Art. 9 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation provides: “land and other natural resources may be in private, state, municipal and other forms of ownership.” The subjunctive mood used in the wording of the article, as well as the admissibility of other forms of ownership, seem to give Art. 9 of the Constitution has a broad meaning, allowing the issue of forms of ownership to be resolved without being bound by strict time, territorial and other criteria.
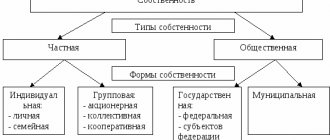
In practice, all three forms of land ownership listed in the Constitution of the Russian Federation are presented:
- state,
- municipal,
- private.
Kinds
During the existence of the USSR, the only acceptable option for owning plots was state ownership. For this reason, it was not appropriate to conduct a property analysis. Currently, the Constitution states that there are several types of ownership in relation to land.
It is indicated that lands can belong to private individuals, organizations or the state. There are also municipal and public forms of ownership, and mixed types are allowed. Persons in a marriage relationship, as well as members of partnerships and peasant farms, may have rights to own real estate.
The essence of ownership
The more common of the above are the rights of individuals and government bodies. Today, the principles of democracy apply, according to which almost every person can obtain land ownership. Considering what type of property is assigned to the plot, certain rules are established regarding its use.
For example, when the state owns land, it is endowed with different rights compared to the situation if the owner is a citizen.
Private property
Individual citizens, as well as a company carrying out a certain type of activity, can have rights to land plots. In addition to the land itself, the rights extend to buildings located on the site, vegetation, trees and other immovable objects.
Private ownership of land
The exception is the location of a monument of cultural significance on the territory, which cannot be demolished. The state body has the authority to do so. A private person may have closed reservoirs located on the site. They are small in size.
You can obtain the rights to the allotment in question using:
- passing the privatization procedure;
- inheritance legal relations;
- drawing up a deed of gift;
- concluding purchase and sale agreements;
- exchange for other property and other transactions.
It can also be said that the allotment may be part of the contribution that is invested in the capital of the newly created company. Land legislation has a separate provision regarding the ownership rights of private individuals. All powers are described in detail as follows. It is indicated that the owner has the opportunity to own and dispose of the property at his own discretion.
Entity
Civil and land legislation indicates the peculiarities inherent in the procedure for registering rights regarding an allotment for organizations.
It is indicated that such an owner is endowed not only with the powers of ownership, but is also allowed to carry out activities of an economic nature. The owner has the opportunity to own the plot and also carry out actions aimed at its alienation in the manner prescribed by law.
Types of property in settlements
A person can realize the allotment by selling it in full or some part. You can also register a mortgage on the property, draw up a deed of gift, and transfer it through inheritance legal relations. Structures located on the land plot can be alienated separately or together with the plot. This rule is established in land legislation.
To determine the size of the part of the plot that is subject to alienation, the provisions of the Land Code are used. When land is withdrawn from circulation, actions to alienate it cannot be carried out.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that the presence of rights regarding the site implies the presence of responsibilities on the part of the owner. An example is that the owner undertakes to monitor compliance with environmental standards on his site.
Responsibilities also include land surveying requirements, compliance with boundaries established with neighboring plots, and monitoring the environmental condition of the site as a whole. These provisions must be taken into account during the use of plots.
When a person commits actions that violate the boundaries of plots, or the environment is polluted, it is likely that the violator is threatened with visiting the judicial authority conducting proceedings on this issue. If the use does not violate any rights, it can be carried out by the owner in any convenient form.
Public and municipal property
Civil and land legislation contains the nuances of ownership of property owned by the municipality, which is of general importance. It also indicates how ownership of a land plot that was previously recognized as ownerless occurs.
Municipal property rights
Currently, you can find the option of owning plots under consideration:
- on farms engaged in farming and peasant activities;
- partnerships with a horticultural focus;
- collective farms;
- enterprises engaged in agricultural cooperative activities;
- cooperatives engaged in livestock farming activities with a housing and garage orientation.
There are two forms by which ownership of municipal property is carried out. In the first situation, a certain land plot is established for each owner, which becomes his possession (this form is called shared).
Common property right
The second situation is related to the fact that shares in real estate are not subject to determination, since all land is in common ownership. The purpose of creating such a form is to satisfy people's needs. The needs are communal and agricultural in nature.
When a person owns a certain share of land in a municipality, he has the opportunity to realize it through sale. It is worth keeping in mind that those who own the remaining shares of such land have priority rights to purchase.
State uniform
All plots that are not subject to private or municipal ownership are automatically considered Russian property. This rule is enshrined in civil law. There are two levels of state ownership:
- property belonging to the federation;
- property of the regions.
When it comes to ownership at the federal level, we can say that the country has rights to individual land plots. They mean:
- lands where parks and reserves are located;
- plots created for security purposes;
- occupied with space-oriented systems;
- necessary for the location of nuclear power facilities;
- other allotments specified in the Constitution.
The authorities can transfer these territories to municipal ownership on the basis of a lease agreement, as well as to private individuals for the purpose of erecting buildings or growing various crops. A land easement may be established.
The state has the authority to acquire plots of land from private individuals, provided that the lands have been put up for sale.
