Construction of a residential building is not only an expensive undertaking, but also a responsible one, since it must meet safety requirements, both during construction and during operation.
Gross violations of urban planning standards, as a rule, lead to the creation of dangerous situations in human life, therefore, such objects that violate them must be demolished according to the law.
Safe and sanitary living conditions should be provided not only for home owners, but also for their neighbors. To do this, the developer must strictly observe the permitted gaps between residential and auxiliary buildings on the site up to the boundaries with neighbors.
Why are standards needed?
Construction Norms and Rules (SNiP) is a basic state document in the field of urban planning, which outlines the rules that a developer must follow during the construction of any residential and non-residential facility.
It specifies standards for site allocation, design, selection of acceptable materials, construction, and acceptance of the facility into operation. A separate section of SNiP is devoted to the rules for the location of buildings, fences and green spaces on the site area.
It is important to take into account the following documents:
- SNiP 30-02-97;
- SNiP 2.07.01-89;
- SNiP 2.04.01-85;
- TSN-40-301-97.
Compliance with the requirements of SNiP is a guarantee that the house will last the entire required period, all the necessary sanitary and safe conditions will be created in it in terms of fire, energy efficiency and environmental standards, and the functioning of all house structures and utility networks will be trouble-free.
If the developer fulfills all the requirements of SNiP from allotment of the site to putting the house into operation, he will not be afraid of any disputes, including in court with neighbors and regulatory government bodies regarding the boundaries of the land plot and the location of objects on it.
List of documents
Since the area covered by the regulations is huge, from the start of construction to commissioning, it is regulated by several dozen regulations.
In order for the developer to easily navigate this package of regulations, specialists have prepared a Code of Rules (SP) for certain objects. In 2021, SP No. 55.13330 was issued for residential households, and similar sets of rules have been prepared for other construction projects.
It is important to consider the following standards :
GOST 27751-2014;- GOST 30494-2011;
- GOST R 53780-2010;
- SP 1.13130.2012;
- SP 4.13130.2013;
- SP 7.13130.2013;
- SP 30.13330.2016;
- SP 32.13330.2012;
- SP 256.1325800.2016;
- SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10;
- SP 11-106-97;
- VSN 59-88;
- RDS 30-201-98;
- SanPiN 2.1.4.027-95.
Such standards have been updated with recent changes in legislation to increase the safety of people in buildings and protect property in accordance with the requirements :
- according to technical safety regulations;
- sanitary and epidemiological standards;
- fire safety and energy efficiency.
This Code of Rules must be applied when performing design, research, and construction work for houses with no more than three storeys.
They separately highlight sections on obtaining technical specifications for connecting engineering and transport infrastructure, rules for the location of sites and the placement of objects within the boundaries of the land plot, taking into account the requirements of fire and sanitary and epidemiological safety for living conditions.
There is also a separate section in connection with which the developer, during the construction process, must carry out the necessary set of measures to protect the environment from threats that may arise during the construction process or during the operation of the facility, for example, when installing utility networks or placing cesspools.
SNiP for the construction of private houses
A number of requirements are imposed on a residential building, in particular:
- fire safety requirements;
- norms of soil hydrological characteristics;
- rules for the construction of load-bearing walls;
- material consumption standards;
- requirements for location relative to roads and neighboring areas and other structures;
- standards for planning the interior of a residential building.
SNiP of an individual residential building with a complete list of requirements for the construction of a residential building can be found here SNiP SP 30-102-99.
The main requirement is for the layout of interior spaces.
So, for a building to be considered suitable for habitation, it is necessary:
- there should be no industrial premises in the building itself;
- the building must have facilities for housing, food and hygiene procedures;
- there must be a central heating system, and in its absence, heat generators;
- bathroom and storage room.
Moreover, the presence of a bathroom and storage room inside the building is not necessary if there are external buildings on the site that can be used for these purposes.
The procedure for constructing a private cottage
Minimum distances between objects are established by three departments:
- construction;
- firefighters;
- sanitary.
Many building rules and regulations were developed back in the Soviet period, some of them are still in effect without changes, and some have been updated to meet modern requirements.
