Property tax is calculated taking into account the cadastral value of real estate. Depending on the type of real estate (land, private house, apartment, garage, etc.), there are rules for calculating tax based on the cadastral value.
In this article we will briefly and step-by-step analyze examples of calculating tax based on cadastral value in 2021. To do this, we will consider all the components of the tax calculation formula taking into account the types of real estate.
Types of real estate for paying tax at cadastral value
Taxes are imposed only on those properties that are registered in the cadastral register. Registered real estate is assessed by the state and each property has its own cadastral value.
Taxes are paid based on the cadastral value and taking into account tax rates and benefits. Let's look at how taxes are paid based on the cadastral value of the following types of real estate:
- land plot
- residential (private) house
- garden house
- apartment (room)
- other real estate objects
Let us briefly consider the procedure for paying tax at cadastral value in 2021 for each type of real estate separately.
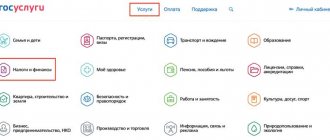
How to check debt
You can find out the amount of debt:
- at the Tax Service office (have your IIN or BIN and passport with you);
- on the e-government portal:
on the E-Government portal, you need to go to the “Customs and Taxes” section:
In the “Taxation” subsection, select “View and pay tax debt”:
In the window that opens, click the “Order a service online” button:
Then fill in the fields and click the “Next” button:
If the data is filled out correctly, the “Table of debts by state revenue authorities” will appear on the screen:
- on the website of the State Revenue Committee.
Land plot - how to calculate tax in 2021
Land tax is a local tax and is calculated based on the tax rates set by the local municipality. To pay land tax, the following information is required:
- cadastral value of the land plot;
- land area;
- tax rate for a specific land plot adopted by the municipality in 2021;
- availability of benefits for the owner.
When we know all this data, then we can easily calculate the tax on your land plot:
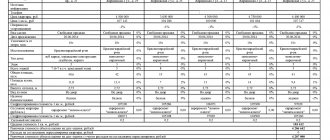
For clarity, here is an example :
| We calculate land tax | Definition, basis, magnitude |
| Taxpayer | Individual – pensioner |
| Land plot | 13 acres |
| Cadastral value | 5 million rub. |
| Tax rate | 0,3 % |
| Federal benefit under Art. 391 item 5 | Reduction of the tax base by 600 sq.m. |
According to the example given in the table, the formula for calculating land tax based on cadastral value is as follows:
(5,000,000 – 2,307,692)*0.3% = 8,077 rub . – the amount to be paid in our case.
(Explanation: if the cadastral value for 13 acres of land = 5 million rubles, then the cadastral value of one hundred square meters = 384,615 rubles, the cadastral value of 6 acres = 2,307,692 rubles - this amount is not taxed; accordingly, only 7 acres are taxed land).
Each specific case will have its own calculation, taking into account the cadastral value, area, rate and benefits. You can read more about the features of calculating land tax here.
What is land tax
Land tax
–
a tax paid by legal entities and individuals who have a land plot on the right of ownership, on the right of permanent land use or on the right of primary free temporary land use.
In this case,
tax is not paid on land plots :
- public use of populated areas;
- occupied by a network of state public highways;
- occupied by objects that are under conservation by decision of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- purchased for the maintenance of rental houses;
- occupied by buildings and structures acquired by the state Islamic special financial company under contracts concluded in accordance with the terms of the issue of state Islamic securities.
