Having a plot of land in the private sector, everyone wants to quickly develop it by building a home and other buildings on it. To implement the planned buildings, in addition to financial savings, it is necessary to become familiar with the standards for the construction of various buildings. To facilitate this task, it is recommended to contact a design organization, which in its work will take into account all the nuances of the requirements of the standards for the construction of private houses - SNiPs, as well as urban planning standards. In this article we will help you figure out the issue yourself!
What can be built on a plot of land?
To begin with, it is worth noting that not all types of structures erected on a dacha plot, on a plot in a garden partnership, or simply provided for individual housing construction are regulated by SNiP 30-102-99. Basically, it indicates the general rules for developing a plot of land, standards for the location of a residential building and utility structures, materials that should be used for the construction of structures, etc. Therefore, first you need to decide which buildings will be located on the site.
What can be built on individual housing construction lands?
In general, in accordance with construction standards, the following structures can be built on a land plot:
- House;
- sheds;
- outdoor toilet;
- bath;
- compost pit;
- garage;
- other economic objects.
The category of other economic objects can include additional barns, water towers, windmills, etc.
Of course, the main building is the residential building itself. Unlike other structures on the site for individual housing construction, the residential building is the main one and permission must be obtained for its construction. Such permission is not required for sheds or other outbuildings. The only exception is the water tower, for which a license is issued and a tax is paid.
How to start construction
Before you build a home, be sure to carry out some preparatory work:
- Collect information about the properties of materials that will be used for construction, in particular, their fire resistance, durability and environmental friendliness;
- Develop a project: for this it is better to contact a construction or design company; specialists will take into account all the parameters that you may not know or forget about;
- Prepare the necessary documentation for issuing a document permitting construction work.
SNiP for the construction of private houses
A number of requirements are imposed on a residential building, in particular:
- fire safety requirements;
- norms of soil hydrological characteristics;
- rules for the construction of load-bearing walls;
- material consumption standards;
- requirements for location relative to roads and neighboring areas and other structures;
- standards for planning the interior of a residential building.
SNiP of an individual residential building with a complete list of requirements for the construction of a residential building can be found here SNiP SP 30-102-99.
The main requirement is for the layout of interior spaces.
So, for a building to be considered suitable for habitation, it is necessary:
- there should be no industrial premises in the building itself;
- the building must have facilities for housing, food and hygiene procedures;
- there must be a central heating system, and in its absence, heat generators;
- bathroom and storage room.
Moreover, the presence of a bathroom and storage room inside the building is not necessary if there are external buildings on the site that can be used for these purposes.
Distance between objects
In order for you to be allowed to carry out construction work, you must make a plan that will comply with all SNiP rules and local administrative recommendations. To ensure fire safety, observe the length of the segments from one object to another:
- if your or a neighboring property has a fireproof, metal or concrete frame (with fire resistance of the third degree) - retreat 6 m;
- concrete, foam concrete, brick or sand buildings (with fire resistance of the first or second degree) have a setback of 8 m;
- if one of the buildings is wooden, the likelihood of a fire increases, so retreat 15m.
Distance from the site boundary to the building
The standards for determining the building boundary are determined in two ways, depending on;
- on the distance of buildings from the neighboring plot;
- on the distance between buildings according to SNiP within the site.
Thus, the offsets from the adjacent section of the structure must be equal to no less than:
- the residential building itself is at least 3 meters away from its neighbors;
- sheds - 4 meters;
- baths, toilets - 2.5 meters;
- greenhouses and greenhouses – 4 meters;
- garage - at least 1 meter;
- other structures - 3 meters.
The distance from the so-called red line of roads to any structure on the site should not be less than 5 meters. You can determine the distance from the fence to the house at your own discretion.
Indentations depending on the type and number of storeys of the building
The location of a residential building and its distance from the neighboring plot, outbuildings or buildings is regulated by SNiP 2.07.01-89. In Moscow there are separate design standards, MGSN 1.01-99, which are also used in the Moscow region. The government of St. Petersburg also adopted separate resolutions in order to preserve the historical features and accepted development trends of the unique city.
