General information on land use
By the term “land use,” the theory of urban planning understands the management of land resources and their exploitation in various ways, depending on the intended purpose of the land.
In accordance with Art. 14, land use is carried out at the municipal level - it is within the competence of local authorities that the law refers to the issues of determining the rules and conditions for the operation of the land fund. As part of this work, local authorities:
- Approves master plans for settlements and documentation on territorial planning.
- Carry out urban planning zoning.
- Issue permits for construction and commissioning of structures.
- Approved by local urban planning standards.
- Land is reserved and confiscated for municipal needs.
- Exercise municipal land control.
- They approve local development and land use rules (LRU) and so on.
All of these activities are subject to local regulations.
Learn more about what land use is.
One of the main legal acts is the rules of development and land use, so it’s time to figure out what PZZ is in land use.
General information about the rules of development and land use
In general terms, one can imagine many forms of land use - this includes use for agricultural purposes, and for the development of environmental zones, and even for the creation of artificial reservoirs.
But in the case under consideration, land use is primarily urban development/development for the purpose of sustainable development of municipal territories. Therefore, the rules of both land use and development within the municipality are inextricably linked.
pp. 8 clause 1 art. 1 helps to understand what the PZZ of a land plot is. This is a kind of town planning charter that defines the rules, conditions and procedure for dividing and planning land within a specific locality for the purpose of its further development or other development of the municipal territory.
The need to approve a set of rules is established not only by the Town Planning Code, but also by the Land Code. These rules define:
- the boundaries of any land plot within the settlement;
- their legal regime, intended and permitted use;
- assignment of a specific land plot to a specific zone (urban zoning map);
- minimum and maximum sizes of plots within the zone;
- boundaries of a settlement, location of infrastructure facilities, roads, master plan of a settlement, and so on.
As mentioned above, PZZs are adopted by the municipal authorities for each specific settlement separately and approved by the town planning or architectural committee of the subject.
For those who are interested in how to obtain a PZZ for a land plot, we will tell you: such documents are usually posted on the websites of municipalities.
In some localities, an extract from the PZZ is even provided on the State Services website. For example, you can get an extract for Bryansk.
The document itself, as a rule, consists of three parts, several dozen articles and appendices to it. Typically this is:
- The general part, including the procedure for applying approved urban planning standards and the conditions for making changes to them.
- Graphic part, including a map of urban planning zoning (dividing territories into land use zones).
- A special part is urban planning regulations.
Let us dwell on the components of the PZZ in more detail.
Public cadastral map of the Russian Federation on
- Find your plot of land on the map.
- Among other data, the coordinates of the site are displayed (to do this, click on the “Details” button at the bottom of the window).
The location of the allotment must be looked at on the map when, for example, you plan to purchase it. Then you are interested in the infrastructure closest to it, the shape of the site, and its location relative to other objects. You can do this using the following instructions:
Public cadastral maps include 22 republics: Adygea Altai Bashkortostan Buryatia Dagestan Ingushetia Kabardino-Balkaria Kalmykia Karachay-Cherkessia Karelia Komi Crimea Mari El Mordovia Sakha (Yakutia) North Ossetia-Alania Tatarstan Tyva Udmurtia Khakassia Chechnya Chuvashia
General part: application of PZZ
The general theoretical part of the PPP should first of all establish the procedure for applying the rules. According to Part 3 of Art. 30 GrK, this order determines the conditions:
- regulation of development of municipal territories;
- making changes to the procedure and purposes of use;
- carrying out territory planning and preparing documentation for it;
- holding public hearings at which new land use and development rules for urban areas are approved, and so on.
The general part usually contains:
- the scope of the PZZ and a decoding of the concepts used in it;
- correlation of the approved rules with other urban planning documentation;
- principles of urban planning and working conditions of the land use commission;
- the procedure for conducting urban planning preparation;
- the procedure for providing land to citizens for use;
- conditions for reserving land, issuing construction permits;
- types and procedure of permits for putting buildings into operation and similar standards.