And organizations of
railway transport, energy and electrification systems, communications, organizations engaged in the production and transportation of oil and gas
pay tax for land plots: occupied by railway tracks, rights-of-way, railway stations, train stations, areas occupied by power line supports and substations, oil pipelines and gas pipelines, communication line supports
DO NOT PAY land tax:
- taxpayers applying the SNR for peasant or farm enterprises
, for land plots used in activities to which this SNR applies; - state institutions
and
state educational institutions
of secondary education; - state enterprises of correctional institutions
of the authorized state body in the field of execution of criminal penalties; - religious associations;
- participants and disabled people of the Great Patriotic War and persons equated to them
, on land plots provided for personal household (auxiliary) farming, gardening and summer cottage construction, including land occupied for buildings and garages, as well as on land plots occupied by housing stock, in including buildings and structures attached to it and adjacent land plots, for which taxes are also not paid: - mothers of many children
, awarded the title “Mother Heroine”, awarded the “Altyn Alka” pendant; - separately living pensioners
.
How to calculate residential house tax in 2021
In the same way as the land tax (example above), we can figure out how to pay the tax on a residential building. This is also a local tax, the so-called property tax. Payment of tax on a residential building is regulated by Chapter 32 of the Tax Code.
At the moment, the tax on a residential building is determined based on the cadastral value of the residential building. At the same time, tax payers are exempt from paying for 50 square meters of the total area of this residential building. (Clause 5 of Article 403 of the Tax Code).
For more details on how the tax is calculated based on the cadastral value of a residential private house, read a separate article: “Calculation and determination of the tax on a private residential building based on the cadastral value”
When to submit tax returns
The calculation of current payments
(TNF 701.01 )
for land tax is submitted no later than February 15 of the current tax period, that is, for 2021 -
before February 15
, 2020.
In this case,
no later than 10 calendar days before the next due date for payment of current payments:
- calculation of current payments
- if tax obligations arise during the tax period, with the exception of those arising after the last deadline for payment of current payments, since in this case the calculation is not submitted; - additional calculation of current payments
with appropriate adjustments in amounts - when tax obligations for land tax change during the tax period.
a Declaration (TNF 700.00 ) is submitted to the tax authorities at the location of the land plots of the year following the reporting tax period:
- legal entities
; - Individual entrepreneur
– for tax obligations determined for land plots
used
(to be used)
in business activities
; - by individuals
(including persons engaged in private practice) - for tax obligations determined for land plots
used
(to be used) in
business activities
and (or) in activities related to such private practice.
CONCLUSION:
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs at ESD - submit Calculation of current payments and Declaration
;
Individual entrepreneur on SNR (if there is land used for business purposes) - only submit the Declaration
;
Individuals (if there is land used for business purposes) - submit only the Declaration
.
Calculating tax on a garden house
There is an opinion that registering your dacha house as a non-residential building is more profitable for paying taxes. But this opinion is wrong. For tax purposes in 2021, a residential building is a house and residential building located on plots for private household plots, individual housing construction, gardening and vegetable gardening.
Therefore, a garden house is also subject to tax, like a residential building, if information about it is included in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. In order to calculate the tax on a garden house, you should also know the components for paying the tax: cadastral value, area, tax rate, availability of tax benefits.
It should be remembered that if your property has several houses - for example, two or three, then tax exemption for 50 sq.m. only applies to one of them.
How to calculate land tax based on cadastral value
Organizations carry out tax calculations independently. In order to find out in advance what the tax will be for individuals, use online services or trusted agencies.
We do the calculations ourselves. To do this, we multiply the cadastral valuation by the product of the area of the object minus the deduction, and multiply by the appropriate rate. We recommend paying the fee on time and in full to avoid problems with the law.
The calculation rules are simple, the main thing is to know the formula. Multiply the data and find out how much you need to pay for the whole year. For example, in one region of the Russian Federation, when calculating for a residential building, a coefficient of 0.3% is used, in the capital region it reaches 0.4%. As an example: the tax on the cadastral value of an apartment is 0.1%; for “luxury options” it can be increased up to 1%. To find out the price per 1 sq. m, before making the calculation, divide the indicator by the entire area.
A fundamental nuance: the duty is not paid on the entire area, but only on that which is subject to taxation. Now you understand how simple, accurate and competent it is to calculate property taxes on your own.
