General information
Housing and communal services are aimed at ensuring comfortable life of citizens in the sphere of receiving utility services, developing the transport structure, safe use of residential and non-residential facilities, as well as providing for other human needs. Housing and communal services are a social institution that is designed to make the daily lives of citizens easier, but the enterprise also performs economic functions aimed at providing paid services and monitoring their work.
In 2021, the powers of the economy include the responsibilities of providing for people:
- light;
- water;
- gas;
- central heating;
- sewerage and ventilation.
The success of completing assigned tasks (even paid ones) does not always depend on the business department. Despite the work of engineers, timely maintenance of communications and major repairs, there is a violation of the performance characteristics of plumbing, wiring and heating devices. This requires additional cash injections, which local authorities do not always have enough.
Untapped potential
But this is not the only factor in the investment attractiveness of a management company’s business. In addition to growing “in width”, this business is also scaling “in depth”.
The management company is the “last mile” between residents and the outside world on all housing and communal services issues: at least 2 times a month they go to the website or mobile application to perform a number of mandatory actions there: pay for management services, submit meter readings, etc.
As a result, the management company knows everything about its residents: their number, gender, age, income, etc. This is the same “big data” on which many are based. In particular, in relation to the management business, on the basis of this data, you can target additional services (cleaning, dry cleaning, home help, grocery delivery, etc.) and receive a commission from the providers of these services. Moreover, all these services can be added to the same mobile application of the management company itself to make it as convenient as possible for residents.
Finally, through the use of IT solutions, the economics of the management company itself can be significantly improved. For example, instead of keeping all the service personnel on staff (who will be underutilized most of the time), you can hire third-party companies for various types of services through a B2B platform that works on the principle of the YouDo service.
To clean water. Why are tariffs for housing and communal services inflated?
Housing and communal services of the city of Moscow
Housing and communal services in the Russian Federation are divided according to territorial principles, and each region has its own pressing difficulties that require urgent solutions. The local administration of the capital is also forced to solve problems related to house management. Thus, given the population of the city of Moscow and the number of buildings that require constant attention, the issue of financial support is especially acute.
The city government notes the following features of the activities of the capital’s housing and communal services authorities:
- active exploitation of communications;
- irregular maintenance of engineering complexes, which is due to the lack of a sufficient number of specialists;
- the impossibility of carrying out timely major repairs, which is due to the lack of financial support;
- assistance to citizens is provided primarily in emergency situations;
- The tariff payments made are not enough to ensure the efficient operation of the economic service.
Each urban district has its own local department, the dispatcher of which is authorized to accept written and oral statements from citizens with the subsequent dispatch of specialized specialists to eliminate identified problems.
Consequences
Territorial authorities are not always able to fulfill their obligations. This has led to widespread administrative coercion of performers and contractors in violation of current legislation. Control over the production and provision of quality services to citizens and the validity of established tariffs has significantly decreased. Insufficient funding explains the lack of interest in forming HOAs. The inability to fulfill budgetary obligations, the lack of transparent and effective procedures for setting and adjusting tariffs make the sector unattractive for private investors. This indicates the presence of a systemic crisis both in the industry as a whole and separately in the regions. Solving the problems that have arisen is possible by using the program-target method.
Financial problems of housing and communal services
The housing and communal services sector is financed by budget funds, and therefore in 2021 the problem of lack of funds is felt especially acutely. The occurrence of difficulties is due to the following reasons:
- non-payment of the cost of services used (as practice shows, in every area of housing and communal services there are debts);
- change in payment standards for services (cost reduction due to subsidies, standard consumption indicators);
- loss of a large share of subsidies that were previously allocated to the Ministry of Construction;
- lack of meters, so actual consumption exceeds usage standards several times and, accordingly, payment.
Maintenance of plumbing, electrical and other communications is carried out by housing and communal services specialists, who are not enough to timely check the condition of the systems. The practice of attracting specialists from outside can be used, but municipal budgets do not have enough money to finance external specialists.
Current standards
The changes that affected the rules for the provision of utility services include not only the division of responsibilities into items, but also the procedure for calculating and paying for receipts. Not counting heating, payment is divided into a common house payment and individual payment for each apartment owner. Receipts also arrive separately.
