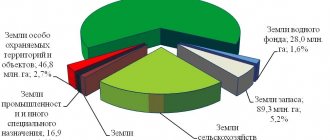
This is done to establish control over the intended use of land. There are seven categories in total. The most common category of land - agricultural land.
The law gives a clear definition of agricultural land, classifies it into types and sets out the options for use. Detailed information about this is contained in Chapter 14 of the Land Code.
Types of agricultural land
Agricultural land varies in quality and method of use. Here are the main types:
- Arable lands are areas that are subject to regular cultivation, sowing and harvesting.
- Fallows are cultivated but not sown arable land. This is done with the aim of increasing the fertile properties of the land.
- Hayfields are areas intended for cutting grass into hay for animal feed.
- Pastures are areas where cattle and other types of domestic animals are grazed.
- Fallow lands are areas that have not been used for sowing or plowing for several years.
- Perennial plantings are areas that are used for planting perennial plants (herbs, trees, shrubs) that regularly produce crops.
The structure of agricultural land also includes forests. Also included are ravines, swamps and ravines that are not used for agricultural purposes, but could potentially be transferred to the appropriate category.
Definition
What is agricultural land? The definition of this concept is quite specific (unlike categories). Agricultural land is land intended for growing crops, raising livestock and performing related work. Each such area has closed boundaries and a specific location.
Agricultural land includes the following groups of plots: arable land, pastures, hayfields, perennial plantings, fallow land. One subspecies in the process of conducting economic activity can transform into another. But this happens very rarely.
Purpose
According to the purpose of agricultural land in an agricultural economy, they can be divided into two key types:
- Designed for growing crops and grazing livestock.
- Designed to accommodate roads and other communications. On such lands it is permissible to place buildings and structures, warehouses, reservoirs and other facilities serving agricultural production.
Hayfields and pastures
Agricultural plots can be used not only for crop production, but also for livestock production. Thus, hayfields include those plots on which perennial grasses grow. The main purpose of this type of land is to feed livestock with mowed vegetation in the winter. Such lands, in turn, are classified into several more groups. Hayfields are distinguished based on their quality:
- Clean. There are no hummocks, stumps, large stones, trees or bushes on such lands. Mowing on plots of this type can be done with maximum efficiency.
- Scabbed. This group includes areas covered with hummocks by at least 10%.
- Forested and bushy. Such areas are not uncommon in our country. Lands covered with trees and shrubs by 10-70% are included in this group. Mowing in such areas is difficult and time consuming.
There are about 10 million hectares of fodder land overgrown with forests and shrubs in Russia, and about 2.2 million hectares of grassland.
Depending on the degree of moisture, such agricultural land is classified into:
- aspic;
- upland;
- swampy.
From the first two groups, improved areas are additionally distinguished.
Pastures are lands intended for grazing livestock in the warm season, not related to hayfields or fallow lands. There are only two types of such areas: wetlands and dry lands. The latter are usually located in the floodplains of rivers and streams and are flooded for a short time during spring floods. Wetland pastures are located in lowlands, on the edges of swamps and in poorly drained areas.
Dry land areas are divided into long-term cultural and improved ones. Like hayfields, pastures can be classified by quality. In this regard, a distinction is made between clean, tussocked and forested areas. In our country, unfortunately, there are quite a lot of low-quality lands of this group. However, if agricultural enterprises have funds and well-developed management projects, the situation can be improved.
Usage
In 2015, a classifier was approved in the Russian Federation that determines the areas of use of agricultural land. They can be used for the following purposes:
- agricultural activities of enterprises;
- farm activities;
- growing vegetables and fruits;
- organization of dacha partnerships;
- livestock and fish farming;
- research activities related to identifying problems and searching for ways to improve the quality of land.
Legal status of agricultural land
Until 2015, local governments were responsible for determining the intended use of a particular agricultural plot. Then a classifier came into force, clearly indicating the types of permitted intended use (PUR).
At the moment, arable land (land for growing crops) is under the strictest control of the legislator. They are the property of the state and violation of the rules for the use of such sites is fraught with heavy fines, including alienation.
Peculiarities
Agricultural land is a special category of land, which has a number of significant features. Here are the main ones:
- Fertile lands are under state protection as a natural heritage and an important strategic resource.
