The classifier of types of permitted use of land plots was adopted in 2014.
The new classifier contains 155 types of permitted use.
In this article I will show:
- how to use an online classifier of types of permitted use of land plots for free;
- what to do with old types of permitted use that were not included in the classifier;
- how to establish compliance of the type of permitted use with the new classifier.
So let's get started.
Free online Classifier of types of permitted use of land plots.
At the bottom of the article you will find an online service with a classifier of permitted use.
The information in the classifier is divided into 3 columns:
- name of the type of permitted use,
- description of permitted use,
- code.
Each column (vertical column) has a built-in sorter.
The first and second columns sort the types of permitted uses in alphabetical order.
The third column sorts by numerical code of the type of permitted use.
Sorting works in forward and reverse order.
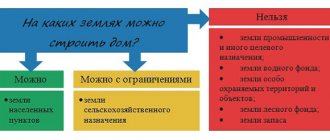
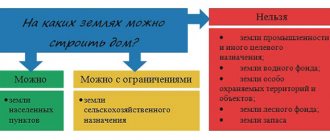
Which VRI are suitable for individual construction?
Residential buildings for permanent residence
They are built in areas with the following code:
- 2.0. – residential development;
- 13.2. – gardening;
- 13.3 – maintaining a dacha farm.
Seasonal residential properties
They are being built on areas with the code:
- 13.1. – vegetable gardening (only non-capital construction);
- 13.2. – gardening;
- 13.3. - maintaining a dacha farm.
Non-residential buildings, structures and structures
Possible on lands with code:
- 1.0. – agricultural use (auxiliary structures for farming);
- 4.0 – entrepreneurship (construction of non-residential buildings for the purpose of making a profit).
The classifier of types of permitted use has 155 positions.
In other words, the legislation establishes one hundred and fifty-five types of permitted use of sites.
For ease of use, the online classifier of types of permitted use has a built-in search.
When entering characters, the service automatically displays the types of permitted use corresponding to the request.
The search works across all rows and columns of the classifier.
If you know the exact code, then enter the numbers in the search field.
The service will display the type of permitted use corresponding to the entered code.
If you type the text, the permitted use classifier will display all matching results.
After viewing the result, find the desired VRI.
Where to clarify the type of your allotment
To find out what type of use of the plot is available to the owner, you must contact the cadastral registration and cartography department of the municipality and request data from cadastral documents.
The applicant must have with him originals and copies of cadastral and civil passports. You can submit the corresponding application during a personal visit to the department, or use postal services by sending an application and copies of documents certified by a notary.
Sample cadastral passport
There is also the possibility of obtaining the necessary information through the official website or the Government Services portal. The cadastral registration department provides up-to-date information to all users who apply; you just need to formulate your request by indicating the cadastral number of your land plot.
Initially, all plots have a type of permitted use that belongs to the main group. This information is also indicated in the municipality. Changing the type is possible only after receiving a corresponding resolution from the administration.
The received documentation is subject to storage and is the main evidence of changing the main group to a conditionally permitted or auxiliary one. In case of its absence, the land is assigned the main type.
Obtaining a cadastral passport of a land plot through State Services
Only the owner of the land has the right to initiate a change in the type of permitted use, based on the form of ownership of the land. When drawing up documents recording the emergence of legal ownership, it is recommended to indicate the type of permitted actions on the territory, along with other characteristics of the property.
What to do with old types of permitted land use?
The legislation answers this question very clearly.
Old types of permitted use established before the adoption of the classifier are recognized as valid.
In this case, it does not matter whether the old VRIs correspond to the classifier or not.
In other words, the type of permitted use established before December 24, 2014 is considered valid.
The correspondence or non-compliance of the old VRI with the new species from the classifier has no legal significance.
Varieties
In addition to the list of main types, divided by subject content, there are types of permitted use, which play an important role in the disposal of the territory by the landowner. Thus, the actions permitted on the territory can either be strictly tied to the classification, or leave the possibility of a non-standard approach to the use of the land to the owner of the territory.
Main group
This type requires strict adherence to regulations in accordance with the requirements of urban planning legislation and its legal acts. In the classifier list, the main group is determined by a full digital code.
Using the example of paragraph 1, which allows agricultural work, they will be limited to subparagraphs 1-18 following the main paragraph code. For the remaining points there are 13 in total) the same rule applies.
The owner of a plot with the main type of permitted use is obliged to responsibly comply with the resolutions of the organizational and administrative documentation of the business entity, determined for execution on nearby lands. The personal intentions of the owner of the site are not taken into account, and unregulated work on the site owned will be prohibited.
