If a spouse dies, then his husband or wife can take advantage of the property rights that are prescribed by law. They are considered the closest relatives, which gives them the opportunity to inherit certain material objects in the form of an apartment, dacha, car, garage and other things. The question of what rights a spouse has when inheriting in 2022 most often arises when, in addition to the wife or husband, other claimants to the inheritance also claim their rights.
It is advisable to consider the problem of marital rights in inheritance in two aspects. It all depends on the circumstances under which the property previously came into the possession of the deceased. For example, it could have been purchased before the wedding or after it.
The spouse has a share
If there is one, then in addition to the inheritance itself, the spouse can claim rights to half of everything acquired during the marriage. For example, if housing was purchased using joint financial assets, then both spouses have completely similar rights to it. The fact that official documents are issued for only one of them will not matter here.
When deciding on the issue of inheritance rights, the notary will first deal with the registration of the marital share and only after that - the allocation of shares for all heirs.
If you follow the law, then the shares of the spouses are equal, therefore exactly half will be given to the property of the surviving husband or wife. What remains after this allocation will be at the disposal of the heirs. Moreover, the spouse will also participate in this process.
To make the process of distribution of shares clear, it is better to illustrate this with an example.
A middle-aged man died. Some time passed after the funeral when the relatives decided to start filling out the paperwork. This is where a dispute arose about who has more rights. Relatives include his wife, teenage son and elderly parents. The object over which the conflict flared up was a three-room Khrushchev house. The couple bought it seven years after the official registration of the marriage. Obviously, half of this housing will go to the wife. The other part will be divided equally between the wife, son and parents.
Taxes
When donating real estate, you often have to pay a tax of 13% of its value (inventory or cadastral).
But the law exempts from paying the fee if the parties to the transaction are close relatives. Spouses also fall into this category.
Therefore, when donating a share of an apartment, the wife does not need to worry about having to pay taxes.
Can a spouse be left without an inheritance?
This result is quite possible if a will has been drawn up. Current legislation gives the sole owner the right to dispose of his belongings as he wishes. This principle also applies to the hereditary sphere.
In simple terms, the owner of the property has the right to name any citizen in the will. If this is done, the spouse may lose his inheritance rights. But there are some exemptions that allow him to receive part of the property in any case.
For example, if a husband or wife has reached the age of 65 or 60 years, respectively, then they receive the status of a compulsory heir and can count on a share, even if a complete stranger or another relative is called to inherit by will according to the will of the deceased.
True, it is no longer possible to talk about equal distribution in this case. The share of the obligatory heir will be less than what the citizen specified in the will will receive.
Agreement on donating shares to children using maternity capital
The measure of state support in the form of maternal capital is very significant for families, but one of the important points is that the parent who has received the certificate and wants to use it to purchase real estate must draw up a notarized obligation to allocate shares to the spouse and children.
The shares must be allocated within six months after the transfer of funds by the Pension Fund in favor of the seller. To transfer them, a gift agreement is often used if a marriage contract has been concluded between the spouses or the property is already in shared ownership.
Important! When using maternity capital to purchase an apartment, shares will have to be allocated to the spouse and children, even if a marriage contract has been drawn up, according to which the property belongs to the woman alone.
Inheritance within marriage
Sometimes one of the spouses becomes an heir. For example, parents died and bequeathed a house to their son or daughter. In divorce proceedings, the question may arise: does the other person have the right to claim this property and demand a full division?
When it comes to the equal division of a property, it is understood that the husband and wife participated jointly and equally in its acquisition, that is, they allocated funds from their common budget to pay for the transaction.
Receiving a house by inheritance does not involve spending marital funds; the property is transferred to the heir free of charge. A simple conclusion follows: such real estate will not be classified as jointly acquired property. Its division will be impossible, with the exception of one case.
If the spouses decide to reconstruct the premises and invest joint finances in its renovation and expansion, then the situation may change radically. The other spouse has the legal right to claim part of the house.
Rights and obligations of the parties
Any contract contains conditions that the parties must fulfill. The rights of the donor include the following:
- refusal to donate an object for reasons provided for by law;
- claim for compensation for damage caused to the donated property.
His responsibilities include:
- transfer the object of donation after concluding the agreement;
- provide the recipient with all the information necessary for the correct use of the gift;
- bear the costs of completing the transaction.
The recipient also has the rights:
- refuse to accept a gift;
- demand compensation for damage on the grounds provided by law.
The recipient is obliged:
- use the gift without damaging it;
- return the gift if there are legal grounds for doing so.
The parties are obliged to comply with the terms of the transaction. Otherwise, the gift agreement will be terminated.
