Perhaps the topic of taxes for bathhouses and sheds, and now also for greenhouses, will not lose its relevance. Summer residents still don’t understand what they will have to pay for and what they won’t. At the same time, the tax office has already given explanations more than once, and in 2021 the Federal Law on gardening and gardening by citizens came into force... and everything became even more confused.
The media is full of reports that greenhouses are now subject to taxation, that they urgently need to be registered, and if this is not done, a Federal Tax Service quadcopter will fly in, take a photo of the building, and later a fine will be sent to your address.
There were so many rumors and questions that Deputy Chairman of the State Duma Irina Yarovaya asked the head of the Federal Tax Service Mikhail Mishustin to check the information and once again clarify “to pay or not to pay.” And now we have prepared explanations. Let's capture the main thing!
Principles of the building tax system
Buildings with a foundation, interconnected with the ground without the possibility of their movement, are real estate (Article 130 of the Civil Code of Russia). Each owner of a plot with real estate and capital adjacent buildings is required to pay tax. The fee amounts are not the same; its exact amount will be notified after registration of the object.
Buildings without a foundation are considered temporary – they are movable property. The fee is not charged due to the lack of a strong connection between the buildings and the land. To confirm this fact, a certificate from the cadastral authority or BTI is required.
The fee is calculated for the previous calendar year. Payment is made before December 1st of the next tax period.
The tax on lands for horticultural and agricultural purposes is calculated at the cadastral price with a rate approved by the municipality. In 2021, the draft changes to this tax are being tested.
Which outbuildings can be taxed and in what case?
Tax is imposed only on those capital outbuildings, information about which was submitted to the tax authorities by the Rosreestr authorities from the Unified State Register of Real Estate or was submitted to the tax authorities from the BTI.
The object of taxation can be: economic, household, auxiliary capital buildings, auxiliary structures, including summer kitchens, bathhouses and similar capital real estate objects.
Criteria determining the amount of property tax
The correct calculation of the tax on a plot with a house and adjacent buildings is carried out taking into account the following parameters:
- Choice of cadastral or inventory tax base. Information about the region’s transition to calculations based on cadastral prices is contained in the Federal Tax Service.
Information can be found in the Federal Tax Service
- The percentage rate of levy imposed by the municipality. In the absence of data, federal standards are used (Article 406 of the Tax Code). The rate depends on the square footage of the building and ranges from 0.1–0.5% of the cadastral price. For a residential building, dacha - 0.1%, regardless of the area.
- Reducing factor for the three-year transition period. It increases annually. In the 1st year its value is 0.2, in the 2nd – 0.4, in the 3rd – 0.6. Then there is no coefficient, the individual pays the entire amount of the fee.
The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate calculates the amount of the fee and notifies the taxpayer of the payment amount.
Tax benefits
Citizens with the title of Hero, pensioners, disabled people, and family members of fallen soldiers are exempt from real estate taxes. The list of persons is given in Art. 407 NK. Regional self-government bodies have the right to supplement the list of beneficiaries. Owners of the following structures do not pay tax on buildings on a land plot:
- Outbuildings, blocks built on the territories specified in the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia; the area of buildings should not exceed 50 m².
- Buildings for creative activities and the creation of cultural values.
- Non-residential portable buildings of a temporary nature of any size.
If you are an artist or sculptor, you will definitely be exempt from taxes on the building in which the creative process takes place
. See also: Catalog of the most popular plots for the construction of suburban real estate in the Moscow region.
The benefit is provided only for one commercial building. Municipal authorities may change preferential conditions. Constructions that contradict established standards are subject to a fee on a general basis.
The benefit application template can be downloaded from the Federal Tax Service website. Options for serving it:
- personally visit the local branch of the Federal Tax Service;
- through a notarized intermediary;
- by post;
- from the “Personal Account” of the Federal Tax Service portal.
It is allowed to request benefits for several buildings in one application if the rights are documented.
Taxation of specific types of buildings
Let's look at what buildings on a summer cottage you have to pay tax for. The fee is paid for large extensions with a foundation - veranda, barn, cellar, gazebo, summer kitchen. Unregistered ownership of the house and buildings in time creates problems. The Fiscal Inspectorate regularly receives data on registered real estate properties from the registration service and notaries. Detection of late registration threatens the property owner with a notice of 3 years of arrears in fees, fines and penalties.
Portable awnings, greenhouses without foundations, light temporary structures, and toilets are not subject to tax.
You don’t have to pay tax for a small collapsible greenhouse
Residential building
Houses, dachas, cottages, shares in them, located in areas included in the cadastre, are subject to payment of tax. The homeowner has the right to receive a deduction in the amount of the standard area (Article 403 of the Tax Code). A fixed deduction is the value of the cadastral value of 50 m², by which the amount of tax is reduced.
If there are several buildings of the same type, the owner chooses which one to apply the deduction to. No deduction is provided when taking inventory of a home. The interest rate is determined by the price of the building:
- If the price is less than 300 thousand rubles, the rate is minimal - 0.1%.
- At a price of 300–500 thousand rubles, the rate limit increases to 0.3%.
- Above 500 thousand rubles - from 0.3 to 2%.
Are there any benefits?
Yes, a benefit is provided for one outbuilding registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate: if its area does not exceed 50 square meters.
m, then no tax is charged. The benefit applies provided that the outbuilding is not used for business purposes. Information from the Federal Tax Service website.
VAT – 2022
The best speaker on tax topics, , will prepare you for filing your return on January 14 . There are 10 out of 40 places left for the online workshop . The flow is limited, as there will be live communication with the teacher live. Hurry up to get into the group. Sign up>>>
Home taxation
The existing procedure obliges the owner of capital buildings to pay real estate tax. For a country house, a fee is charged at the residential premises tariff.
Pensioners and owners of holiday homes receive a tax notice if they are not included in preferential categories. In some areas, taxation standards for pensioners are introduced by local governments. Preferential categories are formed depending on the period of ownership of the plot or building. This is a decisive factor when providing financial relief.
In the legislation of 2021, there were changes regarding the dacha amnesty. The simplified procedure for free registration of property and its incorrect inclusion in the cadastre ceased to operate ahead of schedule. New rules have been established; now the tax on buildings on a summer cottage is calculated according to the usual scheme. The changes affected beneficiaries, the period of ownership of the dacha, and rates.
There have been reports that the government is coordinating with the Duma the possibility of returning to the original version, extending the amnesty until March 1, 2020.
When selling a dacha, a citizen of the Russian Federation is obliged to pay 13% of the cost to the budget. The period of ownership of a residential building, after which no tax is charged, is 5 years. In some cases, the seller of a dacha has the right to receive a deduction.
There is no need to pay tax if you have been the owner of the dacha for more than 5 years
Categories of persons exempt from paying personal income tax when selling a dacha:
- Citizens who received a dacha property as a gift from a spouse or relative.
- Persons who became the owner of the building as a result of privatization.
- A person using a dacha under a lifelong maintenance agreement.
The tax amnesty has not ceased for owners of land plots and houses. Debts incurred before the beginning of 2015 are forgiven automatically. Since the Federal Tax Service hopes to collect arrears, the issue of write-off is difficult to resolve.
Percentage tax rate for baths, greenhouses, sheds.
Since the tax on bathhouses, greenhouses, sheds is a property tax, the interest rates on it are similar.
Thus, in accordance with the norms of tax legislation, rates for dacha buildings range from 0.1% to 0.5%. However, personal property tax is a local tax. Therefore, in each specific municipality, local authorities have the right to determine their own tax amount, but not exceeding the federal rate.
In most regions of Russia there is a tax rate of 0.3%.
The tax service should be notified of the presence of outbuildings and their area. This will eliminate the emergence of controversial issues and erroneous assessment of taxes.
Property tax is mandatory for all individuals. As a result, every citizen must notify the Federal Tax Service about the objects they own by the end of the year. Failure to comply with these requirements may be interpreted as tax evasion and is subject to penalties in the form of a fine, as well as tax accrual at a higher interest rate.
Country house
Payments are calculated according to the generally accepted scheme. Owners of rural houses often do not register their homes. It is impossible for the owners of newly erected buildings and those who have started construction to evade registration of real estate. The authorities strictly control new buildings.
Pensioners are exempt from payments for the house in which they live, and additionally for one building with an area not exceeding 50 m². Rural houses are valued relatively inexpensively by the cadastral authority due to their distance from social institutions.
Tax benefits for baths, greenhouses, sheds.
So, capital structures with an area of less than 50 square meters are exempt from tax contributions. As well as outbuildings not included in the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
It is worth noting that this benefit applies to buildings for personal use. If they are used in the course of business activities, they are not exempt from paying annual contributions.
At the same time, the regulations of the Russian Federation define groups of persons who are granted tax benefits. These include:
- Heroes of Russia or the Soviet Union;
- Disabled people;
- Participants in hostilities
- Veterans of the Civil, Great Patriotic and Afghan Wars;
- Pensioners;
- Victims of the Chernobyl disaster, as well as victims of nuclear tests and other nuclear accidents.
- Retired military personnel;
- Family members of military personnel killed while performing military service duties;
- And other groups of citizens.
A more detailed list of preferential categories of taxpayers is contained in Article 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Signs of a taxable object
Typically, the need to apply to the Unified State Register and register a kitchen, bathhouse or shed, and pay taxes on them, is determined by the owner himself. It turns out that if you don’t want it, don’t apply and don’t pay, and this is quite possible if the buildings do not have signs of real estate. These include:
- strong connection with the ground - a capital foundation;
- stationarity – the inability to move an object to another location without damage resulting in loss of functionality.
That is, in order not to pay taxes on any structures other than a house and garage, there is no need to build capital objects on concrete foundations. Fortunately, current technologies make it possible to build “temporary buildings” that will last for many years. On the other hand, it is unlikely that the presence of a bathhouse or summer kitchen will increase the tax burden too much. As usual, everyone chooses for themselves.
You can verify the accuracy of the information on the Federal Tax Service website, and how to easily sell surplus products from your garden or vegetable garden - see details in one of the previous articles.
Subscribe to our Telegram channelExclusive posts every week
Nuances of tax payment
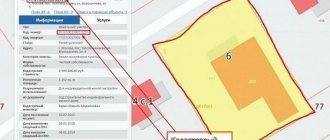
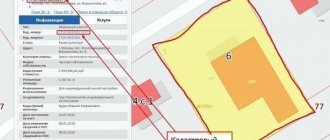
If the bathhouse is a detached and permanent building, then a fee will have to be paid for it. Property tax depends on the cadastral value of the property. This indicator is determined by engineers working in Rosreestr. In your personal account on the website of this institution you can find out what the cadastral value of any object is.
If a citizen believes that this indicator is too high, he can challenge it in court. If the bathhouse has not been registered in the cadastral register, then you will not have to pay a fee for it.
The Ministry of Finance, by letter No. 03-05-04-01/29325 dated May 16, 2021, provided clarification regarding the tax on commercial buildings:
You can find out about the possibility of registering an object directly at the Rosreestr branch when transferring documents for a bathhouse to the employees of this institution.