Types of permitted use of land plots and capital construction projects
The owner of the territory either fits into the program established in the surrounding territory, or defends his constitutional rights through the courts and seeks from the municipality to change the group of permitted use from basic to conditionally permitted.
Important! In the interests of the state, municipality or population, a land easement can be issued on land that is privately owned. In this case, third parties have the opportunity to limited use of this territory.
Conditionally allowed group
The regulations for the use of the allotment of this permission group are more extensive. It is limited to one item on the list, but its sub-items can be interpreted depending on the personal interests of the owner of the territory.
Using the example of paragraph 1, which allows farming, it can be understood that only the first part of the numerical code is mandatory, and the remaining 18 subparagraphs can be replaced and migrate among themselves.
Thus, the buildings permitted on the site may be limited to certain regional features, but it is allowed to introduce creative elements into them.
Sample application for permission for a conditional type of use of land plots
To obtain official permission for such a building, the owner must contact the department of architecture and urban planning of the administration and submit a draft of the planned building for approval.
If there are no comments from the municipality, the applicant will receive permission to carry out the requested type of work. In case of refusal, the owner has the right to demand motivation in accordance with existing regulations and rules.
If a case of misuse of a land plot is detected, the law provides for punishment in the form of:
- administrative liability provided for in Art. 8.8 of the Code of Administrative Offences;
- forced seizure of land;
- fine;
- issuing an order to eliminate certain violations that caused harm or damage.
It is not uncommon for a property to be misused by third parties who are not the owners of the site. In this case, the main owner is responsible, therefore it is in his interests to constantly monitor and protect the territory from unauthorized use.
For these purposes, the owner is obliged to conduct regular inspections of the property for unauthorized plantings or illegal use. Even if the land is not cultivated or used, its condition must be monitored regularly.
Auxiliary group
The types of activities included in this group are not endowed with legal force and act as an addition to the types of the main or conditionally permitted group. These types can expand the range of functions of the site, supplement it with certain nuances, without losing its main characteristics, without violating the requirements of regulations.
As an example, consider an area with an agricultural permit on which a pasture is located. The territory is remote from places of residence of the population and the construction of individual housing construction on it for the needs of the owner is prohibited.
Types of land plots allowed for building a house
The regulations exclude the possibility of changing the type of permitted use of the site due to the location of unique water meadows on it. In this case, the municipal authorities, having entered into the position of the owner and understanding the need to provide him with a place for seasonal residence, can give him an auxiliary permit and allow him to erect a seasonal building of a limited size.
Thus, the owner gets the opportunity to live on the territory of his land, enhance its efficiency and productivity, without violating the established regulations.
How to establish compliance of the type of permitted use with the new classifier?
The owner of the land plot has the right to establish compliance of the permitted use with the classifier.
As a rule, the need to establish compliance arises for areas with old VRI.
To establish compliance, you must submit an application either:
- to a government agency,
- or to a local government authority.
The authority is selected depending on the authority to establish and change the types of permitted uses.
For reference.
For 2 ways to change the type of permitted use of a site, see the article at the link.
There you will also find a tool for filling out the Declaration to change the type of permitted use of the land.
Most often, the authorized body is the local government.
If you are in doubt about which body to submit an application for establishing compliance, then submit it to the local administration.
How to find out the VRI of a site?
The main function of code systematization is to reflect land use conditions. Re-registration of status is regulated at the level of local legislation, and each VRI is determined by a separate document.
You can obtain information about a plot of land purchased in the Moscow region in the following ways:
- Visit the Rosreestr website . To obtain the necessary data, you must pay the state fee, send a request, and review the information provided;
- Take an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate . This document has come to replace the cadastral passport. In it you can see information about technical information and rights in relation to the land plot. The extract can be obtained from the cadastral office or on specialized websites. The list of required documents includes a receipt for payment of the state duty, power of attorney, and passport.
Codes for other activity types
- 12.0 - land for public use , for example, roads and sidewalks in cities and any other populated areas that can be visited by anyone for free.
- 12.1 - funeral and ritual activity . An example is the plots of land allocated for cemeteries.
- 12.2 - plots of land for special work and purpose. This includes landfills, namely: domestic and industrial, as well as cattle burial grounds.
- 12.3 - spare areas where there is no human activity.
You can find out how to choose the right site for building a house here
Codes denoting human manipulation of forest resources
- 10.0 - activities on plots of land related to the use of wood, namely: its harvesting, removal and processing. In addition, this block includes activities aimed at maintaining the balance of forest resources and protecting forest heritage.