In territories located in the neighborhood there may be lands owned by the state, but belonging to different categories. Some sites imply that construction work and scientific research may be carried out on their territory. At the same time, it is not permissible to do this on other plots. An example is the territory where parks, nature reserves, etc. are located.
The history of the country as the history of property
For centuries, land ownership in Russia served as the economic basis of the power of feudal lords, the first serious shock for which was the land reform of 1861. An attempt to more actively introduce capitalist relations into agriculture - the Stolypin agrarian reform of 1906-1907. ─ it was not destined to prevent the fundamental changes that followed a decade later in the life of the state, one of the iconic symbols of which was the Decree on Land, which abolished private ownership of land. Seven decades of socialist construction ended with a renaissance of market relations.
The process of economic transformations in land use accelerated significantly after the law granted every citizen the right to acquire ownership of a plot of land.
Nuances
The peculiarities of the issue under consideration are related to what types of property rights exist regarding plots and how land is distributed. You should also know how to establish an existing type of property.
Distribution of land by type of ownership
The procedure for delimiting state ownership into plots is carried out in accordance with legal norms. Federal property includes plots in respect of which rights are recognized at the legislative level, or rights were formed during the delimitation of property. Also, the grounds may be prescribed in the Civil Code.
Federally owned storage facility
Regional property includes allotments that receive their status in accordance with accepted norms of law, if this happened in the process of delimitation of powers, or the grounds are specified in the provisions of the Constitution. Subject ownership includes:
- plots that are not allocated to citizens;
- where the real estate objects belonging to the subject are located;
- provided to regional authorities to conduct activities;
- classified as special protection zones;
- forest fund lands;
- areas where privatized property is located;
- if the plot is recognized as such in accordance with laws adopted at the federal level;
- if the acquisition occurred in accordance with the rules enshrined in civil law.
Municipal property
The municipality owns lands that are not owned by individuals. The grounds are presented in the law. This type of property may include lands transferred to the Ministry of Defense by the state, even if they are located outside the boundaries of the entities. Exceptions are cities of federal significance, since there is no transfer of plots to the ownership of the municipality.
Types of property rights to land
When it is necessary to evaluate a site, in all cases it initially evaluates the rights that apply to it. In theory, they indicate that property rights consist of a set of powers that can be divided. In Russia, land rights regarding plots are divided into groups:
- those that determine the ownership of land (ownership);
- use, which means the validity of a lease agreement, concession, etc.
Property rights can be transferred together with a plot of land, or as separate objects in the event of establishing a procedure for the assignment of debts or claims.
It should be said that only the rights of ownership imply the use of the allotment to the maximum extent possible. In this case, restrictions that are established by government bodies through the development of legislative acts must be taken into account.
Other types of rights to plots have some restrictions in their implementation. According to the current rules of law, there are types of rights to land:
- own;
- use established on a permanent basis;
- possession valid for life, transmitted by inheritance;
- use allocated for a certain period of time free of charge;
- rental legal relations;
- restricted use of someone else's property.
The category of other rights to plots is also considered, such as the right to conclude lease agreements, lease of land divided into parts, collateral relations, etc. Other powers related to the use of allotments are also established. ZU cannot be owned by the right of operational management or economic significance.
Land lease right
If we talk about the right of ownership to land plots, then it is expressed in the powers to use, dispose and own land. Ownership refers to the possession of real estate as one’s own, which means, for example, for organizations – reflection of property on the balance sheet, etc. You can get various benefits from using the plot, including using it yourself or selling the grown products.
A person who owns land has the right to use groundwater, minerals and other natural resources for his own purposes. When an order is considered, we need to talk about determining the fate of the allotment from a legal point of view. The owner can sell the allotment by selling, leasing, pledging or making a gift to any person.
Such persons can use the land for their own benefit in such a way that their actions do not cause harm to surrounding people and the environment. Otherwise, it will not be possible to avoid responsibility. This possibility is limited by what regime is established for the category of land to which the allotment belongs.
Purpose of land plots
In addition to the 7 categories of sites, the concept of intended purpose is used in the right field.
The purpose of a land plot is the form of land use agreed upon with the authorities within specific boundaries.
Forms of acceptable use:
- The main ones , which determine the main purpose of the land and are regulated in the Town Planning Regulations.
- Conditionally permitted . Legal activity requires approval from a special commission.
- Auxiliary . They are a clarifying addition for more optimal use of space.
The clarifying type of auxiliary VRI is relevant when placing a transformer booth, garage building, fence, etc. This will allow the developer to legally introduce the structure into the general purpose of the land plot.
State rights to land
Before you begin to deal with the subjects of public ownership of land, it is necessary to clarify what the state is. In the case of the Russian Federation, according to the law, the state is usually called the totality of federal government bodies.
Regional power structures are designated by the term municipalities.
This is very important, because public property includes both the property of federal bodies and the property of regional government structures. But meanwhile, the legal status of land under the control of federal authorities differs from the possessions of regional authorities.
Thus, the list of state-owned lands includes the following types:
- lands of nature reserves and other environmental zones;
- border lands;
- lands of federal tracks;
- locations of strategic minerals;
- hazardous waste disposal areas;
- territories of forests and water bodies.
All other lands are the property of municipalities and can only be disposed of by regional authorities.