Remember the fairy tale about the wolf and the three little pigs? The perfectionist Naf-Naf built a house of stone with an oak door and a strong bolt.
The house survived the invasion of the evil wolf: the gray one did not have enough breathing space.
The main moral: diligence and thoroughness always win. Construction morale: a permanent house is stronger and more reliable .
This is the second publication about unauthorized buildings: how a permanent structure differs from a non-permanent one and what does unauthorized construction have to do with it.
About movable and immovable
A thing is a part of the material world, some kind of property, something that can be touched.
Movable and immovable things are two legal categories of things that do not always coincide with the common understanding.
Sometimes an immovable thing moves, but a movable thing cannot always be moved
Real estate, otherwise known as real estate, is land, subsoil plots and everything that is firmly connected to the land .
Real estate also includes aircraft, sea vessels, and inland navigation vessels, if they are subject to state registration. This is exactly the case when an immovable thing moves.
“Everything that is firmly connected to the earth” - buildings, structures and structures located on the ground, including unfinished ones.
Residential and non-residential premises, parking spaces in buildings and structures are also real estate.
Inextricable connection with the earth and the inability to move without disproportionate damage
This is the main distinguishing feature of an immovable property.
There are no criteria in the law by which damage is considered proportionate or disproportionate .
However, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation clarified this issue:
- Inability to use for intended purpose
- Significant deterioration in technical condition
- Decreased material or artistic value
- Inconvenient to use
These and other similar consequences allow us to qualify the damage as disproportionate.
With movable property everything is simpler. A clear and simple rule:
Movable things - everything that does not belong to real estate
A movable thing does not have a stable connection with the earth . Therefore, it can be freely moved without compromising its intended purpose or with minor damage.
These include cars, temporary buildings, kiosks, sheds, and even money and securities.
Types of temporary structures
A temporary structure is a structure made of lightweight structures, without a deep foundation, and with no underground facilities. For example:
- Facilities for roadside service - car parks, payment terminals, telephone booths, etc.
- Entertainment facilities - attractions, children's/playgrounds, tents, etc.
- Facilities for technical, industrial, and municipal purposes - recycling points, change houses, warehouses, parking lot sheds, garages, etc.
- Covered underground or air passages, ramps, etc.
- Mobile structures of prefabricated/dismountable type - storerooms, warehouses, hangars, auxiliary premises, pavilions, etc.
Real estate is always capital
“Everything that is firmly connected to the earth” is the result of capital construction.
Synonyms for the word “capital” are solid, solid, fundamental .
Fundamental from the word “foundation” (Latin fundamentum), means “having a strong foundation.”
Capital = fundamental = having a strong foundation
Capital construction is not only the construction of a foundation. Also the construction of load-bearing structures, installation of utilities and much more.
However, it is the presence of a foundation, or rather the depth of its laying (more on this later), that is the main criterion for a capital structure.
If a structure is on a strong foundation, then it is firmly connected to the ground. There is a strong connection with the land, which means the building is an object of real estate.
The presence of a foundation (capitality) = a strong connection with the land = an immovable thing
At their core, the concepts of “capital construction object” and “real estate object” are identical . They are united by a strong (inextricable) connection with the earth.
Toilet and cesspool
A rustic toilet with a simple pit cesspool is not a property. It does not need to be registered or formalized in the registry. But if the toilet is built on a solid foundation, has modern communications and water supply, a laundry complex and other functions, you need to register the building and obtain all rights to it.
This also applies to the construction of commercial toilets that will serve a large volume of people and generate income for their owner.
Recessed foundation
The foundation is part of the building, its supporting structure. The main purpose is to transfer the load from overlying structures to the ground.
Foundations can be strip and slab, monolithic and prefabricated, there are many types.
However, a building is considered capital, and accordingly belongs to real estate, if its foundation is buried in the ground.
Deep foundation = capital object = real estate
The presence of a buried foundation is the main criterion by which a structure is classified as a capital construction project.
It doesn’t matter whether the foundation is shallow or deep.
Buried in the ground, it means firmly connected to it
A buried foundation is when its base is below the surface of the soil .