How to pay taxes for an apartment and room in 2021
Owners of small-sized apartments will receive good news - apartment living space up to 20 square meters is not subject to tax. m., or rooms - up to 10 sq.m. This benefit is established at the federal level and enshrined in Art. 403 of the Tax Code.
That is, if your apartment is 25 square meters, then in fact only 5 square meters are taxed. There are also additional benefits for paying apartment taxes. These benefits are established at both the federal and local levels. Read our article: “Apartment tax based on cadastral value.”
Odds
Calculation of the tax rate, in general, is made by multiplying the cadastral value (CV) of the site by the tax rate (TS), which is established in the given area by local authorities.
The federal law only introduces restrictions on the upper limit of this rate, which depends on the intended use of the land. This NS can be equal to 0.3% or 1.5%.
A rate of 0.3% is used when calculating the taxable income for owners who use their land for housing or agricultural purposes (for example, for summer cottages, gardening or vegetable gardening).
In other cases, an SS of 1.5% is applied.
In some cases, when calculating the tax, coefficients are used to reduce or increase the tax amount. For this purpose, these coefficients are added to the ZN calculation formula as factors.
Tax on other types of real estate at cadastral value
In addition to individuals, legal entities can also be owners of real estate. They are required to pay taxes in advance payments quarterly, and at the end of the tax period submit a tax return. Unlike individuals, organizations are required to independently calculate taxes in accordance with current legislation.
The property tax of organizations is a regional tax and is regulated by Chapter 30 of the Tax Code.
Regarding taxes on personal property. persons, such as outbuildings, garages and unfinished objects - they are also taxed if taken into account by the state.
Determination of the tax base
When determining the tax base, not all property is included in it. Only real estate that is accepted for accounting by the taxpayer and is listed on the organization’s balance sheet is considered taxable. Objects that do not participate in determining the tax base are divided into two groups: exempt and preferential.
The list of property that is not recognized as an object of taxation is given in paragraph 4 of Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, land plots and other environmental management objects (water bodies, natural resources) and others. At the same time, all movable property objects are excluded from the tax base.
Read more: Property tax return: filling out a new form
As for benefits, taxpayers who have the right to use them are enshrined in clause 3 of Art. 56, paragraph 2 of Art. 372 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There are only two types of privileges:
- Federal benefits that apply throughout the country. Those taxpayers who meet the stated requirements have the right to use them. They are enshrined in Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Regional relaxations, which are approved by the authorities of the constituent entities of Russia. The rules on benefits apply exclusively within a specific region.
IMPORTANT!
If an organization applies a regional benefit, then it is necessary to follow the legislation of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
It is convenient to check the current regulations on the official website of the Federal Tax Service. If a specific type of benefit is not approved, abolished, or canceled for the current calendar year, then you cannot use the privilege. You will have to calculate the amount according to general rules.
Land tax for individuals - calculation and payment procedure from 2021
Payment of land tax is the fiscal responsibility of land owners
The collection of taxes into the state treasury began in ancient Roman times. Money, as well as records of public debts and obligations, tax documents, lease agreements on state property, financial statements of magistrates, inventories of fields, written oaths, decisions of popular assemblies were kept in the erarium (treasury).
Under Emperor Octavian Augustus, revenues from the imperial provinces were collected into a fiscus (the Latin word fiscus means "basket"). Cash flows flowed into this single financial center of the Roman Empire. From it came instructions on the procedure for collecting taxes, minting coins, making payments, etc.
The goals and objectives of the fiscal laid the historical foundation for the formation of the tax and legal system in a number of states. In Russia, for example, even under Peter I, a secret fiscal service was established in 1911. Fiscal officials served the interests of the Russian treasury and took care of its replenishment. It was also their responsibility to ensure that there was no dishonesty or abuse in the collection of taxes.
Taxes and fees remain the main source of revenue for the Russian state budget and municipal budgets. They are regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In 2021, it was amended as established by Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2019.
