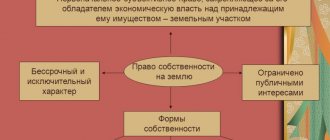
Privatization of a land plot is based on the registration of ownership rights of a once allocated object for farming and other grounds. At the moment, the legislative framework regulates the free privatization of land, carried out by future owners or employees of agencies providing such services.
As a rule, the services of companies are not always financially beneficial for the user of the land plot, so those who wish to do so carry out the registration procedure independently. How to privatize land under special conditions for the provision of use.
Privatization of a private house
Privatization is done for houses that were owned by the state or municipality and were allocated under certain conditions.
Law No. 1541-1 of July 4, 1991 establishes the basic provisions for the procedure:
- The need to obtain the consent of all residents. If one of the residents does not want to participate in the procedure, then a notarized refusal is written.
- After registration, the house is divided in equal shares between all participants in the procedure.
- An adult citizen can register ownership of state real estate only once. Repeated participation in privatization is allowed only if the first time the owner was under 18 years old.
- Residents must have no utility debts.
Reference! Minors registered in the house are automatically included in the list of owners and cannot be excluded from the procedure. But the interests of children are represented by parents or legal representatives if they are under 18 years of age.
Deadlines
The procedure for considering citizens' applications takes about 1-2 months. More often than not, less is more. It also takes about 1 month to register ownership. Each document will also have to wait, but for the most part the wait will not last more than 2 weeks; in some cases, a cadastral passport can take up to a month and a half. On average, privatization takes from 3 to 4 months if you actively address this issue. The time frame can be reduced if you use the services of experienced lawyers who know exactly when, how and where which document can be obtained as quickly as possible.
Is it necessary to privatize the land under a private house?
When registering ownership of a private or country house, citizens may wonder whether privatization of the site on which it is located is necessary.
Property owners can use the land based on a lease agreement. In this case, the owner remains the municipality. Land can be withdrawn at any time for government needs.
Registration of ownership of the plot will allow you to dispose of it at your own discretion. Citizens can sell, donate, and inherit land.
Such transactions are prohibited with a non-privatized plot, which may cause problems when concluding a purchase and sale agreement for a house.
Shares and common allotments
In some cases, applications for privatization of plots are carried out by co-owners who have shares in the land and are also owners of common plots.
In this case, the possibility of privatizing the plot remains, however, the emergence of ownership rights to it does not imply the division of the plot into several parts. Thus, the applicants automatically become co-owners of a common plot, which will be listed under one cadastral number and be a single whole.
Is it necessary to do this?
Registration of the site where the property is located is not a mandatory procedure.
Residents can only privatize the house, and the municipality or state will remain the owner of the land. Among the advantages of this solution is that you will not need to pay property taxes. The disadvantages include the fact that it will not be possible to make transactions with real estate that require registration steps.
The owner will not be able to erect outbuildings on the site, as they will be considered “self-construction”.
Free privatization according to a simplified scheme
Individuals who previously owned the land and have a building on it as personal property can privatize a plot of land free of charge according to a simplified scheme.
Perhaps the building was not properly registered even before the new law on dacha amnesty came into force, i.e. before 2008 and the documents are outdated. Previously, they were issued administratively and today have lost their legal force.
The land, as well as the house on it, must have title documents, i.e. The registration procedure in Rosreestr has been completed in accordance with all the rules, the plot has been registered in the cadastral register and entered into the register database.
Also, until 2021, certain categories of citizens can privatize a plot free of charge on preferential terms:
- large families;
- participants of military operations and veterans of the Great Patriotic War;
- children are orphans if left without parental care;
- other vulnerable population.
In addition, every citizen of the Russian Federation can once go through a paid procedure for purchasing any plot of their choice that is on the balance sheet of a municipality or state, thereby purchasing it for a fee.
Until when has the amnesty been extended?
Residents of country houses built on dacha plots are offered a simplified procedure for registering ownership of both the land and the building.
This opportunity is provided by the “dacha amnesty”, which has been in effect since 2006. Many owners of garden plots are interested in until what year they will be able to take advantage of the simplified registration of land and buildings. The law has been extended until 2021, but is considering making it in force until 2026.
