Landscaping is a set of measures that are carried out with the aim of creating an attractive appearance of the local area and improving environmental conditions. During the landscaping of the territory, paths are paved, architectural forms are constructed and flower beds and flower beds are formed that correspond to a certain style.
Normative base
The term “site improvement” was introduced into the legislative framework relatively recently. We are talking about Federal Law No. 131-FZ of October 6, 2003 “On the general principles of organizing local self-government in the Russian Federation.” One of its points mentions activities that are carried out with the following goals:
- maintaining territories in proper condition, taking into account various standards;
- increasing the comfort of living;
- placement of objects and structures on the ground in accordance with the project.
The list of objects to be improved includes: municipal and private courtyards, neighborhoods, sites and other areas.
Also worthy of attention is Order No. 613 from the Ministry of Regional Development of Russia, which was approved on December 27, 2013. It lists the basic rules for caring for surrounding areas. Thus, one of the paragraphs states that landscaping is work that is carried out to achieve the following tasks:
- proper preparation of engineering systems;
- lighting planning;
- installation of architectural forms and monuments on the territory;
- establishing security and carrying out landscaping activities.
Landscaping of the territory is carried out using various elements, which include vegetation, small architectural forms, temporary and permanent buildings, decorative elements, as well as information and advertising stands.
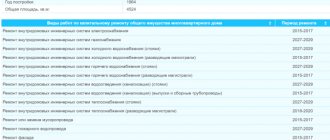
List of landscaping works and frequency of their implementation
3.1. Owners or other owners of land plots are obliged to ensure timely and high-quality cleaning and cleaning of these land plots in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the Penza region, Rules and other municipal legal acts.
The organization of cleaning of other territories is carried out by the administration in accordance with an agreement with persons entrusted with the authority to clean the territory (hereinafter referred to as a specialized cleaning organization), within the limits of the funds provided for these purposes in the settlement budget.
3.2. Cleaning of the territory of the settlement on streets with traffic is carried out at night from 23:00 to 07:00, on other streets - during the day, in case of force majeure circumstances (emergencies, natural disasters) - around the clock.
Cleaning of public places is carried out throughout the day.
3.3. Removal of chipped asphalt during road repair work is carried out by the organizations carrying out the work: on streets with moving traffic - immediately (during the work), on other streets and in courtyards - within 24 hours.
3.4. The removal of debris from the demolition (trimming) of green spaces is carried out by organizations carrying out work on the demolition (trimming) of these green spaces.
Garbage from the demolition (trimming) of green spaces from street areas is removed within 24 hours.
Stumps remaining after the demolition of green spaces are removed within ten days.
Fallen trees are removed by owners or other occupiers of the territory immediately from the roadways, sidewalks, from live wires, facades of residential and industrial buildings, and from other territories - within 6 hours from the moment of discovery.
3.5. Work on the maintenance of improvement objects includes:
1) daily inspection of all improvement elements located on the relevant territory;
2) elimination of damage to individual landscaping elements within 3 months from the date of discovery;
3) measures for caring for trees and shrubs, lawns, flower beds;
4) carrying out sanitary cleaning of ditches, pipes, drainages intended for drainage of storm and groundwater from debris once in the spring (after the snow melts) and then as it accumulates (from two to four times every three months);
5) cleaning of small architectural forms and elements of external landscaping (fencing) as they become dirty, painting and (or) whitewashing if there are defects in the paintwork covering more than 30% of the total area, but at least once a year;
6) daily cleaning of the territory (washing, sweeping, removing snow, ice, carrying out other technological operations to keep amenities clean);
3.6. Repair work (current, capital) of improvement facilities includes:
1) restoration and replacement of road surfaces, driveways, sidewalks and their structural elements;
2) installation, replacement, restoration of small architectural forms and their individual elements;
3) installation of containers, trash cans in accordance with sanitary rules and regulations;
4) repair and restoration of destroyed fences and equipment of sports and children's playgrounds;
5) restoration of outdoor lighting objects, painting of outdoor lighting poles;
6) demolition of dry, emergency and loss of decorative trees and shrubs with uprooting of stumps, planting trees and shrubs, reseeding lawns, sanitary pruning of plants, removal of growth, cutting and booking of hedges, treatment of wounds;
3.7. Work to create new improvement facilities includes:
1) landscape work: installation of surface coverings (including the use of paving slabs), paths, parking lots, platforms, installation of small architectural forms (sculptural-architectural and monumental-decorative compositions, installation of flower beds and lawns, decorative ponds, monuments, devices for design of mobile and vertical landscaping, water features) and external landscaping elements (fences, lawn fences);
2) work to create green areas: planting trees and shrubs, creating hedges and other work in accordance with project documentation developed, agreed upon and approved in the prescribed manner;
3) measures to create outdoor lighting facilities and artistic lighting design for the settlement;
4) work related to the development of soil, temporary disruption of the improvement of the territory of the settlement, which is carried out in accordance with the requirements of regulatory legal acts regulating the implementation of construction and repair work, after notifying the authorized local government bodies of the settlement at the place of work.
