To check the property you can order a report
*or you can also order a report WhatsApp +79232492328 or Email
We are often contacted with these or similar questions:
- I am interested in an extract from the USRN for an individual in all regions of the Russian Federation. How to get a?
- How to get an extract about all real estate owned by a person?
- I need an extract with full name about all real estate.
- Can I order an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate about the rights of an individual to the real estate he/she owns?
All these questions relate to one thing - people want to find out what kind of real estate another individual has .
Correctly, such an extract is called “On the rights of an individual to the real estate he/she has.”
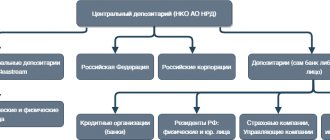
It contains information about the presence or absence of real estate owned by an individual on a certain date or period of time . Moreover, the cost of such a certificate depends on the number of regions of the Russian Federation for which the request is made.
Now carefully:
Information about an individual about the presence/absence of real estate can only be obtained by the copyright holder himself or his representative by proxy . In other words, it is impossible to find out what kind of real estate is listed on a person by his full name.
But what if you still need to find out information about real estate?
As we have already found out, it is simply impossible to officially find out about the presence of any real estate in a person . This information refers to classified information from the Unified State Register of Rosreestr.
But there are still some tricks with which you can, although perhaps not completely, try to find out the information of interest.
Reason No. 3. The transaction was completed recently
Like any public service, Rosreestr works slowly. Typically the database update takes 7–10 days. Therefore, do not worry if a day after the sale you do not see new owners in the statement. Wait for the specified period and order the document again.
Use Rosreestr’s explanations in your work
Explanations from Rosreestr on the issues raised will help management organizations, HOAs and owners:
- to understand whether the extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate and/or the register of owners correctly reflects changes in the rights to premises in the house in the event that one of the owners of the shared apartment has died - this affects the number of votes of the OSS participant;
- together with the residents of the neighboring house, agree on the delimitation of land plots under the apartment building, resolve conflicts over the use of the local area and understand whether a land survey plan is needed and where the boundaries will be;
- choose the right contractor to order information from the Unified State Register when preparing general meetings of owners, and do not become a client of a duplicate site that provides prohibited low-quality services.
At the same time, organizations and citizens who provide information from the Unified State Register to order can still do this if the information transferred to the customer is not formalized as an official extract from the register. The document must not have the signature of an official of Rosreestr and cannot be executed in the form of an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
When choosing a contractor, pay attention to how long the company has been on the market, read reviews about it on the Internet. Analyze how quickly the organization promises to order extracts, whether they are official, in what format the register of owners is compiled and whether they comply with the requirements of No. 120-FZ.
Types of property
The definition of property rights is contained in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to Article 209, this is the right “to freely dispose, own and use one’s own property.” This applies, of course, not only to real estate.
In general, there are only three of them - state, municipal and private. The latter, in turn, is divided into five types: individual, collective, shared, common shared and general joint. And, of course, each type of property has its own characteristics and definition in the law.
The owner of state property is, of course, the Russian Federation itself. This is enshrined in Article 214 of the same Civil Code of the Russian Federation. There are two subtypes of such property - federal and constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Both can be disposed of only in the interests of citizens; transfer of state property into private hands is possible only on a temporary basis, for rent. The country owns natural resources, as well as real estate such as public roads, cultural monuments and valuables, defense plants and buildings occupied by the armed forces.
Municipal property belongs to similar entities: cities, various villages and towns, etc. As a rule, these are public facilities - parks, squares, schools, kindergartens, medical institutions, administration buildings, etc. This is enshrined in Article 215 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Municipal property may also include individual apartments owned by local authorities. Such housing cannot be rented out, donated or sold - but social rent is provided for it: within the framework of such an agreement, citizens can use municipal property.
Private property appeared in legal practice in 1990 after a sixty-year hiatus. Its wording is similar to the definition of Article 209 given above: with regard to residential real estate, it also means full ownership. There is no limit on the amount of private property (both legal and private), and the number of possible actions in relation to it (sale, donation, rent, etc.) is very diverse. We will talk about its types below.
Private property and its types
As already mentioned, there are five types: individual, collective, shared, common shared and general joint. The division is determined by the number of owners, as well as their rights to property (in our case, real estate).
Individual ownership (sometimes called complete or personal), as you might guess, involves registration of only one person in the housing (for example, there are no other family members or they have filed a refusal). The owner solely uses, manages and owns the apartment or house. The right can be obtained through purchase, inheritance or gift, privatization and participation in a housing partnership or shared construction; it comes into force only after entry into the Unified State Register, and not after the conclusion of the corresponding transaction.
Collective property is not recorded in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, but in practice it exists. This is the case when real estate is owned by a collective, and all its members have equal rights to housing. This can happen in three cases:
- pooling the funds of several people to form a new joint-stock company or cooperative;
- reorganization of a state-owned enterprise and creation of a new entity on its basis;
- transfer to a state company for lease.
There are three forms of collective ownership - cooperative, partnership and joint stock ownership. The first involves the joint activity of many of its members, the second - co-ownership in equal rights of several people, the third combines the collective form with the personal one. The key feature of collective property is that the subject here is not a person, but a community or group of individuals.
Common shared ownership as a concept is fixed in Article 245 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is regulated by Art. 245-252. It occurs when the property parts of the parties to the transaction are not determined - and are considered equal by default. In this case, taxes and housing costs are divided equally among all owners.
If the agreement allocates unequal parts to the owners, then we are talking about shared ownership. Its key difference from the common one is the division of shares not into ideal ½ or ⅓ (as in the common share), but into real ones, calculated in square meters or parts of the living space. Some rooms can be divided equally according to shared ownership, but some (kitchen, corridor, bathroom) cannot: they will be classified as common shared ownership with conditional division. Taxes and expenses in the case of shared ownership will be paid depending on the size of the owner's share.
You can obtain the right to any shared ownership through privatization, inheritance, donation, purchase or sale, etc. There can be any number of owners. You can sell your share in real estate even without the approval of other owners - however, they will have the preemptive privilege of purchasing.
Common joint ownership does not imply the allocation of shares. It arises between spouses and their minor children (i.e., closest relatives). According to Article 253 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, all of them are endowed with equal rights to dispose, use and own joint property. If you need to sell the apartment, this can only be done with the consent of all owners.
It will not be possible to buy housing in common joint ownership for 2-4 people who are not close relatives - only in shared ownership.
Legal examination of documents
More details
200-60-91
How to purchase an apartment as private property
There are five ways to do this:
- buy from the developer;
- draw up a purchase and sale agreement (for example, on the secondary market);
- donation, inheritance and other similar methods;
- participation in cooperatives such as housing cooperatives;
- privatization.
Let's talk about the latter in a little more detail. Each person, by law, can buy housing once through privatization, i.e. draw up a social rental agreement between the state and the citizen. Emergency, service, rural housing, as well as dormitories and social security institutions cannot be privatized. A child who grew up in a privatized apartment and owns part of it according to documents can, upon reaching adulthood, privatize another apartment for free - also once. Such housing can only be taken away through the courts; All real estate transactions are available with it. The only disadvantage of privatization is the costs. Utility bills will be higher than in non-privatized apartments, and for the housing itself you need to pay a tax every year - from 0.1 to 2% of its price.
Reason No. 7. Real estate has no owners
It also happens that real estate actually does not have a copyright holder. Most often this happens when dividing an inheritance, when the heirs do not come to an agreement and the process is delayed. Houses located on the outskirts of villages or in holiday villages also often find themselves without an owner.