Indentation standards according to SNiP and law
The primary requirements for the relative location of a residential building and a building of the same type, children's and medical institutions, public buildings and enterprises is maintaining the distance required for the following:
- ventilation and lighting, when living or carrying out core activities;
- fire safety standards are given in the Appendix of this mandatory document;
- household gaps amounting to 15 m for low-rise buildings and 20 m starting from 4 floors; they are sometimes reduced if other requirements are met;
- the distance to the boundaries of the site from outbuildings is at least a meter, but this distance is minimized by mutually blocking buildings of the same type;
- if we are talking about the remoteness of the side of the street, then in this case the distance from the red line is determined according to the construction plans approved by the local territorial community and RS authorities.
Norms and rules for individual housing construction and SNT
To accurately determine the distance, it is necessary to study the master plan.
The figure depends on the category of the street, the presence of utilities (gas pipes, power lines, ground heating, operating conditions of the facility and its safety). The distance from the red line can be from 3 to 10 meters, and this will comply with the law.
Fire safety standards for the construction of an individual residential building
In fact, requirements to maintain the distance between buildings have been introduced, including for the purpose of ensuring fire safety. So, if there are wooden buildings on the site, then the distance between them should not be less than 15 meters. In addition, there are special fire safety standards for the construction of an individual residential building regarding the selection of building materials and fireproof finishing of walls.
Ideally, the walls should be covered with thermal insulation or other fireproof material. Therefore, building a house on an individual housing construction plot in which fire safety standards are fully complied with is not a cheap matter.
Fire standards for the construction of a private house also affect electrical wiring, the technical condition of electrical and gas equipment, and the condition of heating systems.
For this reason, it is recommended to contact specialists when resolving the relevant issue.
Risks of non-compliance with the rules
Building your own home today is a very expensive undertaking; it must be done correctly, starting with the design of the site, so as not to lose all the money spent.
Strict compliance with building standards when constructing objects on a personal plot is to protect the owner from emergency situations in the house, from claims from neighbors and regulatory authorities.
The owner of a residential building who violates the boundaries of his property and the interests of his neighbors may incur civil and administrative liability . According to the first option, the house can be demolished at his expense, and if he does not do this voluntarily, then the site will be seized, in accordance with the requirements of Art. 285 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Administrative liability for violations is determined by Art. 9.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, implies the imposition of penalties from 1.5% of the price of the storage unit, but not less than 2,000 rubles. for violation of construction, fire and sanitary legislation, and if they caused harm to human health and the environment - 4,000 rubles.
Neighbors affected by the illegal actions of the owner can apply to the court with an independent claim for the demolition of the illegal building, to the prosecutor's office and the administration with a corresponding complaint.
About the height of private buildings
So, are there requirements limiting the height of private buildings? The legislation does not put forward specific requirements regarding the height of private buildings. However, a private single-family residential building should not be higher than three floors. The height in meters is not indicated.
At the same time, the attic is recognized as a separate floor. But the basement and other underground floors are not taken into account. But it is prohibited to arrange residential premises there. Also, if the top of the basement extends more than 2 meters outward, it will be considered a separate floor.
However, SNiP establishes the maximum permissible fence height . The rules for building a fence determine that it should not exceed two meters. Exceptions are cases when the site is adjacent to the roadway. In such cases, the fence according to SNiP may exceed the specified height.
The fence between neighboring plots should not be higher than 1.75 meters.
Regarding other structures on a private plot, the legislator does not put forward requirements for their height. But in any case, you need to be ready to resolve disputes with neighbors.
Rules for individual housing construction
Their observance is mandatory:
- It is prohibited to plant tall trees near the fence; you must retreat 3 meters. Plants of medium height are allowed to be planted after 2 m, and small shrubs - after 1 m;
- It is permissible to violate the boundaries between your building and a nearby plot only if a legal agreement has been concluded with its owner. Otherwise, he will still have the right to complain about you in court, as a result of which you will be required to pay a fine;
- If you have a new neighbor, then you will also need to take legally certified consent from him, otherwise he will also have the right to go to court;
- If you nevertheless violated the rules without concluding any agreements, and no one has filed a complaint against you in three years, then you can rest assured that no one else will file a complaint against you.
Construction standards for individual housing construction
The construction standards for individual housing construction, in addition to fire safety standards, also include requirements regarding the area of individual premises inside the building. So:
- The total area of the main living space (living room, hall) should not be less than 12 square meters.
- The kitchen or dining room-kitchen should not be less than 6 square meters.