Development in the individual sector is regulated by the requirements of SP 30-102, 1999 edition, and the location of the construction site on the site in relation to its boundaries and the red line of urban facilities is regulated.
SP 30-102 also specifies fire and sanitary standards for private housing construction, which are reflected in the development plan and other design documentation when exposing buildings on a land plot.
Fire regulations
Such distances are established by the Law of the Russian Federation No. 123, issued on June 22, 2008, and Fire Safety Standards No. 106, issued in 1995.
They are aimed at ensuring that fire safety gaps between houses are maintained, so that in the event of a fire at one facility, the fire does not damage nearby buildings, and special equipment can also pass through to extinguish fires and there is the possibility of installing hoses and access to extinguishing fires.
Minimum fire distances between objects in the storage area:
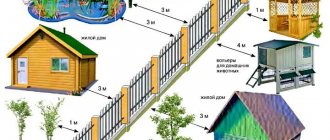
- From auxiliary premises to the fence: utility block, gazebo, garage and bathhouse, 1 m, barn for animals and poultry, 4 m.
- From the toilet in the individual housing construction zone, 1 m.
- From the toilet in the SNT zone, 2 m.
- House of DNP, individual housing construction and SNT, 3 m.
- Shrub, 1 m.
- Medium tree, 2 m.
- Tall tree, 4 m.
- Between two neighboring households:
- wooden - 15 m;
- wooden and stone - 10 m;
- both stone - 6 m;
- with wooden floors - 8 m.
- From a stationary barbecue to any object - 5 m.
- From a warehouse with a flammable substance: liquefied gas, diesel fuel to any object - 10 m, from an adjacent 3-meter zone without grass and trees.
- From the road to the house and the bathhouse - 5 m.
- From the forest area to the house - 15 m.
Homeowners should not use fire clearances for any business purposes, such as storing equipment, building materials and parking. They must keep this area clean and remove grass and weeds in a timely manner. It is also prohibited to light fires or burn waste in these areas.
Sanitary requirements
Sanitary restrictions are aimed at ensuring sanitary and hygienic living standards for protection from harmful emissions, for example, from a chimney or sewer, and ensuring a sufficient level of illumination of the territory and its noise protection.
Minimum sanitary gaps between objects from the boundaries of the landfill:
- Residential property, 3 m.
- Barn for livestock and poultry, 4 m.
- From the house to the bathhouse: wooden - 12 m, stone - 8 m.
- From a residential building to an animal barn, 15 m.
- From a residential building to a well or toilet - 8 m.
- From the toilet to the well, 8 m.
- From the toilet and cellar, 12 m.
- From the fence to the treatment plant, 1 m.
- From the compost pit and well, 8m.
- From any building to the gazebo, 4m.
The procedure for setting the distance: in the case when the roof of the house extends beyond the cut of the load-bearing wall by less than 0.5 m, the distance is measured along the foundation, otherwise it is measured according to its projection onto the ground. This is due to the fact that precipitation from the roof cannot enter the neighboring territory.
Summing up communications
Construction of utilities begins with obtaining specifications for laying networks from service providers :
- water;
- sewerage;
- gas;
- heating and electricity.
In the technical specifications, the supplier must indicate the insertion point and parameters of utility networks.
Based on the specifications, a house design is carried out with a section on engineering networks, which contains graphic materials in the form of drawings and laying diagrams with clarification of the maximum distance for each type of network.
Electricity supply
The distance of electrical networks is determined by the Electrical Installation Rules (PUE):
- Electrical wires from the street pole to the subscriber input of a residential building must be installed at a height of at least 2.75 m from the ground level.
- For a branch that is powered from another street and crosses the road, a minimum height of 6 m is established; in this case, an auxiliary support is placed at the border of the site at a distance of up to 15 m.
- The length of the branch line from the main support should not exceed 25 m.
All areas where wires and cables touch the surfaces of the house, as well as passage through walls, are made with fireproof materials and are reliably insulated. At the entry point, the outer end of the insulating pipe should be directed downward to prevent precipitation from entering it.
Gas supply
The procedure for installing gas supply networks is established by SNiP 2.04.08, published in 1987. It clearly defines the place where the gas pipeline enters the house - from the kitchen or furnace room. For old households with stove heating, gas entry is allowed through the room, provided that an external shut-off valve or valve is installed.