Among modern fiscal obligations of citizens, defined by Russian legislation, a special role is assigned to land tax for individuals. It is sent to the municipal budget. The updated rules and procedure for paying land tax, in accordance with its “hierarchical status,” are spelled out in the regulations of local authorities.
From January 1, 2021, individuals and legal entities in all regions of Russia will pay land tax according to new rules. The taxable base was the cadastral value of the plot, valid as of January 1 of the reporting period.
Information on the cadastral value of land plots is posted on the official website of Rosreestr on the Internet.
Land tax payers
The obligation to pay land tax applies to all citizens of the Russian Federation and organizations that own land plots used for industrial, commercial or domestic needs.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 388), individuals become payers of land tax under the following cumulative circumstances:
- land plots belong to citizens with the right of ownership
- permanent (unlimited) use
- lifelong inheritable ownership
- registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate
Individuals using the plots on the right:
- free use
- rental
- free urgent use
are not taxpayers.
Object of taxation
The object of taxation is land plots located within the boundaries of:
- municipality
- federal cities: Moscow
- St. Petersburg
- Sevastopol
on the territory of which a land tax has been introduced.
The following are not recognized as objects of taxation (Article 389 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- land plots: included in the common property of an apartment building
- withdrawn from circulation
- from the forest fund lands
- occupied by water bodies within the state-owned water fund
- especially valuable objects of cultural heritage of the peoples of the Russian Federation
The tax base
To calculate land tax, the cadastral value (CV) of land plots specified in the Unified State Register is used. This value forms the tax base (Article 390 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When calculating tax, tax authorities use the value of the KS that is relevant as of January 1 of the year, which is the tax period.
The cadastral value changed during the tax period is applied from the date of entering information about it into the Unified State Register of Real Estate on grounds that arose from January 1, 2021. This procedure for applying the CS is established by Federal Law No. 63 of April 15, 2019.
Thus, in cases where during the tax period:
- a land plot was formed
- the qualitative and/or quantitative characteristics of the memory have changed: area
- appointments
- permitted use
- categories
- etc.
When calculating land tax, the new cadastral value of the land plot is applied from the date of registration of information about it in the Unified State Register.
During the tax period, the Tax Code may change for other reasons:
- correction of a technical error in the USRN information
- reduction of the capital cost due to the correction of errors made in determining the cadastral value
- challenging the Constitutional Code and establishing the market value of the taxable object by decision of the commission under the management of Rosreestr
- adoption by the court of an appropriate decision due to the unreliability of the information used in determining the Constitutional Court
In such cases, from January 1, 2021, to calculate land tax, the changed cadastral value (as the tax base) is applied in the same manner, that is, from the day it is recorded in the Unified State Register.
Taxation condition for all cases of changes in the Constitution
In cases where, when changing the CS:
- there was a decrease in cadastral value
- when recalculating land tax for previous tax periods (until 2021), the amount of tax paid turned out to be greater than that calculated under the new tax system
recalculation and refund of funds not made (clause 17 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Starting from 2021, the new cadastral value values recorded in the Unified State Register of Real Estate will be used exclusively in the following tax periods.
Land tax rates
Land tax is a direct tax, that is, mandatory. It is levied on the value of the taxpayer’s property, including the cadastral value of the land plot.
For direct taxes, the law establishes the percentage of income withheld in favor of the corresponding budget. For a number of direct taxes the following are provided:
- payment benefits
- complete exemption in some cases
Land tax is paid by landowners to the local budget, and to federal cities (Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol) to their city budgets.
The object of taxation is plots located on the territory of the municipality in which land tax has been introduced.