- When combining a bathroom, the total area should not be less than 4 square meters, when dividing: toilet - at least 0.96, bathroom - 1.8 square meters.
- Bedrooms – 8 square meters.
Moreover, if these premises are located in the attic, then their area can be reduced by 2 square meters.
The width of passage corridors and staircase openings must be at least 0.9 meters. If the house has an entrance hall, then its area should be at least 1.8 meters.
As for the ceiling height in the premises, it should be at least 2.5 meters. But the ceiling height on the ground floor should not be more than two meters, unless it is intended to be used for economic purposes (to build a bathroom, storage room, etc.).
Home construction.
SNiP 12-01-2004 Organization of construction
2.1. Foundations and concrete structures
2.1.1. SNiP 3.02.01-87 Earthworks. Foundations and foundations
2.1.2. GOST 7374-2010 “Concrete mixtures. Technical specifications"
2.1.3. GOST 30515 Cements. General technical conditions
2.1.4. GOST 10178 Portland cement and Portland slag cement. Technical conditions.
2.1.5. GOST 10181 Concrete mixtures. Test methods
2.1.6. GOST 18105 Concrete. Rules for monitoring and assessing strength
2.1.7. GOST 10180 Concrete. Methods for determining strength using control samples
2.1.8. Concreting foundations. Methodology. V.M. Galuzin
2.1.9. Do not bury foundations deep into V.S. Sazhin
2.1.10. The rest of the necessary information for building a foundation can be found in: SNiP 2.02.01-83; SNiP 31-02; SNiP 2.02.03-85; SNiP 2.02.04-88; SNiP 2.02.01.
2.2. Walls of the house.
2.2.1. SNiP 3.03.01-87. Load-bearing and enclosing structures. Stone structures
2.2.2. GOST 21520-89 Small cellular concrete wall blocks
2.2.3. Recommendations for the use of fiber foam concrete blocks
2.2.4. Albums of technical solutions for ventilation facades
2.2.5. Album of Poromax technical solutions
2.2.6. Album of technical solutions for cellular concrete
2.2.7. Recommendations for the use of 3-layer blocks from the Kucherenko Research Institute
2.2.8. Album of technical solutions for the installation of houses made of LSTK
2.2.9. SNiP 2.08.01-89 “Residential buildings”
2.2.10. SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”
2.2.11. SNiP II-22-81 “Stone and reinforced stone structures”,
2.2.12. SNiP 23-01-99 “Construction climatology”,
2.2.13. SNiP 2.03.11-85 “Protection of building structures from corrosion”,
2.2.14. SNiP 2.01.02-97 “Fire safety of buildings and structures”,
2.2.15. GOST 6133-84 “Concrete wall stones. Technical conditions",
2.2.16. GOST 30108-94 “Construction materials and products. Determination of the specific effective activity of natural radionuclides.”
2.2.17. SNiP 2. 07. 001-89 – Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements.
2.2.18. GOST 24454-80 – Softwood lumber, GOST 9685-61 – Softwood timber.
2.3. Selection of design and installation of windows.
2.3.1. SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”
2.3.2. SNiP 2.01.02-97 “Fire safety of buildings and structures”,
2.3.3. GOST 30971-2002 “Mounting seams of junctions of window blocks to wall openings. General technical conditions"
2.3.4. Standards for double-glazed windows and glass: GOST 30698-2000. “Tempered building glass. Technical conditions"; GOST 24866-99. "Glued glass units for construction purposes. Technical conditions."
2.4. Albums of technical solutions for roof installation
2.4.1. Flat and pitched roofs SNiP II-26-76
2.4.2. MDS 12-47.2008 Methodology for laying metal roofing
2.4.3. Installation instructions for composite tiles
2.4.4. Installation instructions for flexible tiles Katepal
2.4.5. Installation instructions for metal tiles
2.4.6. Regulatory documents for roofing materials: GOST R 1110-2008; GOST 30547-97; GOST R 52146-2003; GOST R 52246-2004;
2.5. Albums of technical solutions for installation of insulation and sound insulation.
2.5.1. Album of technical solutions for ecowool
2.5.2. Album of technical solutions for polyurethane foam insulation
2.5.3. ROCKWOOL Insulation systems
2.5.4. Rockfacade. Facade insulation system 2014
2.5.5. Soundproofing Knauf
2.5.6. Sound insulation ROCKWOOL
2.5.7. Regulatory documents for insulation materials: GOST 15588-86; GOST 52953-2008; GOST 30244-94, SNiP 21-01-97*; GOST 12.1.044-89, SNiP 21-01-97*; SNiP 3-04-01-87; SNiP 23-02-2003; GOST 16381-77-1992; GOST92; SNiP 23-03-2003; GOST 17177-94; GOST 9573-96; GOST 52953-2008; GOST 21880-94; GOST 22950-95
2.6. Finishing work
Produced in accordance with SNiP 3.04.01-87 “Insulating and finishing coatings”
Is it possible to build an apartment building or townhouse on an individual housing construction plot?