Conclusion
What rights does a spouse have when inheriting in 2022? The surviving husband or wife has legal property rights provided for by law, for example, to an apartment, car and other property. If it is necessary to divide residential premises acquired during the marriage, the notary will follow the following algorithm. First, he will allocate half to the surviving spouse, and after that he will deal with the distribution of the inheritance.
The right to the spousal share will be confirmed by a certificate issued at a notary's office. In addition, the surviving spouse has the right to claim a part of the inheritance, since the law gives him the rights of a first-priority heir.
If property is donated or received as a result of inheritance, the spouse has the right to inherit, and in priority order. But it happens that the spouse is left with nothing. For example, if during the marriage the spouses did not acquire anything, and the testator considered it necessary not to leave an inheritance to his relatives, including his own spouse. His will must be done.
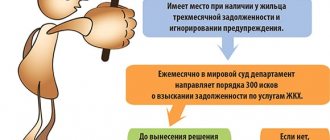
Family guarantee: children will be responsible for their parents’ debts
FAMILY GUARANTEE: CHILDREN WILL BE RESPONSIBLE FOR THE DEBT OF THEIR PARENTS
Should children be held subsidiarily responsible for property donated to them?
Transferred property to a minor child and will he forever be in debt?
At the end of December 2021 The Supreme Court gave all children a New Year's gift in the form of the possibility of bringing them to subsidiary liability (Determination dated December 23, 2019 in case No. A40-131425/2016 (305-ES19-13326)).
The children of the subsidiary defendants, Daniil Vadimovich Samylovskikh and Dmitry Vadimovich Samylovskikh, born in 2002 and 1997, received expensive property as a gift from their parents in 2017. The highest authority agreed that the children at the time of 2012-2014. did not control the Debtor's activities. Also, based on their age and the specifics of family relationships, they were unlikely to know about the origin of the property. However, harm to creditors can be caused, among other things, by deliberate actions to hide property by relatives. Children should not be used as tools for hiding property!
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation considered it legal to bring parents to subsidiary liability. Additionally, the Moscow Arbitration Court has been entrusted with investigating the case materials regarding the Samylovskys Daniil and Dmitry.
At the new trial, the court had to check whether Samylovskikh Daniil and Dmitry became the real owners of the property donated by their parents, and whether, by receiving the property as a gift, along with acquiring ownership rights, they pursued another goal - to free this property from foreclosure by creditors.
A day ago we received the first judicial act in Russia on bringing children to subsidiary liability. The Moscow Arbitration Court gives us answers to terrible questions (Determination of the Arbitration Court of the Arbitration Court dated October 27, 2020 in case No. A40-131425/16-30-203B):
Are children controlling the debtor:
“The presumption of a controlling beneficiary is not applicable to minor children of controlling persons (subclause 3 of clause 4 of Article 61.10 of the Bankruptcy Law) due to the objective features of the relationship between minor children and their parents, which are usually characterized, on the one hand, by the desire of parents to protect children from negative information, on the other hand, an increased level of children's trust in their parents.
At the same time, the foregoing does not exclude the possibility of parents using their children’s identities as a tool for concealing property belonging to the parents from foreclosure upon claims of creditors for compensation for damage caused by the parents to these creditors.”
According to Art. 61.10 of the Bankruptcy Law, a person controlling the debtor is understood as an individual or legal entity who has the right to give instructions that are binding on the debtor or the ability to otherwise determine the actions of the debtor, including the execution of transactions and the determination of their conditions.
However, according to paragraph 5 of the same article, the Arbitration Court may recognize a person as a person controlling the debtor on other grounds.
Currently, there is a tendency to expand the understanding of the status of a controlling debtor of a person (CDL). The list of CDLs is not limited by law; the court can recognize them as the president of the debtor, chief accountant, lawyer, group of companies and other citizens and organizations. Indeed, children are not automatically included in the CDL; the standard of proof when involving them is higher.
The children are the actual beneficiaries of the Debtor's assets. The provisions on the actual beneficiary are disclosed in paragraph 7 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2017 No. 53; a person who has received a significant benefit in the form of an increase (saving) of assets (including through a chain of successive transactions) can be recognized as a controller.
Benefit - any increase in a material or intangible benefit protected by law, any changes in a legally protected benefit that is favorable for the CDL, which can be either property or non-property (intangible).
Such a transaction for the alienation of property must be carried out by the head of the debtor to the detriment of the interests of the headed organization and its creditors for deliberately dishonest purposes. In our case, donation is such a gratuitous transaction for the withdrawal of assets.
An actual beneficiary should not be confused with a controlling beneficiary. In relation to the “controlling beneficiary”, a legislative presumption has been established (Article 61.10 of the Bankruptcy Law) and the standard of proof is simpler. As expressly stated in judicial acts, the presumption of “controlling beneficiary” does not apply to children. However, a person who does not directly control the activities of the Debtor and does not have the ability to give binding instructions may be recognized as a person controlling the debtor. It is enough for an organization or citizen to receive a large asset of the debtor and these actions cause harm to creditors.