- Can only be used for agricultural purposes. Misuse is punishable by law.
- Land with a high cadastral value cannot be transferred to other categories not related to agriculture.
- In agricultural areas under state protection, the construction of any buildings is prohibited.
- All lands included in agricultural land have certain benefits for the agricultural industry.
- The most valuable and productive (and also expensive to maintain) are arable lands.
What it is?
The category of agricultural land contains areas that are not part of cities and villages , intended for carrying out various agricultural work on them.
Agricultural lands are in second place in terms of area among all categories, second only to forest lands.
On the territory of the Russian Federation they occupy approximately 386 million hectares. For comparison, the area of land in populated areas is approximately 20 million hectares.
Agricultural lands are under special state control.
They are a valuable resource and source of food .
Therefore, it is important to use the land for its intended purpose, to prevent its littering and pollution, deterioration of the soil condition, and exposure to harmful factors.
Appraisal
A bonitet score is a characteristic of agricultural land that determines the quality of soils in bonitet scores, which are relative units. When grading, experts determine to what extent the soil in a given area is better or worse than another in terms of fertility. Moreover, such a comparison is possible only with comparable levels of agricultural technology used.
The main purpose of valuation is to identify lands that are most suitable for cultivating or growing certain crops. This technique is also used when planning agricultural production and identifying the level of profitability of land. The quality score is affected by humus concentration, granuometric formula, clay content, soil acidity, erosion, rockiness and other indicators.
Particularly valuable land
In terms of quality, agricultural land existing in Russia can be classified into:
- Areas with a cadastral assessment above the regional average.
- Particularly valuable in this region.
- Disturbed lands.
Particularly valuable agricultural lands, which, among other things, may include experimental sites of scientific and educational organizations, are often included in the list of lands, the use of which for purposes other than agricultural ones is not allowed.
Redistribution Fund
Agricultural land is an important category of land that is under strict control of government agencies. In particular, it is worth paying attention to such a concept as the redistribution fund. This is a database of agricultural plots that are temporarily not used for their intended purpose.
The main function of the redistribution fund is the formation of a database of unused agricultural land. The goal is the transfer of land for intended use under certain conditions. This is important from the point of view of preventing long-term idle land, because this is economically unprofitable.
A site may fall into the redistribution fund for the following reasons:
- voluntary refusal of the owner to use the land plot;
- absence of heirs after the death of the owner of the plot;
- forced seizure of a site by government agencies upon detection of misuse or other offenses.
Principles of formation of the composition and ratio of land
When implementing this process, factors such as the organizational and economic structure of the enterprise, its financial and economic capabilities, and the availability of material and labor resources are taken into account.
In addition, the area and composition of land largely depend on the natural features of the territory and the differences between individual land plots and tracts. These factors require a differentiated approach to establishing, transforming and improving the structure of land.
For example, in forest zones characterized by low fertility and waterlogging, arable lands occupy a small area. The shortage of arable land makes it impossible to further develop and improve the efficiency of agricultural production, therefore it is necessary to expand the area under arable land through the development of suitable lands.
Ownership of agricultural land
Agricultural land is land that is intended to be used for agricultural purposes. The following entities can obtain ownership of them:
- individuals;
- legal entities (agricultural enterprises, dacha cooperatives, farms).
Foreigners and stateless persons cannot become owners of agricultural land. Municipal authorities have the priority right to receive ownership of the site.
The owner of a land plot has the right to perform the following operations with it:
- transfer the plot by inheritance;
- lease land (subject to intended use);
- sell land;
- transfer the plot under the terms of donation;
- pledge the land.
Agricultural lands: legal regime and features of their use
27.09.2021
The legal regime of agricultural lands is a theoretical concept that generalizes their legal characteristics as an object of land relations.
An analysis of the current land legislation allows us to conclude that this regime is determined by the set of rules established by this legislation for their use, inclusion in civil circulation, protection, accounting, and monitoring. We'll tell you about all the nuances.
The legislative framework
The purchase and sale, as well as the use of agricultural land, is regulated by the Land, Civil, and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation, laws and regulations. It is advisable to study the laws:
- On the turnover of agricultural land.
- On state regulation of ensuring the fertility of agricultural lands.
- About agricultural cooperation, etc.