The sole, in other words the base of the foundation, is the lower horizontal plane of the foundation, the one on which the foundation rests on the ground.
It is impossible to build a non-permanent object on a buried foundation - the structure will already be permanent.
Bath
The decision to register a bathhouse in the state register depends on whether the building has a permanent foundation, what size the bathhouse building will be, and on the characteristics of the site.
For a small rural bathhouse, which is installed directly on the ground and can be moved to another location, a building permit does not need to be issued. But for a large bath complex with a swimming pool and sauna, a massage room and a winter garden, it is better to issue permitting documentation and calmly enjoy the healing water procedures.
What else indicates capital
The presence of a buried foundation is a prerequisite for classifying a building as a capital construction project.
However, there are a number of additional criteria, compliance with which also indicates the capital construction.
Temporary nature
The first additional criterion for classifying an object as non-capital is the limitation of the period for which it was built .
This indicator is logically related to the main criterion: the arrangement of a buried foundation during the construction of a temporary structure seems unnecessary and economically infeasible.
The period is usually indicated in the initial permitting documentation.
If the period is not specified, it is considered that the structure has no time limit for which it is erected.
Prefabricated does not mean temporary
In judicial practice, non-capital and temporary are synonymous. In court rulings this is what they indicate - “non-capital (temporary)”.
Often the plaintiff tries to replace the concept of “ prefabricated facility ” with the concept of “temporary (non-capital) facility.”
This substitution is built in the following logical chain:
- The building is constructed from prefabricated structures, which means
- The structure is temporary - not permanent, therefore
- The entry in the Unified State Registration Register of ownership of the building is illegal, violates the rights of the plaintiff, and as a result
- The claim for recognition of the right as absent is subject to satisfaction
However, these two concepts are not identical
The rapid construction of the facility is determined by the short period of installation and construction work.
The temporary (non-capital) nature of the structure is due to the lack of a strong connection with the ground and the presence of certain design characteristics.
In the first case, the determining criterion is construction time , in the second - operation time .
Engineering Communication
Electricity supply from cable networks, hot and cold water supply, heating, sewerage and wired telephone communications are all engineering communications.
Bringing such communications to the structure indicates its construction for long-term operation .
The presence of a connected heating system indicates the possibility of year-round operation .
All this is indirect, but indicates that the structure is not temporary.
Area and weight of the object
The size of the building also matters, especially its area.
In most cases, temporary structures erected for a certain period have a small area compared to capital construction projects.
For example, a kiosk is a non-capital object with a total area of no more than 20 m², designed for only one salesperson’s workplace.
If the area of the building is several hundred square meters, most likely it contains not only the main premises (for example, a sales area), but also ancillary (auxiliary) ones .
Auxiliary premises include: locker rooms, toilets and showers, a room for eating, etc.
The presence of such premises (again indirectly) indicates the long-term nature of the structure
The large area of the building implies its significant weight.
Such buildings are much more often assembled from prefabricated blocks , and the buildings themselves have access roads.
If the weight of the structure is several tens of tons, it is more appropriate to talk about a permanent structure than a temporary one.
Significant weight implies a strong foundation
However, we remember that the main indicator of a capital structure is the presence of a buried foundation, that is, a strong connection with the ground.
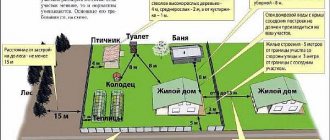
What is allowed to build on the site
The construction of individual housing construction buildings on your personal plot is regulated by the State Town Planning Code. You can build a residential building only if you obtain permission from city or village authorities.
Authorities' permission for individual housing construction is issued for a period of 10 years. Then it is necessary to formalize the commissioning of the building. This process involves the complete completion of all construction work and the preparation of all necessary documentation.
Then the building is registered with the city and checked for compliance with the regulatory requirements of GOST. The owner receives documents on the ownership of his property.
For the construction of a garage, outbuildings, sheds, etc., a permit is not required and ownership is not issued.
If an individual housing construction building does not have a permit, then it is considered an unauthorized construction and is subject to demolition.