When laying a pipe along the outer wall of a building, its maximum diameter cannot exceed 50 mm. All connections must be welded; when crossing pedestrian paths, they must be placed at a height of at least 2.2 m from the ground.
Minimum distances when laying a gas pipeline:
- From the underground gas pipeline to the foundation of the house:
- D<300 mm P up to 0.005 MPa - 2 m;
- P < 0.3 MPa - 4 m;
- P = 0.3 - 0.6 MPa - 7 m.
- The distance from the above-ground gas pipeline to the house is not standardized; compliance with the condition of the intersection of the pipe with windows and doors above 0.5 m, and for the roof below 0.2 m is checked.
- Permissible distance from the gas main P = 0.3 - 0.6 MPa:
- road - 7 m;
- water supply - 1.5 m;
- sewerage - 2.0 m;
- electrical network - 5 m.
- Security zone of 2 m on each side of the low pressure gas pipeline.
Water supply
Water supply on the site can be centralized and autonomous: from wells and springs, through a receiving storage tank, while the pressure in the supply pipeline must be at least 0.1 MPa.
Minimum distance from existing water supply:
- The distance to the foundation of the house is 5 m; in cramped conditions this figure can be reduced to 1.5 m when using steel and polymer pipes.
- At least 3 m from fences.
- From a tree trunk with foliage D=5 m - 2 m.
- Location from other utility networks:
- height above the sewer not less than 0.4 m;
- the step between two water lines is 1.5 m;
- between sewers from 1.5 to 5 m depending on the diameters.
- The location of water wells to the foundation of the house is at least 15 m.
The location of water wells should be at least 50 m away from places of possible contamination: landfills, cesspools, fuel and lubricants storage.
Sewerage
These networks, as a rule, in adjacent areas are gravity-fed, and if violations are made during pipe laying or operation, flooding of the territory or even residential premises will occur.
To ensure that neighboring territories and sanitary-protected facilities are not contaminated, the minimum diameter of the external sewer system is accepted as 100 mm, with a guaranteed slope of 8% in relation to the general collector, while the minimum level in the ground should be 0.3 m.
Minimum clearances from the sewer pipe to the foundation of the household:
- pressure gasket - 5 m;
- household gravity - 3 m;
- rain or storm drain - 3 m;
- drainage - 3 m;
- accompanying drainage - 0.4 m.
Requirements for the location of the building
The location of the house on the site is of great importance. There is a fairly impressive list of rules on this matter. It is important to understand that these laws are designed for safety and must be followed.
Rules regarding the location of the building on the site:
- First of all, you need to consider the distance that must be maintained between residential buildings. There should be a distance of 6 meters between structures made of non-combustible materials. There is 8 meters between buildings, partially finished with wood. There is a distance of 10 meters between a wooden building and a building made of non-combustible materials. There are 15 meters between two wooden buildings.
- The house must be located at a distance of 3 meters from the border of the land plot. In this case, you need to retreat 15 meters from the forest.
- Livestock sheds must be built at a distance of four meters from the fence.
- The restroom should be located at a distance of 12 meters from neighboring residential buildings and at a distance of 8 meters from neighboring saunas and baths.
- The height of the basement should not exceed two meters.
- Outbuildings may be located a meter from the neighbor’s fence.
At the same time, buildings located on the same site can be built at any distance from each other. However, we must remember that their total area should not exceed 30% of the entire plot.
Development relative to the red line
The red line (RL) is a symbol of the boundary of the landfill, located between it and the road or other municipal or urban infrastructure facilities.
What needs to be taken into account according to SNiP when erecting any buildings on a site relative to the red line:
- The placement of a residential building is at least 5 m from the street line, and from the roadway at least 3 m.
- The interval from outbuildings to cable lines of streets and driveways must be at least 5 m.
Houses located on opposite parts of the driveway must take into account fire breaks. It is possible to build a garage directly adjacent to the fence, if there is appropriate approval from the board of the dacha or garden association.
The user, when using the allocated land plot, should never go beyond the red line. If regulatory authorities in the field of land use find that the owner is violating the red line, he may be held administratively liable , a fine may be imposed on him in court, and the controversial object will most likely be demolished.