In order to build an apartment building on an individual housing construction plot, it is necessary to change the type of plot to “public settlement land”. However, without changing the type of permitted use, it is possible to build a townhouse.
In general, on a privately owned plot of land for individual housing construction, any structures can be erected that do not contradict the law. A townhouse in this sense is a completely legal building. However, the problem arises in connection with the ownership of individual apartments within a townhouse.
The maximum that each tenant can receive is a share of the townhouse. Of course, in court it is possible to determine clear boundaries of the share, indicate the premises that are assigned to the share of a particular tenant, etc. However, in general, the implementation of such a construction is considered undesirable, since there is a high risk of demolition at the request of third parties or the prosecutor's office. Disputes with neighbors will also become a constant occurrence.
What should the fence be like?
In the construction of fences there are regulations not only on distances, but also on their height and the passage of light. They exist again in order to prevent unnecessary shading.
- For fences dividing territories, the maximum height is one and a half meters. Moreover, it is necessary to maintain its transparency by at least 50%. It can be made from any material: chain-link mesh, trellises or picket fence. Only the lower part up to half can be made continuous;
- The size of the external fence is not limited by regulatory documents, but if it exceeds 2 m, agree on this in writing. This will save you from further complaints. Here, maintaining transparency is not necessary; you can, for example, make it from corrugated sheet metal;
- In fact, if you draw up a written agreement with your neighbors and have it legally certified, then you can install any fences to your taste. This is convenient when both parties want to completely block the visibility of their yard.
Construction of a garage on the site: standards
There are also rules and regulations for constructing a garage on the site. A garage on a private plot can be built in different ways:
- withdraw it as a separate structure;
- build as a room inside a residential building.
Primary requirements:
- When constructing a garage as a separate building, the distance from the red line must be at least 1 meter, and from the neighboring site - at least six.
- When arranging a room inside a residential building as a garage, a separate ventilation system is required for the specified room.
SNiP contains other requirements regarding building materials, the use of which in the construction of a garage is permissible.
Plant placement
Many people build country houses to be closer to nature, so they want there to be live trees in the yard. But not everyone knows that they also cannot be planted wherever you want. Green spaces create extra shadow on the neighbors’ territory, which they are unlikely to like, because it interferes with growing homemade food. There are strict requirements:
- small bushes can be planted 1 m from the neighboring hedge;
- plants of medium height - beyond 2m;
- tall trees - beyond 4m.
The footage is calculated from the center of the trunk, and not from the edge of the crown.
Sanitary standards
General sanitary standards for the construction of a residential building consist of the following:
- Bathrooms cannot be located directly above bedrooms. When building a two-story house, a bathroom can be installed above the kitchen.
- The entrance to the bathroom should not be installed opposite the bedroom or kitchen door. It is allowed to arrange the entrance to the bathroom from the bedroom itself.
Sanitary requirements for the heating system of the house:
- heating pipes should not release harmful substances and unpleasant odors into the air;
- all heating equipment must be accessible for cleaning and maintenance;
- heating power should not exceed 90 degrees.
Ventilation requirements:
- the kitchen and bathrooms must have separate ventilation systems;
- bedrooms must be equipped with a regular ventilation system (windows, window valves, etc.);
- Ventilation of bedrooms and common living rooms must not be combined with the systems of other utility rooms in the house.
Insolation requirements:
- all living spaces must have access to natural light;
- artificial lighting in premises should not be less than 20 lux at floor level.
In addition, separate sanitary standards have been established for the construction of a private house regarding electromagnetic radiation, noise and vibration, etc.
From the cottage to other objects on the territory
What sanitary standards must be observed during the construction of a wooden house and other objects on the site? There are not many of them, and some errors are allowed. Only if you decide to sell the developed land in the future, you may have some problems, so we recommend that you initially do everything according to the rules.