Non-capital object - movable property
If a building does not have a strong connection with the ground, then it is not permanent.
Trade kiosks, pavilions, sheds, small warehouses, gazebos, greenhouses, box garages and the like - all these are non-permanent buildings .
As a rule, such buildings are made of lightweight and prefabricated structures. This does not require a solid foundation.
Remark: by strong we mean a foundation that is buried in the ground .
Sometimes there is no foundation at all
This design feature allows for dismantling, moving and reassembling without disproportionate damage to the intended purpose.
As a result of disassembly, transportation and installation in another place, the main characteristics of the structure do not change.
We reason as with real estate, only exactly the opposite:
There is no stable connection with the earth, the object can be moved without damaging its purpose or with minor damage, which means the object is a movable thing.
There is no foundation or it is not buried in the ground = no strong connection with the ground (no capital) = movable thing
What is the difference between permanent and non-permanent buildings?
The difference between a capital structure and a non-capital one presupposes, first of all, different types of purposes of objects and technologies for their construction.
Capital buildings in comparison with temporary buildings have the following distinctive features:
- buried foundation;
- high service life;
- long construction time;
- the presence of enclosing and load-bearing structures;
- linking the building to a specific land plot;
- availability of communications;
- mandatory state registration of real estate.
What distinguishes a permanent building from a non-permanent one is the presence of landscaping in the surrounding area, the use of strong, expensive materials, the large size of the structure and a high level of fire safety.
A capital facility is much more difficult to construct and put into operation . It is subject to increased legal requirements. In addition, the construction of a capital facility requires huge financial investments.
Capital objects include all apartment buildings, private residential buildings, retail space, institutions of various types and all other objects built on a foundation.
A capital structure cannot be taken and moved to another location. To do this, it will have to be demolished and rebuilt in another place. From the point of view of financial feasibility, doing this is absolutely ineffective.
Capital facilities, due to the complexity of their construction and commissioning, are tens of times more expensive than non-capital temporary buildings.
Cadastral registration, state registration, construction permit and commissioning
Cadastral registration
“State cadastral registration of real estate” - that says it all.
Non-capital objects are not real estate and therefore are not taken into account in the cadastre.
State registration of rights
“Unified State Register of Real Estate ” (URGN) - and that says it all.
Non-capital objects are classified as movable property, therefore rights to them are not registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Construction permit
A construction permit is a document that grants the right to build or reconstruct a capital construction project.
Again, comments are unnecessary: non-capital construction does not require permission for construction or reconstruction.
There are exceptions to this rule. For example, from August 2021, it is possible to build or reconstruct individual housing construction without permission, after submitting a notification in advance.
Commissioning
Commissioning permit is a document that certifies the construction or reconstruction of a capital construction project in accordance with the permit and design documentation.
It also confirms that the facility meets construction requirements.
Again, everything is banal and simple: a non-capital object does not need to be put into operation by obtaining permission to enter.
Greenhouse and greenhouse
Small greenhouses and greenhouses that are built for oneself without a capital foundation are allowed to be built on individual housing construction without obtaining permits. If the greenhouse complex is planned to be used for commercial purposes, then documentation will still have to be completed in order to avoid penalties and other troubles from inspection authorities.
Why is capitality important?
Constructions are recognized as unauthorized on the basis of Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation - this is the main legal norm for such disputes.
For the purposes of this article, only a real estate object, i.e., a permanent structure, can be recognized as an unauthorized construction.
A non-capital object cannot be recognized as an unauthorized construction
Therefore, first of all, the court establishes the nature of the disputed structure - it answers the question “is the disputed structure real estate.”
If the structure is not permanent, it is movable property. If the capital property is real estate, then the dispute is resolved in accordance with Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
This determines whether the plaintiff has chosen the right method of defense, what rules of law need to be applied, and how to correctly calculate the statute of limitations.
An example from judicial practice
The plaintiff, the owner of the land plot, asked to recognize the building as unauthorized and to oblige the defendant to demolish it.
