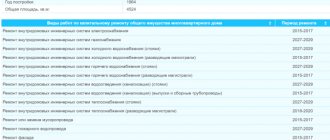
What is a major renovation?
A major overhaul of common property in apartment buildings is an event prepared in advance in accordance with the work plan, aimed at qualitatively updating all communications, carrying out other work and taking measures aimed at qualitatively improving the living conditions of the owners of premises in a particular building.
Clause 14.2 of Article 1 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation means major repairs of buildings and structures as a list of works aimed at replacing or restoring building structures of capital construction projects.
The only exceptions will be load-bearing structures.
Major repairs also mean the replacement of existing utilities that ensure the full functioning of the building.
Compared to current repairs, capital repairs have several differences that can be identified by analyzing the housing legislation currently in force.
These differences include:
- timing of repair work;
- frequency of their implementation;
- a list of necessary activities included in the mandatory estimate;
- formation of a payment fund for work performed.
Major repairs, compared to current ones in this form, are a more complexly organized event that must be carefully agreed upon by all parties.
In the next section, we will present you with a list of major repairs in a multi-storey building and talk in more detail about what work is included in the major repairs of apartment buildings.
Major repairs according to 44-FZ
13.09.2019
At the request of one of the participants in a closed WhatsApp group, we decided to share our experience in supporting purchases that involve major repairs.
This topic continues to be relevant for our clients, even in light of recent changes to Law No. 44-FZ in terms of simplifying the participant’s application to just consent. What caused this interest? As they say, “the devil is in the details” (“the devil is in the details”).
List of works for major repairs of apartment buildings
The major repair work is clearly of a different nature from similar ones, but is being carried out as part of the ongoing renovation of common property.
Their list is given in Part 1 of Art. 166 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
The following list of works on major repairs of buildings and structures can be considered among the activities classified as capital::
- restoration of the waterproofing layer on the roof, and in places where the current condition requires it, complete replacement of the roofing;
- replacement of all necessary communications belonging to common building services (read about what is included in the capital repair program and whether major repairs are included in utilities);
- reconstruction of the building facade or its replacement (if necessary);
- the same actions, but performed in relation to the foundation;
- repair of elevator mechanisms (in cases where these measures are justified from the point of view of the safety of citizens using these mechanisms);
- replacement of window structures and door blocks;
- plastering, whitewashing and painting the walls and ceilings of entrances, as well as all common areas classified as common property and included in the estimate for the work.
The same work is given in Appendix No. 8 to the Rules and Standards for the Technical Operation of the Housing Stock dated September 27, 2009 No. 170.
This list of works is not exhaustive and can be supplemented if additional items have been agreed upon with the organization performing the work.
Now that you know what types of work are included in the overhaul of an apartment building, let’s talk about the list of services and work for the overhaul of common property in an apartment building and what it may have in common with the current one.
Construction and installation work: accounting features and differences during major repairs and modernization
If it is necessary to carry out construction work for the overhaul of buildings and structures, specialists and accountants have many questions: what types of work can be carried out as part of the overhaul and which ones relate to modernization, what is the necessary algorithm of actions in both cases and how to correctly reflect the costs of these works in accounting. This material will help you understand these issues and more.
1. How to determine what type of work construction work is classified as
During the operation of fixed assets, including buildings and structures, they wear out and lose their original properties to varying degrees. This requires restoration and repair work, as a result of which their characteristics may change. General features of work and criteria for changing the characteristics of objects as a result of their implementation are given in Appendix 5 to Instruction No. 37/18/6.
As for construction activities, it is necessary to determine what type of work to be carried out (current or major repairs, reconstruction or modernization) at the planning stage. The correct definition of the construction project and the composition of the necessary documentation (if necessary, permitting, pre-project and design documentation) depend on this.
At the initial stage, a budgetary organization must proceed from the reason for the need to carry out construction work, its types and the changes that should occur upon completion of its implementation. In cases where buildings and structures require significant repairs, most often budgetary organizations resort to such types of construction work as major repairs or modernization.
Law N 300-Z defines capital repairs as a set of works to restore the technical, operational and consumer qualities of a construction project lost during operation (paragraph 17, part 1, article 1 of Law N 300-Z).