When designing objects for improving the living environment, streets and roads, cultural and public service facilities, provision is made for the accessibility of the environment of settlements for people with limited mobility, including equipping these objects with elements and technical means that facilitate the movement of people with limited mobility.
The improvement of the pedestrian zone (pedestrian sidewalks and bicycle paths) is carried out taking into account the comfort of staying in it and accessibility for pedestrians with limited mobility.
3.8. The administration of the working settlement of Mokshan, Mokshansky district, organizes the involvement of citizens in carrying out, on a voluntary basis, work on cleaning, landscaping and landscaping the territory of the settlement.
3.9. In accordance with climatic conditions, the period for winter cleaning of the settlement territory is set from October 15 (inclusive) to April 15 (inclusive).
3.10. Winter cleaning involves work to remove snow and snow and ice formations. This work is carried out in the morning before the start of vehicle movement and as necessary during the day.
3.11. Laying freshly fallen snow in shafts and heaps is permitted on streets, squares, embankments and public gardens with mandatory removal.
3.12. Snow removal is carried out by sweeping, raking, loading and removal to places determined by the authorized local government body of the settlement.
3.13. The priority measures for winter cleaning of roadways of local roads, streets, and sidewalks include:
1) treatment of the roadway with anti-icing materials;
2) raking and sweeping snow;
3) formation of a snow bank for subsequent removal;
4) making breaks in snow banks at intersections, at passenger transport stops, building entrances, exits from courtyards, and parking lots.
3.14. The second stage activities include:
1) snow removal (removal);
2) cleaning road trays after removing snow; ice chipping and removal of snow and ice formations.
3.15. Snow and ice removal on sidewalks and roadways is carried out by specialized organizations. Snow and chipped ice are transported to snow storage areas determined by the Administration of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
3.16. The technological operation of sweeping snow requires the following requirements:
1) mechanized sweeping of the roadway should begin when the height of the loose snow mass on the road surface is more than 3 cm;
2) during prolonged snowfall, cycles of mechanized sweeping of the roadway are carried out constantly;
3) in case of continuous snowfall during the day, constant operation of snow removal machines on the streets must be ensured;
4) after completion of mechanized sweeping, the roadway is cleared of snow and ice.
The technological operation of forming snow banks is that the snow, cleared from the roadways of streets and driveways, as well as sidewalks, is shifted into the tray part of the streets and driveways for temporary storage of the snow mass.
3.17. The technological operation of removing snow and clearing trays involves removing snow from streets and driveways in two stages:
1) priority (selective) removal of snow from public transport stops, above-ground pedestrian crossings, from bridges and overpasses, public places (markets, hotels, train stations), entrances to the territory of healthcare institutions and other socially important facilities is carried out within 24 hours after end of snowfall;
2) final (complete) snow removal is carried out after the completion of primary removal.
3.18. Snow cleared from courtyard areas and intra-block driveways is stored in these areas in such a way that the passage of vehicles, pedestrian movement and the safety of landscaping elements are ensured.
3.19. Snow cleared from paths and alleys of parks and squares is stored on paths, alleys or lawns in such a way as to ensure unhindered pedestrian movement.