Border with neighbors
, the following gaps must be observed between neighboring objects :
- Between neighboring houses 6 - 15 m.
- From the toilet to the neighbor's household - the size of the plot is 12 m.
- From the compost pit to the neighbor’s household - 8 m.
- Drinking well to neighbor's property - 8 m.
- Garage to any neighboring building - 6 m.
Fence height
The fence, despite its simple appearance and design, is not so simple from the point of view of standards; its installation is regulated by SNiP No. 30-02, the updated version was released on March 12, 2001. The main requirements for the appearance of the fence are unhindered access of sunlight to the neighboring area , so it must have a transparent fence: mesh or lattice.
Also for these reasons, the standards limit the height of the fence to 150 cm . It is possible to change this height by agreement with the neighbors, but these agreements must be recorded in writing in the form of an agreement, so that if the neighbor suddenly changes his mind, the owner would not have to redo the fence.
Based on practice results, it is recommended to make external fencing no higher than 2 mm with transparency higher than 50%.
Environmental restrictions
These standards are aimed at protecting water, land and forest resources from possible negative factors that may arise on the land user's site.
These include:
- fires;
- soil and water pollution.
Based on this, SNiP No. 30-02, dated 1997, established the norm for the location of buildings from the border of the forest area over 15.0 m.
The protection of water resources is regulated by the Water Code. In this case, the requirements for the safe design of water supply and drainage systems must be met. Certain restrictions on the use of coastal areas have also been introduced regarding the location of compost pits, animal sheds, fertilizer storage and the organization of recreation areas. Any coastline 20 m wide is protective.
Storage of engineering equipment
In addition, you should pay attention to the requirements regarding engineering equipment:
- Rainwater runoff should not enter the neighboring area.
- Inside the house (in the kitchen) it is allowed to use a gas cylinder with a capacity of no more than 12 liters.
- Cylinders with a volume of 12 liters containing liquefied gas should be located in a metal box near a blind section of the outer wall, at a distance of approximately 5 meters from the entrance to the building.
- Storing cylinders containing liquefied gas in the garden is not permitted.
- A sealed device should be installed in a residential building to measure the amount of electricity consumed.
In addition, there is a SNiP requirement regarding the degree of insolation of residential buildings. According to its terms, during the period from March 22 to September 22, the sun should illuminate the rooms in your home for at least 2.5 to 3 hours.
Differences in the principles of development on individual housing construction and in SNT
These two organizations have a different legal basis: individual housing construction is an individual housing construction with the right of permanent residence in a household of up to 3 floors, and SNT is a gardening non-profit partnership for gardening and vegetable farming, without permanent residence.
In SNT, for a plot of 6-12 acres, it is allowed to develop no more than 30% of the land area and only strictly according to the land plan.
Minimum distances for individual housing construction objects:
- from the base to the border of the adjacent landfill at least 3 m;
- from the animal shed to the border of the neighboring property is at least 4 m;
- from economic objects to the border of the neighboring land plot is not less than 1 m, if less, then the roof slope is directed towards the personal land plot;
- from tall trees to the border of the neighboring land plot is no less than 4 m, medium trees - 2 m, and bushes - 1 m.
In order to correctly carry out measurements, the calculation is performed from protruding elements of the building or from the base.
Minimum distances for SNT objects:
- from the house to the fence at least 3 m;
- from barns for livestock and poultry at least 4 m;
- personal buildings of at least 1 m;
- bushes at least 1m;
- medium trees at least 2 m;
- tall, at least 3 m;
- a garage can be built on the border of the site.
Conditions for the construction of a second residential building on a land plot
It is very important to maintain the correct distances when building a second household on the site. There is no direct prohibition on the construction of such an object by law, however, when legalizing the structure, problems may arise due to violation of the minimum gaps.
The standards for the construction of a second home are related to the maximum permitted percentage of development , as well as the smallest gaps between the house and the boundary of the land plot. These data are determined by the city municipality, so these indicators may differ significantly for each locality.