The amount of land tax is calculated as the product of the cadastral value of land plots and the tax rate:
tax = cadastral value of land plot x tax rate
Land tax rates are set not at the federal level, but by local authorities (Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The laws of municipalities determine:
- land tax: only on the territory of the municipality
- within the limits of the rates established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- in addition to the benefits provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- taking into account the restrictions provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Tax rates adopted in different municipalities:
- may vary
- may be lower than the maximum rates established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
For land tax rates, only one thing is impossible - their excess over the basic values of 0.3% and 1.5% of the cadastral value of the land plot (Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax rate 0.3%
A rate of 0.3% is applicable for taxation on land plots:
- from agricultural lands
- from lands within agricultural use zones in populated areas
- for agricultural production occupied by the housing stock and engineering infrastructure facilities of the housing and communal complex (HCS): with the exception of the share in the right to land plots attributable to an object not related to the housing stock and engineering infrastructure facilities of the housing and communal services complex
- for residential construction
- defense
Note
From the tax period of 2021, the land tax rate is 0.3% of the cadastral value of plots:
- for residential construction
- for private household plots
- for gardening
- for gardening
applies to plots of this group only if they are not used by the owners for business activities.
Violation of the requirement will lead to an increase in land tax:
- for its calculation the rate of 1.5% will be used
- the increased rate will be applied from the reporting period when local authorities established the fact of violation
A return to the minimum rate will be possible after the taxpayer eliminates the violation.
Taxes on general purpose land in SNT/ONT
From 2021, a tax at a preferential rate of no more than 0.3% of the cadastral value will be levied on general purpose land (ZON) in horticultural and vegetable gardening non-profit partnerships (more details here).
Main conditions:
- availability of approved documentation on territory planning
- ZONS should not be used in business activities
ZONS include areas owned or permanently (indefinitely) used by SNT and ONT. They are busy:
- objects of partnerships
- passing through
- children's and sports grounds
- parking lots
- etc.
Tax rate 1.5%
A tax rate of 1.5% applies to taxation of all other land plots.
Rules for calculating land tax in 2021
1. New formula for calculating land tax
From 2021, a new formula is used to calculate land tax. It takes into account the provisions of Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2021, related to the task of reducing the tax burden.
Legislative changes are effective from the moment the law is published. They apply to legal relations arising from the 2021 tax period.
- Limiting the growth of land tax
For housing construction sites, a coefficient of 1.1 was introduced from the 2018 tax period:
- limits the annual increase in land tax for individuals to no more than 10% compared to the previous year
- will avoid a significant increase in obligations to pay land tax from period to period
- does not apply in cases of untimely construction: increasing factors of 2 or 4 have been introduced to calculate land tax in case of delayed construction of plots
The tax cannot increase by more than 10% from last year.
In the event that the calculated tax for the reporting year is higher than in the previous period:
- tax is paid with a coefficient of 1.1 in relation to the amount of tax for the previous period
- coefficient 1.1 takes into account the tax limit of 10%: tax for the reporting period = tax for the previous period + 10% of the tax for the previous period = (1 + 0.1) x tax for the previous period = 1.1 x tax for the previous period
- When comparing these amounts, changes that occurred in the previous period in the provision of tax benefits are not taken into account:
- qualitative and/or quantitative characteristics of the land plot
- Application of increasing coefficients when calculating land tax in case of untimely development of land plots
For land plots where protracted housing construction is taking place (untimely development), increasing coefficients are used to calculate land tax (subparagraphs 15–17 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- coefficients 2 and 4 – for housing construction sites
- coefficient 2 – for individual housing construction plots
2. Calculation of land tax on land plots in case of untimely construction
“Ruble punishment” for violating the deadlines for the development of land plots is quite logical:
- construction of facilities is delayed
- objects under construction are not registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate
- property tax is not charged on a construction project under construction
- The municipal treasury does not receive the income due
- the budget shortfall is partially compensated by increased land taxes
Untimely housing construction (not individual housing construction)
- Tax using increasing factor 2
tax = 2 x (tax base x tax rate)
The calculation of double land tax is carried out in the case of land development and registration of the object after the expiration of the three-year construction period:
- The countdown of time (three years) begins from the date of state registration of rights to the land plot
- The end of the construction period is considered to be the date of registration in the Unified State Register of Rights to the constructed property
If before the expiration of 3 years the owner meets the deadline:
- construction completed
- the rights to the constructed property are registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate
the amount of tax paid for the three-year construction period and calculated using an increasing factor of 2 will be greater than the amount of tax calculated using a multiplying factor of 1.