3.20. After the formation of a snow bank, the following work is immediately carried out:
1) clearing passages in shafts at pedestrian crossings with a width of at least 2 m and in a quantity sufficient for the passage of pedestrians;
2) clearing or loading snow banks at public transport stops to a width of at least the length of one vehicle, and on pedestrian paths to the width of the crossing;
3) clearing or loading snow at intersections and entrances to courtyards, near vehicle parking areas.
3.21. Loading and removal of snow begins after the formation of a snow bank. The order of snow removal from streets is determined by the category of the street.
3.22. Winter cleaning work to clean sidewalks during snowfall (moving and sweeping snow) is carried out at the frequency indicated in Table 1.
Table 1
| Pavement class | Frequency, hours, at air temperature degrees Celsius | |
| Below - 2 °C | Above - 2 °C | |
| 1 | In 3 hours | In 1.5 hours |
| 2 | In 2 hours | After 1 hour |
| 3 | After 1 hour | After 0.5 hours |
3.23. The removed snow should move from the sidewalks onto the roadway into the runway strip.
Snow moved from intra-block driveways should be placed in piles and shafts located parallel to the curb stone, or stored along the driveway using, as a rule, rotary snow blowers.
On sidewalks more than 6 m wide, separated by lawns from the roadway, it is allowed to move snow onto a shaft in the middle of the sidewalk for subsequent removal.
Work on laying snow in shafts and piles must be completed on class 1 and 2 sidewalks no later than 6 hours after the end of the snowfall, and in other areas no later than 12 hours.
3.24. Sections of sidewalks covered with compacted snow should be removed as soon as possible, as a rule, with compacted snow rippers. Raking and cleaning of chips should be done simultaneously with chipping or immediately after it and stored together with the snow.
Snow during manual cleaning of sidewalks and intra-block (asphalt and cobblestone) driveways must be completely removed. In the absence of improved surfaces, snow should be removed, leaving a layer of snow for subsequent compaction.
3.25. If slipperiness occurs, treatment of sidewalk road surfaces with a sand-salt mixture should be carried out at a rate of 0.20.3 kg/sq. m.
The time for treating road surfaces with a sand-salt mixture in priority areas should not exceed 1.5 hours from the moment the formation of winter slipperiness is detected.
3.26. To prevent snow and icicles from falling from the roofs of non-residential buildings, roofs must be cleared of freshly fallen snow if its layer is more than 10 cm, with the mandatory use of precautionary measures to ensure the safe movement of pedestrians and the safety of trees, bushes, and signs. Snow and ice thrown from roofs must be removed immediately upon completion of the dumping.
3.27. Cleaning the tray area in winter should include:
1) clearing the top of the curb for the snow loader to pass through;
2) clearing the area to the curb after the snow loader passes and forming a snow bank;
3) upon the onset of a thaw, immediate and constant clearing of storm drain grates to ensure constant drainage of melt water.
3.28. During winter cleaning the following is not allowed:
1) dumping or storing snow on the roadway;
2) the release of snow through the fences of bridges and overpasses.
3.29. In accordance with climatic conditions, the period for summer cleaning of territories is set from April 16 to October 14.
3.30. The main task of summer cleaning is to remove pollution that accumulates on the territory of the settlement and leads to dust in the air and deterioration of the aesthetic appearance of the settlement territory.
3.31. During the transition from winter to summer cleaning, the following types of work are carried out:
1) cleaning lawns from branches, leaves and sand accumulated over the winter, washing lawns;
2) cleaning of the chute area, roadway, sidewalks, loading and removal of collected waste (dust, sand) to a garbage dump;
3) washing and clearing grooves to ensure the outflow of water in places where it is required for the normal drainage of melt water;
4) systematic removal of melt water to manholes and receiving wells of storm sewers;
5) cleaning of dirt, washing, painting of bridge fences, overpasses, road signs;
6) general cleaning of courtyard areas after the snow melts, garbage collection.
3.32. Summer cleaning of areas includes:
1) sweeping the roadway of roads, bridges, overpasses, sidewalks, intra-block areas;
2) cleaning up pollution from lawns, parks, squares;
3) removal of waste (dust, sand), pollution, leaves to a landfill.
