Search by coordinates on the map through a browser using the Google Maps service
If for some reason you prefer to work not with simplified services, but directly with Google Maps, then these instructions will be useful for you. The process of searching by coordinates through Google Maps is a little more complicated than in the methods described earlier, but it can be mastered quickly and without much difficulty.
To find out the exact coordinates of a place, follow these simple instructions:
- Open the service on your PC. It is important that the full mode must be turned on, and not the light mode (marked with a special lightning icon), otherwise it will not be possible to obtain information;
- Click on the section of the map where the item or point you need is located, with the right mouse button;
Advantages of dual GPS/GLONASS geopositioning
If you determine your position using 2 systems at once, then there are several advantages of this solution:
- The ability to obtain data with minimal error. For example, in the north of Russia, GLONASS is suitable for measurements, but GPS will help for navigation in the central part of the country.
- Since these systems are military, it happens that one of them is inaccessible, then the second one will help out. They are interchangeable.
- Flexibility. In some areas the American version will be better, in others - the Russian one.
Now you know how GLONASS differs from GPS.
The era of space has arrived. And near-Earth space is used not only for research, but also to assist in navigation, land surveying and other needs. The main thing is to know about the accuracy of each system, how GPS works and use them correctly.
Positioning accuracy
When determining coordinates, the error of GLONASS is 2–6 meters, for GPS it is 2–4 m. The operation of systems is influenced by a number of factors.
Factors of influence
The accuracy of GLONASS and GPS is influenced by 6 factors:
- Ionosphere and troposphere. As the signal passes through these layers, it slows down greatly. And if there are also solar flares or “disturbances” in the ionosphere, then accuracy becomes practically unattainable.
- Noise from navigation receivers.
- Errors in satellite clocks.
- Multipath reception.
- External interference from other devices.
- Location. As satellites move in orbit, their location can affect accuracy. Some may not be available at all in some regions.
These factors relate only to the work of the satellite, but there are also those that are related specifically to the person:
- The quality of the GPS module in an electronic device.
- The location of a person in space. Distortions and reflections are created when staying near structures or indoors.
- Driver in the OS in the smartphone.
Differential correction system
Since the operation of the satellite is influenced by several factors, a correction system was invented - SDCM. What it consists of is shown in the table.
| Component | Target |
| Network of measurement collection stations. There are about 56 of them in Russia | Collection of primary information from a mobile satellite and sending it to the processing center |
| Data center or data center | They record and correct the error (those 2–6 m) and ensure delivery of information to the user |
| A complex for delivering data to the consumer, consisting of fixed satellites and several stations on the ground | On Earth, at special stations, data is processed and sent to special non-rotating satellites, which transmit certain coordinates to humans |
Above, the entire system is shown in a simplified form for ease of understanding; in fact, it includes dozens of stations, employing thousands of specialists. And all in order to increase the accuracy of navigation systems to 10–20 cm.
QZSS, a Japanese system, operates together with GPS, thanks to which the error in data transmission is reduced.
How to improve accuracy
Some areas of life, such as geodesy, do not tolerate errors in accuracy. A person himself can take a number of measures to reduce the likelihood of error:
- Install the GPS Test application. It will show the number of satellites available for use by the module, tell you about the probable error and signal quality. Based on this data, specific steps are taken to eliminate the problem.
- In the “Location” tab in the smartphone settings, select “Geolocation”. Some phones have the “Detect More Accurately” function. In the same settings, you can “help” the geomodule by allowing it to use data from Bluetooth and Wi-fi.
- Calibrate the compass in the device. This will update the geolocation signal.
- Use external, additional antennas to receive the signal.
ATTENTION. It will not help much if you are indoors, underground, or next to high-rise buildings at the time of determining the coordinates. The signal from the satellite will not only be distorted, but also reflected. Because of this, accurate geolocation will be impossible.
Satellite monitoring systems
There are many options for satellite monitoring systems, for example, Galileo (European), BeiDou (Chinese). But due to the popularity and accuracy of determining coordinates, American GPS and Russian GLONASS are more used, so it is worth comparing them.