However, the definition of modernization as an independent term is not provided in the law. Modernization in construction activities is considered as an element of reconstruction carried out within existing dimensions - a set of works and activities related to improving the consumer qualities of buildings, structures, communications, their parts and (or) elements, bringing operational indicators to the level of modern requirements (clause 3.3 .5 TKP 45-1.01-4-2005, approved by order of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture dated July 18, 2005 N 172).
During modernization, the layout can be changed without changing the purpose of individual premises, the installation of built-in rooms for staircases, elevators, garbage chutes, the construction of balconies, loggias, the replacement of certain types of load-bearing structures (walls, stairs, ceilings, coverings), improvement of the architectural expressiveness of the building, reconstruction of roofs , insulation and noise insulation of buildings, equipping with missing types of engineering equipment or increasing its level, reconstruction of external networks (except the main ones) (note to clause 3.3.5 of TCP 45-1.01-4-2005).
According to the clarifications of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture, types of work and services related to construction activities are determined on the basis of:
— design documentation developed for construction, reconstruction, restoration, major repairs, improvement of the facility, demolition;
— TKP 45-1.04-206-2010 “Repair, reconstruction and restoration of residential and public buildings and structures. Basic design requirements", approved. order dated July 15, 2010 N 267 (according to appendices A - D).
For reference, Decree No. 7 introduced the term “technical modernization”. According to the letter of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture dated December 24, 2019 N 02-3-05/17228, it was introduced to expand the term “technical re-equipment” by expanding the list of works that are carried out when replacing (installing new) technological equipment only at production facilities.
For reference, administrative liability for violations in the field of architectural, urban planning and construction activities is provided for in Chapter. 22 Code of Administrative Offences.
2. Classification of costs for construction and installation works for major repairs and modernization
Expenses for major repairs of all types of buildings, premises, structures (with the exception of major repairs and modernization of the housing stock of organizations that are not budgetary organizations), engineering infrastructure facilities, expenses for payment for work on the modernization of facilities, work performed during the restoration of historical and cultural values, as well as work on the reconstruction of individual structural elements included in the summary of costs for major repairs of the facility, are reflected under subarticle 2 40 03 00 “Major repairs” of the economic classification of budget expenditures. This subarticle also includes the costs of developing design estimates for major repairs and modernization of facilities (subclause 48.3, clause 48 of the Instruction on the economic classification of budget expenditures No. 208).
Thus, financing and payment for all types of construction work related to both major repairs and modernization of buildings and structures is carried out under the specified subsection.
3. Procurement procedure in construction: changes from July 1, 2021
From July 1, 2021:
1) Decree No. 223 has expired (part 3, paragraph 6 of Decree No. 223);
2) Resolution of the Council of Ministers dated January 31, 2014 N 88 cannot be applied when carrying out public procurement for construction (paragraph 1 of resolution dated January 31, 2014 N 88);
3) carrying out procedures for the procurement of goods (works, services) for construction at the expense of budgetary funds and (or) funds from state extra-budgetary funds must be carried out in accordance with Law No. 419-Z.
According to MART’s explanations, if procurement procedures have been started or contracts for the supply of goods (work, services) during construction are concluded before July 1, 2021, then such procurements are not subject to the law on public procurement. They are carried out in accordance with the legislation in force before July 1, 2021, i.e. in accordance with Decree No. 223 and Resolution of the Council of Ministers dated January 31, 2014 No. 88 (part 4 of section 2 of letter MARCH N 14-01-10/1598 K).
In accordance with Law No. 419-Z, public procurement is carried out by recipients of budget funds and (or) funds from state extra-budgetary funds (paragraph 2, part 1, article 1 of Law No. 419-Z).
Thus, the budget organization, as the recipient of budget funds, is the customer in government procurement in construction. According to MART’s position, it is the customer who must purchase goods (works, services) using such funds. The general contractor who received funds as part of the execution of a public procurement contract concluded as a result of the public procurement procedure does not need to be guided by the norms of the legislation on public procurement (parts 10 - 12 of section 2 of letter MARCH N 14-01-10/1598 K).
4. Algorithm of actions and reflection of the cost of construction and installation work in accounting
For a comparison of action algorithms and reflection of the cost of construction and installation work in accounting for major repairs and modernization, read ilex.
What work can be performed in both major and current repairs?
If you refer to the above articles and analyze the list of works that is presented in the overhaul, comparing it with a similar list from the current one, you can see that there are still similarities in the work performed.
What kind of work relates to major repairs of an apartment building and to current ones?
So, during both current and major repairs, the following activities can be carried out::
- Restoration of roofing waterproofing if necessary.
- Insulation of buildings by working on facades (their insulation and painting can be carried out both during current repairs and during major repairs, if required by the operating conditions of the building).
- Partial or complete replacement of door blocks and window frames, as well as restoration of lost glazing.
- Cosmetic repairs of entrances with the elimination of violations of paint and varnish coatings and plaster.
In general, the scope of work for major repairs of apartment buildings, and for the current one, is formed individually in relation to each specific apartment building by making a joint decision between the homeowners and the organization hired to carry them out.
By the way, in the regions there are special capital repair programs, within the framework of which repairs of buildings and structures in cities and towns are carried out. The order of work is determined by the list of the regional capital repair program, which can be found in local governments.
What does the legislation say?
According to the current legislation, the burden of maintaining the common property of apartment buildings lies with the owners of apartment buildings; this requirement is established by Part 1 of Art. 39 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. And in accordance with clause 16, part II of the “Rules for the maintenance of common property in an apartment building”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 13, 2006 N 491, the proper condition of the common property, depending on the method of management of the apartment building, is ensured, including:
- owners of premises;
- management organization (in most cases in Moscow, the management of apartment buildings is carried out by Management Companies and regional state budgetary institutions Zhilishchnik);
- a homeowners' association, housing, housing-construction cooperative or other specialized consumer cooperative;
- the developer (if the premises have not been transferred from the moment the house is put into operation);
- and other variations.
At the same time, in accordance with clause 8, article 55.24 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, proper condition is understood as: “...maintaining the parameters of stability, reliability of buildings, structures, as well as the serviceability of building structures, engineering support systems, engineering support networks, their elements in accordance with the requirements of technical regulations and design documentation.” At the same time, maintenance and repairs must be carried out to maintain proper condition.
In accordance with Article 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the common property of apartment buildings includes:
- roofs (roofing, covering, drainage system, etc.);
- load-bearing structures (foundation, floors, columns, walls, pylons, etc.);
- enclosing structures (external walls, covering, facade structures, etc.);
- engineering communications and technical equipment (elevator, sanitary, ventilation equipment, etc.) serving more than one room in a given house;
- premises that are not parts of apartments and do not belong to individual owners in the building (staircases, corridors, elevator halls, etc.), as well as premises intended to meet the social and living needs of the owners of premises in a given building.
Summarizing the above, we can conclude that, depending on the method of managing the apartment building, the operating organization is entrusted with the responsibility to maintain the common property in proper condition, for this purpose maintenance and routine repair work is carried out.
Now it is necessary to decide in which cases repair work will be classified as routine repairs, and in which cases as major repairs. To do this, it is necessary to understand the essence of these terms, and also to establish what scope of work is provided for each of the repairs.
Differences in timing
The timing of major repairs is established by VSN 58-88 (r), approved by the State Committee for Architecture in 1990. According to this document, the minimum service life before inclusion in the overhaul program, years:
- panel houses - 15-20;
- brick - 10-15;
- foundations - 40-60;
- building walls - 30-50;
- wall joints - 8-15;
- rafters - 50-80;
- roofing (depending on materials) - 10-60;
- drains - 6-10;
- wooden doors and windows - 30;
- water pipes - 25;
- gas pipes - 12;
- garbage chutes - 25;
- sidewalks, transport entrances, blind areas - 7;
- children's playgrounds - 4.
Current repairs are carried out on the basis of regular inspections of the building structures, engineering structures and local area. The decision to include certain works in the routine repair plan is made by the management company, homeowners association or housing cooperative.