3.33. Sweeping is carried out at the following times:
1) roadways - around the clock, as pollution accumulates;
2) courtyard, adjacent and intra-block areas - daily until 7 a.m. and then as needed.
3.34. The frequency of summer sidewalk cleaning depends on the intensity of traffic on the sidewalk and is indicated in Table 2.
table 2
| Pavement class | Frequency of cleaning work |
| 1 | Once every two days |
| 2 | Once a day |
| 3 | Twice a day |
3.35. Cleaning of vacant lots and areas adjacent to railway tracks and roads within the boundaries of the settlement is carried out regularly, as they become clogged, but at least once every six months.
3.36. Lawns, parks and public gardens are cleaned weekly.
Paths and areas of parks and squares must be cleared of debris, leaves and other visible contaminants.
3.37. Removal of waste (garbage, dust, sand) from the chute area is carried out by mechanized sweeping with special transport, as well as raking it into piles using mechanisms or manually with further loading of the waste and transporting it to specially designated areas.
3.38. To avoid stagnation of rainwater, the gratings of rainwater wells must be constantly cleaned of debris (debris, dust, sand), leaves and other contaminants.
3.39. During leaf fall in areas of lawns, parks, and public gardens, daily cleaning of leaves is required.
3.40. Cleaning the tray area in the summer should include:
1) daily cleaning and sweeping of the tray area by removing debris (garbage, dust, sand);
2) keeping the gratings of storm sewer wells always clean.
3.41. During summer cleaning the following is not allowed:
1) dumping waste (garbage, dust, sand) onto green spaces, into inspection wells, storm sewer wells and rivers;
2) throwing garbage, grass, leaves onto the roadway and sidewalks when cleaning lawns;
3) removal of waste (garbage, dust, sand) to places not designated for this purpose.
3.42. Activities aimed at improving public highways, elements of the development of public highways, are carried out to the extent that does not contradict the Federal Law of November 8, 2007 No. 257-FZ “On highways and road activities in the Russian Federation and on introducing amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation" and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation and regulatory and technical documents establishing requirements for public roads.
The improvement and maintenance of public roads of local importance are carried out by legal entities or individuals with whom a contract for their maintenance (maintenance) has been concluded, and in the absence of a contract for maintenance (maintenance) - by the owners of the roads.
3.43. In order to preserve road surfaces on the territory of the settlement, it is not allowed:
1) transportation of cargo by dragging;
2) during loading and unloading operations on the streets, dropping rails, logs, iron beams, pipes, bricks, and other heavy objects and storing them;
3) driving tracked vehicles along the streets of populated areas with hard surfaces;
4) movement and parking of heavy vehicles on intra-block pedestrian paths and sidewalks.
3.44. Current and major repairs, maintenance, construction and reconstruction of public roads, bridges, sidewalks and other transport engineering structures in the settlement (except for public roads, bridges and other transport engineering structures of federal and regional significance) are carried out by specialized organizations under contracts with Administration of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
3.45. Operation, current and major repairs of traffic lights, road signs, markings and other traffic safety facilities are carried out by specialized organizations under contracts with the Administration of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
3.46. Road surfaces are designed taking into account current building codes and regulations, ensuring the safe movement of vehicles and pedestrians, without cracks and potholes, potholes and depressions, with serviceable drains.
3.47. Pedestrian fencing must be kept in good condition, damage must be repaired immediately (within 24 hours from the moment of discovery).
3.48. Excavation work carried out by individuals and legal entities on the territory of a settlement without permission provided by the administration in the manner established by the decision of the Local Government Committee of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district, Penza region; after the expiration of the permit; failure to restore the improvement of the territory after excavation work within the period specified in this permit, if these actions are not violations specified in Article 3.1 of the Law of the Penza Region of 02.04.2008 No. 1506-ZPO “Code of the Penza Region on Administrative Offences”, entails administrative liability, provided for by this law.
The procedure for carrying out excavation work carried out within the boundaries of the territory of cultural heritage sites, protection zones of cultural heritage sites in order to preserve cultural heritage sites or its individual elements, preserve the historical, urban planning or natural environment of a cultural heritage site is regulated by Federal Law No. 73- dated June 25, 2002. Federal Law “On objects of cultural heritage (historical and cultural monuments) of the peoples of the Russian Federation.”