Thanks to this, in 2021 you can register ownership of the building subject to the following conditions:
- the house or permanent structure is located on a gardening or vegetable plot;
- the building is not intended for commercial activities;
- There is no information about the construction in the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
A country house can be converted into a residential one, where registration is allowed. To do this, the building must meet established requirements.
In order to register property rights according to simplified rules, you will need to prepare the following documents:
- statement;
- technical plan;
- title documents for land.
The state duty for re-registration of ownership of a land plot or buildings on it is 350 rubles. (Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
Which areas cannot be privatized
According to paragraph 8 of Article 28 of Federal Law-178 “On Privatization...” the alienation of land plots is prohibited if the land:
- withdrawn from use (contaminated with dangerous chemicals or subjected to technogenic (biogenic) contamination;
- has strategic importance, belongs to nature reserves (parks);
- reserved for government needs;
- refers to forest or water resources;
- is a square, street, passage, highway, embankment, etc.
Download Federal Law No. 1541-1 On privatization (59.3 KiB, 427 hits)
However, refusal to use certain categories of land, the alienation of which is unacceptable by law, is not acceptable. Such a restriction on the use of land is only restrictive in nature (for example, it is prohibited to engage in some specific type of activity on such lands).
How to privatize a land plot? The procedure itself, in addition to collecting a large package, is not something impossible. It is enough just to follow a certain order of registration.
Where to start privatizing a land plot for a private house?
When registering ownership of municipal or state land that was leased, you will need:
- prepare documents giving the right to use the site;
- contact the housing department at the administration;
- wait for a decision from officials;
- register property rights.
An application for privatization of a land plot must be filled out at the administration or MFC. In some constituent entities of the Russian Federation, it can be submitted through the State Services Portal. But in the future, the applicant will have to visit the housing department to provide original documents and certification of copies.
Free transfer of land into ownership is possible on the following grounds:
- the plot is issued for individual housing construction or personal farming;
- the citizen has been using the house and land since 1991 or earlier;
- the property is located on the territory of a horticultural or vegetable farming enterprise;
- the owner belongs to the preferential category.
In other cases, the land is purchased from the municipality at cadastral value. A non-privatized plot can be sold if it is located on the territory of a non-profit association, but its value will be below market value.
Extension of the “dacha amnesty”
In February 2015, the president signed a decree extending the Dacha Amnesty until March 2021 .
Later, the program was extended again until the end of 2020 .
“Dacha amnesty” is the name of amendments to regulations that specify the procedure for registering rights with a minimum package of documents. This project has been operating since 2006.
The peculiarity of this procedure is as follows: at the stage of submitting documents for privatization of a land plot, it is not necessary to obtain permission to construct a building located on the territory. As a result, we save time on collecting additional documents.
It is expected that the extension of this provision will contribute to the development of the private sector.
Privatization procedure
The procedure for privatizing a house is as follows:
- Submitting an application to the housing department of the local authority.
- Obtaining a cadastral passport from the BTI or an extract from it (if available).
- Registration of a cadastral plan.
- Transfer of a package of documents to the housing department.
- Expect response within 30 days.
- Registration of the transaction in Rosreestr.
If all steps are completed correctly, the owners will receive an extract from the Unified State Register of Property Rights.
documentation
For the procedure you will need to prepare the following documents:
- identification of all residents;
- title documents for the use of the house and land;
- cadastral passport;
- technical documentation from BTI;
- an extract from the Unified State Register confirming the absence of an encumbrance;
- receipts for payment of state fees.
Everyone registered in the house writes a statement about participation in privatization. If someone renounces property, he must put it in writing and have it certified by a notary.
price
The cost of privatizing a private house consists of several factors:
- The state fee for registration of municipal real estate is 2000 rubles. (Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- fee for registering a transaction in Rosreestr is 350 rubles. (Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- fee for registration of cadastral plan and passport (depending on the region);
- Notary services from 1000 rub. (if it is necessary to formalize a refusal of privatization, a power of attorney).
Attention! The size of the state duty does not vary throughout Russia. Payment for the services of a notary or surveyor depends on the subject of the Russian Federation.
List of required documentation and algorithm for drawing up an application
The list of documents required for the procedure is determined by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development No. 475 of 2011. In particular, an individual or legal entity will need to provide the following:
- Copies of documentation that identifies the applicant for privatization. If the applicant is an individual, then it will be sufficient to provide a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation.