Innovations also affected regulatory coefficients. This was done in order to encourage citizens to install individual meters in their apartments. The principle turned out to be very simple: for those who have the technical ability to install a meter, but did not do so, an increased standard was introduced for all types of public services. Further, for the same category of the population, the tariff increased every six months by ten percent to a limit of sixty percent. In other words, further refusal to install meters is fraught with an overpayment of sixty percent just two years after such an innovation, which was approved back in 2013.
The only advantage of such a change is the fact that this percentage overpayment is aimed at saving energy and increasing the efficiency of existing systems.
Procedure for calculating utility bills
The accrual procedure depends on whether individual metering devices are installed or the amount of resources is determined by common house meters. Utility payments for apartment residents also include expenses for the general needs of the apartment building.
If there are meters, payments are calculated based on indicators that are recommended to be recorded approximately on the 20th of each month. In addition, devices are required to be checked every 6 months upon prior notification to residents.
In the absence of individual metering devices, rent is calculated in accordance with the tariff standards established in the given region.
Sector transformation
The development of this industry takes into account current problems and attempts to eliminate them. The main task that falls on the shoulders of regional entities is the organization of a new system of work with maximum monetary savings and maintaining the quality of service.
To this end, the structure of the housing and communal services will be reorganized along the following lines and principles:
- expansion of the housing and communal services system by forming a multi-level vertical control structure;
- granting the right to perform functions on a commercial basis (this became the basis for the emergence of competition, as well as improving the activities of individual local divisions);
- issuance of a Decree on the establishment of various tariffs for payment of services on the territory of the Russian Federation (consumption standards are fixed, as well as the characteristics of residential properties that exclude the right to subsidies and social subsidies);
- gradual transfer to the principles of self-government, when financial responsibility will relate only to a specific housing and communal services (the organization must pay for itself without receiving additional allocations from the budget);
- individual subsidies based on the financial capabilities of consumers.
Such information about the reorganization of housing and communal services gives hope that this will lead to improved financing (self-sufficiency) and will have a positive impact on the maintenance of utility systems.
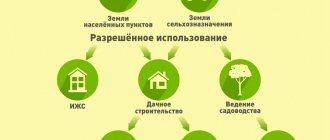
Blocked houses and apartment buildings
And one more nuance. Is there a difference between an MFB and a block structure home? The latter includes an object with a height of no more than 3 floors. I must consist of at least 10 blocks.
What is a block? The block is a separate part of the house intended for occupancy by one family only. With other units they can only communicate only with the general wall. It has access to the common part, but also has its own plot.
Agree, in some ways it looks like a residential building. However, an MPB and an apartment building are different dwellings. However, the Housing Code does not consider such houses as a separate type. For this reason, many consider them to be BCH. However, it should be remembered that apartments and blocks are completely different living spaces.
Social protection of the population
Government resolutions annually adopt new documents in the field of organizing the activities of housing and communal services. The main attention is paid to social protection of the population, which is manifested in the provision of benefits and subsidies when paying for utility services. Thus, the main actions are aimed at carrying out the following activities:
- a subsidy guarantee calculated on the principles of individuality (in practice, this is deciphered by displaying the basic requirements for real estate objects, as well as the financial condition of residents);
- prevention of poor quality performance of entrusted responsibilities for maintaining utility systems;
- unauthorized disconnection of services;
- increase in tariffs.
If there were significant violations on the part of a particular body in the performance of duties, then residents have the right to file a complaint against the actions of the official. You can involve a lawyer in the procedure to help protect your interests.
Explanation of the term
There are several definitions for this terminology.
When we say that MFB is in the housing and communal sector, it means that a team of several residential areas that include access to common spaces or the area surrounding the house.
The interpretation of MFB in the housing and utilities sector is quite simple; First of all, understand that residential buildings do not have one owner, but apartments and other types of premises are the property of different objects.
- legal entities;
- physical people;
- countries.
It should be remembered to minimize the risk of various misunderstandings.
Tariffication
Receipt of utility services by apartment owners requires mandatory mutual payment. But today the problem of collecting payments from citizens is associated with unreasonable tariffs. Thus, accounting of consumed resources occurs on the basis of accepted standards, which may differ significantly from the services actually used. In addition, citizens who pay fixed amounts without taking into account the services used consider it their responsibility to spend more than was paid.