3.49. Public transport stops must be kept clean and in good condition.
3.50. Cleaning of large objects that have fallen onto the roadway is carried out in two stages by the owners or other holders of these territories:
1) at the first stage - cleaning is carried out immediately to ensure smooth and safe traffic movement;
2) at the second stage - within 24 hours the fallen objects are removed to designated places.
3.51. Owners or other owners of land plots are obliged to ensure the protection and reproduction of green spaces located on these plots.
3.52. Pollution of green spaces, lawns and flower beds with garbage, construction materials, sewage and other emissions that are harmful to plants is not allowed.
3.53. The organization of landscaping of the territory of settlements is carried out by the Administration of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
The use, protection, protection and reproduction of urban forests, forests of specially protected natural areas of local importance located within the boundaries of settlements, as well as the implementation of municipal control in the field of protection and use of forests of specially protected natural areas of local importance is carried out by the Administration of the working village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
3.54. Urban planning activities are carried out based on the principle of maximum preservation of green spaces in the settlement.
3.55. Individuals and legal entities are obliged to take measures to preserve green spaces and not allow illegal actions or inactions that could lead to damage or destruction of green spaces.
3.56. Individuals and legal entities are obliged to take measures to compensate for green spaces in the event of demolition, destruction or damage to green spaces.
3.57. When carrying out construction, reconstruction, and repair work on capital construction projects, the person carrying out the work is obliged to:
1) take measures to ensure the safety of green spaces that are not subject to demolition;
2) install temporary tree trunk fencing for preserved trees in the form of solid panels 2 m high;
3) to preserve the root system of trees located closer than 3 m from construction, reconstruction, and major repair projects, arrange a flooring of boards with a radius of at least 1.6 m around the tree fencing;
4) when laying underground communications, ensure the distance between the edge of the trench and the root system of the tree is at least 3 m, and the root system of the bush is at least 1.5 m;
5) when carrying out work using the method of horizontal drilling in the root zone of trees and shrubs, work should be carried out below the location of the skeletal roots, but not less than 1.5 m from the soil surface;
6) when asphalting, paving roads and sidewalks, observe the dimensions of the near-trunk soil zone: around trees - 2 x 2 m, around bushes - 1.5 x 1.5 m;
7) felling (transplanting), rejuvenating pruning of landscaping elements, including those falling on the construction site, laying underground communications, roads, installing power lines and other structures is carried out only after the provision of a felling ticket and (or) permission to replant trees and shrubs from the Worker's Administration village of Mokshan, Mokshansky district.
3.58. Lawns are mowed and weeds are mowed down to a height of 3–5 cm when the grass reaches a height of 10–15 cm. The mown grass must be removed within 12 hours.
3.59. Watering of green spaces on landscaping objects is carried out in the morning no later than 8 - 9 o'clock or in the evening after 18 - 19 o'clock.
3.60. Owners or other owners of power lines ensure timely pruning of branches under power lines.
3.61. Branches covering signs for street names and house numbers, road signs, traffic lights, intersection visibility triangles are cut off by persons responsible for the maintenance of the relevant areas.
3.62. All green spaces, as well as landscape and architectural objects of green areas of general, limited use and special purpose, located within the settlement, having established boundaries and provided for use (possession, disposal) to individuals or legal entities are subject to inventory.
During the improvement of the territory, the following work is carried out:
- arrangement and repair of pedestrian paths (coating the road with asphalt, paving stones and tiles);
- landscaping;
- cleaning the area from dirt, debris, snow, branches and leaves, followed by removal of garbage and waste;
- Sprinkling slippery surfaces with sand;
- care of decorative elements and structures;
- arrangement of fences and fencing;
- installation of lighting lamps and benches;
- construction of monuments.
The maintenance of squares, parks and green areas in proper condition, as well as landscaping of adjacent areas should be carried out by the relevant municipal organizations, however, this work can also be carried out privately, using the services of specialized companies.
What part of the land plot is the property of the house owner
To clearly understand the boundaries of his property, the owner of a private house must learn how to define these zones. There is nothing difficult about this process.