The theoretical part, in fact, is the main one, since specific rules for the use of municipal lands are established precisely in it. The use of the graphic part is carried out according to the conditions of the general part.
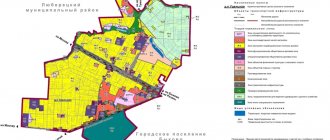
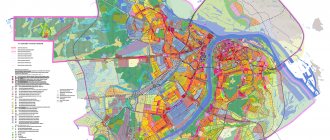
Graphic part: zoning map
The second, graphic part of the PZZ is a map of land use and development. According to paragraph 4 of Art. 30 GRK, it defines the boundaries of territorial zones and assigns specific land plots to such zones.
We are talking about zones within which areas of the same intended purpose and type of use are located. Bringing different plots into one zone or forming one plot from them is not allowed.
The card must include:
- boundaries of the territories of settlements within the jurisdiction of the municipality;
- limits of development zones and economic activities, scale of development;
- areas with special operating rules;
- limits of sanitary, water, coastal territories and coastal strips;
- the boundaries of areas of special cultural or historical significance;
- limits of zones of historical settlements of local significance, and so on.
The graphic part can be executed on several cards, depending on the zones located on it.
If we are talking about large cities, then the division is made by city districts or districts. For example, zoning within the North-Eastern Administrative District of Moscow.
For more information on how such maps are compiled, read the material “Cartography of Land Plots”.
What is included in the document?
The standard structure of the PPP includes two parts.
- General. Determines land use requirements in accordance with the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, maximum construction parameters, and the establishment of urban planning regulations for each territorial zone.
- Territorial. Contains maps of administrative-territorial entities, which indicate the zoning of the territory with a clear location of the boundaries of the territorial zones.
The legal nature of the PZZ consists in the validity of the document on the territory of a certain settlement - urban or rural. The rules are binding on all legal entities, including:
- government authorities;
- regulatory authorities;
- developers and customers;
- design and contracting organizations.
The provisions of the PPL are used to resolve conflict situations - both pre-trial and in court. The rules take precedence over other types of urban planning and land management documents, including the general plan of the territory.
Special part: urban planning regulations
In accordance with Art. 36 of the Civil Code, regulations determine the legal regime in relation to a site that is part of a specific zone. Each zone has its own regulations.
As a rule, a development and land use project includes a number of separate territorial zones, the division into which takes into account the intended purpose of the land and the types of its permitted/actual use.
In addition, the characteristics of the plots and their target compatibility are taken into account for the possible combination of close plots within one zone.
For each zone, taking into account the data contained in the master plan, urban planning regulations must establish:
- forms of use and purpose of specific areas within the zone;
- maximum plot sizes;
- permissible scale of development/reconstruction of construction projects;
- restrictions regarding the purpose and use of plots.
Please note that the regulations do not include:
- lands of cultural and historical value;
- public lands;
- mining areas;
- forest and water fund lands;
- specially protected areas;
- agricultural lands.
The procedure for preparing a PPP
Local rules for development and land use are developed in accordance with Art. 31 GrK. They can be created in relation to all territories of a municipal settlement or its parts, taking into account:
- provisions of the general plan of the city or settlement;
- terms of technical documentation;
- issues of public discussions and public hearings.
The decision to develop a PZZ within a populated area is made by the head of the local administration, who determines the stages of development of the PZZ, the procedure and timing of preparatory work.
Simultaneously with the decision to develop the Rules, the head of the administration establishes the composition and regulations of the activities of the commission for the development of the PPP. She will also be the initiator of public discussions on the project being developed.
After 10 days, the decision made is published on the administration’s website or distributed in other media. The decision notice also states:
- composition of the commission for the preparation of the PPP;
- stages of implementation of zoning of territories of a settlement;
- procedure and preliminary deadline for developing the draft Rules;
- rules for sending proposals from interested parties to the commission and other important information.
After the development of the draft Rules, the local government body checks them for compliance with the master plan and technical regulations.
The approved project is sent to the head of the settlement, and if inconsistencies are found, it is returned to the commission for revision.
The head of the settlement, within 10 days from the receipt of the draft Rules, schedules a public discussion of it. The procedure for conducting discussions is also established at the local level, its duration is 2-4 months.
Based on their results, the commission makes the necessary changes to the project, after which it again sends it to the mayor or other official heading the administration. He decides within 15 days whether to send the project for approval by the local council or return it for revision.
Fire protection requirements
There are several federal regulations that outline the requirements for PP. But among them there are key points.
- PZ systems must be installed strictly according to approved designs made for each facility. Changes cannot be made.
- Livestock systems must respond quickly to the occurrence of fires, no matter in what parts of the facility they occur. In this case, people should be immediately notified, and their organized evacuation should begin.
- Fire extinguishing agents must be supplied to the fire area in such a way that they do not cause spillage, splashing or spraying of flammable liquids. And the latter did not cause the formation of explosive and toxic gases.
- Projects must take into account the need to remove fire extinguishing agents from the fire zone after extinguishing the fire.
- Fire safety system control panels must be installed in separate rooms, where specially trained personnel are on duty around the clock.
- Evacuation routes must be provided with detectors and signs along the entire route.
- If automatic extinguishing systems are used at the facility, they must be provided with a sufficient volume of fire extinguishing agent. Moreover, such systems are equipped with manual control in case of power failure, devices that are responsible for monitoring the system, and devices that are responsible for delaying the supply of fire extinguishing agents during the evacuation of workers and employees.
Pumping units AUPP
The procedure for approving the PZZ
In accordance with Art. 32 of the Civil Code, the draft Rules are approved by the representative body of local government - the city council. Approval must take into account questions and suggestions made by the public at the hearing.
Based on the results of its consideration in the local council, deputies can either approve and accept the project, or return it to the head of the administration for revision. If approved, the PZZ is subject to publication on the municipal website or otherwise published for public access.
If PPLs affect the rights of citizens or organizations, interested parties have the right to challenge them in court. State and regional authorities also have the right to challenge, but only when the Rules contradict the territorial planning schemes of the region or country.
Within 10 days from the date of approval, the PZZ must be published in. Using this search engine it is easy to find out where to find the PZZ or where the extract is.
After approval of the Rules, you can obtain up-to-date information from the PZZ at the town planning department / local administration department or through the MFC and the State Services website.
Since the document itself is quite lengthy, an extract is provided only regarding the requested data. The form of application for its issuance is usually established by local administrative regulations.
Sample extract from the land use and development rules:
If an extract is required in relation to a specific site, then the application usually indicates:
- cadastral number;
- total area;
- land category;
- location address;
- other identifying information.
Such an extract, in turn, will contain all current data regarding the conditions of use of the land, its size, the possibility of changing the type of use and other information.
How is APPP managed?
Many electronic modules are connected to each other by wired and wireless low-current networks and form a set of APPPs.
All elements of the system participate in management. They are monitored and controlled from a central post . The post can be supplemented with dispatching means for manual control or triggered automatically.
APPP complexes operate in parallel with other engineering systems at the site and are integrated with access control, video surveillance and security systems. In order for fire services to receive a timely signal, communication networks must be connected.
Despite the complexity and multi-component nature of the fire protection system, it is the best way to protect the building and people from fire, minimize property damage and reduce overall losses from the elements.
The procedure for making changes to the PZZ
According to Art. 33 of the Civil Code, the law allows for changes to the rules of land use and development in the following cases:
- detection of discrepancies between the PZZ and the territorial development and redevelopment plan;
- appealing the Rules;
- expansion/reduction of the settlement territory.
As a rule, petitions for amendments are submitted by state, regional or local executive authorities if the adopted Rules impede the operation or construction of facilities under their jurisdiction.
However, the law does not exclude the possibility of introducing changes at the initiative of private individuals and organizations. Changing the PPL in relation to a land plot at the initiative of citizens is possible if, as a result of applying the Rules:
- land and construction sites are used inefficiently;
- harm is caused to owners or other persons who have rights to land and construction projects;
- land value decreases;
- copyright holders cannot fully realize their rights.
The request for amendments is sent to the address of the commission, which within 30 days considers the issue and prepares a conclusion on it on the need to make changes or on refusal.
The algorithm for preparation and approval is identical to the procedure for adopting new PZZs, only without holding public hearings.
How to make changes?
The procedure for making changes to existing PZZs is somewhat different from that described. The initiator of the event can be any interested person if there are grounds provided for in Part 3 of Article 33 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In most cases, we are talking about the ineffectiveness of previously approved rules.
The procedure for making changes to the PZZ involves the following actions:
- sending proposals for amendments to the rules to the commission created by the municipality to develop the document;
- preparation by members of the commission of an opinion on the feasibility of changes to the current rules;
- adoption by the head of the municipality, based on the conclusion of the commission, of a decision to reject or introduce proposed changes;
- if the decision is positive, preparation of a draft amendment to the PZZ;
- agreeing on a new version of the rules with interested and regulatory authorities;
- public hearings or discussions on planned amendments;
- consideration of the results of hearings or discussions;
- making a decision to reject or amend the PPP. Carried out by the representative body of the municipality.
For the city of Moscow, the regulations for amending the PZZ are prescribed in a separate resolution of the Moscow Government No. 457-PP dated May 17, 2018
It is not difficult to notice the complexity of the described procedure – both legal and organizational. Therefore, amendments to the PZZ are carried out not by the direct initiators of the event - developers, investors or designers, but by specialized organizations that provide cadastral, legal and other similar services.
This approach guarantees not only the successful completion of the event, but also the efficiency of its implementation at a reasonable level of associated financial costs.
What territorial zones are there?
It's time to find out what zones are established by land use and development rules. They are usually established by town planning regulations taking into account the type of use and are divided into:
- Residential development zones, which, in turn, are divided into zones of different number of storeys.
- Public and business zones where educational and healthcare institutions, commercial and government organizations, sports facilities, and so on are located.
- Recreational areas: forests, beaches, green areas.
- Production zones: municipal and private production enterprises.
- Zones of transport and engineering infrastructure: roads, railway tracks, zones where utilities are located.
- Agricultural zones: garden, country house, peasant farm, agricultural production zones.
- Special zones: for cemeteries and others.
To determine such zones, the land use and development rules of the municipality require preliminary zoning.
Read about how it is carried out in the article “Land Zoning”.
What is a master plan
This is a territory planning document. It indicates the main directions of development of territories, corresponding schemes (maps) and regulations for their implementation. The main part is a large image in the form of a drawing. The object can be either a separate storage unit or an entire city or region.
What is a cadastre, read in this article.
Cadastral quarters and PZZ
Land use rules are also of great importance for cadastral registration: urban planning documentation is actively used by departments of Rosreestr for conducting cadastral registration.
One of the stages of cadastral registration is the additional zoning of territories and their division into certain territories depending on their intended purpose and use.
The smallest unit of cadastral registration is the cadastral quarter. It usually includes small towns, urban areas and other areas.
Details are contained in the material “Cadastral Quarter”.
Why is there no plot on the cadastral map?
It must be indicated with colons and contain 4 groups of numbers. For example, 77:08:0009005:8 Print map
Addresses can be complex, so it is more accurate to find an object by cadastral number. Look it up in the docs. For example, 77:08:0009005:8
The map shows
only areas for which land surveying has been done (that is, the exact coordinates of the corners have been measured).
On the public cadastral map you can find any land plot or capital construction project that has been cadastrally registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate and for which a land surveying procedure has been carried out.
It must be indicated with colons and contain 4 groups of numbers. For example, 77:08:0009005:8
Below the map there is a list of regions by which you can narrow your search. When you select the desired area, the territory will be zoomed in on the map.