This leads to the fact that commercial organizations that are service providers incur additional expenses that are not justified by the needs of citizens. Thus, according to recent changes in legislation, in order to reduce tariffs, a decision was made to force the installation of meters for water, gas and electricity. This is a single option for maintaining low utility costs while maintaining quality of work.
Symptoms of pathology
The most important symptom of urolithiasis is pain, which is localized in the lumbar region. As the stone moves toward the exit, there will be pain throughout the entire abdomen, and MCD is often mistaken for a symptom of another disease, such as appendicitis or an ulcer.
The disease is also accompanied by symptoms such as:
- frequent urge to urinate, which is also painful;
- blood in urine;
- excretion of urates in urine;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- rapid weight loss;
- weakness throughout the body;
- emotional instability and irritability;
- temperature increase;
- colic in the kidney area;
- Tachycardia may occur.
In advanced forms of the disease, convulsive syndrome may develop.
Objectives of tariff regulation
Prices for utility services are checked taking into account departmental instructions. Thus, the average calculation of material costs of commercial enterprises providing services is taken as the basis. Average rates of consumption of services are also considered. These figures are conditional, and therefore in practice providers receive a very small amount of income. And if technical equipment (for example, a pipeline) breaks down, the provider will have to fix the problem themselves, which entails additional costs.
By order of the Ministry of Construction, the following recommendations have been developed to stabilize payments and bring them to an adequate level, namely:
- reducing the costs of organizing work while maintaining the quality of the activities performed;
- use of external investments;
- development of competition;
- preparing a financial basis for work;
- increasing the independence of organizations.
Privileges
In an unstable economic situation, paying for utilities becomes simply unaffordable for some categories of citizens.
That is why the Government of the Russian Federation supports the population by introducing benefits for:
- large families raising three or more children under 18 years of age;
- WWII participants and members of their families;
- disabled children, groups 1 and 2;
- participants in combat operations, persons performing public service, labor veterans;
- residents of besieged Leningrad;
- honorary donors of the Russian Federation and the Soviet Union;
- persons injured during the Chernobyl accident.
Benefits provided to certain categories of citizens extend to utilities and housing services.
Planning
Deciphering current tariffs involves several aspects. The first is the average service consumption rates, and the second is the estimated costs that the utility service provider will incur. The third is the solvency of citizens, but this is a conditional indicator, since it takes into account the average salary of the population, and it can vary greatly depending on the region and the position held.
The planning process involves analyzing current performance, revising historical figures, and forecasting future costs. The result obtained is the norm for using one unit of a specific type of service.
List of utilities in 2021
According to clause 4, ch. II of Government Resolution No. 354, the list of utility services provided to owners and users of residential and commercial premises in 2021 includes:
| Cold water supply | Round-the-clock supply of cold water of proper quality (purified from pathogenic microorganisms, harmful chemical compounds) through a central or intra-house network. |
| Hot water supply | 24-hour supply of hot water of proper quality, temperature from +400 to +750C. A break in the supply of hot and cold water is permissible within 8 hours or a day (subject to major accidents). |
| Water disposal | Discharge of wastewater through centralized networks. |
| Electricity supply | Uninterrupted supply of electrical energy in volumes sufficient to operate appliances installed in an apartment building. |
| Gas supply | 24-hour gas supply via a centralized network. In the absence of the latter, it is permissible to provide the resource in gas cylinders. |
| Heating | Supply of heat energy through centralized or intra-house networks throughout the entire heating season to maintain the temperature in heated rooms at least 180C. We allow a break in supply no more than a day per month, in this case: Ø no more than 16 hours in a row at an average daily temperature of +120C; Ø no more than 8 hours in a row at an average daily temperature of +100C; Ø no more than 4 hours in a row at an average daily temperature of +80C. |
| Solid waste removal | Collection, removal, neutralization and disposal of household waste in quantities generated by users of residential and commercial premises. |
Utilities paid by users cannot include an item that is not related to a specific home, for example, a fee for gas supply, in the absence of it, cannot be charged.