DocumentationIf an enterprise or organization applies for the procedure, it will need to provide a certificate of state registration, constituent documentation and charter. If the application is submitted by a proxy, then he must have a power of attorney to represent interests (notarized).
- If a plot with erected buildings or structures is being privatized, an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate is required, confirming the existence of rights to real estate. In some cases, such extracts are not issued - this may be due to the fact that the state registration mark itself is missing.
In such situations, the applicant is issued a certificate stating that there are no objects located on the territory of the privatized site.
It is worth noting that most applications for the privatization of a plot with buildings are carried out as a result of a donation or purchase and sale of an object located on land owned by the state or a separate municipality.
- If possible, the applicant also provides an extract from the unified state. register on the existence of registered rights to the site. For example, this option becomes possible when concluding an agreement for the right to perpetual use of a plot of land or signing a lease agreement that contains in its text a clause on the possibility of further acquiring the right of ownership through privatization.
- Cadastral passport (sometimes it will be enough to provide an extract for it). Such a document can be used directly when the plot is being re-registered and already during the period of receiving documents confirming ownership.
Sample cadastral passport of a land plotThe cadastral passport contains a list of information that gives an idea of the boundaries and size of the plot. If there is no such information about the site, then the applicant must initiate a land surveying procedure, during which its boundaries and dimensions are determined.
Before surveying, it will be necessary to agree on the location of the boundaries of the site with the owners of adjacent territories or plots, since their official consent will be required.
The survey procedure is paid for by the applicant independently and to carry it out, you can contact either the cadastral register or a third-party organization (which has the appropriate license). In addition, based on the cadastral value of the plot (as reflected in its passport), the amount of land tax that must be paid annually by the owners will be calculated in the future.
Land surveying procedure - Cadastral extracts for individual objects located on the privatized site (if they are available). Such a document will contain data on cadastral numbers assigned to buildings, location addresses assigned to them, etc.
- Application for privatization, drawn up in accordance with legal requirements.
It is worth noting that when submitting documents, depending on various factors, the list of documentation may be somewhat expanded.
When filling out an application, you must adhere to the general rules for its preparation and reflect mandatory information, which includes:
- name of the body to which the application for privatization of the site is submitted;
- Full name of the applicant, his address (in accordance with registration data), individual tax number, series and number of passport;
- purpose of application after privatization;
- the address of the site, which will allow you to determine its exact location;
- category of land to which the privatized plot belongs;
- information about whether there are restrictions and encumbrances imposed on the site;
- the basis (its type) for the emergence of the right to use the site;
- data regarding the real estate objects available on the site (their number and type);
- documents on ownership of constructed objects (if any);
- data contained in the act of alienation of a plot from state ownership;
- documents on the basis of which the right to privatization arose;
- list of documentation that is attached to the application.
Features of privatization of land under a private house with shares
It happens that a private house is decorated with shares.
Registration of a land plot as a property is permitted with the consent of all owners (Article 39.20 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, in order to privatize a plot, it is necessary that all property owners contact the registration authorities. If it is not possible to come to an agreement with one of the neighbors, then you can divide the house, even if it is in shared ownership. The allocation of shares is carried out by agreement between the co-owners on the basis of Art. 252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. If it is not possible to reach an agreement, you can go to court with a request to divide the property in kind.
After the share is allocated in court, the owner of the property can apply for documents to register ownership of the land on which his part of the house is built. The consent of the second owner is not required in this case.
What to do if there are no documents for the land
If there are no documents for the land, they need to be restored or drawn up from scratch. Usually it is this process that extends the entire privatization over time. It’s one thing to receive the same cadastral passport in 1-2 weeks, and quite another to wait several weeks for a specialist who will conduct a geodetic survey and only then begin to draw up the relevant documents. As practice proves, the remaining papers are usually much easier and cheaper to collect.
Privatization is a complex procedure due to the requirement of a large number of documents. It is not always obvious and clear where exactly you should go for them. Our experienced lawyers will be able to clarify the key points during a free consultation, but in order to resolve the issue as quickly as possible, you will need to use them as representatives.
