General information
In Russia, a program to eliminate dilapidated housing has been operating for quite some time. Despite the fact that it has been in operation for a long time, a small number of residents have been relocated.
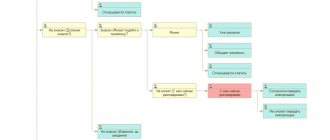
Resettlement according to the project works like this:
- A regional program to eliminate unsuitable housing is being formed;
- Objects are recognized as unsafe and subject to demolition;
- A list of dilapidated and emergency housing is being created;
- A conclusion is made on the reconstruction of the specified house or its removal;
- Before demolition, an equivalent living space is found.
Typically, housing is selected in the same area where people from the house that is being demolished previously lived. The owner of a residential property has the right to write a statement of desire to move to another area.
Any citizen has access to information about whether his house is classified as unsafe and unfit for habitation - special websites have been created for this with a search form by address. Instead of housing, it is possible to provide him with any monetary compensation based on the size of the living space.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that relocation in accordance with the civil code cannot be regarded as a way to improve living conditions or increase living space. When searching for new housing, the area of the previous housing and its condition are taken into account.
The provision applies to all cases, even when a person owned residential premises less than the accounting norm. A person receives the same area that he had.
If the owner wants the new housing to be larger, he will have to pay extra out of his own pocket for the excess meters. There are no strict parameters when choosing the type of housing - the main thing is that it is not in emergency condition.
Responsibilities of the commission
After the appointment of an interdepartmental commission to resolve housing issues, its responsibilities are as follows:
- Determine the suitability of a house, apartment, or other premises for housing, referring to legal requirements and regulations on the assessment of residential real estate;
- Consider complaints received from owners or organizations within the prescribed period;
- Determine the technical capabilities of carrying out major repairs, reconstruction, redevelopment, etc.
The activities of the interdepartmental commission are controlled and directed by its chairman, who in turn is authorized to:
- Involve a variety of housing inspection specialists, other relevant organizations, and management companies in the process;
- Carry out opening of structural elements of the building;
- Involve employees of housing maintenance institutions in the examination;
- Interview property owners and tenants to clarify the nuances and make the final decision of the commission;
- Order the elimination of identified defects and instructions within a specified period;
- Call responsible department officials to a meeting to consider the issue of a specific house.
Basic Concepts
It is important to distinguish when a house can be considered unsafe and when it is considered dilapidated, since these are two big differences. Resettlement is not carried out from a dilapidated house - it is considered old, but suitable for living. The emergency premises are considered completely unsuitable for habitation.
The main requirements for an emergency house are its location in a dangerous or emergency area, a serious violation of sanitary standards and a threat to residents. In this case, it will be simply dangerous to stay in such a room any longer - hasty resettlement and demolition are being carried out.
Even if a private house, recognized as dilapidated, and the land plot under it are 75% uncomfortable, but do not threaten life and health, then resettlement will not take place. Therefore, most buildings in disgusting condition are still in use, awaiting recognition as unsafe.
What is the difference between dilapidated, emergency and uninhabitable?
The term “dilapidated housing” is found in methodological manuals, for example, in the manual concerning housing and communal services, issued in 2004. Dilapidated buildings are recognized as buildings, as well as individual structures, with a deterioration of more than 70% for stone buildings and 65% for wooden ones. In this case, the structure itself may remain strong and not collapse, but the housing becomes unsuitable for habitation.
So, sometimes a house is quite safe, but due to holes appearing in its walls, a torn off roof, and rotten floors, it becomes impossible to live in it. The indicated percentage is approximate and is not documented anywhere.
Those in charge usually determine the dilapidation of housing by eye, based on their own ideas about what a building suitable for habitation should look like.
unsafe if it is dangerous to live precisely because of violations of the standards for safe accommodation of people. It is theoretically possible to live in a dilapidated house (fix the hole with film, patch up the roof, insulate the walls), but living in a dilapidated house is dangerous, since it can collapse at any moment.
Dilapidated housing can remain idle in this state for years; unsuitable housing gradually collapses. People are relocating from dilapidated housing less often than from housing that is deemed unsuitable. There is always a chance for high-quality repairs or restoration that will return the building not only to its former appearance, but also to its quality.
An unusable building can rarely be restored or repaired. The foundation or walls cannot be restored.
Building assessment
The legislation is applicable in housing conditions that do not meet sanitary standards, safety regulations, and also threaten health and life. The criteria for assessing accident rates are given in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 47:
- Dangerous location of the house - an area with a high probability of landslides, avalanches, floods, flooding;
- Man-made danger – being near objects of man-made danger and accidents;
- Communication hazard - placing housing too close to power lines;
- Geological factors - destruction or damage to a house as a result of storms, earthquakes, blizzards, with the impossibility of its restoration;
- Being near highways means exceeding noise standards by more than 55 decibels;
- Hygienic violations – the inability to comply with sanitary and epidemiological standards.
