The area behind the fence of a private house is called the adjacent territory and is a public area. Often, local authorities literally force owners and tenants to monitor it, mow the grass and clean it up, threatening them with fines. Where such requirements are prescribed, as well as how many meters from the fence the territory must be cleaned by law in a private house, in organizations (in a kindergarten, in a school) we will look in more detail.
Rights to the territory behind the fence and obligations to clean the adjacent territory according to the law
What rights do we have to the territory behind the fence and what are our responsibilities under the law?
In order to find out whether it is necessary to clean and mow the area near the fence and for how many meters, let’s turn to the current legislation.
In accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (clause 37 of Article 1), the adjacent territory is a public area that is adjacent to a building, structure, or land plot that is formed and is registered in the cadastral register. In this case, the boundaries of the adjacent territory are determined by the rules of improvement adopted in the municipality in accordance with the legal norms of the subject on whose territory this formation is located.
We conclude that the area from the fence must be cleared as many meters as established by local authorities. This means that we need to turn to local acts. At the same time, it would not hurt to study the laws of the subject, so that local authorities do not exceed their powers and demand more.
The Civil Code (clause 9 of Article 55.25) states that persons responsible for the operation of buildings MUST take a direct part, including financial participation, in maintaining the surrounding areas in order.
Law No. 131-FZ of October 6, 2003 (as amended in December 2019) “On Local Self-Government” also obliges owners of land plots and buildings to maintain adjacent territories in order, including in the form of financing such an order. (Article 45.1).
This obligation does not apply to owners of high-rise apartments. (If you are interested in details about the rules for using the adjacent territory of an apartment building, read here).
Thus, having become the owner of a plot of land, we a priori agree to monitor the adjacent territory, clean it, and, if necessary, mow the grass.
What rights do we have to this territory? We cannot fence it off, since it is public property. We have exactly the same rights to it as all other persons - rights of general use. Compared to the responsibilities, it’s not a lot. (Read more about the rights and obligations to the territory behind the fence of a private house here.)
Now let’s begin to study the most important question: who determines the footage of the adjacent territory and how many meters from the fence it needs to be removed.
The area behind the fence of a private house - at what distance should it be kept clean?
Laws at the federal level give general concepts of maintaining the territory in order, but no specifics. In order to find out how many meters from the fence of a private house you need to remove, you should refer to local regulations.
Local rules and decisions contain more specific information; in addition, they should not contradict the law of the subject in whose territory they are located.
For example , your private house is located on the territory of the municipality of Podolsk, Moscow region.
In the Moscow region, the rules for improvement were approved by the Law on Improvement dated December 30, 2014 No. 191/2014-OZ; in Podolsk the rules were enshrined in the Decision of the Council of Deputies dated December 28, 2018 No. 56/13. These two acts practically duplicate each other, except that the decision contains additions regarding local features.
Local Laws and acts define a number of minimum responsibilities for keeping the area outside the fence of a private house clean and tidy, namely:
- mow lawns and other grassy vegetation;
- maintain outdoor utility equipment;
- remove garbage from the area behind the fence;
- maintain the pedestrian road surface in order;
- carry out snow removal;
- do not allow storage of fuel, building materials, fertilizers in the adjacent territory for more than 7 days.
What area in a private house behind the fence needs to be kept clean and in order?
Also, the landscaping rules for the region indicate the specific size of adjacent territories for private owners:
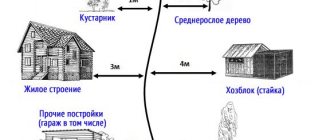
In relation to land plots and territories of individual households - NO MORE than 5 meters from the boundaries of such plots and possessions.
In relation to SNT - NO LESS THAN 5 meters and NO MORE THAN 30 meters of territory behind the fence.
As for dacha plots in SNT, here we are talking about a public territory and rules for footage are established regarding the boundaries of the SNT itself.
Accordingly, the charter of a gardening partnership may stipulate rules for cleaning the area behind the fence of a private house on your site within this area.
But what if the adjacent territory belongs to both one building and another? For example, the area between the fences of two private houses is only 5 meters. How many meters from the fence will need to be removed then? In this case, the adjacent territories are suppressed, and it is divided equitably - half is removed by one owner, and half by the other. At least, according to the law of the Moscow region, such rules apply.
Attention! In your region, the area that must be cleaned outside the fence of your property is regulated by the rules of the local administration and may differ from the example above.
What do regulatory documents say about grass cutting?
The maintenance and care of landscaping and landscaping elements is included in the work on the maintenance of common property (subclause “g”, clause 11 of the Rules for the maintenance of common property No. 491). Cleaning and mowing lawns is also included in the Minimum List of Works for the Maintenance of Common Property No. 290 (clause 25). “Lawn mowing” as part of summer cleaning is mentioned in clause 6.3.1 of GOST R 56195 - 2014. National standard of the Russian Federation. Housing and communal services and management of apartment buildings. Maintenance services for the local area, collection and removal of household waste. General requirements".
These documents lack specificity. It can be found: - in your management agreement (unlikely, but if you find it, it will be a good argument in a dispute with the management company); — in local landscaping rules (very often, the difficulty is only in finding the current version of this municipal legal act); - in Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 29, 2020 No. 758n, which approved the Rules for labor protection in housing and communal services.
