Would you like to consult a lawyer for free? Write to the chat on the bottom right or call the hotline, calls within the Russian Federation are free. We accept questions any day of the week.
The concept of “agricultural land” is defined in clause 1 of Article 77 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. This category includes facilities located outside populated areas and provided for agricultural activities. Their owners can be citizens, legal entities, municipalities, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and the state. Sometimes owners need to use these objects for other purposes. In such cases, it is important to understand whether it is possible to transfer agricultural land to another category and how to do it.
Why change the category of land plot
Agricultural land can be used exclusively for the purpose of growing crops and raising livestock. Within these objects, the construction of the following buildings is allowed:
- storage;
- cowsheds;
- pigsties;
- cellars for storing root crops, etc.
These buildings cannot be used for human habitation and do not require a postal address to be assigned to them.
But often owners have a desire to build a residential building within the site, for example, a cottage or a dacha, in relation to which they could register ownership in their name in order to subsequently be able to pass it on by inheritance.
Sometimes land owners decide to change their type of activity. In this regard, there may be a need to build an industrial enterprise on the site.
In both cases, in order to achieve the set goals, the owner needs to transfer agricultural land to another category.
When is it allowed to transfer agricultural land to another category?
The full list of grounds for changing the category of agricultural land is defined in clause 1, article 7 of Federal Law No. 172-FZ of December 21, 2004 “On the transfer of lands or land plots from one category to another.” These include:
- land conservation;
- location within the land plot of monuments (historical, architectural or natural) or a nature reserve and the creation of specially protected areas;
- establishing or changing the boundaries of settlements;
- placement of industrial facilities on the site;
- installation of power lines, construction of roads and other linear facilities, carried out on the basis of a project for the reclamation of part of the land;
- inclusion of territories unsuitable for agricultural work into forest or water fund lands or reserve lands;
- mining operations carried out on the basis of a reclamation project;
- installation of public utility facilities, if their other placement is impossible;
- taking measures to fulfill obligations under international treaties to ensure state security.
Farmland use
According to paragraph 1 of Article 77 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, agricultural lands are lands located outside the boundaries of a populated area and provided for agricultural needs, as well as those intended for these purposes.
Agricultural lands can be used for agricultural production, the creation of protective forest plantations, research, educational and other purposes related to agricultural production (Clause 2 of Article 78 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Such lands can be occupied:
- on-farm roads, communications, forest plantations designed to protect land from the effects of negative (harmful) natural, anthropogenic and man-made phenomena;
- water bodies;
- buildings, structures, structures used for production, storage and primary processing of agricultural products;
- farmland. They include arable land, hayfields, pastures, fallow lands, lands under orchards, vineyards and other perennial plantings. They are subject to protection as especially valuable lands.
Agricultural land is divided into three categories, the minimum size and location of which are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
1. Lands of priority use, subject to special protection, which include experimental production units of research organizations and educational and experimental units of educational institutions of higher vocational education. The cadastral value of these lands significantly exceeds the average level of cadastral value for the municipal district (okrug).
2. Particularly valuable productive land, the use of which for non-agricultural needs, for dacha and other construction is not allowed.
3. Agricultural land unsuitable for agricultural production, therefore, land of poorer quality according to cadastral valuation.
The use of an agricultural land plot provided for farming for the purposes of housing construction is not allowed (letter of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated December 21, 2010 No. D23-5270).
For the construction of buildings, structures and structures necessary for the activities of a farm, land plots can be provided and acquired in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 11 of the Federal Law of June 11, 2003 No. 74-FZ “On Peasant (Farm) Farming”.
In what cases can a transfer be refused?
Refusal is possible in the following cases:
- upon receipt of negative results of an environmental assessment, if this procedure is necessary;
- based on the restrictions established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation;
- if the declared category does not comply with the approved territory development plan.
In addition, changing the category of agricultural land is impossible under the following circumstances:
- the cadastral value of the plot is 50% or more higher than the average cadastral value of land established for the region (Article 79 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- The site is classified as particularly valuable agricultural land.
If a refusal to transfer land to another category is received, the owner of the plot has the right to appeal this decision in court within 3 months. Satisfaction of the claim is possible only if the applicant provides a clear justification for his claims.
The legislative framework
In addition to the Administrative Code, regulation of land relations is also carried out by the Land Code of the Russian Federation. If a citizen has violated the relevant laws, then he is subject to administrative liability in the form of a fine. In addition to the penalty, this person will have difficulty selling the property.
To prevent such problems from arising, it is necessary to change the category of the plot in time, followed by its registration with certain authorities (defined in the Land Code).
The procedure for changing the category of land is a rather troublesome process, which will immediately begin with difficulties in obtaining permission to change the intended use. In addition, the Federal Law is constantly updated (additions and adjustments are made to it), which makes the procedure for changing categories even more complex.
The use of land and its intended purpose are interrelated concepts that complement each other (read about the nuances of various types of permitted use of land here, and from this article you will learn about the penalties for using land for other purposes). They determine how the site will be used, as well as what buildings will be located on it (in some categories there cannot be any).
IMPORTANT! Categories of land plots must be used only for their intended purpose (except for those that do not yet have official status), otherwise this will be considered a direct violation of Article 8.8 of the Code of Administrative Offences, entailing the imposition of large fines.