In addition to the main regulations, the use of agricultural land is also regulated by orders of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation (for example, the Ministry has developed a Procedure for state monitoring of agricultural land and other acts).
The concept of status and general characteristics of plots
Let's consider the general characteristics of such lands and their importance in meeting the needs of future owners. According to Art. 77 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, land plots are recognized as agricultural if they are located outside the city and are used for agricultural needs. Such lands include:
- fields for growing agricultural crops;
- roads;
- forest plantations;
- ponds;
- buildings for the production, storage and primary processing of grain, vegetables or fruits.
Lands can be used:
- for farming business;
- for personal farming;
- summer cottage construction; livestock farming;
- haymaking and grazing;
- scientific research;
- gardening activities.
The use of the plots is also permitted for hunting. Particularly valuable land, the cadastral value of which significantly exceeds the average level of the district cadastral value, may be included in the list of lands, the use of which for other purposes is not permitted. The owner of these lands has the right of ownership to all crops and plantings, the resulting products and income from their sale.
Important! There are a number of restrictions for agricultural land. They are mainly purchased by farms and agricultural enterprises that plan to use them exclusively for agricultural purposes.
Who can claim these lands?
Not only legal entities, but also citizens and individual entrepreneurs can buy agricultural land. Problems with the purchase of plots can only arise for foreigners (individuals and legal entities). They are allowed to own agricultural land only on a leasehold basis.
Subjects and objects of rights to land plots
The subjects of ownership of land plots can be individuals, agricultural companies, cooperatives, educational and research institutes, and some types of public associations, provided that their activities are related to agricultural production.
Land rights may be limited. For example, individuals are prohibited from purchasing plots of property in an amount exceeding the established maximum standards or using them in ways contrary to their intended purpose. Foreigners are prohibited from buying and selling plots of agricultural land.
The object of ownership can only be a separate plot of land or part of this plot (Article 6 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The plot must have its own cadastral number, as well as all title documents. If the land is not registered, then first you need to go through the procedure of registering it with the cadastral register.
Reference. Agricultural areas include fertile arable land, hayfields, pastures, orchards, and vineyards, which are subject to special protection.
Who is the owner?
The owner of the plot can be an individual or legal entity or the state. In accordance with Art. 209 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the owner has the right to perform any legal actions in relation to the property he owns (not contrary to the purpose of the land).
Is it possible to obtain private property?
If the land is owned by the state, it can be purchased by a citizen or an agricultural company, farmers, members of a cooperative and other organizations. If the plot has not yet been registered with the cadastral register, then:
- An application for preliminary approval of the provision of land must be submitted to local authorities.
- Carry out land surveying and create a package of documents for registration.
- Then submit another application and conclude a purchase and sale agreement.
If there are no people willing to buy the plot at an open auction, then within a month the transaction will be finalized and all that remains is to register the owner’s rights with Rosreestr. You can buy agricultural land by participating in an open auction. For example, this can be done by a bona fide tenant (according to Article 10 of the Law “On the Turnover of Agricultural Land”).
A plot of land allocated for shares in municipal ownership can be sold to those farmers who use it without holding a tender within six months from the date of registration of the right to the plot. In this case, the price is set at no more than 15% of the cadastral value of the land plot.
Regulation of turnover
Important! The main rule for all owners of this category of land: intended use. This requirement is enshrined in the law “On the turnover of agricultural land” and the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
A plot of land can be forcibly seized if its owner is not engaged in agriculture, but, for example, has opened a hazardous industry or organized a landfill.
Not allowed:
- the formation of a plot that is part of artificially irrigated plots and the size of which is less than the established minimum size;
- purchase of a plot of more than 10% of agricultural land in one municipal district;
- non-use of the land plot for its intended purpose for more than three years.
Agricultural lands have other legal restrictions. Before selling the land, you need to send a notice to local authorities with an offer to buy the site. Only if there is no response within a month or a refusal is received can the plot be put up for sale. There are no such restrictions with lands of other categories.
Rules and restrictions
Agricultural land that is in state or municipal ownership is granted ownership at an open auction or at the request of the applicant (if the plot is not registered and there are no people willing to buy it at the auction).
The following restrictions apply:
- You cannot buy more than 10% of the land in one district;
- it is prohibited to sell land without obtaining a prior refusal from the municipal authorities to purchase;
- the shareholders are required to waive their pre-emptive right to purchase;
- Foreigners do not have the right to buy land as their own.
Tenants who do not violate the terms of the lease agreement and use the land for their intended purpose have the preemptive right to purchase land that belongs to the state. If the land is privately owned, then the parties draw up a purchase and sale agreement and register it with Rosreestr. It can be sold to outsiders only at the price at which the plot was previously offered to local authorities.
On a note. Land plots located at a distance of no more than 30 km from the borders of rural settlements cannot be used for purposes not related to agriculture (Article 78 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Features of use
Private individuals. On agricultural lands, individuals have the right to carry out only activities specified by the Land Code of the Russian Federation. This is about:
Farming.
- LPH.
- Haymaking.
- Vegetable gardening.
- Cattle grazing.
- Fish farming, etc.
Objects of land legal relations of individuals:
- land;
- land shares;
- rights for land shares and land plots.
Land can be bought and sold (with mandatory notification to government agencies), leased and subleased, as well as transferred as a gift, inheritance, or the authorized capital of a joint-stock company. Individuals have equal rights with legal entities in the use and opportunity to buy and sell land. Restrictions exist only for foreign individuals who do not have the right to acquire agricultural arable land as their property.
Commercial organizations. Plots of agricultural land can be purchased, leased and used by any commercial organization. All lands used by commercial organizations have a special legal status as land users of agricultural lands.
Types of agricultural organizations:
- production or consumer cooperatives;
- peasant (farm) farms.
Different agricultural organizations may have their own legal regime. For example, for farmers, minimum sizes of land plots are not established if their activity profile is: gardening, greenhouse vegetable growing, viticulture, seed farming, poultry farming, beekeeping, commercial fish farming or other activities important for the development of agriculture in the region.
Agricultural organizations may be provided with land for ownership, permanent use or lease. If an allotment is granted, members of cooperatives receive the right to a land share. Unclaimed land shares become state property.
Important! In addition to commercial associations, land plots are also provided for ownership by religious organizations, scientific institutes and Cossack societies (non-profit organizations).
Cooperatives. Cooperatives have the right to buy and sell agricultural land. According to the Law “On Agricultural Cooperation,” cooperative transactions for the alienation and acquisition of land plots are carried out only with the consent of the general meeting of all members (Article 38). Participants may, for a certain period not exceeding 10 years, be required to sell the agricultural products they produce, or part of them, to the cooperative and not to other organizations.
Enterprises. Commercial enterprises (JSC, LLC and other forms of ownership) also have the right to use agricultural land. These can be agricultural farms, breeding and stud farms, enterprises for the reproduction of valuable fish species and other companies.
The acquisition and sale of plots for enterprises follows the same principles: the land can only be used for agricultural purposes and before selling the plot it must first be offered to local authorities, who have priority rights to purchase.
To complete the transaction, you will need to show a power of attorney from the representative or confirm the authority of the director of the company. If permission from the founders is required to sign an agreement under the company’s Charter, then this document will also need to be provided.
Control
The condition of agricultural lands is constantly monitored. The Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation monitors the condition of plots and assesses the level of soil fertility. In addition, in order to redistribute land for agricultural production in the Russian Federation, there is a land redistribution fund. This fund is needed to establish the boundaries of specially protected areas or areas with a special legal regime.
On a note. The state controls the process of land use and withdraws it if it is not used in accordance with its intended purpose. In addition, arable land is purchased if it is valuable for the agricultural enterprise.
Conclusion
Agricultural lands have a special legal regime for use. They can be confiscated from the owner if he does not use the land for its intended purpose or pollutes valuable soil. In addition, sales are possible only after local authorities refuse to purchase agricultural plots.
Source: urexpert.online
Agricultural land in Russia
One of the main national resources of Russia is fertile land, which allows the production of environmentally friendly agricultural products with the prospect of leadership in the world market. The Russian Federation ranks fifth in the world in terms of agricultural land area. The state accounts for 12% of all arable land in the world (0.8 hectares per capita). Russia also has 50% of the world's reserves of chernozems. About 10% of the Russian population is employed in agriculture.
The area of agricultural land is the sum of the areas of land allocated for arable land, pastures and perennial plantings. The indicator is determined by measuring plots, as well as interviewing owners and members of farms. This figure in the Russian Federation is 220.7 million hectares, of which about 70% is arable land, which is considered not a very rational approach.
Arable lands, fallow lands and perennial plantations
Most of the agricultural land consists of areas intended for sowing crops. Such plots are classified as arable land. But only if they are systematically processed. In addition to fields with cultivated plants, this group includes crops of perennial grasses in crop rotation areas, hatchery fields and pure fallows. The total area of all arable land on Earth today is about 1.3 billion hectares. This is about 3% of the land surface. The total area of farmland in Russia is 2434.6 thousand hectares. At the same time, arable land accounts for 60% of all land.
The definition of “fallow land” includes areas that were previously plowed, but have not been used for growing plants for more than a year, and have not been prepared for fallow. Perennial plantings are areas artificially planted with trees, shrubs and perennial grasses. This group includes, for example, berry fields, orchards, vineyards, hop fields, tea plantations, etc.
Agricultural land of other countries
For every country, agriculture is one of the most important industries in any country. In different regions of the world, the following situation is observed regarding land:
- European countries are characterized by a high level of arable land (about 30%). This is due to intensive agricultural production associated with growing population density and favorable climatic conditions. European countries account for 10% of the world's agricultural land.
- The average plowing ratio in Asia is 15%. But the indicator cannot be considered in a generalized form, because the situation in the region is heterogeneous. Thus, in India the coefficient is 80%, and in Saudi Arabia it barely reaches 1%. Asia accounts for 30% of the world's agricultural land.
- In North America, the tillage ratio is 20%. The region accounts for 15% of the world's agricultural land.
- The lands of Latin America are 7% arable. This is due to the extreme climate.
- The arable land ratio in Africa is 7%. This region accounts for 20% of the world's agricultural land. But their productivity is very low.
- In Australia, the degree of arable land barely reaches 6%. In global agriculture, land occupies only 5%. This is due to the arid climate and poor soil chemical composition. The main emphasis is on forage areas.
Practical implementation of the plan to change the composition and ratio of land
The transition from the current composition and size of the area to the design one is possible subject to the following measures:
- drainage of waterlogged land plots;
- cultural and technical work (uprooting forests and shrubs wedged in and interspersed with agricultural land, removing stones);
- eliminating closed depressions and leveling the surface of the territory, including the creation of microrelief for drainage of runoff from waterlogged land plots;
- cultivation of non-agricultural land (liming of acidic soils, soil cultivation, application of mineral and organic fertilizers, sowing of green manure plants);
- construction of roads, road structures.
In the forest-steppe zone, arable lands usually have a high specific gravity, but are dissected by ravines and ravines with different slope steepnesses. In such conditions there is always a risk of water erosion, to prevent which the following work is carried out:
- grassing of heavily eroded arable lands;
- repairing existing forests and planting new ones to protect areas from degradation; it is also necessary to correctly design after-protection, water-regulating, ravine and ravine forest belts;
- organization of small irrigation systems (usually anti-erosion ponds are used for this);
- terracing of slopes, construction of various hydraulic structures (for example, water-retaining shafts);
- systematization of agrotechnical, organizational, economic and other anti-erosion measures;
- rationing of animal grazing.
The main task when reforming land in these conditions is to prevent a reduction in the area of arable land. To achieve this, all land plots suitable for growing forage and field crops are converted to arable land, simultaneously reducing forage land to a minimum. Areas and beams unsuitable for plowing are used for grazing animals.
Deterioration of land quality
The share of agricultural land may decrease in the future due to intensive deterioration in land quality. This is caused by the following main factors:
- Irrational, wasteful and consumptive use of land. Due to the fact that agricultural production is carried out in violation of technology and environmental requirements, land is subject to degradation and loses its fertile properties. The practice of reclamation of disturbed lands is almost completely absent.
- Wind and water erosion. This problem is typical for 70% of arable land in the Russian Federation. The fertile layer is destroyed very quickly, and restoration occurs extremely slowly (2.5 cm in 500 years).
- Waterlogging, flooding and flooding of lands. This problem affects 12% of the country's agricultural land. Waterlogging is typical for the Northwestern, Ural, Central, Volga, Southern, Far Eastern and Siberian regions.
- Desertification of lands. This is salinization, solonetzation, which makes it impossible to grow crops. The problem is typical for the Volga, Siberian and Southern regions.
- Soil dehumification. We are talking about a sharp decrease in the concentration of nutrients, which may be associated with intensive use of soils, cessation of fertilizer application, and ignoring soil protection measures.
- Chemical pollution and waste litter. The problem is associated with excessive application of chemical fertilizers, proximity to industrial enterprises or unauthorized organization of landfills.
Reasons for changes in soil quality
The area of farmland can be significantly reduced if its quality deteriorates. The following factors can cause changes in the properties of the earth:
- Exhaustive and unreasonable exploitation of the site in violation of conditions can lead to a decline in the quality of the soil and its fertility. It is practically impossible to restore the destroyed lands later.
- Soil erosion (water and wind) is a problem common to more than half of all arable land. The top layer of the earth, which is considered the most fertile, is easily destroyed under the influence of destructive factors, and its restoration may require a single century.
- Excessive soil moisture leading to waterlogging.
- Degradation of fertile soil into desert soil. In such lands, the amount of mineral salt increases, as a result of which it becomes unsuitable for growing crops.
- A strong decrease in nutrients in the soil (dehumification). The reason for this may be the cessation of tillage and fertilizing, as well as the active exploitation of the site.
- Contamination of land with chemicals or waste. May be caused by excessive use of chemical fertilizers, proximity to industrial production, or landfilling without proper permission.
How to find out the category of land by cadastral number
- Open the public cadastral map of Rosreestr;
- Enter the cadastral number of the land plot into the search line;
- Get information about the category of land and the type of permitted use online.
To document the information, I recommend ordering an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Please note that in Rosreestr an extract from the Unified State Register costs 350 rubles (700 rubles for legal entities). If you want to find out the category of land and the type of permitted use cheaper, I recommend ordering a certificate through Quick Documents - this way you will receive a document for only 250 rubles. The order is completed within a day, the official data is from the Unified State Register of Russian Registers of Rosreestr.
I am ready to advise you free of charge by phone (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
The call is free for all regions of the Russian Federation
Certificate from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, which I recently ordered through Quick Documents
Legal grounds for translation
The burden of preparing the site for transfer falls entirely on the applicant
In 2004, land legislation was supplemented with a separate document on the procedure for changing the categories of land plots. The new law No. 172 has been changed and supplemented over time.
The latest adjustments were made in July 2021, with the introduction of changes to the procedure for registering land and the mandatory entry of data into the Unified State Register of Real Estate. The translation process is regulated and requires careful preparation, including:
- collecting information about the allotment;
- soil research and expert assessments of their quality based on soil quality scores;
- possibilities for land reclamation;
- linking the cadastral value to the average for municipal districts;
- accounting for urban planning and other land plans of the state.
The burden of preparing the site for transfer falls entirely on the applicant. The package of documentation that will need to be collected has been expanded.
It is expected that decisions to change the category to allotments will be more meaningful and objective. The information collected should prevent the disruption of ecosystems, help improve soil quality and ultimately lead to the regulation of all existing lands in the country.
It is important to remember that it is much easier to transfer land in settlements to a different category than to change the category of farmland.
You should apply for approval of a draft change only in extreme cases that have a legal basis. After all, even in the law such a procedure is designated as exceptional.
Fine for misuse of land
For the category of agricultural land, the legislation limits the permitted use and, in case of violation, provides for punishment under the Code of Administrative Offenses. Thus, if the owner violates the intended use, then a fine is imposed on him:
- for individuals - 0.5-1%, not exceeding 10 thousand rubles;
- for officials - 1-1.5%, not more than 20 thousand rubles;
- for legal entities - 1.5-2%, not exceeding 100 thousand rubles.
When harming the environment as a result of misuse of land, the actions of the perpetrator are considered aggravated, and the maximum fine is applied.
Control
The condition of agricultural lands is constantly monitored. The Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation monitors the condition of plots and assesses the level of soil fertility. In addition, in order to redistribute land for agricultural production in the Russian Federation, there is a land redistribution fund.
This fund is needed to establish the boundaries of specially protected areas or areas with a special legal regime.
On a note. The state controls the process of land use and withdraws it if it is not used in accordance with its intended purpose. In addition, arable land is purchased if it is valuable for the agricultural enterprise.