The criteria also include the condition of the foundation and load-bearing elements of the building - if they are worn out and deformed, the housing is considered unsuitable for use.
Violations of sanitary and hygienic conditions
Homeowners and interested parties can also exercise the right to conduct an examination if sanitary and hygienic conditions are violated. These include the lack of lighting in the room or the absence of rooms, windows opening under hanging arches or covered galleries, regular vibrations, the level of which cannot be reduced. It is impossible to determine their maximum permissible level on your own. This requires special devices. The same applies to increased noise levels, which are strictly regulated by law. Noise is the reason for declaring housing unsuitable for normal and safe living if its original cause cannot be eliminated or reduced with the help of any sound insulation.
Sanitary and hygienic violations include humidity and temperature conditions of the room. You can’t do without specialized equipment here either. Just as in the previous paragraphs, the defect must be eliminated or citizens must be relocated to safe housing. Harmful fumes are also taken into account when a house is located next to an industrial facility.
What you need
A house that is in real emergency, and which according to documents belongs to the housing stock as complete and safe, must be recognized as unfit for use. The requirement to recognize an accident may be put forward by:
- Owner of residential property;
- Tenant of the property;
- Authorized bodies - Rospotrebnadzor, housing and fire inspections.
A corresponding application is submitted to these authorities, and the work of the commission begins. If the house is unfit for use, a conclusion is prepared, and on its basis resettlement is carried out.
This is how the procedure should ideally proceed, but in practice it is significantly delayed. If the owner of the house and the plot underneath it does not agree with the commission’s decision, it is possible to challenge it within three months from the date of its adoption.
To do this, you need to go to court, but you need strong arguments to challenge it. An independent examination of the house and plot that has been privatized should be ordered. The expert’s conclusion will become the main argument in court.
How to apply for recognition of a house as unsafe?
The application and attached documents can be submitted:
- on paper in person to the commission (although this method is provided for by the Regulations, however, taking into account the epidemiological situation and the difficulties with making an appointment in person, you should not count on it);
- by mail with acknowledgment of delivery;
- in the form of electronic documents through the Unified Portal of State and Municipal Services;
- through a multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services (MFC).
An application submitted as an electronic document must be signed with a simple electronic signature. The electronic documents attached to it must be signed by officials of the bodies (organizations) that issued these documents, strengthened by a qualified electronic signature (unless the legislation of the Russian Federation establishes another type of electronic signature for signing such documents).
Where to contact
If the owner considers the repair of his residential premises impossible, and its condition is emergency, it is necessary to submit an application to the executive bodies of local government.
Often these are housing or fire inspections, or similar structures. You can address the application to the local administration, and from there it will be forwarded to the place of execution.
After submitting the application, an interdepartmental commission is created, which makes an appropriate decision within a month. The applicant is notified of the results of the work within five days after the decision is made.
The following documents are attached to the application:
- Title documents for the house or their copies certified by a notary;
- Technical passport and floor plan;
- Cadastral number and papers on land privatization;
- Certificate of an independent examination, if any.
If an accident report is received, the owner has three options:
- Receiving material compensation - calculations are based on average market prices per square meter;
- Relocation to a new apartment at municipal expense;
- Purchasing larger housing with an additional payment for excess square meters.
Since land plots are usually small, many owners often choose compensation. In this case, money from the budget is transferred to the owner’s account within a month.
The procedure for declaring an apartment unfit for habitation
In order for housing to be declared unsuitable
, first you need to go to the housing department of the municipal administration and write an application for the creation of an interdepartmental commission and its inspection of the required premises in order to decide whether it is suitable or not.
What documents are needed
To submit an application, you need to have copies of documents:
- a document establishing the right to this housing;
- a design organization plan made as a result of an examination of all load-bearing and enclosing structures;
- if desired, the applicant can provide written complaints and statements from other residents, photographs of the property.
It must be remembered that if, when submitting an application, a citizen does not provide a legal document for housing or a conclusion from a design organization for consideration, then his question will not be taken into account and all documentation will be returned.
To get a conclusion
The design and survey organization needs:
Shared privatization
If the plot was privatized for several people, then when preparing documents for a new apartment, the shared ownership in it will be calculated according to the property in the former plot.
If the site under the house in question is already private property, it does not require privatization. If it is state or municipal land, it must first be privatized. But before this, mandatory privatization of the house is required, even if it is in disrepair. A privatized house is the main reason for privatizing the land underneath it.
Often executive bodies try to delay resolving issues of this nature. This is due, to a large extent, to the fact that the housing stock is not enough to relocate all the residents of dilapidated buildings in Russia.