In the Labor Safety Rules these are paragraphs 250 – 264:
- Lawns must be mowed during daylight hours;
- mowing lawns during rain, thick fog (visibility less than 50 m) and strong wind (more than 6 points) is prohibited;
- immediately before mowing, it is necessary to inspect the mowed area and remove foreign objects located on it;
- It is prohibited for unauthorized persons to be in the lawn mowing area;
- when working with a lawn mower, it is prohibited to use lawn mowers equipped with a mechanical engine when mowing lawns to a height of less than 2 cm; — use lawn mowers when mowing grass more than 20 cm high. Hay mowers should be used for this purpose; — smoke while refueling the lawn mower, as well as while the lawn mower is operating;
- when mowing lawns with a manual scythe, workers must be trained in mowing techniques, cutting techniques and sharpening scythes; when moving from section to section, the hand scythe should be covered with a cover or wrapped in cloth;
- When mowing lawns with a hand scythe, it is prohibited to leave the scythes in the areas after mowing, or to hang the scythes on tree branches and shrubs.
How many meters from the fence does the organization’s territory need to be cleaned?
If everything is more or less clear with cleaning the areas behind the fence of private houses - it falls on the shoulders of the owner, then with cleaning the adjacent territories of legal entities, things are more complicated. Janitors are hired for cleaning and payment directly depends on the amount of work.
For example, how many meters from the fence do you need to clean the area in a kindergarten or school? Perhaps there are some standards for organizations? The standards really exist and they are all contained in the same acts of local authorities. In an amicable way, city authorities should develop a scheme for cleaning up the areas. At the same time, owners and persons responsible for the operation of buildings must be familiar with it. But such schemes have not been developed everywhere. In addition, due to the continuity of cadastral registration (preparation of new technical plans, boundary plans, land surveying) and updating of Rosreestr data, such schemes may become outdated.
Typically, organizations clean the area behind their fence (or around the building, if there is no fence as such), mow the grass, take care of the bushes, clear the snow, according to already established rules.
In fact, this adjacent area can reach 30 meters - again, everything is individual and depends on the landscaping rules established in your area. Most often, the adjacent territory of organizations ends where the curbs of the roadway or neighboring home areas begin.
Definition of the local area
The name of the local area is used to designate a site that is separated by boundaries into a separate territory when a house project is being created. It is usually approved as part of the development plan.
The standards for local areas are described in detail in SNiPs. They indicate exactly where specific objects should be located on this land. They even describe at what distance one object should be from another.
Each owner owns part of such territories. Its share corresponds to the occupied living space.
When apartments are purchased, the new owners automatically become owners of the plot. There is no need to think about completing additional documents.
It is unacceptable to carry out transactions such as sale with allocation with individual plots. Such territories always belong to common property.
Responsibility and fines for violation of landscaping
We found out who should clean the adjacent territory - the owners or persons representing them. What will happen if you do not comply with the instructions of the authorities and refuse to clean and maintain public places? After all, in fact, these are municipal lands, which means the authorities must monitor them at the expense of the budget.
Many people think this way, but this opinion is wrong. The authorities really need to keep order locally, including on the streets. And at whose expense is a moot point. Moreover, federal laws directly stipulate that the owners of adjacent territories must take a financial part in their cleaning. If you want to live in a private house, buy a lawn mower, a shovel and go ahead – improve your plot and everything around it.
But no one has the right to immediately fine the owner for non-compliance with the rules of landscaping without an appropriate order. First there must be an act of warning - an order (decree, presentation, decision), and if there is no reaction - then a physical fine. individuals up to 500 rubles, and organizations up to 20 thousand rubles (Article 19.5 of the Administrative Code). However, paying a fine does not relieve you from the obligation to clean the adjacent territory.
So, ownership of land and real estate is not only rights, but also responsibilities, and the range of these responsibilities can be much wider than we imagine. But there is no need to criticize the legislation. We must consciously approach public property, because it is much more pleasant to see clean streets around us, and to understand that each of us makes our own contribution to this cleanliness. It is better not to seek instructions, but to do everything on time.
Responsibility of the management organization
Civil liability.
Failure to comply with the above rules may result in employees of the management organization damaging the property of the owners.
For example, the Seventh Court of Cassation of General Jurisdiction considered a case involving a claim by a car owner against a management company for the recovery of material damage (Determination No. 88 – 1755/2020). The organization's workers mowed the grass in the yard of the house so hard that the paintwork on the car was left chipped after the work. The organization was charged 25 thousand rubles for these damages. The management organization, before the cassation instance, pointed out that the owner did not prove a cause-and-effect relationship between the actions of the defendant and the damage that occurred. However, all courts rejected the company's arguments, supporting the owner of the car.
Administrative responsibility.
If the housing supervision authority reveals violations of the rules for maintaining common property: - the management organization may be charged for violating licensing requirements (Part 2 of Article 14.1.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation); - a service organization with direct management of the house, as well as a homeowners association or cooperative - for violating the rules for the maintenance and repair of residential buildings (7.22 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If a violation of local improvement rules is revealed by a local government body, then they may be held accountable under the regional law on administrative offenses. In the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, article numbers and penalties vary.