The difference between the tax amounts is recognized as the amount of overpaid tax. Surplus. at the discretion of the developer (taxpayer), it will either be offset or returned to the taxpayer in the prescribed manner.
- Tax using increasing factor 4
tax = 4 x tax base x tax rate)
The calculation of fourfold land tax is carried out in the case when the construction time of the object exceeded 3 years.
Tax calculation begins from the moment the plot was registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Untimely individual housing construction (IHC)
- Tax using increasing factor 2
In the case where the owner of an individual housing construction site completed the construction of a residential building over a period longer than the required 10 years, the tax is calculated using the formula:
tax = 2 x tax base x tax rate
The reason for paying double land tax is the impossibility of collecting property tax (construction project).
The tax amount will be reduced only when the residential building is built and registered. A barn, summer kitchen, bathhouse and unregistered residential building will not be an escape from double taxation.
Land tax benefits
Federal benefits for land tax and property tax for individuals have been retained in full. The categories of citizens entitled to benefits are listed in paragraph 5 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Large families have joined the ranks of beneficiaries. They have the right to a tax deduction in the amount of the cadastral value of 600 m2 of land area they have.
The tax base (tax deduction) for beneficiaries of all categories is reduced in relation to one plot of land:
- at the taxpayer's choice
- regardless: from the category of land plots
- type of permitted use
- location of the storage facility within the territory of the Russian Federation
To implement a tax deduction, you need to send a notification to any tax authority about the land plot selected for preferential taxation.
Applicants will be able to receive the due tax benefit for periods starting from 2021 without an application. It is provided automatically after registration of the status:
- large family
- disability: child
- 1st and 2nd degrees
If the taxpayer notices that the benefit was not taken into account in the tax notice received, he needs to send a statement of disagreement with the tax to the Federal Tax Service.
After considering it, the tax authority sends in response:
- or notification of a tax benefit
- or a message about refusal to provide a tax benefit
An application for benefits must be submitted only once. Afterwards, the benefit applies automatically.
The described procedure was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. MMV-7-21 / [email protected] dated November 12, 2019. It comes into force on February 3, 2021.
Deduction for personal property tax
1. General rules
A deduction for property tax for individuals is a reduction by a certain amount in the cadastral value of the following objects (clauses 3–5 of Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- apartment and part of a residential building: for cadastral value of 20 m2
- for the cadastral value of 10 m2
- for the cadastral value of 50 m2
2. Additional deduction for property tax for large families
Persons with three or more minor children will be subject to both the rules above and the new rules for reducing the tax base. The latter will come into force on April 15, 2020 (Part 6.1 of Article 3 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ).
Additional deductions
Additionally, the tax base will be reduced for the following items:
- room, apartment and part of an apartment for a cadastral value of 5 m2 per each minor child
- for the cadastral value of 7 m2 per child
Procedure for receiving a deduction
All categories of beneficiaries can receive a tax deduction for only one of the objects of each type (clause 6.1 of Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- apartments
- parts of the apartment
- rooms
- residential building
- parts of a residential building
This means that if a citizen owns, for example, 1 apartment and 3 rooms, then to receive a tax deduction you need to indicate:
- or just an apartment
- or one room
The tax deduction is provided for periods starting from 2021 (Part 6 of Article 3 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ).
Procedure for paying land tax
Individuals pay land tax on the basis of a tax notice. It, together with the receipt, is sent by the Federal Tax Service to the taxpayer’s place of residence.