Important
Each distance is calculated from the external wall.
- to the toilet on the street - at least 12 m (preferably 15);
- baths (or showers) are located every 8 meters;
- barn with livestock and poultry - after 12-15m;
- compost - after 8 m;
- economic facilities - after 4 m;
- Placing a garage is allowed close to the cottage or even inside it.
Toilets or composts should not be located near the well; the minimum distance is 20 m, otherwise the water in it will become infected with dangerous bacteria.
Take the rules seriously if you decide to build baths. They are usually built of wood, and the stoves are heated with wood, so the likelihood of a fire is very high. Place it further from the home, retreating 8m. In this case, it is better to make an additional drain, which requires another sewer pipe or gutters.
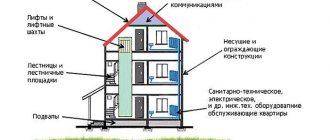
Standards for utility networks
A residential building must be connected either to central communication systems or have its own autonomous system of engineering networks. When connecting to central systems, the developer is relieved of responsibility for the correctness of the networks. This is the responsibility of the suppliers who provide the connection. But when installing an autonomous utility network, certain rules must be followed.
Sewerage
The cesspool and filter well must be located at a distance of at least 8 meters from the residential building. All leading sewer pipes must have a mandatory diameter of 150 mm or more. Such pipes must be installed at a depth of at least 30 centimeters. In this case, the angle of inclination of the pipe must be more than 0.007. However, there is also a dependence on the diameter of the pipe.
Conducting gas
Under no circumstances should gas pipes run through a foundation or living space. It is allowed to carry pipes through the kitchen to other rooms, provided that there is a central switch in the kitchen. Also, gas heaters should not be installed in the bathroom.
When using gas cylinders, cylinders with a volume of no more than 12 liters are allowed to be installed inside the house. Larger containers should be installed outside a residential building.
Electricity
If electricity is attracted from a pole located more than 25 meters from the final connection point, then another pole must be installed. In this case, the pole should not block transport and pedestrian routes.
The height of the wires must be at least 2.75 meters from the ground. When crossing transport and pedestrian paths - 6 meters.
Design, preparation for construction of a house
1.1. Architectural and general construction standards.
First you should familiarize yourself with the Code of Design Rules SP 11-III-99. After reading this document, you will know exactly what papers are required to begin construction on your individual site. When constructing a residential building and various outbuildings, there are standards for their location on the site, according to the following documents: - “Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation” dated December 29, 2004 N 190-FZ; — “Planning and development of gardening associations of citizens, buildings and structures” SNiP 30-02-97; — “Residential buildings” SNiP 2.08.01-89* and SP II 106-97; — “Single-apartment residential houses” SNiP 02/31/2001; — “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements" SNiP 2.07.01-89;
This is the approximate layout of buildings on the site in accordance with RSN 70-88.
Having carefully studied RSN 70-88 (republican building codes), SNiP 31-02-2001 and SNiP 2.08.01-89 (Building Norms and Rules), you will learn what restrictions apply to the areas and heights of premises in a residential building.
There are minimum restrictions on floor heights (SNiP 2.08.01-89). A house may be declared unsuitable for permanent residence if the height of the residential floors is below 2.5 m from floor to ceiling. In the attic floor the standard height is 2.3 m. The number of storeys of a house is usually determined by the above-ground floors, which also includes the attic floor. Living rooms are not allowed to be located in the basement or basement floor. The basement floor can be equated to above-ground floors if the top of its ceiling is at least 2 meters above the planning level of the ground. If it is decided to place utility rooms in the basement or basement, then the height from floor to ceiling must be at least 2 meters.
The area of a residential building is defined as the sum of the areas of all rooms on the floors. Balconies and loggias are also included in the total area. The areas of stairwells at the level of a given floor are calculated.
If you are planning to build a house on the territory of a gardening association, then you must take into account the requirements of SNiP 30-02-97 “Planning and development of gardening associations of citizens, buildings and structures” as amended in 2011.