Plan of the boundaries of the land plot of a private house
It is enough to simply study in detail the cadastral passport, which fully describes the limits of the land plot that are the property of the owner of the real estate.
On the territory of his plot, the owner can carry out any transformations, organize a personal plot, in the space of a house and land plot, the owner can implement any project that is convenient for a comfortable life for a private owner. The main thing is that all actions meet the prescribed standards and requirements of legislative projects.
Improvement of the territory - key tasks
Land improvement is a whole range of activities, the main purpose of which is to improve the quality of life of people and ensure order. All work is carried out to ensure that the area is maintained in a pleasant, well-groomed appearance. Improvement also includes activities related to the cultivation of various natural areas. Thanks to this approach, it is possible to properly design the territory without causing any damage.
Landscaping of the site is aimed at improving conditions for recreation and life, implying the following:
- optimal living conditions, taking into account aesthetic needs - the site should look attractive and neat;
- optimal design of the territory - all decorative elements are decorated in the same style, the space is highly functional and harmoniously combines with the surrounding nature.
To achieve such goals, you need to be well versed in various subtleties. Not everyone can cope with this task on their own, so it is better to take professional help. Our company’s specialists provide high-quality services for landscaping local areas, parks and public gardens.
What is included in the improvement of the city: goals, objectives and basic rules
Street improvement of urban areas is a set of measures aimed at creating and maintaining the urban environment in a functional, environmentally friendly, aesthetic and informative state. It affects public spaces of the city, residential and recreational areas. They all have their own landscaping features, but in most cases the work follows the same scenario:
- The relief, soil type and other features of the site are examined.
- A project is being developed that determines the types, volumes and costs of work.
- Work is underway with the relief: soil is being developed, communications are being laid, territories are being zoned, etc.
- Coverings are laid, lighting is organized, roads and paths are laid.
- Work on landscaping and landscaping is underway.
- Design elements for the urban environment are being installed.
Site maintenance - basic work
Thoughtful design of the local area, taking into account the real needs of the owners, makes living on the site much more comfortable. A unique atmosphere of comfort is created. It is important to understand that even before starting various work to improve the area, it is necessary to complete various construction works:
- install communications - water supply, drainage, sewerage;
- build various additional facilities on the site. structures;
- clear the site of construction waste and debris;
- carry out the installation of fencing elements for the territory, thanks to which the possibility of unauthorized persons entering the site will be minimized, as well as a decorative function will be implemented. An equally important factor is the division of property boundaries between the owners of neighboring plots;
- establish a route grid on the site, highlighting an area for recreation;
- consider the optimal location of parking spaces for vehicles and a playground.
When carrying out landscaping work, it is very important to analyze and take into account the needs of a particular family. Every effort must be made to ensure comfort for adults and children.
All of the above work requires a responsible approach, the availability of specialized tools, knowledge, effort and time. In this regard, most people order such services from companies specializing in landscape design. Experts will analyze your requirements and offer different design options for your local area, taking into account the terrain, climate and other factors.
Who can own the local area?
Depending on whether the land plot outside the fence is privatized or whether it is not the property of the owner of private houses, the powers to dispose of this plot are determined. The land located outside the fence may belong to:
- A person who is the owner of a private house.
Sample certificate of registration of real estate ownership - Municipal district services that carry out cleaning of the local area, as well as the opportunity to use this area for personal interests.
If the land plot belongs to the owner of the house
If the adjacent area is registered to the owner, then his responsibility is as follows:
- To carry out the improvement of land plots located outside the perimeter of the private sector using our own resources.
- If the owner is the owner, he is also responsible for lighting the local area, without the right to demand that municipal services fulfill this mission.
- Landscaping of the local area is also required by the owner of a private house.
- The owner of the land plot is also responsible for the cleaning and aesthetic appearance of the site.
A complete list of the rights and obligations of the owner to whom the local area is registered can be studied by reading the Land Code; everything is described in detail in this legislative document.
It is imperative to know these rights and responsibilities in order not to encounter difficulties and to fully understand whether it is really necessary to spend time on registering the land plot of the local area as personal property.