There is no need to independently calculate land tax. The tax amount will be calculated by the tax inspectorate (clause 4 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The payment document contains:
- payment details
- exact tax amount
If the calculation is made with errors, the taxpayer does not bear any administrative responsibility. In this case, you need to clarify the cadastral value of the land plot. Information about it is contained in an extract from the Unified State Register, which can be obtained from Rosreestr or the MFC.
If inaccuracies or unreliable information are found in the tax notice, you must send an application to the Federal Tax Service indicating the errors made:
- false information: about the object of taxation
- about the taxpayer himself
The application is written on a form. You don’t have to look for it, since it is sent to the tax office along with the notification.
After checking and confirming the information specified in the application, the Federal Tax Service:
- will recalculate the tax amount
- will send a new notification to the taxpayer
Failure to receive a tax notice from the Federal Tax Service
In the event that the owner of the property has not received notification of payment of land or property taxes for the period of ownership of the plot or property, it is necessary:
- take the initiative
- independently inform the tax authority about the availability of real estate: this is an obligation established by law (clause 2.1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
You can choose the tax authority at your discretion. The message is presented once. The filing deadline is December 31 of the year following the expired tax period (calendar year).
The message can be sent by Russian Post or transmitted in person to the tax office. It is convenient to get an appointment by making an online appointment using this service.
You can also send a message using online services:
- "Taxpayer's personal account"
- “Contact the Federal Tax Service of Russia”
If the tax authority did not have information about the site, the payment will be calculated for the year in which the message was submitted.
In the event that the owner has not received a notice of payment of land or property tax for other reasons:
- The taxpayer's address is incorrect
- notification was lost in the mail
tax will be charged for all 3 years.
For failure to provide a notice of failure to receive notice and information about the property within the prescribed period, the owner will be held accountable and fined.
The fine will be 20% of the unpaid tax amount for the item for which he did not submit a report (clause 3 of Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Deadline for payment of land tax
Tax payment is made no later than December 1 of the year following the expired tax period. The taxpayer pays tax for no more than 3 tax periods preceding the calendar year of sending the tax notice.
Taxpayers will receive their 2021 tax notices for 2021 between April and September.
For all regions of Russia, a single deadline has been established for the payment of property taxes for 2021 - no later than December 1, 2020.
Failure to comply with the deadlines for paying land tax will result in the accrual of penalties in the amount of arrears for each calendar day of delay. The amount of the penalty is 1/300 of the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
The tax office may also apply other measures:
- send the debtor's employer a notice of debt collection at the expense of wages
- impose on the debtor a restriction on leaving the Russian Federation
There is no fine imposed on individuals for non-payment of taxes.
Note
Local authorities retain the right to appoint advance payments in the region. The final date of payments for 2021 is shifted, but not earlier than February 1, 2021.
Useful online services
- Calculation of land tax and property tax for individuals - tax calculator
- Information about established benefits for land tax - this page of the tax service website
- Cadastral value of the land plot:
- official website of Rosreestr
- public cadastral map – PKK
- Making an appointment with the tax office through the online service
- Tax debt – State Services website
- Payment of land tax - Federal Tax Service service
- Information about debtors whose cases are in enforcement proceedings - website of the Federal Bailiff Service (FSSP of Russia)
Helpful information
- You can get acquainted with the characteristics of agricultural land, the concept of quality score, and the mode of use of such land here
- The provisions of the upcoming “garage amnesty” 2021 – 2026 can be found here
- Provision of public land plots from agricultural lands for farming and running private household plots - here
- Read about a new approach to the integrated development of settlement territories (SDT) and achieving housing comfort for citizens here
- “Dacha Amnesty” 2021 – 2026: new opportunities – read here
- How to get a plot from a municipality or state - read here
- What is a land encumbrance can be found here
- Risks from establishing red lines on a land plot – here
- What is a “development spot” on a land plot – read here
- Read about the procedure for including sites within the boundaries of settlements here