Additional tasks
In addition to providing utility services, housing and communal services perform the functions of landscaping areas near houses, carrying out routine repairs, as well as organizing major repairs. To improve interaction between residents and municipal organizations, special representative bodies are being formed. These could be residents' associations or commercial management companies.
As practice shows, every year the costs of citizens to cover the cost of water, gas, electricity and other resources continue to grow. Today, people compensate for more than 60% of the cost of resources, whereas at the beginning of the century this figure varied within 4%. The government hopes that by 2040 housing and communal services will be fully financed by the population.
Is it possible not to pay for the maintenance of residential premises?
According to Part 3 of Art.
154 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, homeowners bear the costs of maintaining and repairing their housing, as well as paying for utilities in accordance with the concluded agreement. In accordance with Art. 162 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the management company (housing and communal services, housing and communal services, etc.) and the homeowners draw up an agreement in two copies and seal it with signatures. The agreement establishes a list of services provided, terms, price, payment procedure, restrictions on the supply of utilities in case of debt, etc. By virtue of Art. 307 of civil legislation, one party is obliged to fulfill the stipulated obligations, and the second is obliged to pay them in accordance with the established tariffs.
Expert opinion Smirnov Alexander Stanislavovich Lawyer with 12 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
Thus, the absence of an agreement for the management and maintenance of apartment buildings is grounds for refusal to pay invoices. In other words, there is no formalized contractual relationship – there is no violation of the terms of the contract.
Important: It is illegal to charge a fee for a specific service not provided for in the contract. As judicial practice shows, in case of non-payment due to inflated tariffs or their establishment without the consent of homeowners, the courts side with the tenants
As judicial practice shows, in case of non-payment due to inflated tariffs or their establishment without the consent of homeowners, the courts side with the tenants.
Improper fulfillment of contract terms
If the management company still demands payment in full from residents, taking into account all the corresponding tariff increases, but at the same time fulfills its obligations in bad faith or does not fulfill them at all, then the law provides for certain actions. For example, if garbage is not removed in a timely manner, the surrounding area is not cleaned, there are no lamps in the entrance and windows are broken, then this and other violations must be recorded in an appropriate act. It can be drawn up by any resident of a given building, together with two neighbors and the chairman of the homeowners’ association.
It is worth considering that the reference period for the provision of low-quality utility services will be the date when the act was signed. In case of identified violations and mass discontent of residents, it is necessary to prepare a collective complaint with specific claims. The complaint must contain the last names, first names, patronymics, residential addresses and signatures of each resident participating. Such a document is submitted to the management company or housing and communal services. The complaint should clearly indicate the date by which the tenants demand that the deficiencies be corrected. You must keep a copy of it for yourself.
Next, a similar letter is sent to the Housing and Communal Services Department of the locality with a request to take appropriate measures and bring violators to justice. This is done if the first complaint has no effect. Further, if the second option does not work, you should go to court.
Sources
- https://uslugi-zhkh.ru/kommunalnye-uslugi/
- https://101jurist.com/nedvizhimost/obsluzhivanie/zhilischno-kommunalnye-uslugi.html
- https://PravoNedv.ru/kvartira/zhkh/chto-vxodit-v-kommunalnye-uslugi.html
- https://J.Etagi.com/ps/chto-vhodit-v-soderzhanie-zhilya/
- https://o-nedvizhke.ru/zhkx/kommunalnye-platezhi/kommunalnye-platezhi-chto-v-nix-vxodit.html
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59dce336a815f198eb6a6e3f/5a851b124826770db7606a6a
Payment procedure for communal housing and utility services
The 2012 rules for the provision of utility services made it possible to calculate heating standards in a new way. Previously, you had to pay for the entire home area; today, heating common areas is not included in housing and communal services costs. There is also no need to pay for general sewerage. Firm standards have been established for the consumption of total hot and cold water - 90 liters per person every month.
Management companies are aimed at saving common housing and utility services. If the limited standard is exceeded, then the difference is paid by the management organization, not the residents. The exception is HOAs, where the owners themselves decide to pay the difference. If housing and communal services are provided by a resource supplier, then the excess is divided between consumers taking into account the occupied square meters.