personal farming.
At the same time, if the family does not intend to receive funds for construction, but to compensate for the costs incurred with the help of maternal capital, the purpose of the land is not important (in order to receive payment in this case, the plot may be intended for dacha construction). The pension fund only needs that the object built on the site be documented as a residential building. Most families follow exactly this path: they buy a dacha plot, build a house, register the constructed object in a simplified manner under the “dacha amnesty”, and then submit documents for maternal capital to the Pension Fund.
Land surveying procedure
Although today there are no restrictions on the sale of undemarcated land, the purchase of a plot without established boundaries is associated with certain risks for the buyer. For example, it may later turn out that the purchased plot has a smaller area than what was stated by the seller. After land surveying, the owner receives a cadastral passport of the plot, in which the boundaries of the land plot are established. To carry out the work, you must contact cadastral engineers. The cost of the costs depends on the area and configuration of the site and is approximately 7.5 thousand rubles.
“I would recommend conducting land surveying when preparing for a transaction. Otherwise, it will turn out that a person buys a share in the field,” says Denis Sheshko, “and in cases where a demarcated plot is being sold, I advise, when preparing for the purchase, to call cadastral engineers who will once again verify its boundaries, the buyer will incur additional costs, but there will be have a complete understanding of what exactly is being purchased.”
The current practice of selling undemarcated land will become impossible in the future. From 2021, changes to the legislation should come into force that will not allow Rosreestr to register transactions with land plots that do not have boundaries. Land surveying will be required if buyers plan to use a loan to purchase land. According to the specialist, mortgages today are issued for land plots with any purpose suitable for building a house on them, but the presence of boundaries is a prerequisite.
Land allocation procedure
According to land legislation, every citizen of the Russian Federation has the right to receive a plot of land that is in state or municipal ownership. Land for vegetable gardening or horticulture can become the property of an individual or a non-profit association if it is registered with local authorities for this purpose.
The priority is determined on the basis of submitted applications.
If applicants have any benefits that give them a preferential right to receive a land plot, they are included in a separate list.
The authorized bodies, having determined the applicants' need for an allotment, taking into account the zoning schemes of the territory, offer one or another type of land or decide to refuse to issue it.
The plot is provided as a property or on the basis of other property rights.
In accordance with the procedure established by law, a fee is charged for the transfer of land into ownership, which cannot be higher than the standard price of the plot. In other cases, no payment is provided.
Restrictions on the use of plots for gardening and vegetable gardening
The permitted use of land for gardening and vegetable farming has some restrictions regarding:
- type of construction. It should not be intended for permanent residence;
- type of land. As a rule, this applies to agricultural areas, but this may also include settlement lands;
- the size of a permanent structure - no more than 25% of the total size of the site;
- use of at least part of the plot for its intended purpose, for example, for growing crops.