1.2. Concrete structures.
1.2.1. Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy concrete (without pretensioning)
1.2.2. SNiP 52-01-2003 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Basic provisions"
1.2.3. GOST 25485-89 “Cellular concrete. Technical specifications"
1.3. Thermal technical standards. Resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures.
1.3.1. SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”
1.3.2. Heat loss of the building. Reference manual.
1.3.3. Order of the Ministry of Regional Development dated May 23, 2008.
1.3.4. Design and construction of enclosing structures made of cellular concrete STO 501-52-2007
1.3.5. Example of thermal engineering calculation
1.3.6. Properties of foam concrete and heat capacity
1.4. Engineering Communication.
1.4.1. Power supply in accordance with PUE (electrical installation rules).
Electrical wires from a street pole to the entrance to a residential building must pass at a height of at least 2.75 m from the ground. If the diversion is carried out on the other side of the street along which vehicles are moving, then the permitted height is 6 m. The length of the branch line from the main line to the residential building should not exceed 25 m; if it turns out to be more, an additional support is installed. All places where the cable comes into contact with the surface of the building and passes through the walls must be fireproof and reliably insulated, and at the entry points the outer end of the insulating pipe must look down to prevent precipitation from entering there.
It is strictly forbidden to throw an electrical wire over the roof of a house. External wiring should be inaccessible from balconies and windows of a residential building.
1.4.2. Sewerage in accordance with SNiP 2.04.03-85.
If the rules for installing sewer networks are violated, the developer faces regular clogging. He is doomed to frequent cleaning of drain-clogged pipes. According to standards, daily sewerage costs per person are about 200 liters. The smallest diameter of the external sewer pipe must be 100 mm, with a slope to the common collector of at least 8%. The minimum depth for laying a pipe in the ground is 0.3 meters. If there is no centralized street sewage system, then the construction of filter wells and trenches is allowed with the obligatory installation of a septic tank (industrial treatment device) in front of them. The base of artificial filters should be 1 meter above the groundwater level.
1.4.3. Heating, ventilation in accordance with SNiP 2.04.05-91. Contact specialists so that they can correctly calculate the power and number of heating devices for satisfactory heating of the premises of the house.
Typically, the technical specifications of devices indicate power in watts or kilowatts. The heat flow coming from heating devices should be no less than 10 W per 1 square meter of floor space. As a rule, radiators and convectors are placed under the light openings of windows. It is not allowed to place them in vestibules that have external doors, as this can lead to the system defrosting. Attention should be paid to the inadmissibility of using ventilation ducts to remove combustion products from a boiler or water heating column. The room where the heating boiler is located must have a window with an area of at least 0.03 square meters per 1 cubic meter of the volume of this room. If a solid fuel boiler is used, then it is allowed to arrange a storage room for fuel storage on the first, ground or basement floor.
In individual residential buildings, duct ventilation is required to be installed in bathrooms and toilet rooms if there are no external windows there. Sometimes, ventilation ducts are placed near external walls, without taking into account the influence of weather conditions. This leads to rapid cooling of the exhaust air and loss of draft. In this case, the wall is constantly waterlogged with condensation moisture and collapses.
Quite a lot of high-quality information can be obtained from STO NP “ABOK” 2.1-2008 Air exchange standards. Residential and public buildings.
1.4.4. Gas supply design must be carried out on the basis of SNiP 2.04.08-87.
If you have the appropriate knowledge and experience, you are allowed to independently install utility networks, with the exception of gas communications. There are very strict requirements for the acceptance of a gas supply system. Only a specialized organization has the right to install a gas pipeline and connect gas appliances.
Gas pipes can be introduced into a residential building only from the furnace or kitchen side. If the house is old and has a heating stove, then it is allowed to enter communications into the living room, provided that the disconnecting device is located outside the building. Under no circumstances should a gas pipe be inserted into the house through or under the foundation. If the pipe is laid along the outer wall of the house, then its nominal diameter should not exceed 50 mm. It is not allowed to install detachable pipeline connections under window openings and balconies. In general, all connections must be welded, threaded connections only in places where shut-off valves and gas appliances are installed. If the gas pipe according to the project passes over pedestrian paths, then it should be mounted at a height of at least 2.2 meters from the ground.
You cannot install more than two heating devices in one room. It is strictly forbidden to install a water heater in the bathroom, otherwise you may end up with a wonderful gas chamber.
The room for a gas boiler and water heater must be at least 2 meters high. When installing one device, the room has a volume of at least 7.5 cubic meters, and with two devices - at least 13.5 cubic meters.