In his legal justification he referred to Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on the examination, the court found that the structure declared for demolition is not permanent - it is not an object of real estate.
In this case, Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is not applicable ; the structure cannot be recognized as an unauthorized construction.
The claim was denied: the plaintiff chose the wrong method of legal defense
Depending on the circumstances, the plaintiff should consider dealing with:
- negative claim - on the basis of Article 304 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on eliminating a violation of the right not connected with deprivation of possession of a land plot
- vindication claim - on the basis of Article 301 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the reclaiming of a plot from the illegal possession of the defendant
- preventive claim - on the basis of Article 1065 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the prohibition of activities for the operation of a structure that creates a danger of harm
By the way, claims within the framework of a negatory claim are not subject to the statute of limitations, which is often very important.
About reconstruction, redevelopment, re-equipment and new facility
Reconstruction
Reconstruction - changing the parameters of an object: area, volume, height, number of floors.
Rebuilding, superstructure, expansion, replacement of load-bearing structures - all this is reconstruction.
The term applies only to capital construction projects
Like the construction of an unauthorized building, reconstruction can also be unauthorized and entail similar consequences.
The court will oblige the demolition of an unauthorized reconstructed object only if it cannot be restored to its pre-reconstruction condition.
However, this is only possible if, as a result of reconstruction, a new property is created (more on this below).
Key Aspects
As a rule, the implementation of most goals requires the use of permanent structures. They are more durable, versatile and durable.
When registering construction or registering a property, the documentation must indicate the type of construction.
Its estimated value, tax rate, purpose of further use, etc. depend on this. Therefore, when constructing an object, it is important to determine whether it belongs to a permanent structure.
What it is
Legally, what a permanent structure is is defined by the Town Planning Code. It lies in the following concept.
A capital structure is a structure, building or structure that, according to certain standards and characteristics, belongs to this category.
As a rule, their distinguishing feature is the presence of a capital foundation. During construction, all processes are accompanied by appropriate documentation.
During their construction, there are three main stages:
- survey work,
- design work,
- commissioning works,
- installation of real estate.
It is believed that capital construction objects include independent buildings that are equipped with the necessary equipment, means of communication, etc.
Capital buildings include both finished objects and unfinished construction, the construction process of which has been suspended in accordance with the law.
What are the types
When constructing buildings for capital construction projects, design and estimate documentation is drawn up and maintained.
Legal conflicts often arise regarding the issue of classifying buildings as capital or temporary. To avoid or resolve them, it is necessary to resort to a number of regulations.
It is advisable to refer to these acts before the construction of a building begins in order to avoid further conflicts with government officials and other persons whose rights may be violated during the construction of an unauthorized structure.
How to prove the degree of relationship during inheritance, read here.
Redevelopment and refurbishment
Redevelopment is a change in the configuration of a room, requiring changes to the technical passport.
Examples of redevelopment: relocation, dismantling, construction of partitions or doorways.
Redevelopment, also known as re-equipment , is the installation, replacement or transfer of utility networks or equipment that requires changes to the technical passport.
Examples of reconstruction (re-equipment): replacing a gas stove with an electric one and vice versa, moving heating and gas appliances.
If as a result of reconstruction (re-equipment) a new property does not arise , Article 222 of the Civil Code does not apply.
New facility after reconstruction
Whether a new object emerges as a result of reconstruction is not an easy question; the answer depends on the specific situation.
If, as a result of reconstruction , the parameters of the building have changed, for example, the area has increased or another floor has been added, it will be considered a new object.
As an object of law, the building will remain the same: the location address and cadastral number will not change - no new right will arise.
However, the expanded facility will differ from the original in size, area, number of floors, and layout.
In fact, it will be a different building, a new object
If, during the reconstruction, the load-bearing structures of the building were only replaced or restored, then there is no reason to consider it a new object.
At the same time, replacing such structures with similar ones or with improved performance is not at all a reconstruction.
What is considered a new object if it has been added?
If the reconstruction was carried out in the form of an extension, then the structure in its already reconstructed form is considered a new object.
The extension itself ≠ a new object
Original property + extension = new property