Satellite systems
GPS
When orienting using navigation systems, a signal is transmitted to a GPS satellite from a module built into an electronic device (for example, a telephone). The spacecraft “answers” and shows where the person is. However, tunnels, rooms and clouds make adjustments to the positioning accuracy, sometimes making it simply impossible.
GLONASS
GLONASS is the Russian analogue of the world famous GPS. The principle of operation is the same - the smartphone sends a signal to one of 24 satellites, which transmit the location.
IMPORTANT. The Russian system has only 24 devices in space, while the American system has up to 32, so the coverage area of the world is 70%.
How to determine the coordinates of a plot of land using a smartphone
We have all been using GPS navigation for a long time. However, it is worth understanding that telephones operate on a simplified system and do not always reflect the area as it really is. Surely you have encountered at least once the fact that the navigator periodically “goes stupid” and gets lost on the road. The same thing happens when you try to find the desired coordinate on the ground.
In phones, cell towers are usually used to improve accuracy; in fact, this leads to an error of several meters. Of course, if the plot measures tens of hectares, then this deviation is negligible, but if you want to know the area or boundaries of a plot of 5-6 acres, then the difference in fact will be colossal.
If you still decide to use your phone and use it to determine the coordinates, then use a navigation program - save or write down the geographic coordinates of each point on the ground, and then using these coordinates, find the location of the site on the public cadastral map and make sure whether the actual boundaries coincide with borders of the map.
General principles for determining coordinates
The basic principle of operation is based on radio waves sent by satellites at a constant speed. What is also important here is the time it takes for the signal to travel from the source to the receiver. It is determined by the atomic clock on the spacecraft. The speed, time and location of the satellites allow one to calculate their distance to the person requiring navigation.
IMPORTANT. Data from one device is not enough. For maximum accuracy, at least 4 devices are required, located in different locations.
The intersection of the signal of 4 or more satellites allows you to determine where a person is with a minimum error. Some navigation programs also take into account the distance to cell towers, data from the built-in compass and accelerometer, and even the speed of the person requesting coordinates. But no matter what technology is used, there are many factors that influence how positioning works.
GPS and GLONASS satellite orbits
Geographic coordinates of some cities in Russia and CIS countries
| City | Latitude | Longitude |
| Abakan | 53.720976 | 91.44242300000001 |
| Arkhangelsk | 64.539304 | 40.518735 |
| Astana (Kazakhstan) | 71.430564 | 51.128422 |
| Astrakhan | 46.347869 | 48.033574 |
| Barnaul | 53.356132 | 83.74961999999999 |
| Belgorod | 50.597467 | 36.588849 |
| Biysk | 52.541444 | 85.219686 |
| Bishkek (Kyrgyzstan) | 42.871027 | 74.59452 |
| Blagoveshchensk | 50.290658 | 127.527173 |
| Bratsk | 56.151382 | 101.634152 |
| Bryansk | 53.2434 | 34.364198 |
| Velikiy Novgorod | 58.521475 | 31.275475 |
| Vladivostok | 43.134019 | 131.928379 |
| Vladikavkaz | 43.024122 | 44.690476 |
| Vladimir | 56.129042 | 40.40703 |
| Volgograd | 48.707103 | 44.516939 |
| Vologda | 59.220492 | 39.891568 |
| Voronezh | 51.661535 | 39.200287 |
| Grozny | 43.317992 | 45.698197 |