Owner municipal service
If the land plot located outside the fence does not belong to the owner of a private house, the district municipal service has full rights to dispose of the space. The responsibilities of the structure are:
- Ensure proper lighting of the local area;
Example of lighting for the local area of a private house - On the territory of the land located outside the fence, municipal services have the right to install video surveillance devices aimed at the central alleys, if this is necessary for the safety of residents of the locality;
- Also, the municipal service has the authority to landscape design a given section of land at its discretion;
- If the area located outside the fence belongs to the district service, then this structure is obliged to ensure order in this territory;
- Landscaping and beautification of the local area, as well as municipal services, can be carried out at their discretion.
The rights of the municipal service can also be found out in detail by reading the land code. Everything is clearly and comprehensively described in it.
Gazebos in the yard
You can buy a gazebo ready-made, today this is not a problem. But, often they build it themselves, because this way they have the opportunity to bring their fantasies and ideas to life. Structures can be open, closed, attached to a building, for example, to the wall of a house or to the wall of a summer kitchen.
To create closed gazebos, polycarbonate is used, the service life of which is up to 50 years.
The following options for gazebos are installed in the garden:
- Open buildings. They are practical and simple, built from supports (wooden, metal, brick) and a canopy.
- Closed gazebos, more similar to garden houses. They house a barbecue stove, which will warm the gazebo on cold days.
- “Living” frame gazebos covered with climbing crops ,
such as roses or ivy. - And a chic option is to build a barbecue.
- Photo of the patio:
How to arrange a gazebo inside, it all depends on the design, area and purpose. When a fireplace is built in the gazebo, a second zone is also set up - a dining room with pieces of furniture.
Package of documents for registration of property rights
In order to legally correctly register the territory adjacent to the house, you need to find out how many and what documents should be submitted to the municipal district service of the district or city. Regardless of whether parking is planned in the local area or the owner of a private house simply wants to expand the boundaries of the property, it is necessary to submit the following package of documents:
Example of registration of parking on private territory
- Civil passport and its photocopy to leave at the appropriate service.
- Taxpayer identification code.
- Cadastral passport for the private sector.
- Documents confirming ownership of real estate.
- A statement indicating the reasons why the relevant services are required to make a decision on the registration of a land plot located outside the fencing of the applicant’s property.
When the package of documents is accepted for work, the authorized services announce to the applicant the review period. When this deadline approaches, the owner of the land plot needs to submit documents for privatization of the land plot. The video describes the process of determining the boundaries of the local area.
How the territory can be used
The adjacent area, which is registered to the owner of a private plot, can be used for the following purposes:
- To ensure proper lighting of the living area;
- You can also decorate the above part of the land with various landscape ideas or place beautiful decorative elements;
- Parking can be arranged in the local area;
- Also, owners of a private house can use the local area to arrange parking lots for public use. In this case, you need to obtain a number of documents prescribed by law that give the right to such use of the land plot;
- The territory of the local area, previously beautified by municipal services, can be remade at your discretion;
Option for installing paths on site - Also, with the help of the influence of the local area in the total area, a new layout of the land plot located near a private house can be implemented;
Option for planning a plot near a private house - Many people use the adjacent land to increase comfort. For example, they set up a bench, swing or stools near the fence, on which you can relax while communicating with neighbors in the area;
- And also some, instead of decoration, use the territory of the local area for storing firewood and building materials.
Everyone is free to decide how to organize the space.
Organizing space in the backyard
And also, the owner of the property will be able to decide whether their local area belongs to a useful area or a piece of land that will be developed after registration of ownership. In any case, registration of the property adjacent to the house is an excellent opportunity to arrange beautiful flower beds and devices for illumination of the necessary areas of the garden or garden.
An example of finishing and landscaping a recreation area
The adjacent territory of a private house, photo boundaries, which can be seen on various resources, opens up wide opportunities for the owner of the land plot. The main thing is to understand who should assist in the process of registering a piece of land.
Stages of landscaping
In order to achieve significant results in the cultural and aesthetic improvement of the territory with plants, it is necessary to perform the following stages of landscaping:
- Planting large trees and shrubs. This will prevent damage to the lawn and small plants.
- Arrangement of flower beds and flower beds. Flowers are selected taking into account preferences, climatic conditions and soil capabilities, drainage system, and care.