FREE CONSULTATIONS are available for you! If you want to solve exactly your problem, then
:
- describe your situation to a lawyer in an online chat;
- write a question in the form below;
- call Moscow and Moscow region
- call St. Petersburg and region
Save or share the link on social networks
Author of the article
Natalya Fomicheva
Website expert lawyer. 10 years of experience. Inheritance matters. Family disputes. Housing and land law.
Ask a question Author's rating
Articles written
513
- FREE for a lawyer!
Write your question, our lawyer will prepare an answer for FREE and call you back in 5 minutes.
By submitting data you agree to the Consent to PD processing, PD Processing Policy and User Agreement
Useful information on the topic
2
Agreement for the sale and purchase of a share of land
When selling part of a plot of land that is in common shared ownership to both...
13
Shared ownership of house and land: rights and obligations of owners
Real estate objects can be divided between subjects of legal relations. Receiving in…
8
How to survey a land plot in shared ownership
In some cases, owners of a common plot of land are faced with the need...
9
How to sell a share in a house without land
Selling a house that is in shared ownership has its own characteristics. Owner…
3
Determining the procedure for using a land plot in shared ownership
By determining the procedure for using a land plot, you can avoid tensions between...
1
Privatization of land under an apartment building
You can privatize not only a separate residential building, apartment or land...
Arbitrage practice
The administration of the municipality does not always meet the needs of the residents of the house and allows them to register the property as their own.
The refusal may be justified if the potential owner has already participated in privatization, has not provided all the papers, or there are errors in the documents. Land will not be transferred to the ownership of a citizen if it is located on the territory of a water or environmental protection zone. When the residents of the house believe that the negative answer does not have valid reasons, they can go to court. Judicial practice shows that the law is often on the side of future owners when a good evidence base has been prepared that they have the right to own the property.
In 2009, citizen T. filed a claim with the Sestroretsky District Court of St. Petersburg to challenge the refusal to register real estate. She purchased the house in 2003, and in 2008 it was reconstructed. Then the citizen turned to the administration department with a request to register her right to the updated property. The employees refused, citing inconsistency with the reconstruction permit.
The plaintiff considered the refusal to be inconsistent with legislative norms on a simplified procedure for registering certain real estate objects. The court considered the case and made a decision in favor of the owner of the house.
Statement
To draw up an application, you must contact the district administration, write an application with documents attached and reflecting the request for privatization of the land, reflecting its size and intended purpose. . It takes up to 2 weeks to review your application. After a positive decision is made by the authorities, the applicant will be able to receive the plot free of charge for free use.
A sample application can be downloaded from this link.
Basic concepts and legislative framework
Today, the privatization procedure is regulated by Federal Law No. 178-FZ of December 21, 2001 “On the privatization of state and municipal property.”
What does privatization mean according to Law No. 178-FZ: it is a paid transfer of state and municipal property into the ownership of individuals and legal entities .
In practice, the following situation arises: a person owns and uses a plot of land owned by state or local authorities. Possession and use are carried out on the basis of some document - an order to allocate land in favor of a person, a contract of perpetual use, lifelong possession, etc.
But without ownership rights, the owner of the plot cannot dispose of it:
- pass on by inheritance;
- give;
- sell;
- exchange;
- pawn, etc.
To obtain all these rights, it is necessary to register the land as property, i.e., privatize it. Despite the presence of the word “paid” in the legislative definition, you can become the owner of land not only for a fee, but also for free.
The paid procedure mainly concerns commercial lands - intended for conducting economic activities. And non-commercial lands, as a rule, are transferred by municipalities free of charge, subject to all privatization rules.
Which lands does this apply to:
- Intended for individual housing construction.
- Gardening, gardening, for personal farming.
- Garage construction, etc.
Since 2006, the so-called “dacha amnesty” is a simplified procedure for free registration of land by individuals . This procedure is in effect in accordance with Federal Law No. 93-FZ of June 30, 2006.
Not all types of land that fall under privatization can then be used for the construction of a full-fledged residential building. On some it is allowed to build dachas, and on some only movable objects (garage, carriage, etc.).
It is impossible to privatize lands that are not intended for ownership, use and disposal by private individuals.
These territories are withdrawn from circulation or limited in circulation:
- forest and water resources, reserves;
- defense, strategic purposes;
- exclusion zones;
- used for communication needs, transport, etc.
For example, the municipality does not have the right to transfer to an individual a plot along the railway for vegetable gardening, gardening, and, especially, the construction of a residential building.
If such a situation occurs and even privatization is carried out, then the city planning authorities have the right to declare the action illegal and recognize all buildings and objects on the land plot as illegal with further unpleasant consequences.
Advantages and disadvantages of privatization
Despite the fact that privatization is a mandatory procedure for all owners of garden plots, it has its advantages.
These include:
- gaining the opportunity to dispose of property based on your needs, including selling it, donating it, exchanging it or breaking it into shares;
- the state does not have the authority to take away land from a subject that is being privatized, including to compensate for debts on membership fees;
- The land plot can be used for buildings of any purpose: residential, commercial, temporary.
There are disadvantages only when the site is not registered as a property:
- Fraudsters often falsify membership books and try to take possession of property, which they often succeed since there is no confirmation of the right to land;
- if the dacha plot is not used for 3 years, it is transferred to another tenant;
- non-privatized plots are prohibited from being used for construction; accordingly, all structures erected on them will be subject to demolition.
The benefits of amnesty overlap with the regular procedure, but it is worth mentioning as it is a more popular trend for 2021.
These include:
- the opportunity to register for permanent residence at the dacha;
- obtaining protection of property interests;
- There is no need to register to obtain a cadastral number.
Construction and disposal of the garden plot at the owner’s own discretion are also available.
There are not many disadvantages, but they are also worth mentioning:
- in the process, the boundaries of the site are of great importance and sometimes they are divided incorrectly, as a result of which it may be necessary to challenge this fact through the court;
- after the privatization process is completed, the owner will have to pay tax.
The so-called dacha amnesty is relevant for plots that are part of communities or partnerships, mainly with a security zone in the middle. People often live in such areas on a permanent basis.
In what cases is this not possible?
It is always better to check the cleanliness of the site and whether there are any prohibitions on privatization in advance. There have been cases when people began to build a house on land that was completely not subject to privatization, and the construction simply became illegal.
So, it will not be possible to privatize land if it:
- Belongs to the armed forces, the Federal Security Service.
- Has a strategic purpose.
- Belongs to a territory located nearby a national park or nature reserve.
- Occupied for military and civilian burials.
- It is a cultural heritage site.
If you purchase a plot of land without documents and build a house, you can count on the fact that privatization will certainly not be refused. But nuanced, controversial issues arise often.
Before building a house, you must first find out the ownership of a particular site. After all, it is simply impossible to privatize land near a coastal or protected zone, forest area and defense sites, and the court is unlikely to rule in your favor.
Before embarking on the privatization procedure, you need to weigh the pros and cons so as not to encounter obstacles and end up with nothing. There is a lot of empty land in Russia, however, not all of it is subject to free privatization.
Design nuances
- If the plot was inherited after 2001 and the house is owned, then privatization is carried out free of charge. If the inheritance was accepted before 1991, then it is no longer possible to do without purchasing the plot, taking into account its cadastral value.
- If the plot of land has 2 owners at once, then privatization is possible only in the case where there is an owner or 2 owners of the building at once, but there is a certificate of ownership in hand, and privatization of the plot is impossible without the written consent or refusal of the second owner of the property.
Free procedure: for whom and why?
Free alienation by the state and municipalities of land to the private sector is carried out in relation to plots acquired by citizens under Federal Law No. 137-FZ of October 25, 2001, according to which the Land Code of Russia came into force.
Owners of land plots received before 2001 for:
- individual housing construction;
- personal subsidiary plot.
Any areas for:
- dacha farming;
- gardening;
- gardening.
Also involved in the process are plots owned by citizens on the basis of the right of lifelong ownership or permanent use, and the plot contains residential real estate with registered ownership;
The terms of free privatization were extended several times, and in the latest version of Law No. 178-FZ, the gratuitous transfer of lands of municipalities and government agencies into the hands of individuals became indefinite.
At the same time, the simplified procedure for processing documents (“dacha amnesty”) for plots is valid until March 1, 2021.
Where to contact?
In order to privatize a plot of land for a private house, you must contact the local authorities at your place of residence, the district administration or the territorial district attached to this plot of land. Next, write and submit an application, a complete package of documents.
If you wish, you can hire a lawyer for a fee and entrust him with the full completion of the privatization procedure, having issued a notarized power of attorney to represent the interests of the owner in all instances.