We recommend that you read our other articles about the nuances of using different categories of land:
- special purpose;
- forest fund;
- water fund;
- agricultural purposes;
- settlements;
- recreational purposes;
- stock;
- specially protected areas and objects.
Procedure for changing the category of a site
The procedure for transferring agricultural land to another category is regulated by Federal Law No. 172-FZ of December 21, 2004. It consists of the following stages:
- Drawing up a petition. The document must indicate the following data: current cadastral number of the land plot; the status that the land has at the moment; the category into which the applicant requests to transfer the object, indicating the rationale for his request.
- Collecting a package of necessary documents.
- Submission of all collected papers to the authorized body, namely, to a state authority or local government. The application may be returned without consideration if there are errors in the documents, if the documents do not comply with legal norms, or if an incomplete package of papers is submitted. In this case, it is recommended to correct these shortcomings and resubmit the application.
- Waiting for the results of document review. The decision is made by local authorities within 2 months from the date of filing the application, and by state authorities - within 3 months. Based on the results of reviewing the documents, an act is issued to change the category of the site or to refuse to satisfy the request without explanation. The document is sent to the applicant within 14 days after completion of the application consideration procedure. The act of transferring land to another category must indicate the following data: the basis for the decision to change the category, boundaries, area and cadastral number of the plot, the previous and new category of land.
- Making appropriate changes to the Unified State Register of Real Estate on the basis of an act on the transfer of land to another category (if the authorities make a positive decision).
Risk of buying and selling agricultural land
Federal Law of July 24, 2002 N 101-FZ “On the turnover of agricultural land”
Article 8. Purchase and sale of land from agricultural lands
- When selling a plot of agricultural land, a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or in cases established by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a municipal entity has a pre-emptive right to purchase such a plot of land at the price for which it is sold, with the exception of cases of sale at public auction and cases of seizure of the land plot for state or municipal needs.
- The seller of a land plot of agricultural land is obliged to notify in writing the highest executive body of state power of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or, in cases established by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a local government body of the intention to sell the land plot, indicating the price, size, location of the land plot and period, before the expiration of which mutual settlement must be made. The period for making mutual settlements for such transactions cannot be more than ninety days.
The notice is delivered against signature or sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery.
The seller of a land plot of agricultural land is obliged to notify government agencies in writing about the sale, price, term, location.
Notification of transfer of land to another category of Crimea
- If a subject of the Russian Federation or, in accordance with the law of a subject of the Russian Federation, a municipal entity refuses to purchase or does not notify the seller in writing of its intention to purchase the land plot being sold within thirty days from the date of receipt of the notice, the seller has the right to sell the land plot within a year to a third party at a price not lower than the price specified in the notice.
When selling a land plot at a price lower than the previously stated price or with a change in other essential terms of the contract, the seller is obliged to send a new notice according to the rules established by this article.
Government agencies respond to the owner within 30 days about their desire to buy his land. If you do not answer, then you can sell for one year without notice.
But under the same conditions.
- A transaction for the sale of a land plot made in violation of the pre-emptive right to purchase is void.
If the price or terms have changed, then you need to notify government agencies again about the sale of agricultural land.
Required package of documents
The following documents must be attached to the application:
- extract from the state land cadastre;
- a copy of the applicant's passport;
- a copy of the document confirming the applicant’s right to own the land plot;
- act of environmental assessment, if its implementation is provided for by law;
- calculation of losses in the agricultural or logging industry;
- consent of the owner of the land plot to transfer this property to another category.
Legal entities, in addition to the listed documents, must attach an extract from the Unified State Register and a copy of the company's Charter.
Citizens of foreign countries must provide a translation of documents confirming the identity of the applicant, executed in writing and certified by a notary.
A package of documents can be submitted to the authorized body personally by the applicant, his representative (if there is an appropriate power of attorney) or by registered mail with notification and a list of enclosed documents.
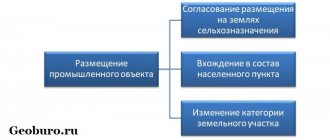
Conversion of land from agricultural to industrial purposes
Industrial plots are lands that are intended to support the activities of enterprises and the operation of production facilities. They may include protected areas and sanitary protection zones.
The transfer of agricultural land to the industrial category is possible subject to mandatory compliance with two conditions:
- the average cost of land in the region is not lower than the cadastral value of the site;
- There are no other options for locating the industrial facility.
The procedure for changing the category of land is carried out according to the standard procedure established by Federal Law No. 172-FZ of December 21, 2004.
When using industrial land plots, compliance with certain sanitary norms and rules is required, for example, planting trees along the entire perimeter of the facility, which helps reduce the level of pollution of the territory.
Violation of the procedure for transfer of lands and invalidation of the transfer act
Problems of land transfer occur quite often, therefore, if the distribution of the land fund by land category is carried out in violation of the norms established by law, acts on the assignment of lands to certain territories will be declared invalid.
As judicial practice shows, such decisions occur quite often. For example, some acts provided by public authorities quite often lose their force due to the fact that this body does not have any authority to carry out such actions to transfer property.