- 10.1 - cutting down natural forest resources. Cutting down forest resources that have grown without human intervention in natural conditions.
- 10.2 - plantations of forest resources. This activity consists of planting trees, cultivating them, and then cutting them down for people’s economic needs.
- 10.3 - forest cutting. Gathering or cutting of non-timber resources, such as oleoresin, wild plants or mushrooms.
- 10.4 - reserve forest resources. Activities aimed at protecting and protecting these resources.
Objects required for public purposes
- 3.0 - buildings firmly connected to a plot of land, with the help of which the most diverse and numerous needs and wants of people are satisfied.
- 3.1 - buildings that provide the primary functioning of people. On these lands, buildings are built that are necessary to provide people with gas, telephone communications, electricity, and sewerage.
- 3.2 - serving social needs. This number in the documents marks the land on which objects are located that provide the opportunity to provide assistance to those in need from society.
- 3.3 - designation of the type of site required to meet the requirements of household maintenance. This includes bathhouses, funeral homes and dry cleaners.
- 3.4 - health protection. These areas contain facilities whose purpose is to assist doctors in providing medical services.
- 3.5 - educational services. On such lands there are structures and buildings built for the education of both children and adults.
- 3.6 - cultural and development facilities. These are, in particular, museums and aquariums.
- 3.7 - institutions of a religious nature in which people satisfy their spiritual needs.
- 3.8 - management of society. On these lands, facilities are being built to house government authorities and organizations involved in ensuring and maintaining the activities they carry out.
- 3.9 - lands used as a foundation for science. This is expressed in the construction of structures needed for scientific research on them.
- 3.10 - services for animals that live with people at home and are not used for industrial purposes. The purpose of these plots of land is to contain targeted facilities created for the treatment and care of animals not related to agricultural species.
Placement of business objects
- 4.0 - on these lands there are structures and buildings that are used by people in order to benefit from activities based on the principles of entrepreneurship, for example, trading, insurance, banking or other activities.
- 4.1 - business management. Designed for the construction of exchanges or buildings where the governing bodies of corporations and other business organizations are located.
- 4.2 - shopping centers with an area of over five thousand square meters, intended for the sale of various services or goods.
- 4.3 - markets where an individual retail space cannot exceed two hundred square meters, which can operate on both a temporary and permanent basis.
- 4.4 - stores with an area of up to five thousand square meters, which are built for the sale of various goods.
- 4.5 - insurance or banking activities.
- 4.6 - public catering.
- 4.7 - hotel services.
- 4.8 - entertainment. This category includes buildings built to accommodate: nightclubs, hippodromes, bowling alleys, discos, playgrounds.
- 4.9 — transport maintenance. Garages, auto repair shops, car washes, roadside service and gas stations are located on these lands.
Transport
- 7.0 - on such lands there are communication routes and structures that ensure uninterrupted transportation and movement in space of people and goods, including the transfer of chemicals, for example, oil through a pipeline.
- 7.1 - railway transport, including the metro, monorails and cable cars.
- 7.2 - road transport.
- 7.3 - water transport, including the construction of water canals.
- 7.4 - air transport.
- 7.5 - pipeline transport, including the construction of facilities that ensure the proper operation of pipelines.
Ensuring the security of the state and its defense
- 8.0 - this code is used to display on official documents the lands on which structures are located that were built to support the army and other armed forces of the state in combat-ready condition.
- 8.1 - facilities supporting the armed forces, namely: weapons factories, test sites, repair bases, places for the destruction of explosives and waste disposal, military equipment warehouses.
- 8.2 - protection of the border of the Russian Federation, in order to ensure which border signs, barriers and other engineering communications are installed, checkpoints are built and control strips are equipped on lands allocated for the implementation of these tasks.
- 8.3 - ensuring internal law and order, namely: placement of buildings that support the functioning of rescue services and the police.
- 8.4 — ensuring the functioning of state bodies responsible for the execution of punishments.
Codes for production activities
- 6.0 - intended for the placement of objects aimed at manufacturing things or objects industrially, or developing subsoil.
- 6.1. – subsoil use.
- 6.2 - heavy industry.
- 6.3 - light industry.
- 6.4 - food industry.
- 6.5 - petrochemical industry.
- 6.6 - construction industry.
- 6.7 - energy.
- 6.8 - communication.
- 6.9 - warehouses and structures created for the purpose of storing things.
- 6.10 - objects created to support space activities.