Earth
6
Agricultural activity is inextricably linked with the use of land for agricultural purposes. The plot can be owned or long-term leased, but you need to know the intended purpose of the land, which is subject to a certain type of classification of permitted use. This will determine what activities are not prohibited from being carried out on a particular piece of land in order to avoid unpleasant misunderstandings.
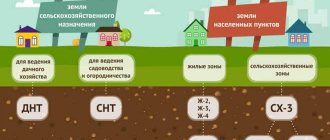
Agricultural lands are areas and territories of all settlement boundaries used for agricultural needs or similar purposes. Unlike lands for agricultural use, they are intended for the full cycle of growing and processing products. This makes it possible to build warehouses there to store products collected from the fields, as well as organize the necessary infrastructure.
Permitted use of land for agricultural production
You can use land belonging to this type of intended purpose in the manner defined by law:
- conducting agricultural production;
- formation of protective plantings in the form of forests;
- carrying out scientific and research activities;
- conducting training events;
- organization of peasant farms and private household plots;
- growing grain crops, flax, hemp and vegetables;
- creation of business partnerships or other non-profit organizations;
- use by consumer cooperatives for their needs;
- for the formation of agricultural educational institutions;
- poultry farming, beekeeping and pig farming;
- placement of public lands and public services.
In addition, the specified lands and areas within such territories can be used for hunting and other activities not prohibited by law.
When determining permitted types of activities, it is necessary to take into account the minimum setbacks from boundaries, maximum plot sizes and other nuances. Additionally, the placement of capital construction projects that may be required for agricultural production is permitted here. This also has its own rules and restrictions.
Seizure
The legislation stipulates that the state has the right in some cases to forcibly confiscate agricultural land from the owner.
This decision is made in court and can be challenged within the appropriate period. The main reasons for the seizure of farmland:
- the agricultural plot has not been used for its intended purpose for three or more years,
- the site is used irrationally, which leads to a decrease in soil fertility and deterioration in the quality of agricultural land.
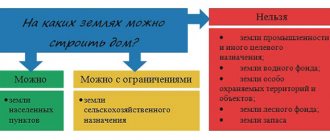
What can be built on land for agricultural production?
When constructing capital construction projects in a given area, it is necessary to take into account the maximum building density, the maximum height of buildings and the number of floors, and other features. Owners and tenants may use land for agricultural production for the purpose of developing certain properties. Such structures include:
- objects intended for storing agricultural products: warehouses, vegetable stores, elevators;
- facilities for storing and servicing agricultural machinery;
- facilities for primary processing of agricultural products;
- commercial dairy farms, pigsties, poultry houses, pond farms;
- objects necessary for public utilities or consumer services for agricultural enterprises;
- buildings for scientific or educational activities, as well as public administration;
- shops, catering establishments;
- hydraulic structures.
Legally, communications can be laid here for farming or other targeted activities, internal roads can be built, etc. The construction of facilities for the primary processing of agricultural goods is allowed on the territory. These include refrigerators, dryers, etc.
The list of objects permitted for construction includes houses for temporary
residence of workers. To build a residential building, you will have to register a peasant farm, otherwise a building permit will not be issued. Such a procedure should be entrusted to the land lawyers of our company. They will also help you understand the nuances of using land for agricultural production.
The legislative framework
The purchase and sale, as well as the use of agricultural land, is regulated by the Land, Civil, and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation, laws and regulations. It is advisable to study the laws:
- On the turnover of agricultural land.
- On state regulation of ensuring the fertility of agricultural lands.
- About agricultural cooperation, etc.
In addition to the main regulations, the use of agricultural land is also regulated by orders of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation (for example, the Ministry has developed a Procedure for state monitoring of agricultural land and other acts).
How to convert a plot of land from farmland to land for agricultural production?
Agricultural land is especially valuable productive agricultural land, including arable land, hayfields, pastures, fallow lands, and land occupied by perennial plantations. Farmland is subject to special protection, construction is limited, and the use of farmland for other purposes is not allowed.
It is possible to remove land from agricultural land only by proving its low agricultural efficiency or by challenging the classification of this plot as agricultural land, contrary to previously issued documents, in court.
To convert a plot of farmland into land for agricultural production, it is necessary to apply for amendments to territorial zoning and local land use and development regulations. Changes are being made at the municipal level. The application for transfer of land to agricultural production is considered by the head of the local administration.
Before starting the procedure, it is advisable to study the land plot in detail and order an expert assessment of the value of the site for agricultural activities. You should also prepare documents for transferring the plot to agricultural land:
- title papers;
- extract from the Unified State Register for the site;
- identification;
- results of expert assessment;
- consent of the co-owners to the transfer.
Other documentation may be required. The exact list depends on the situation. When the documents are collected, an application to the administration (architecture department) is prepared. This department delegates the powers to a special commission to create a draft of changes and organize public hearings.
Based on the results of open discussions, recommendations are made on the project - whether to approve the changes or not. They are sent to the head of the administration for a final decision. At each stage a refusal may be issued. Whether the plot will be allowed to be transferred from farmland to agricultural production depends on the grounds given in the application.
After considering the application and the results of public hearings of the main administration, he makes a decision. You must contact the Rosreestr authorities with this resolution if updated information has not appeared in the Unified State Register within 15 days.
Redistribution Fund
The Land Redistribution Fund is a unified database of agricultural plots that have temporarily fallen out of circulation, that is, not used for their intended purpose.
Its main function is the formation of a fund of land and their further transfer for use to individuals or legal entities under certain conditions.
This is done so that strategically important farmland does not stand idle, because this is economically unprofitable.