· Amount of responsibility of children:
Regarding the amount of subsidiary liability, it should be noted that children will be liable only to the extent of the value of the property received. The amount of benefit received is equal to the amount that could be included in the debtor's bankruptcy estate. Here we can draw an analogy with restitution when challenging transactions.
Collection from relatives is possible only within the limits of the value of the property, “although the owner has changed, but, in fact, left in the family.” This position applies to any property that was transferred to them, both related to the bankrupt company and not related, follows from the definition of SKES.
Establishing a specific size is necessary in case of further alienation of such property.
“The court comes to the conclusion that the statement of the authorized body to hold the Samylovskys Dmitry Vadimovich and Daniil Vadimovich vicariously liable for the obligations of the debtor Alliance LLC in the amount of RUB 93,111,576.40 is justified. (the value of the property alienated in their favor).”
How to determine the value of such property:
As part of this case, there was a donation of real estate, buildings, land and a garage. The court determined the cost of the damage caused based on the cadastral value of each object. With regard to the PAZ machine, the definition does not indicate the basis on which its cost was calculated. The value of alienated property can also be established by an Independent Appraisal when creditors file a claim against the heirs.
If the Defendants do not agree with the determination of the value of the alienated property, then they can challenge it as part of determining the amount of subsidiary liability by providing their evidence of the market value of the price.
· Why was it impossible to challenge the transactions?
Collection from relatives can occur in two ways: as part of the recognition of a transaction for the transfer of property as imaginary, or in the order of compensation for harm, indicated the SKES of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. In this case, the Applicant is not obliged to first challenge the transaction; he has the right to choose any method of protecting his rights. Bringing to subsidiary liability when obtaining a significant benefit is an effective mechanism if the deadline for challenging transactions has already expired.
The Moscow Arbitration Court examined the nature of this transaction: “thus, the court comes to the conclusion that the transactions made by N.A. Kiriyenko and Samylovsky Daniil Vadimovich and Dmitry Vadimovich regarding the alienation of property have signs of imaginaryness.
No evidence was presented in the case materials confirming the income of D.V. Samylovskikh, allowing him to purchase the said property, nor was there any evidence confirming the income of D.V. Samylovskikh. and D.V. in an amount sufficient to cover the burden of maintaining the property, namely the need to perform the following duties: maintain the suitability of the property for use; keep property in a safe condition; bear the costs of maintaining the property; pay taxes; pay other obligatory payments; register property; insure the risk of liability for harm that may be caused to other persons when using the property.”
As Sergei Domnin, representing the interests of the bankruptcy trustee of Alliance, clarified to Kommersant, the eldest son has already sold all the property received from his parents, and the younger son’s three apartments have been combined into one (with an area of 231 sq. m.): “Therefore, talking about how realistic it will be It is difficult to recover the awarded amount from the defendants. The court did not establish the current property status of the children[1].”
Sadly, children can be held responsible for the “sins” of their parents if they acted in bad faith towards their descendants. The position of the RF Armed Forces, which was applied by the ASGM, gives us a clear vector - that parents are responsible for the fate of their children, and such concealment of property can hang on the family for many generations. With the responsibility of the hereditary estate, everything is simpler - if you don’t want to, don’t accept debts. And then the parents gave their children a very fat pig!
[1] https://www.kommersant.ru/doc/4551138?fbclid=IwAR1CeLPHAHw4jt0LKS-7LW1_uCIThhofy8cp3MtBy4VpsId2akh1XOLbUF8
Lawyer's answers to frequently asked questions
Is it possible to gift real estate to an adopted child?
Yes, adopted children are legally treated as biological relatives.
My wife gave our son an apartment without my knowledge. Can I challenge this?
Yes. According to Art. 35 of the RF IC, a spouse whose consent was not obtained has the right to challenge the transaction within 1 year from the moment he became aware of it.
Is it possible to draw up a donation agreement for a PC and household appliances to a minor child so that the property is not seized by bailiffs?
Yes, but this does not guarantee 100% protection from arrest or seizure: if there are grounds, the deed of gift can be cancelled.
My mother drew up a deed of gift for her great-grandson. Can I claim a mandatory share as an heir?
No. The obligatory share is allocated only to the dependents of the testator who executed the will. The mother is still alive, and the donation is her voluntary expression of will.
Can I sell a donated home given to me by my mother when I was 17 years old, if now she is against the sale? I'm 20.
Yes. According to the law, the right to dispose of real estate passes to the donee after registration with Rosreestr.