- Lawn installation . The final stage of landscape work, creating a finished look.
As a rule, landscaping is carried out on a pre-prepared area according to a specially developed project.
Installation of fencing around the building
According to clause 2.5.1 of Methodological Recommendations No. 613 , for the purpose of landscaping on the territory of a municipality, it is recommended to provide for the use of various types of fencing, which differ:
- by purpose (decorative, protective, combination thereof);
- in height (low – 0.3 – 1.0 m, medium – 1.1 – 1.7 m, high – 1.8 – 3.0 m);
- by type of material (metal, reinforced concrete, etc.);
- according to the degree of permeability to view (transparent, deaf);
- by degree of stationarity (permanent, temporary, mobile).
In accordance with OKOF, fences are taken into account as part of fixed assets (code 12 3697050 “Metal fences”, all others refer to code 12 4540000).
Thus, by virtue of Instructions No. 65n, expenses for paying third-party organizations for the construction of fences should be attributed to Article 310 “Increase in the cost of fixed assets” of KOSGU. Constructed objects – fences – are accounted for in account 101 13 “Structures – immovable property of the institution.”
Let us note that Instruction No. 183n does not contain any features of accounting for the costs of erecting fences, therefore their initial cost is formed using account 106 01 “Investments in fixed assets” ( clause 130 of Instruction No. 157n ).
An autonomous institution entered into a state contract for the production and installation of metal fencing (fence) on the territory of the institution for a total amount of 236,000 rubles. (including VAT - 36,000 rubles). The terms of the concluded contract provide for payment of an advance in the amount of 30% of the contract value (RUB 70,800). The work performed will be paid for through a subsidy allocated for the implementation of the state task.
In accordance with Instruction No. 183n, in the accounting records of the institution, the expenses that form the cost of the fence will be reflected as follows:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| An advance payment was made to the contractor in the amount of 30% of the contract value | 4 206 31 000 | 4,201 11,000 Off-balance sheet account 18 | 70 800 |
| The costs of manufacturing and installation of fencing are reflected | 4 106 11 000 | 4 302 31 000 | 236 000 |
| The previously transferred advance was offset | 4 302 31 000 | 4 206 31 000 | 70 800 |
| The installed fencing has been accepted for accounting | 4 101 13 000 | 4 106 11 000 | 236 000 |
| The debt to the contractor for the installed fence has been repaid | 4 302 31 000 | 4 201 11 000 Off-balance sheet count 18 | 165 200 |
How to prepare and implement a yard landscaping project
To prepare and implement the project, it is necessary to create an initiative group from among the residents. They will have to solve the following questions:
- Study the legislative framework, find out about existing programs for assistance in the design of courtyard areas, and calculate the expected costs.
- Think about what issues need to be brought to the general meeting of owners (GMS).
- Establish a period during which residents can submit their proposals for improvement.
- Collect and review the proposals received and organize a second OCC to approve them.
- Engage in the development of technical specifications for the development of local land, search for contractors, and a source of financing.
At the next OSS, the final project and the estimate for improvement are approved.
If it is possible to receive assistance from the state, all owners sign an application for inclusion in the program, according to the model approved by the city administration. Attached to it is a drawing with planned objects marked.
When do you need SRO membership?
Landscaping with the help of SRO membership is necessary in cases where the beautification activities are related to the safety of construction projects on the site. The entire list of such events is prescribed in the Letter of the Ministry of Regional Development of Russia dated August 31, 2010 N 31330-IP/08. This category includes:
- Asphalted surface.
- Construction of fences necessary for the safety of the protected object.
- Construction of roads.
SRO membership is also required if a construction contract has been concluded between the developer and the owner of the property. If it states an amount exceeding 3 million rubles, then the performer of the work is obliged to become a member of the SRO.
Gate to the territory of a private house
Any area is fenced. And the fence should not only serve as a fence, but also be a reliable, durable and beautiful structure.
For the gates of a private estate, the following options are used:
- fences can be original, expensive, made to order according to an individual project;
- modern shutter gates with an automatic mechanism;
- classic fencing.
Gates are built from different materials. Some people also like wooden ones, like in this photo: