In accordance with the provisions contained in the updated edition of the set of rules for urban planning, redevelopment and development of urban and rural settlements, the distance between residential buildings and other buildings must comply with accepted standards. The purpose of these rules is to increase the level of public safety in structures, as well as ensure the safety of material property, referring to Federal Law No. 384, adopted on December 30, 2009. In addition, in accordance with Federal Law No. 261, approved on November 23, 2009, rules are necessary to increase the level of compliance with the standards and requirements of current European regulations and documents through the use of a single effective method for determining operational characteristics.
This document is used in the design and reconstruction of urban and including rural settlements. It includes a list of the main significant requirements for the development of proposed territories and the layout of real estate. More specific requirements are developed by regional legislative acts in the field of urban planning.
Referring to the current standards according to SNiP, it is important not only the safety and sustainability of the health and life of citizens, but also the rational use of existing national natural resources and the healthy environment, ensuring legislative safety for cultural and including historical monuments, protecting the city from the possible adverse effects of natural and man-made disasters.
Distribution of territorial zones
Each standard used to determine the distance directly between high-rise and other buildings necessarily takes into account the distribution of territories in the city. The peculiarities of operation, intended purpose, in accordance with urban planning regulations, and the presence of environmental and sanitary zones are taken into account. Separately, territories are allocated for general use, which can be occupied by streets, driveways, squares, embankments, roads, parks, reservoirs and other objects aimed at meeting the public needs of the population. You can learn about the procedure for exploiting public land from local authorities, since they are the ones who develop regional legislative acts.
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right →
It's fast and free!
Or call us by phone (24/7):
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call us by phone. It's fast and free!
+7 Moscow,
Moscow region
+7 Saint Petersburg,
Leningrad region
+7 Regions
(toll-free call for all regions of Russia)
Urban planning activities may also be limited if there is a historical building nearby, a cultural reserve, an area where cultural and historical monuments are protected, a specially protected natural area, a coastal protective strip, an area with minerals, territory , where development is prohibited due to the possible occurrence of natural and man-made emergencies.
Zones that can be placed on the site
Recreation area. An area where a children's playground, gazebo, and playing field will be located. This area should not be near flammable materials.
Outbuildings. It is best to place them side by side for ease of use. In this area it is worth placing chicken coops, livestock pens, outdoor toilets, and sheds.
Local area. Here you should place a house, a garage, a well and all the outbuildings that will be necessary for people to live in.
Correct zoning of the territory will ensure the most favorable, and most importantly, safe residence for people near the house. For example, if the toilet is located too close to the house, an unpleasant odor will constantly be felt, and the location of buildings close to the barbecue increases the chance of a fire.
What guides the establishment of standards?
The standards that are adopted directly during the construction of real estate in the city largely depend on where exactly the planned objects are located. In urban conditions, the planning structure is formed taking into account:
- Compact placement and interconnection of land plots, certain zones, taking into account the level of their compatibility;
- Zoning and structural distribution of land in interaction with public centers and transport interchanges, utility systems;
- Effective use of territories, referring to their urban planning value;
- Comprehensive consideration of architectural traditions in urban planning, climatic conditions, and other features;
- Effective functioning, as well as development of life support systems, saving resources, protecting the environment and cultural and historical monuments;
- Natural Resources Conservation;
- Conditions to ensure that persons with disabilities have unhindered access to transport and social infrastructure.
In cities that have historical value, in order to calculate the distance between buildings, it is necessary to take into account that the planning structure and architectural appearance of a given locality cannot be changed.
Construction legislation
Currently, everyone who wants to build a building on their site must be guided by the SP (set of rules). To understand at what distance houses can be built, you should familiarize yourself with SP 4.13130.2013. It sets out fire protection standards for structures. If the zone in which the house is being built is classified as environmental protection, then local GPZU and PZZ will have to be taken into account.
Minimum Requirements
Minimum distances between residential buildings in cities are necessary to ensure fire safety and ensure structural integrity.
Thus, the standard for brick, concrete, that is, stone houses with concrete floors, suggests that the distance between them should be at least six meters. From the same house to a stone (concrete, brick), but with wooden floors - eight meters, and to a prefabricated building - ten. Accordingly, between two brick, concrete houses with wooden floors there cannot be less than eight meters, and in the case of prefabricated ones, they should be located ten to fifteen meters from each other and from other houses.
In addition, the adopted standard regarding a residential multi-storey building stipulates that it cannot be located less than ten meters from a gas control point with low pressure and less than fifteen meters from the same object with high pressure.
Even when developing regional rules, the administration refers to the above-mentioned SNiP, construction rules for low-rise buildings, fire safety requirements and areas for the location of communication systems.
Standards for country houses
If your site is located in gardening, buildings must be planned in accordance with SNiP 30-02-97. According to the rules, a building in a dacha should not be closer than 15 meters to the forest planting.
As for the distances to the border with neighbors, the standards given above apply. That is, the distance from the fence with neighbors to the country house should be at least 3 meters . But there are also requirements for the fence between sections - it should not be higher than one and a half meters, and the fence should be mesh or lattice .
Recommendation. If you still want to build a blind fence between areas, then first you should determine the feasibility of such a fence. If there is a reason, then having received the WRITTEN consent of your neighbor, you can calmly erect such a structure. Only a written document can help you in case of litigation.
Other significant distances
In accordance with the requirements of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation and a number of current rules, the minimum distance is observed not only between multi-storey buildings, but also between other objects next to them.
So, for example, the distance from the driveway to the street cannot be less than three meters. The gap between the windows of a residential building and the windows of any other building should be from six meters, between the building and tall trees - from four meters, between the building and low-growing trees - from two meters. No less important are the utility systems, which should not come into contact with the foundation of the house. Thus, a distance of five meters is maintained from the foundation to the water supply and sewer pressure system, and from four to ten meters to the gas pipeline, depending on whether the pressure in the systems is low, medium or high. From power cables to the foundation - sixty centimeters, to communication channels - two meters, and to heating networks - you should be guided by the standards of SNiP 41-02-2003.
It is important to keep in mind that if any conflict situation is brewing, before filing a claim in court, you must consult an experienced lawyer and find out what regulations were in force at the time of construction of the disputed building.
Basic concepts when observing distance standards between houses
We draw your attention to several legal rights when constructing all types of construction projects on your own site. All of them operate in our country and have legal force.
- First of all, this is the so-called priority right of the first developer. It is used in cases where sanitary standards in areas are not met. For example, if one developer has approved a plan for the location of objects on its territory, then the neighboring sites (where such a plan has not been approved before) should build on the already built and decorated buildings, creating a plan on their territory. Namely: maintain the required distance not only from the fence, but also from neighboring objects - if, for example, they are located closer to the fence than 3 meters. And also between residential buildings there must be at least 6 meters. And again, during construction you will have to build on already built and documented objects on your neighbor’s property. If these measures are not followed, the project registered by the land committee earlier will be recognized as the correct project. This is the priority right that the first developer has.
- The second point is the construction of summer cottages. As practice shows, they comply with the norms less. Because in such territories, as a rule, there are few underground communications (or none at all), and the area of the plots is larger. In fact, often for such situations it is not the existing SNiPs that are taken into account, but the charter of the garden society and the association of owners and plot owners.
For example, it must indicate certain principles for the construction of residential buildings, adopted at a general meeting of owners. Typically this is: the maximum size of residential properties, 3–4 meters from buildings between neighbors, 3–4 meters from non-residential properties, at least 4 meters from large trees, 1–2 meters from shrubs. By the way, the court will not consider cases of non-compliance with construction standards on non-commercial territory. Therefore, it is often worth sending all complaints to the owners’ association, which adopted the existing provisions. - Legally, on land allocated for individual housing construction, a maximum of three-story buildings can be erected. At the same time, it is important to comply with the following requirements: at least 10 meters to neighboring objects, no division of the house into apartments, and a common area for all residents. According to the standards, such a thing as shading is also checked. Thus, it is not allowed for neighboring areas to be actually shaded by a multi-story building for more than half a day. Approximately the same rule applies to neighbors - their house should not cast a shadow in such a way as to completely block your residential property from the sun for more than 2 hours a day.
It turns out that you can’t just build a house wherever you want. It is necessary to fulfill several norms and legal requirements at once, so as not to disturb the lives of neighbors, not to create problems for emergency services, and to create safe housing.
Because all these standards have been tested by time, by several generations of people and builders. All of them are designed to make our lives safer and more comfortable.
About territorial boundaries
When calculating the boundaries by territorial zones in the city, the rules of land use and construction must be taken into account, namely:
- The ability to combine different target zones within one territory;
- The functionality of the selected site, as well as the parameters and planning of its development in accordance with the master plans of the city, region, and municipal areas;
- Layout of the territory and the current target category;
- Planned changes to land boundaries, different target categories depending on urban layout;
- Eliminating the possibility of causing damage to immovable capital construction projects.
At the same time, for existing and planned buildings it is necessary to calculate the passage of the border. They will be determined by the main lines, lines of passages and streets that divide the traffic flow, by the red lines of the boundaries of land territories, lines dividing settlements within the municipality, internal municipal boundaries, demarcation lines of natural objects and others. Zones that are subject to special operating conditions and cultural heritage sites, in accordance with Russian legislation, may have diverging boundaries, so it is necessary to clarify them with the local administration.
Fine for violation of SNiP
SNiP is not a normative act, therefore the legislation does not provide for any liability for its violation . However, it's not that simple. The fact is that your actions should not violate the interests of your neighbors, especially in terms of the use of housing.
For example, you built a house in violation of the norms, a meter from the border with the neighboring plot. At the same time, water from your roof pours directly onto your neighbors’ beds. This is a violation! A neighbor can easily go to court, and the judge, according to the law, will make a decision in order to restore the neighbor’s rights and at the same time exclude a violation of building regulations.
Consequences of violation of SNiP When restoring the rights of a neighbor through the court, there is only one way out - demolition! In this case, all costs for restoring your neighbor’s rights are yours. That is, in order to restore your neighbor’s rights, you will be required to demolish your house if it is not built in accordance with SNiPs .
It is precisely in order to protect yourself from enormous financial losses in the future that you need to take into account the subtleties when planning a site:
- what distance should be between private houses;
- how many meters should separate the red line from the nearest building;
- where you can build a garage or bathhouse.
Similar articles:
- How to achieve a recalculation of utility bills Know how to recalculate utility bills using 354...
- Who is eligible and how to get social housing? Article 40 of the Constitution guarantees the provision of housing to all Russians who...
- How to properly connect your plot to the power grid Making full use of your dacha (garden) plot without…
- Construction in progress. Problems and their solutions Today in Russia, unfinished construction is not nonsense,...
General distribution of building plots
The planning structure of a residential area provides not only the distance between apartment buildings, but also the formation of infrastructural development in accordance with the urban planning plan as a whole, as well as the natural features of the territory. Moreover, it is important to provide for the relationship between located real estate objects, public buildings and structures, road networks, their landscaping in common areas, and other objects that can be placed in a residential area in accordance with sanitary and hygienic standards and safety rules.
Since the development of individual regions affects the entire country, it is equally important to pre-determine the overall size of the residential area. In a city where the average number of floors of a residential apartment building is up to three floors, ten hectares are allocated for development if the development is without a land plot, and twenty if with a plot. For cities with houses from 4 to 8 floors this is 8 hectares, for cities with houses of 9 floors or more - 7 hectares. At the same time, it is forbidden to place objects of urban significance in a residential block or microdistrict, as well as to develop transit passages through the territory, which are united by a common yard. The territory of a group of residential apartment buildings usually does not exceed 5 hectares.
What is SNiP
There are codes of rules (SP) intended for use in the construction and design of all kinds of structures and buildings. For example, SP 30-102-99, developed in 1999, applies to planning and development of the private sector. There are codes regarding the construction of residential high-rise buildings, factories, enterprises or engineering structures.
The code contains rules (SNiP) regulating certain issues of construction and planning that must be followed. SNiP are building codes and regulations, compliance with which is mandatory when developing sites. If GOST standards are provided for goods, then SNiPs are provided for construction projects. Both concepts arose in the USSR to standardize construction or production of goods.
Modern legislators did not abandon Soviet standards, because during the many years of developing the rules, a group of engineers took into account all possible aspects of construction, which is why SNiPs are still in effect.
Permissible building density in the city
For cities, the population density of territories is no less important. The accepted standards are given above:
| Territory zone | Coefficient value - density |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Experimental fields and testing grounds, reserve territories and sanitary protection zones are not taken into account. However, only specialists can help calculate the density in a particular case.
Fire safety in multi-storey buildings
Fire safety of multi-storey buildings is achieved not only through the location of houses at a safe distance, but also through the use of modern fire extinguishing equipment and planning solutions. Evacuation and fire safety requirements for multi-storey buildings are divided into three groups: buildings with a height of 6-9 floors, from 10 to 16 and buildings with a height of more than 16 floors.
The weakest safety requirements are imposed on buildings with a height of 6-9 floors, this is due to the length of fire escapes. In this regard, in small towns it is not uncommon for buildings to consist of nine-story buildings. Such houses are the easiest to evacuate in case of fire. As a rule, there are no smoke exhaust devices, and staircases are installed inside the house, made exclusively from fireproof materials.
In houses with a height of more than 5 floors, an additional rescue ladder is installed. Such stairs are made vertical and placed in apartment balconies.
In houses with a height of more than 10 floors, open or semi-open stairs are installed; such stairs are often built outside the house in the form of loggias. Smoke removal ventilation made of non-combustible materials is also installed in elevators and internal cages.
It is worth noting that the number of external staircases in new houses is increasingly being reduced in comparison with Soviet housing construction. External stairs are very convenient to use during evacuation, but during normal operation of the house it is much more practical to use internal structures. The reduction in the number of outdoor structures is due to complaints from residents of houses about the possibility of unauthorized persons entering the territory of the house and the danger of using such stairs in winter. Now when designing a ten-story building, no more than 1-2 stairs are provided.
Distance between windows of residential buildings, playgrounds and public buildings
| p/p | Venues | Specific dimensions of sites, m2/person. | Distances from sites to windows of residential and public buildings, m |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | For games for preschool and primary school children | 0,7 | 12 |
| 2 | For adults to relax | 0,1 | 10 |
| 3 | For physical education | 2,0 | 10-40 |
| 4 | For household purposes and dog walking | 0,3 | 20 (for household purposes) 40 (for walking dogs) |
| 5 | For parking | 0,8 | according to table 3 |
Notes:1. Distances from physical education sites are set depending on their noise characteristics:
2. It is allowed to reduce, but not by more than 50%, the specific dimensions of the sites:
| |||
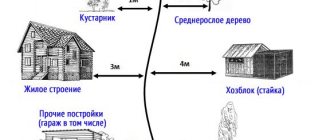
According to SNiP 2.07.01-89* clause 2.19* - in rural settlements there are sheds for livestock and poultry
should be provided at a distance
from the windows of the living quarters of the house
:
- single or double
- at least
15 m
, - up to 8 blocks
- at least
25 m
, - over 8 to 30 blocks
- at least
50 m
, - over 30 blocks
- at least
100 m
.
Groups of sheds located in rural settlements
should contain no more than 30 blocks each.
The construction area of semi-detached sheds for livestock
should not exceed
800 m2
.
NOTE: For residents of sectional houses
in rural settlements,
outbuildings for livestock
are allocated outside the residential area.
For sectional houses,
it is allowed to install built-in or free-standing
collective underground storage facilities for agricultural products
, the area of which is determined by regional (territorial) building codes, and in their absence, a design assignment.NOTE: According to SNiP 2.07.01-89* clause 2, blocking of outbuildings
on adjacent plots of land
by mutual agreement of homeowners, taking into account the requirements given (according to Table 1) (see below).
Distance between 1-2 apartment buildings
on neighboring plots of land, including
garages and outbuildings
, are taken taking into account fire safety standards - in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.01.02-85 * (according to Table 1).
Minimum distance between houses and auxiliary buildings of I and II degrees of fire resistance
to industrial buildings and garages of fire resistance levels I and II,
at least 9 m
.
When choosing a house design, you should also take into account the orientation of the site to the cardinal points. Orientation of all living rooms
on one northwest or northeast side of the house is NOT RECOMMENDED.
It is allowed to orient no more than 50% of all living rooms in the house
.
The windows of the common room
, as a rule, are oriented towards the street.
Summer room
(glazed veranda, terrace, porch) it is advisable to combine it with the entrance to the house.
The location and orientation of kitchen windows
depends on many factors and is decided in different ways.
However, if you have a utility yard
, it is convenient when the kitchen has a visual connection with it.
the bedroom windows
towards the garden.
According to the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01-89*p.2.13 - when designing a residential block
of areas for recreation, games, etc.
should be provided. , the dimensions of which and the distances from them to residential and public buildings should be no less than those given (according to Table 2)
According to the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01-89*p.6.39* - distances from above-ground and above-ground-underground garages, open parking lots
, intended for permanent and temporary storage of passenger cars, and
service stations
-
to residential buildings and public buildings
, as well as to
school sites, kindergartens and
hospital-type hospitals located in residential areas, no less than those given in table should be taken .3
TABLE 3: DISTANCE FROM GARAGES AND OPEN PARKING PARKS TO RESIDENTIAL AND PUBLIC BUILDINGS.
| p/p | Buildings to which the distance is determined | Distance, m | |||||
| from garages and open parking lots depending on the number of cars | from service stations with the number of posts | ||||||
| 10 or less | 11-50 | 51-100 | 101-300 | 10 or less | 11-30 | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | Residential buildings | 10** | 15 | 25 | 35 | 15 | 25 |
| 2 | Including the ends of residential buildings without windows | 10** | 10** | 15 | 25 | 15 | 25 |
| 3 | Public buildings | 10** | 10** | 15 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 4 | General education schools and preschool institutions | 15 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 | * |
| 5 | Medical institutions with inpatient facilities | 25 | 50 | * | * | 50 | * |
| * Determined in agreement with the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision authorities.** For garage buildings of III-V fire resistance degrees, the distance should be at least 12 m. | |||||||
| Notes*:1. Distances should be determined from the windows of residential and public buildings and from the boundaries of land plots of secondary schools, kindergartens and medical institutions with hospitals to the walls of the garage or the boundaries of an open parking lot.2. The distances from sectional residential buildings to open areas with a capacity of 101-300 cars, located along the longitudinal facades, should be at least 50 m.3. For garages of I-II degrees of fire resistance, the distances indicated in Table 10* can be reduced by 25% if there are no opening windows in the garages, as well as entrances oriented towards residential and public buildings.4. Garages and open parking lots for storing passenger cars with a capacity of more than 300 parking spaces and service stations with more than 30 posts should be located outside residential areas in the production area at a distance of at least 50 m from residential buildings. Distances are determined in agreement with the authorities of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.5. For garages with a capacity of more than 10 cars, those indicated in the table. distances can be taken by interpolation.6. In one-story box-type garages owned by citizens, cellars are allowed. | |||||||
According to the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01-89*p.4.12 - distances from buildings, structures, as well as engineering facilities to trees and shrubs
should be taken according to Table 4.
TABLE 4: DISTANCE FROM BUILDINGS AND ENGINEERING OBJECTS TO TREES AND SHRUBS.
| p/p | Building, structure, engineering improvement object | Distances, m, from a building, structure, object to the axis | |
| tree trunk | bush | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | External wall of a building and structure | 5,0 | 1,5 |
| 2 | The edge of the tram track | 5,0 | 3,0 |
| 3 | Edge of sidewalk and garden path | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 4 | The edge of the roadway, the edge of a reinforced roadside strip, or the edge of a ditch | 2,0 | 1,0 |
| 5 | Mast and support of lighting network, tram, bridge support and overpass | 4,0 | — |
| 6 | The base of a slope, terrace, etc. | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| 7 | The sole or inner edge of a retaining wall | 3,0 | 1,0 |
| 8 | Underground networks: | * | * |
| 8.1 | - gas pipeline, sewerage | 1,5 | — |
| 8.2 | — heating network (wall of a channel, tunnel or shell for ductless installation) | 2,0 | 1,0 |
| 8.3 | - water supply, drainage | 2,0 | — |
| 8.4 | - power cable and communication cable | 2,0 | 0,7 |
| Notes:1. The given standards apply to trees with a crown diameter of no more than 5 m and should be increased for trees with a crown of larger diameter.2. Distances from overhead power lines to trees should be taken according to the rules for the construction of electrical installations.3. Trees planted near buildings should not interfere with insolation and illumination of residential and public premises within the limits of the requirements set out in Section 9 of these standards. | |||
According to the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01-89 * clause 2.13 approx. clause 3 - when calculating the area of residential (residential development) territory, territories not suitable for development are excluded - ravines, steep slopes, rocky outcroppings, main irrigation canals, mudflows, land plots of institutions and enterprises
inter-settlement services.
See further section of the site Geodetic work in construction