An agricultural plot falls into the distribution fund under the following conditions :
- in case of voluntary refusal of the owner from the site,
- in the absence of heirs after the death of the owner,
- during forced seizure of land by the state.
Don’t know how to find out the category of your land plot?
If you know its cadastral number or location, read detailed instructions here.This article will help you decide on the category of site for construction.
Is it possible to convert land from agricultural production to horticulture?
This possibility is provided for by law, but in practice a number of restrictions arise. You will have to take into account the purposes of the future use of the site, the presence of real estate on it and other nuances. Before transferring land to horticulture, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the Classifier of types of permitted use.
- If the site will be used for “Gardening on farmland” (clause 1.5), the construction of greenhouses and fences, the creation of wells is allowed here, but the construction of capital real estate is prohibited.
- If the land will be used for “Gardening” (clause 13.2), the Classifier allows the construction of real estate, outbuildings and the cultivation of various crops.
In the first case, the transfer of land from agricultural production is allowed if there are no warehouses on the site that were previously used for storing agricultural products, public catering facilities and other objects prohibited in areas with code 1.5.
In the second situation, there are no such restrictions, although here, too, the construction of certain real estate, which may be located on an agricultural production site, is not permitted.
- Before the transfer, the functional purpose of the objects will have to be changed, or prohibited buildings will have to be dismantled. Otherwise, the application will be denied.
- If a large part of the plot will be occupied by residential buildings or year-round living is planned, as well as under other conditions provided for by law, it is necessary that town planning regulations be approved for the territory (it will have to be included in the boundaries of settlements).
Additionally, you will need a draft site plan indicating the construction sites, as well as passageways in the area being formed. It is also necessary to approve a survey project demonstrating the total number and location of the land plots and public lands being formed.
Some restrictions relate to the presence of other owners, or the desire to organize a non-profit partnership. The land lawyers of our company will help you understand all the nuances of the procedure.
Features of farmland
Farmland has a number of features compared to other types of farmland. They are enshrined in law (Article 79 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
- The most fertile lands are under state protection, as they are its national treasure and most important resource.
- Such lands can be used only for their intended purpose, that is, for agricultural activities. Inappropriate use is punishable by law .
- Farmland with a high cadastral value is not subject to transfer to other categories of land
- The construction of any types of buildings in areas protected by the state is prohibited.
In exceptional cases, in agreement with regional authorities, farmland with poorer soil quality and low cadastral value may be transferred to another category of land.
Among other things, the legislation establishes requirements for persons using farmland:
- the plots must be developed within 2 years,
- while carrying out its activities, maintain soil fertility,
- If necessary, provide authorities with information about the chemicals used.
Is it possible to include land for agricultural production in a settlement?
If there are sufficient grounds for including agricultural land in the settlement, such a procedure is possible. But for this you will need to apply for a gene change. municipal plan, change the planning scheme and undergo many approvals. The legislation contains an exhaustive list of grounds for transferring an agricultural production site to a municipality.
Changing the category of a territory is possible if:
- the plot is unsuitable for agricultural production;
- there is a change in the boundaries of the municipality;
- it is necessary to place objects of communal importance;
- a specially protected natural zone is created;
- mining is planned;
- there is an agreed upon land reclamation project;
- No particularly valuable agricultural crops are grown on the site;
- An environmental assessment of the allotment was carried out.
The conditions listed above can be applied in combination or individually. Sometimes it is enough to confirm that the site is not suitable for agricultural production, and it will be allowed to be included in the settlement. In other situations, an environmental assessment or confirmation of the low productivity of the territory is required.
Options for the subsequent use of the territory will also have to be taken into account. Future activities must be consistent with the grounds for change of category specified in the law. This procedure is labor-intensive and requires many approvals. Particular attention is paid to the package of documentation and the availability of justification for the transfer of land to the municipality. Our lawyers will help you deal with such difficulties.
Providing
Providing agricultural land for use essentially means transferring such land for rent for its intended use. In this case, the plots remain the property of the state.
To obtain a plot you must :
- Submit an application to the appropriate authority.
- Collect a package of documents.
- Wait for a decision.
- Conclude a lease agreement.
The law provides for a number of benefits and advantages when transferring agricultural land to certain categories of persons (for example, small peoples to support and preserve their way of life).
Rules and restrictions
Agricultural land that is in state or municipal ownership is granted ownership at an open auction or at the request of the applicant (if the plot is not registered and there are no people willing to buy it at the auction).
The following restrictions apply:
- You cannot buy more than 10% of the land in one district;
- it is prohibited to sell land without obtaining a prior refusal from the municipal authorities to purchase;
- the shareholders are required to waive their pre-emptive right to purchase;
- Foreigners do not have the right to buy land as their own.
Tenants who do not violate the terms of the lease agreement and use the land for their intended purpose have the preemptive right to purchase land that belongs to the state.
If the land is privately owned, then the parties draw up a purchase and sale agreement and register it with Rosreestr. It can be sold to outsiders only at the price at which the plot was previously offered to local authorities.
On a note. Land plots located at a distance of no more than 30 km from the borders of rural settlements cannot be used for purposes not related to agriculture (Article 78 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Monitoring
Monitoring is carried out with the aim of analyzing and assessing the qualitative state of fertile soil, taking into account the impact of natural and anthropogenic factors. Monitoring is carried out on the status of:
- soil fertility parameters;
- soil degradation processes;
- for changes in the state of vegetation cover.
Information collection is carried out by local authorities. A register of soil fertility is maintained, and analyzes and forecasts are prepared regarding the future use of agricultural land. Its goal is to prevent damage to valuable land that can be used for growing grain, vegetables and other crops.