In order to find these readings, you need to go to the website Rules for land use and development of a specific area, for example, the Moscow region. The archive contains a Town Planning Plan or Zoning Map, the Rules indicate the maximum percentage of development of 40% and the setback from each household to the boundaries of the land plot is 3 m.
For land of 6 acres, two houses (without other buildings) should have an area of no more than: 600X0.4:2 = 120 m2 , and the distance between them should be 6 m. If additional utility facilities are built, the area of the houses should be reduced accordingly.
Is it possible to build a residential building on a summer cottage?
Recently, living in a private house has attracted more and more people, becoming one of the most current trends. And it’s not surprising, because your own home opens up many opportunities, from regular exposure to fresh air to distance from neighbors and city noise. However, many questions arise in connection with such a decision.
For example, a person owns a dacha and wants to live permanently on this land. Here the question arises, what kind of house is allowed to be built on a summer cottage and whether such a process is possible in principle. A more global interest cannot be ruled out. For example, which plot is generally better to purchase and whether it is possible to buy land, say, in SNT, for the purpose of building a private house.
In fact, yes, it is possible to build a residential building on such land. But there are some nuances here. And, first of all, it is necessary to remember that now the concept of “dacha” as such has been abolished. Now there are 2 types of land so-called dacha farming. These are gardening and horticultural areas.
The construction of private residential buildings on horticultural lands is permitted. But in garden plots - no. Construction is also permitted on areas allocated for individual construction or individual housing construction.
Moreover, if we are talking about building a house on a garden plot, then it is necessary to remember two conditions:
- A private residential property can be built and registered on a site located near a populated area. Or rather, within its borders. If the land is located outside the city or town, then the construction and registration of an object built on it as a residential one is not permissible.
- When preparing for construction, it is necessary to be guided by the provisions of the town planning regulations. Additionally, there are a number of technical parameters that are mandatory. Failure to comply with regulations can result in significant financial losses.
If the conditions are met, then in principle any house can be built on the dacha territory. Both garden and residential. The difference will be that a small country house is not suitable for permanent residence. But you can live in a full-fledged residential property all year round. In addition, the latter option allows for permanent registration. However, in this case, both the preparatory stage and the construction process itself will require considerable effort.
Risks of non-compliance with the rules
Building your own home today is a very expensive undertaking; it must be done correctly, starting with the design of the site, so as not to lose all the money spent.
Strict compliance with building standards when constructing objects on a personal plot is to protect the owner from emergency situations in the house, from claims from neighbors and regulatory authorities.
The owner of a residential building who violates the boundaries of his property and the interests of his neighbors may incur civil and administrative liability . According to the first option, the house can be demolished at his expense, and if he does not do this voluntarily, then the site will be seized, in accordance with the requirements of Art. 285 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Administrative liability for violations is determined by Art. 9.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, implies the imposition of penalties from 1.5% of the price of the storage unit, but not less than 2,000 rubles. for violation of construction, fire and sanitary legislation, and if they caused harm to human health and the environment - 4,000 rubles.
Neighbors affected by the illegal actions of the owner can apply to the court with an independent claim for the demolition of the illegal building, to the prosecutor's office and the administration with a corresponding complaint.
Sanitary standards
General sanitary standards for the construction of a residential building consist of the following:
- Bathrooms cannot be located directly above bedrooms. When building a two-story house, a bathroom can be installed above the kitchen.
- The entrance to the bathroom should not be installed opposite the bedroom or kitchen door. It is allowed to arrange the entrance to the bathroom from the bedroom itself.
Sanitary requirements for the heating system of the house:
- heating pipes should not release harmful substances and unpleasant odors into the air;
- all heating equipment must be accessible for cleaning and maintenance;
- heating power should not exceed 90 degrees.
Ventilation requirements:
- the kitchen and bathrooms must have separate ventilation systems;
- bedrooms must be equipped with a regular ventilation system (windows, window valves, etc.);
- Ventilation of bedrooms and common living rooms must not be combined with the systems of other utility rooms in the house.
Insolation requirements:
- all living spaces must have access to natural light;
- artificial lighting in premises should not be less than 20 lux at floor level.
In addition, separate sanitary standards have been established for the construction of a private house regarding electromagnetic radiation, noise and vibration, etc.