| Donetsk, Ukraine) | 48.015877 | 37.80285 |
| Ekaterinburg | 56.838002 | 60.597295 |
| Ivanovo | 57.000348 | 40.973921 |
| Izhevsk | 56.852775 | 53.211463 |
| Irkutsk | 52.286387 | 104.28066 |
| Kazan | 55.795793 | 49.106585 |
| Kaliningrad | 55.916229 | 37.854467 |
| Kaluga | 54.507014 | 36.252277 |
| Kamensk-Uralsky | 56.414897 | 61.918905 |
| Kemerovo | 55.359594 | 86.08778100000001 |
| Kiev , Ukraine) | 50.402395 | 30.532690 |
| Kirov | 54.079033 | 34.323163 |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 50.54986 | 137.007867 |
| Korolev | 55.916229 | 37.854467 |
| Kostroma | 57.767683 | 40.926418 |
| Krasnodar | 45.023877 | 38.970157 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 56.008691 | 92.870529 |
| Kursk | 51.730361 | 36.192647 |
| Lipetsk | 52.61022 | 39.594719 |
| Magnitogorsk | 53.411677 | 58.984415 |
| Makhachkala | 42.984913 | 47.504646 |
| Minsk, Belarus) | 53.906077 | 27.554914 |
| Moscow | 55.755773 | 37.617761 |
| Murmansk | 68.96956299999999 | 33.07454 |
| Naberezhnye Chelny | 55.743553 | 52.39582 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 56.323902 | 44.002267 |
| Nizhny Tagil | 57.910144 | 59.98132 |
| Novokuznetsk | 53.786502 | 87.155205 |
| Novorossiysk | 44.723489 | 37.76866 |
| Novosibirsk | 55.028739 | 82.90692799999999 |
| Norilsk | 69.349039 | 88.201014 |
| Omsk | 54.989342 | 73.368212 |
| Eagle | 52.970306 | 36.063514 |
| Orenburg | 51.76806 | 55.097449 |
| Penza | 53.194546 | 45.019529 |
| Pervouralsk | 56.908099 | 59.942935 |
| Permian | 58.004785 | 56.237654 |
| Prokopyevsk | 53.895355 | 86.744657 |
| Pskov | 57.819365 | 28.331786 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 47.227151 | 39.744972 |
| Rybinsk | 58.13853 | 38.573586 |
| Ryazan | 54.619886 | 39.744954 |
| Samara | 53.195533 | 50.101801 |
| Saint Petersburg | 59.938806 | 30.314278 |
| Saratov | 51.531528 | 46.03582 |
| Sevastopol | 44.616649 | 33.52536 |
| Severodvinsk | 64.55818600000001 | 39.82962 |
| Severodvinsk | 64.558186 | 39.82962 |
| Simferopol | 44.952116 | 34.102411 |
| Sochi | 43.581509 | 39.722882 |
| Stavropol | 45.044502 | 41.969065 |
| Sukhum | 43.015679 | 41.025071 |
| Tambov | 52.721246 | 41.452238 |
| Tashkent (Uzbekistan) | 41.314321 | 69.267295 |
| Tver | 56.859611 | 35.911896 |
| Tolyatti | 53.511311 | 49.418084 |
| Tomsk | 56.495116 | 84.972128 |
| Tula | 54.193033 | 37.617752 |
| Tyumen | 57.153033 | 65.534328 |
| Ulan-Ude | 51.833507 | 107.584125 |
| Ulyanovsk | 54.317002 | 48.402243 |
| Ufa | 54.734768 | 55.957838 |
| Khabarovsk | 48.472584 | 135.057732 |
| Kharkov, Ukraine) | 49.993499 | 36.230376 |
| Cheboksary | 56.1439 | 47.248887 |
| Chelyabinsk | 55.159774 | 61.402455 |
| Mines | 47.708485 | 40.215958 |
| Engels | 51.498891 | 46.125121 |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 46.959118 | 142.738068 |
| Yakutsk | 62.027833 | 129.704151 |
| Yaroslavl | 57.626569 | 39.893822 |
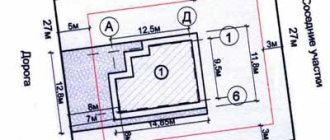
Acceptable norms of discrepancy during surveying
Legislation specifies permissible error values.
- Plots in populated areas 0.1 m
- Land SNT, private plots 0.2 m
- Agricultural land 2.5 m
When we are talking about large values that differ from the specified norms, then we are dealing with a cadastral error.
According to the law, the border can shift in any direction by a distance that does not exceed the error.
When a problem arises within the boundaries between lands of different categories, the coordinates of characteristic points are determined according to the requirements of the lands with higher accuracy. For example, in forest lands the tolerance is 5 m, and in industrial lands 0.5 m, so the border is determined by industrial lands.