In land legal relations, the term “land” is used to designate a separate area of the surface, that is, a plot of land.
The main principle of their use is compliance with the intended purpose of such a site.
All sites are divided into seven categories, each of which has special parameters unique to it, code, purpose and permitted uses.
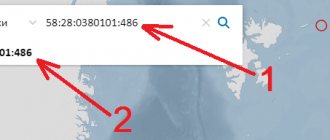
How to find out the category of land by cadastral number
- Open the public cadastral map of Rosreestr;
- Enter the cadastral number of the land plot into the search line;
- Get information about the category of land and the type of permitted use online.
To document the information, I recommend ordering an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Please note that in Rosreestr an extract from the Unified State Register costs 350 rubles (700 rubles for legal entities). If you want to find out the category of land and the type of permitted use cheaper, I recommend ordering a certificate through Quick Documents - this way you will receive a document for only 250 rubles. The order is completed within a day, the official data is from the Unified State Register of Russian Registers of Rosreestr.
I am ready to advise you free of charge by phone (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
The call is free for all regions of the Russian Federation
Certificate from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, which I recently ordered through Quick Documents
Codes
Each land plot that has undergone cadastral registration has a unique code that encrypts its category and intended purpose. There is a special reference book, designed in the form of a table, where each category and subcategory is indicated by the corresponding digital code :
- Thus, agricultural land has the code 003001000000. In order to highlight individual species within this category, the last two zeros are replaced by the subcategory number.
- Arable lands, hayfields, gardens and other farmland have the code 003001000010.
- Lands of settlements are hidden behind the designation 003002000000. And plots allocated for housing construction to citizens (individual housing construction) are encrypted as 003002000050.
- But a code such as 003002000100 denotes other land plots that are not clearly assigned to one of their categories.
- Codes are used, in particular, for tax purposes. For lands of different categories, different amounts of land tax are provided.
- Knowing which category a site belongs to, you can determine its code, as well as vice versa.
To find out which category each specific plot belongs to, you can use the Public Cadastral Map or order a cadastral extract from Rosreestr for the land plot of interest.
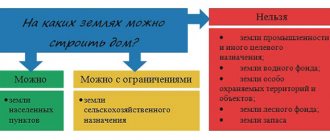
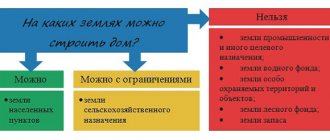
What is the category of land (purpose)
The division of land into categories is a consequence of the zoning of territories and the determination of state strategy. For example, agricultural lands include areas with fertile soil, forest lands should be covered with forest vegetation, and specially protected natural areas should be of great value for science and preserving the optimal properties of the ecological environment.
In accordance with the norms of the Land Code, the belonging of land to a category is the legal regime for its use. From this we can conclude that the category of land is a legally established description of standard properties.
Please note that the category of land and the intended purpose are equivalent concepts; you can use both the first and the second. The Land Code of the Russian Federation defines 7 categories:
- Lands of populated areas (settlements);
- Agricultural land (agricultural);
- Special purpose lands (for example, lands occupied for industrial and energy facilities, communications, country security facilities, etc.);
- Lands of specially protected natural areas (SPNA);
- Forest fund lands;
- Water fund lands;
- State reserve lands.
The last category is distinguished not so much by the principle of use as by underuse. In a large country there will always be land that is not in demand in the national economic system - this is the country’s land reserve. The greatest turnover of land is typical for the categories of agricultural purposes and settlements. In addition, the opportunity has arisen to transfer ownership of forest lands, but citizens are in no hurry to take advantage of it.
Next, we will consider each category and the types of permitted use included in it in more detail.
Land transfer
Lands can be transferred from one category to another.
This can not be done by the owner himself, but only by a competent authority , and only if the law does not directly prohibit such an action. For example, as is the case with protected areas.
An owner of land who wishes to change its intended purpose applies to the local executive authority with a petition.
If there are no obstacles to the transfer, such a request will be granted , and the necessary changes will be made to the land cadastre.
A typical example of such a procedure is the allocation of land for individual housing construction from municipal property.
Citizens can ask to transfer to them both an already existing, that is, allocated plot, and part of the farmland.
If the decision is positive, the selected plot is transferred to a category suitable for individual construction and, as such, is placed on the cadastral register .
a petition is not required to change the purpose of land . This happens, for example, when settlements expand, when part of the farmland or forest plantations falls into the category of settlement land.
But, in any case, a regulatory act of local or federal authorities is needed, by which this transition is fixed and legalized .
Lands of settlements
This is a category of land allocated specifically for compact living of people and placement of infrastructure facilities. Settlement lands have a clear boundary separating them from lands of other categories.
Within the category of land in settlements, the following types of permitted use are distinguished:
- Placement of multi-storey residential buildings. Objects can be located chaotically, forming streets, or in territorial blocks, forming microdistricts;
- Land allocated for individual housing construction (individual housing construction, individual railway);
- Recreational areas. They can be located both inside the settlement itself and in the suburban area. In accordance with Art. 98 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, recreational lands include lands intended and used for organizing recreation, tourism, physical education, recreational and sports activities of citizens. Clause 2 Art. 98 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation establishes the composition of lands for recreational purposes, which includes land plots on which there are holiday homes, boarding houses, campsites, physical culture and sports facilities, tourist centers, stationary and tent tourist and health camps, children's tourist stations, tourist parks, educational hiking trails, highways, children's and sports camps, and other similar facilities. Clause 5 Art. 98 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation prohibits activities that do not correspond to the intended purpose of such a law. Recreational lands are intended for the recreational functions of both citizens and the preservation of natural properties; you can build on them, but only what is specified in Art. 98 Land Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, Art. Art. 285 - 286 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for liability for improper use of a land plot. In the event that the use of a plot is carried out in gross violation of the rules for the rational use of land established by land legislation, in particular if the plot is not used in accordance with its intended purpose, this land plot may be seized from the owner;
- Areas built up with industrial facilities, administrative buildings, public utilities, food and non-food supply facilities, etc.;
- Land allocated for transport hubs - train stations, airports, river and sea terminals, etc.;
- Location of power supply facilities;
- Lands that are part of a populated area, but occupied by bodies of water;
- Areas allocated for the placement of roads, canals, piers, pipelines, air, ground and underground communication facilities, etc.;
- Specially protected natural areas within the boundaries of a populated area. Typically these include: parks, natural monuments, nature reserves, objects of special cultural and historical value, botanical and zoological gardens, open-air museums, etc.;
- Land intended for agricultural use. Despite the consonance with the name of one of the categories, these lands are still within the intended purpose of settlement lands. These include personal subsidiary plots (PHS);
- All other lands that can be represented by the space of streets, squares, reserve areas, special objects that are out of circulation, rights-of-way, security zones, etc.;
- Settlement development reserve zones.
Do not confuse permitted use with land ownership. Objects that are federally owned, privately owned, owned by a municipality, or a subject of the federation can be located on the lands of settlements.
I am ready to advise you free of charge by phone (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
The call is free for all regions of the Russian Federation
In addition, the placement of individual buildings should not be confused with settlements. For example, a forester's house, an apiary, industrial and residential premises at mining enterprises cannot be part of a populated area until the land under them changes its category.
Video description
Interesting information about the rules for developing land plots in SNT in the video:
Form of individual housing construction plot
According to the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, individual housing construction (IHC) is a detached house in which a family can live permanently without exceeding three floors of the building. At the same time, the need for communications (gas, water supply, electricity) remains with government agencies. This form of land ownership makes it possible to register.
Agricultural land
Agriculture is the basis of existence of any society and state. All this forced legislators to allocate lands suitable for agricultural use into a separate category.
The category of agricultural land includes land plots located outside settlements, the economic function of which is to produce agricultural products. However, like the category of settlements, agricultural land includes a number of lands that have their own permitted use.
Within agricultural lands there may be the following types of permitted use:
- Areas occupied by roads along with rights-of-way;
- lands occupied by forest vegetation (forest belts serving the function of protecting fields, forest areas for other purposes);
- plots occupied by outbuildings;
- arable land;
- hayfields;
- pastures;
- gardens;
- fallow lands.
The fallow may be of a special use nature, for example, for the purpose of increasing soil fertility, or it may be forced when the owner or user for some reason stops cultivating the land in accordance with its permitted use. Typically, a deposit refers to the latter case. The deliberate transfer of land to fallow land is usually carried out when the economic and environmental value of the sites is lost due to natural and man-made disasters, long-term pollution, and soil erosion.
Subcategories of agricultural land
As the name suggests, agricultural work must be carried out on these lands, and the agricultural lands themselves must be located outside the settlements. The categorical division of land determines the purpose and content of use. For agricultural land, the legislator distinguishes two subcategories:
- agricultural;
- and non-agricultural land.
Despite the apparent opposition, both types of land are subordinated to the same goal - to provide conditions for agricultural production.
Agricultural grounds
These include land plots used only for the purposes of agriculture or livestock raising. In turn, agricultural land is divided into arable land, hayfields, pastures, fallow land (temporarily uncultivated land), and areas with perennial tree plantations. Moreover, this division is not arbitrary; all types of farmland have a special legal status that cannot be changed arbitrarily.
Areas that have undergone reclamation have a special status. This is due to the fact that in order for them to acquire the necessary resource properties, costly measures were taken to drain, water, restore soil fertility, and minimize erosion. Often such lands require uninterrupted reclamation work.
Non-agricultural land
Non-agricultural land is occupied by various auxiliary structures. These may include: roads, communications, protective forest belts, reservoirs, buildings that support agricultural production.
This non-agricultural status is subject to urban planning regulations, while agricultural land is not subject to its regulations.
Differences between the first and second
It should be noted that there is a difference between agricultural lands and residential areas where farming is permitted. In the first case, the land is a category and has a designated purpose, in the second, it is located within the boundaries of a populated area and has a specific permitted use.
Agricultural land is heterogeneous and has its own divisions based on the cadastral value principle:
- Land with low and medium value. These usually include lands of long-term fallow, areas of low fertility, subject to erosion, pollution, etc.;
- Land with a cadastral value significantly higher (50% or more) than the average for a given territorial unit;
- Land of special value. Their cadastral value far exceeds average values. Typically these include arable lands that have long been involved in agricultural production and have high fertility.
State of the land fund
Russia is one of the most prosperous countries in terms of land resources. At the same time, the huge size of land areas suitable for economic activity is relatively small. Among the main problems of domestic land resources, experts cite the deterioration of soil fertility and the condition of agricultural lands. The top cover of the post is subject to regular pollution, as a result of which the land begins to degrade and loses the ability to reproduce fertility and restore properties.
Advice from Sravni.ru:
Land is one of the main resources of Russia. Until every person, every company realizes this truth, we will treat the land as a consumer, which ultimately will not bring profit either to the Russian Federation or to individual large landowners. The whole country needs to preserve and increase the beneficial properties of the land, and the problem of soil pollution and the lack of simple rules of the game in the land market needs to be solved at the state level, and the sooner the better.
Lands of forest and water fund
The category of forest and water fund lands presupposes their economic use, but only within the framework of the permitted type of activity:
- Forestry is carried out on forest fund lands, which most often involves forest management zoning. According to its results, all lands in this category are divided into areas where logging is carried out and into areas where the forest is restored;
- Water fund lands are territories with water bodies, water protection zones of natural reservoirs, zones of water intakes and other water management structures.
Land Code of the Russian Federation
Regarding agricultural land, the following regulatory framework is used:
- The concept and purpose of land is given in the Land Code of the Russian Federation, art. 77. It is indicated here that this category of land is intended for farming, processing, growing and storing products. Therefore, the construction of appropriate buildings is allowed.
- Legal regulation of the issue of turnover of agricultural land is carried out in accordance with the norms of Federal Law No. 101. It establishes legal relations regarding the disposal and use of lands of this category, and also establishes a number of restrictions regarding their turnover.
Reserve lands and protected areas
These two categories of land are withdrawn from circulation. Lands of specially protected natural areas are, as a rule, state property, although the law allows these areas to be privately owned. There have simply been no such precedents in Russia.
Lands recognized as particularly valuable to society are transferred from one category to another and withdrawn from circulation and economic use. Their transfer back to another category is not provided for by law. Reserve lands cannot be used for economic purposes, but can be transferred to another category and with a certain permitted use.
Let's sum it up
State measures such as recording all land plots, dividing them into categories, establishing restrictions on use, etc., pursue an important goal - the protection of a valuable natural resource , the quantity of which is limited for objective reasons.
Violation of statutory requirements will have a number of unpleasant consequences . The easiest of them will be a fine. The most severe is deprivation of property, that is, seizure of land in favor of the state .
Such measures also indicate the special attention of the authorities to preserving the land fund.
What is the type of permitted land use (URL)
The concept of permitted use of a land plot is of a clarifying nature within the framework of the intended purpose. The introduction of this concept is a consequence of more detailed zoning of the territory on the scale of a federal subject, region or other territorial division. However, a land plot owned by a farmer may have a different permitted use within the same intended purpose.
In addition, there is a division of the permitted use into the following types:
- basic;
- conditionally permitted;
- auxiliary.
Table of the main types of permitted use of land
| Number in the classifier | Comments |
| 1.0-1.18 | This includes lands located outside populated areas that are intended for growing crops, livestock, fur-bearing animals, breeding birds, fish, and insects. It is allowed to erect buildings necessary for agricultural needs. |
| 2.0-2.7.1 | On these lands, it is possible to erect buildings, both single-story and multi-story, which are used for living, as well as the infrastructure necessary for their maintenance. |
| 3.0-3.10.2 | On the lands you can place capital construction projects that are necessary to meet social and spiritual needs - utility companies, healthcare facilities, schools, preschool educational institutions, etc. |
| 4.0-4.10 | The lands are intended for capital construction projects that are used for profit. |
| 5.0-5.5 | The plots are allocated for the placement of sports, tourist facilities, recreation centers, horse riding, etc. |
| 6.0-6.11 | Mining and production facilities are allowed to be located on the lands. |
| 7.0-7.5 | Various communication routes and buildings necessary to service them are placed on the sites. |
| 8.0-8.4 | They house facilities intended for the Armed Forces, as well as customs offices. |
| 9.0-9.3 | Lands on which specially protected natural areas are located. |
| 10.0-10.4 | Activities related to cultivation, logging, logging, and forest protection are permitted. |
| 11.0-11.3 | Water bodies and hydraulic structures are located on the lands. |
| 12.0-12.3 | The areas contain roads, cemeteries, parks, public gardens, etc. This also includes reserve lands. |
| 13.1 | Activities related to the cultivation of agricultural crops for one’s own needs are permitted. Residential buildings cannot be built. You can build outbuildings to store crops and equipment. |
| 13.2 | Activities related to the cultivation of fruit trees and shrubs for one's own needs are permitted. You can build residential buildings, garden houses (not for permanent residence), garages, and outbuildings. |
| 13.3 | The line has lost force since January 1, 2021 - Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated August 9, 2021 N 418 |
Conditionally permitted type of land use
The conditionally permitted type of use of the land plot serves as a supplement within the category and permitted use. This addition occurs when it is not possible to create a classifier for all occasions.
In order to establish an additional standard, it is necessary to go through a special procedure for approvals and public hearings at the Land Use and Development Commission. Such an expansion of the VRI is possible only if it is provided for by local urban planning regulations.
Auxiliary permitted uses
Ancillary types of permitted use specify the actions performed within the framework of other types of use. A clarifying nature may consist, for example, in the placement of some small objects - garages, transformer booths, fences, etc. Thus, a potential developer needs to fit into the intended purpose and main type of permitted use of its territory.
Other types of permitted use can be changed in the official dialogue between the potential and existing owner of the site with state or municipal authorities.
For example, a land plot for building a house must have a category (intended purpose) - land of settlements, and the type of permitted use (AUR) - for individual residential construction (IHC).
The full list of VRI is exhaustive, is contained in a special classifier and is not subject to change in any order. If a new VRI is installed for a given territory, then it must correspond to the list of this classifier.
Legal regime of transport lands
Transport lands include lands provided to institutions, organizations, enterprises of automobile, railway, pipeline, air and water transport, as well as citizens and organizations for the construction, operation, maintenance, repair, improvement and development of structures, devices and other objects of transport systems. Transport lands do not include driveways and pedestrian roads located on other categories of land. Lands occupied by sea and river transport facilities within the lands of the water fund also do not belong to transport lands.
Land for the construction and operation of land and air transport is allocated in the form of a right of way within the established standards. The right-of-way for road and rail transport is a plot of land occupied by the roadbed and security zones. The right-of-way of main pipelines includes land plots along which or under which the pipeline passes, as well as land plots necessary for maintaining and ensuring the safety of the pipeline system. Transport lands are predominantly lands that are state or municipally owned and intended for public use. A significant part of transport routes, especially those of interregional importance, are federal property. These include, for example, federal public highways. Transport lands are under the jurisdiction of the relevant ministries and departments of the Russian Federation or constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Transport lands can be transferred to interested individuals and legal entities on the right of use or lease for the purpose of operating roads, their repair and maintenance, construction and operation of road infrastructure. Within the right of way, the construction of buildings and structures not related to the operation and repair of the road is prohibited. It is planned to carry out forest planting within the right of way of highways and railways.
Forest use within such strips is limited (Articles 135, 136 of the Forest Code of the Russian Federation). Vacant land plots on railway rights-of-way can be leased to citizens and organizations for agricultural purposes, passenger services, and cargo storage. The use of such land plots for storing hazardous substances and materials is not permitted. To ensure safe operation of transport | systems, placement of transport infrastructure facilities and 1 maintenance (service), a special land use regime is established on land plots adjacent to the right of way. A special land use regime is established within the roadside strips of federal highways, occupying land plots with a width of 50 to 150 m on each side. In the roadside strip, land plots are not confiscated from owners, owners, users and tenants, but restrictions on economic activity are introduced.
Land plots in roadside strips and federal highways are provided for the placement of road service facilities (parking lots, entrances, exits, gas stations), utilities, non-permanent buildings and structures, and billboards. The provision of land plots is coordinated with the road service and traffic safety authorities.
In order to create conditions for the construction and reconstruction of transport facilities, land is being reserved. Lands reserved for transport purposes are not provided for other purposes to citizens and organizations.
How to find out the characteristics of land plots for each VRI
- In accordance with paragraph 3 of part 11.2 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, the intended purpose and permitted use of the formed land plots are recognized as the intended purpose and permitted use of land plots from which, during division, merger, redistribution or allocation, land plots are formed, except for cases established by federal laws.
- At the same time, according to paragraph 3 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, urban planning regulations are mandatory for all owners of land plots, land users, landowners and tenants of land plots, regardless of the form of ownership and other rights to land plots. These persons may use land plots in accordance with any type of permitted use provided for by the town planning regulations for each territorial zone.
- Part 8 of Article 36 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation and part 4 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation establishes that land plots or capital construction projects, types of permitted use, maximum (minimum and (or) maximum) sizes and limit parameters of which do not comply with town planning regulations, may be used without setting a deadline for bringing them into compliance with urban planning regulations, except in cases where the use of such land plots and capital construction projects is dangerous to human life or health, to the environment, or cultural heritage sites.
- In accordance with paragraph 70 of the Procedure for maintaining the state real estate cadastre, approved by order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated 02/04/2010 N 42 (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure), information on the types of permitted use of a land plot is entered into the register of real estate on the basis of urban planning regulations or on the basis of an act of a government authority or local government authority. If the formation of land plots is not associated with a change in the type of permitted use of the original land plot, the type of permitted use of the resulting land plots in the register of real estate must correspond to the type of permitted use of the original land plot.
- According to paragraph 52 of the Requirements for the preparation of a boundary plan, approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated November 24, 2008 N 412 (hereinafter referred to as the Requirements), the type of permitted use of the resulting land plots must correspond to the information of the state real estate cadastre on the type of permitted use of the original land plot, except for cases established legislation of the Russian Federation. In such cases, the type of permitted use of the land plot(s) being formed is indicated in detail “4” of the section “Information on the land plots being formed and their parts” if there is a free-form declaration of the interested party on the selected type of permitted use of the land plot, drawn up on the basis of the town planning regulations, or if there is an act of a state authority or local government determining the type of permitted use of the land plot being formed (a declaration or a copy of the act, according to which information about the type of permitted use of the land plot is included in the boundary plan, is included in the Appendix to the boundary plan).
- Paragraphs 6 - 7 of Article 11.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation provide that the formation of land plots should not lead to wedging, interspersing, broken boundaries, interstriations, the impossibility of placing real estate objects and other shortcomings that impede the rational use and protection of land, as well as violate the requirements established by this Code , other federal laws. The formation of a land plot, the boundaries of which cross the boundaries of territorial zones, forest districts, forest parks, is not allowed, with the exception of a land plot formed for carrying out work on geological exploration of subsoil, development of mineral deposits, placement of linear objects, hydraulic structures, as well as reservoirs and other artificial water bodies. objects.
Based on the rules set out above, we can conclude that when establishing the type of permitted use of the land plot being formed, it is necessary to take into account the purpose of its formation, rationality of use, as well as the presence of legislative acts establishing exceptions to the provisions of paragraph 3 of part 11.2 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the basic requirements for the formation of land plots are enshrined in the Land Code of the Russian Federation, the basic requirements for the establishment of certain VRI on the territory are contained in the PZZ of your region. For example, the characteristics of land plots for private plots are enshrined in the Federal Law “On the turnover of agricultural land” and in your regional law on the turnover of agricultural land.
At the same time, any decision of a government body or official can be challenged in court. Only an appropriate examination can establish the exact possibility that a particular land belongs to the required VRI.
Consolidation of several plots and VRI
You can merge areas that have at least one border. By law they are recognized as adjacent. Conditions under which merger is permitted:
- Consent of all owners.
- Each plot has a cadastral passport (you must take an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate).
- The same type of permitted use (indicated in the USRN extract).
- Same land category.
- The plots correspond to the maximum minimum and maximum indicators in a given location area.
If the VRI of the plots are different and the goal is to combine them, you can try to apply to change the type of operation of one of the plots. In order to combine territories, you must contact a cadastral engineer with a previously collected package of documents. He will draw up a plan, which, along with the application, the owners submit to the Rosreestr institution or the Multifunctional Center.
What to do if the category of land or VRI in Rosreestr differs from the data in the PZZ
What if there is different information on the same land plot? For example:
- In Rosreestr it is written on the land plot: Land category: Agricultural land Permitted use: For citizens to carry out gardening and vegetable gardening according to the document: for summer cottage construction with the right to erect a residential building with the right to register residence in it.
- At the same time, the PZZ says: CX-3 - Agricultural production zone. The PZZ is attached to the officially signed Resolution of the Administration of the Ramensky City District of the Moscow Region.
Based on general practice, we use the information contained in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. If the document indicates that the land plot is intended for gardening with the right to build a residential building, then we focus on this information. If reasonable questions or reasonable doubts arise regarding such data as the intended purpose, type of permitted use, location of the site in a particular urban planning zone, you have every right to make a simple written appeal to Rosreestr and the administration of your municipality.
I repeat, as a practitioner, I always rely on information received from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. However, it should also be noted that along with such information, the information contained therein may be unreliable due to any technical problems.
Borders
A boundary is a “line” that separates a populated area from other types of land.
The boundaries of the NP should be located so that there are no overlaps between the boundaries of municipalities and areas that are allocated to anyone.
Both the initial approval of the boundaries of the NP and their changes are recorded in the main documents of municipalities.
Depending on the municipality, such a document may be:
- general plan,
- territorial planning schemes.
of cities with special status are changed :
- Moscow,
- St. Petersburg,
- Sevastopol.
They are approved by the Federation Council .
If some plot from one NP “moved” to a neighboring one, then this does not entail any changes in the rights to this plot.
Lands of other categories cannot be included in the territory of a settlement , therefore the transfer of boundaries involves a change in the category of land (either adjacent lands become NP lands, or NP lands move to another category).
Along the perimeter of the settlement there is a suburban zone ; it is not included in the territory of the settlement, but is, as it were, a “spare” zone in case of expansion of the NP.
Not every space is suitable for creating a settlement. For example, this applies to flooded lands and areas where attempts are being made to preserve wildlife.
What happens if you use the land for other purposes?
The legal regime is a system of prohibitions, restrictions, permissions and obligations. Owners of agricultural land are obliged to:
- use the land in accordance with its intended purpose and permitted use;
- take measures to prevent any impacts on the land plot that could lead to significant losses of fertility and other significant properties;
- maintain the optimal condition of reclaimed lands;
Owners of agricultural land have the right:
- acquire, sell, donate, inherit land belonging to them;
- receive from the state free of charge or on a paid basis lands of this category for ownership or use;
- submit a petition to change the status, category and permitted use of land.
The main restrictions and prohibitions can be summarized as follows:
- Non-use of agricultural land is prohibited. This requirement applies to any plots owned by individuals and legal entities. Only the state that owns the lands of GosZemZapas and reserve areas can not use the land;
- Foreign citizens cannot participate in the turnover of agricultural land. However, they can lease land and use it for its intended purpose, fulfilling all responsibilities for maintaining the plots in proper condition;
- Arbitrary transfer of agricultural land to another category or permitted use is prohibited and punishable;
- There are restrictions on the duration and content of the lease. The law determines the maximum and minimum terms, as well as the regime for using land plots;
- During territorial zoning, particularly valuable land plots that are withdrawn from circulation are determined. They are on the list of territories prohibited from privatization. Disturbed lands are also withdrawn from circulation and transferred to fallow until fertility and other significant properties are restored.
Please note that failure to perform or improper performance of duties entails penalties provided for by law in the form of fines, criminal liability and other measures, including financial liability of a compensatory nature.
I am ready to advise you free of charge by phone (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
The call is free for all regions of the Russian Federation
In the summer of 2021, the procedure for confiscating land that is not used at all or with any violations was simplified. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, after the introduction of these amendments, more than 120 thousand hectares of land were returned to circulation.
Legal regime of lands provided to organizations of the mining and oil and gas industries
The category of industrial land includes land plots provided for the use of subsoil within the land territory of the country. These are lands used for geological study, exploration and extraction of minerals, their storage and primary processing, including mines, quarries, development of various deposits, construction and operation of underground structures not related to the extraction of minerals - storage facilities, industrial production facilities. Land allocated for the use of subsoil from the lands of the water fund (the bottom of reservoirs, the territorial sea), as well as land plots that are privately owned when they are used by the owners for the extraction of common minerals (sand, gravel, clay and etc.). Extraction of mineral resources within the forest fund, which does not require the transfer of forest lands to non-forest lands and their withdrawal, does not entail a change in the intended purpose of the forest fund lands (Article 66 of the Forest Code). The provision of land plots for geological study of subsoil, including the search and exploration of mineral resources, can also be carried out without changing the intended purpose, but with the establishment of a public easement (Article 23 of the Land Code). Land plots for the purposes of subsoil use are provided through the issuance of subsoil use licenses and the allocation of geological (for geological study and exploration of mineral resources) and mining (in all other cases of subsoil use) allotment. A subsoil use license is issued only with the prior consent of the land management body or the land owner to allocate a land plot for subsoil use purposes. When using subsoil resources provided under production sharing agreements, obtaining a license is preceded by the conclusion of such an agreement.
The license is the basis for making a decision on the seizure of the required land plot.
The land plot is provided after registration of the mining allotment, approval of land reclamation projects, restoration of previously mined lands. Particularly valuable agricultural lands, if they are not included in the list, the use of which for non-agricultural purposes is not permitted, are provided after the development of other agricultural lands located within the boundaries of the mining allotment. The land plot is confiscated and provided to interested citizens and organizations with reimbursement of the cost of the plots to their owners. At the same time, a decision is made to transfer the land plot from one category to the category of industrial land. A subsoil plot within a mining or geological allotment is assigned to license holders on the right of permanent or temporary use. The land plot necessary for the use of subsoil is provided for rent or under the right of limited use (public easement). The latter applies in the case of provision of land and subsoil plots for exploration work. Subsoil plots are provided for temporary use for periods from 5 to 25 years for geological study, exploration and mining. The necessary land plots are assigned for the same period. A feature of the legal regime of lands granted for subsoil use is the requirement to remove and preserve the fertile soil layer and to reclaim land after completion of mining operations, conservation and liquidation of mining enterprises and underground structures not related to mining. If necessary, land plots are returned to previous users.
conclusions
From the perspective of building a house, it is advisable to use the following types of permitted use:
- For the construction of an individual residential building (IZHS);
- For the purpose of maintaining personal subsidiary plots (LPH);
- For running a dacha-type household and building a garden house, which is recognized as residential under the dacha amnesty;
- For agricultural production and peasant farms (peasant farms).
How to change the type of permitted use of a land plot
What is land zoning
Identification of agricultural plots in water protection zones
Plots of land located in water protection zones can be transferred to citizens and legal entities for ownership without restrictions, as confirmed by land legislation. However, in accordance with the requirements of the Water Code, the transfer must first be agreed upon with the federal executive authorities in the field of use of the water fund.
Previously, such plots were transferred for permanent (indefinite) use without approval, but when registering them as property, such approval is required. This requirement is due to the introduction of additional restrictions on environmental management in accordance with paragraph 1 of Resolution No. 1404 of November 23, 1996.
Therefore, if a citizen used the land legally, he will be able to easily purchase it if he has agreement with the federal executive body in the field of water use. Upon receipt of a refusal, a clear position on this issue must be stated by the authority, which the citizen has the right to challenge in court.
FacebookVKontakte